Azure Arc-enabled Open Service Mesh
Open Service Mesh (OSM) is a lightweight, extensible, Cloud Native service mesh that allows users to uniformly manage, secure, and get out-of-the-box observability features for highly dynamic microservice environments.
OSM runs an Envoy-based control plane on Kubernetes, can be configured with SMI APIs, and works by injecting an Envoy proxy as a sidecar container next to each instance of your application. Read more on the service mesh scenarios enabled by Open Service Mesh.
All components of Azure Arc-enabled OSM are deployed on availability zones, making them zone redundant.
Installation options and requirements
Azure Arc-enabled Open Service Mesh can be deployed through Azure portal, Azure CLI, an ARM template, or a built-in Azure policy.
Prerequisites
- Ensure you have met all the common prerequisites for cluster extensions listed here.
- Use
az k8s-extensionCLI extension version >= v1.0.4
Current support limitations
- Only one instance of Open Service Mesh can be deployed on an Azure Arc-connected Kubernetes cluster.
- Support is available for the two most recently released minor versions of Arc-enabled Open Service Mesh. Find the latest version here. Supported release versions are appended with notes. Ignore the tags associated with intermediate releases.
- The following Kubernetes distributions are currently supported:
- AKS (Azure Kubernetes Service) Engine
- AKS clusters on Azure Stack HCI
- AKS enabled by Azure Arc
- Cluster API Azure
- Google Kubernetes Engine
- Canonical Kubernetes Distribution
- Rancher Kubernetes Engine
- OpenShift Kubernetes Distribution
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
- VMware Tanzu Kubernetes Grid
- Azure Monitor integration with Azure Arc-enabled Open Service Mesh is available in preview with limited support.
Basic installation using Azure portal
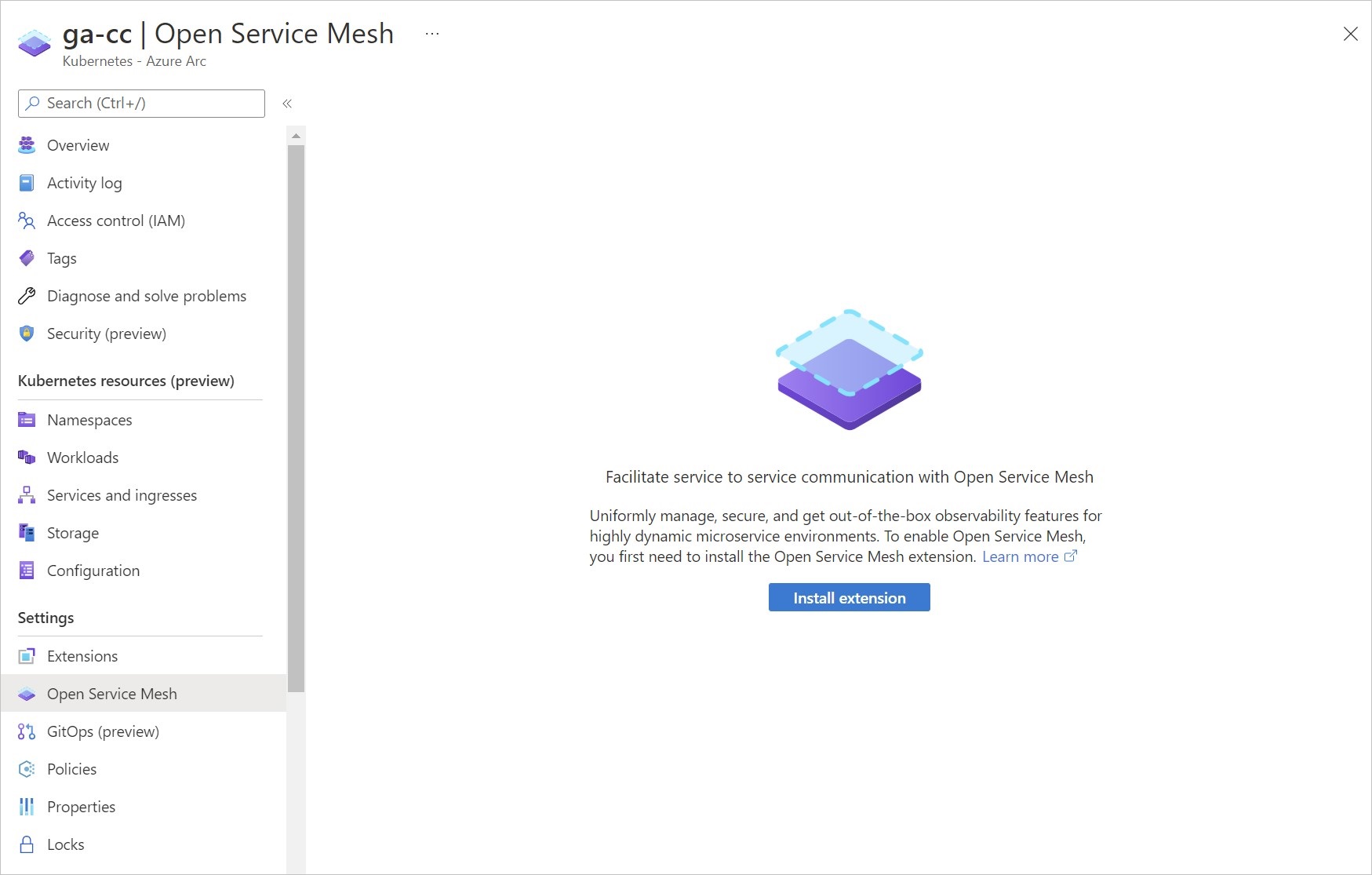
To deploy using Azure portal, once you have an Arc connected cluster, go to the cluster's Open Service Mesh section.
Select the Install extension button to deploy the latest version of the extension.
Alternatively, you can use the CLI experience captured here. For at-scale onboarding, read further in this article about deployment using ARM template and using Azure Policy.
Basic installation using Azure CLI
The following steps assume that you already have a cluster with a supported Kubernetes distribution connected to Azure Arc. Ensure that your KUBECONFIG environment variable points to the kubeconfig of the Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster.
Set the environment variables:
export CLUSTER_NAME=<arc-cluster-name>
export RESOURCE_GROUP=<resource-group-name>
If you're using an OpenShift cluster, skip to the OpenShift installation steps.
Create the extension:
Note
To pin a specific version of OSM, add the --version x.y.z flag to the create command. Note that this will set the value for auto-upgrade-minor-version to false.
az k8s-extension create --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --cluster-type connectedClusters --extension-type Microsoft.openservicemesh --scope cluster --name osm
You should see output similar to this example. It may take 3-5 minutes for the actual OSM helm chart to get deployed to the cluster. Until this deployment happens, installState will remain Pending.
{
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"configurationSettings": {},
"creationTime": "2021-04-29T17:50:11.4116524+00:00",
"errorInfo": {
"code": null,
"message": null
},
"extensionType": "microsoft.openservicemesh",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription-id>/resourceGroups/$RESOURCE_GROUP/providers/Microsoft.Kubernetes/connectedClusters/$CLUSTER_NAME/providers/Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions/osm",
"identity": null,
"installState": "Pending",
"lastModifiedTime": "2021-04-29T17:50:11.4116525+00:00",
"lastStatusTime": null,
"location": null,
"name": "osm",
"releaseTrain": "stable",
"resourceGroup": "$RESOURCE_GROUP",
"scope": {
"cluster": {
"releaseNamespace": "arc-osm-system"
},
"namespace": null
},
"statuses": [],
"type": "Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions",
"version": "x.y.z"
}
Next, validate your installation.
Custom installations
The following sections describe certain custom installations of Azure Arc-enabled OSM. Custom installations require setting values of OSM by in a JSON file and passing them into k8s-extension create CLI command.
Install OSM on an OpenShift cluster
Copy and save the following contents into a JSON file. If you have already created a configuration settings file, add the following line to the existing file to preserve your previous changes.
{ "osm.osm.enablePrivilegedInitContainer": "true" }Add the privileged security context constraint to each service account for the applications in the mesh.
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged -z <service account name> -n <service account namespace>
It may take 3-5 minutes for the actual OSM helm chart to get deployed to the cluster. Until this deployment happens, installState will remain Pending.
To ensure that the privileged init container setting doesn't revert to the default, pass in the "osm.osm.enablePrivilegedInitContainer" : "true" configuration setting to all subsequent az k8s-extension create commands.
Enable High Availability features on installation
OSM's control plane components are built with High Availability and Fault Tolerance in mind. This section describes how to enable Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA) and Pod Disruption Budget (PDB) during installation. Read more about the design considerations of High Availability on OSM.
Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA)
HPA automatically scales up or down control plane pods based on the average target CPU utilization (%) and average target
memory utilization (%) defined by the user. To enable HPA and set applicable values on OSM control plane pods during installation, create or
append to your existing JSON settings file as shown here, repeating the key/value pairs for each control plane pod
(osmController, injector) that you want to enable HPA on.
{
"osm.osm.<control_plane_pod>.autoScale.enable" : "true",
"osm.osm.<control_plane_pod>.autoScale.minReplicas" : "<allowed values: 1-10>",
"osm.osm.<control_plane_pod>.autoScale.maxReplicas" : "<allowed values: 1-10>",
"osm.osm.<control_plane_pod>.autoScale.cpu.targetAverageUtilization" : "<allowed values 0-100>",
"osm.osm.<control_plane_pod>.autoScale.memory.targetAverageUtilization" : "<allowed values 0-100>"
}
Now, install OSM with custom values.
Pod Disruption Budget (PDB)
In order to prevent disruptions during planned outages, control plane pods osm-controller and osm-injector have a PDB
that ensures there's always at least one pod corresponding to each control plane application.
To enable PDB, create or append to your existing JSON settings file as follows for each desired control plane pod
(osmController, injector):
{
"osm.osm.<control_plane_pod>.enablePodDisruptionBudget" : "true"
}
Now, install OSM with custom values.
Install OSM with cert-manager for certificate management
cert-manager is a provider that can be used for issuing signed certificates to OSM without the need for storing private keys in Kubernetes. Refer to OSM's cert-manager documentation and demo to learn more.
Note
Use the commands provided in the OSM GitHub documentation with caution. Ensure that you use the correct namespace in commands or specify with flag --osm-namespace arc-osm-system.
To install OSM with cert-manager as the certificate provider, create or append to your existing JSON settings file the certificateProvider.kind
value set to cert-manager as shown here. To change from the default cert-manager values specified in OSM documentation,
also include and update the subsequent certmanager.issuer lines.
{
"osm.osm.certificateProvider.kind" : "cert-manager",
"osm.osm.certmanager.issuerName" : "<issuer name>",
"osm.osm.certmanager.issuerKind" : "<issuer kind>",
"osm.osm.certmanager.issuerGroup" : "<issuer group>"
}
Now, install OSM with custom values.
Install OSM with Contour for ingress
OSM provides multiple options to expose mesh services externally using ingress. OSM can use Contour, which works with the ingress controller installed outside the mesh and provisioned with a certificate to participate in the mesh. Refer to OSM's ingress documentation and demo to learn more.
Note
Use the commands provided in the OSM GitHub documentation with caution. Ensure that you use the correct namespace in commands or specify with flag --osm-namespace arc-osm-system.
To set required values for configuring Contour during OSM installation, append the following to your JSON settings file:
{
"osm.osm.osmNamespace" : "arc-osm-system",
"osm.contour.enabled" : "true",
"osm.contour.configInline.tls.envoy-client-certificate.name" : "osm-contour-envoy-client-cert",
"osm.contour.configInline.tls.envoy-client-certificate.namespace" : "arc-osm-system"
}
Setting values during OSM installation
Any values that need to be set during OSM installation need to be saved to a single JSON file and passed in through the Azure CLI install command.
After you create a JSON file with applicable values as described in the custom installation sections, set the file path as an environment variable:
export SETTINGS_FILE=<json-file-path>
Run the az k8s-extension create command to create the OSM extension, passing in the settings file using the --configuration-settings-file flag:
az k8s-extension create --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --cluster-type connectedClusters --extension-type Microsoft.openservicemesh --scope cluster --name osm --configuration-settings-file $SETTINGS_FILE
Install Azure Arc-enabled OSM using ARM template
After connecting your cluster to Azure Arc, create a JSON file with the following format, making sure to update the <cluster-name> and <osm-arc-version> values:
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"ConnectedClusterName": {
"defaultValue": "<cluster-name>",
"type": "String",
"metadata": {
"description": "The Connected Cluster name."
}
},
"ExtensionInstanceName": {
"defaultValue": "osm",
"type": "String",
"metadata": {
"description": "The extension instance name."
}
},
"ExtensionVersion": {
"defaultValue": "<osm-arc-version>",
"type": "String",
"metadata": {
"description": "The extension type version."
}
},
"ExtensionType": {
"defaultValue": "Microsoft.openservicemesh",
"type": "String",
"metadata": {
"description": "The extension type."
}
},
"ReleaseTrain": {
"defaultValue": "Stable",
"type": "String",
"metadata": {
"description": "The release train."
}
}
},
"functions": [],
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions",
"apiVersion": "2020-07-01-preview",
"name": "[parameters('ExtensionInstanceName')]",
"properties": {
"extensionType": "[parameters('ExtensionType')]",
"releaseTrain": "[parameters('ReleaseTrain')]",
"version": "[parameters('ExtensionVersion')]"
},
"scope": "[concat('Microsoft.Kubernetes/connectedClusters/', parameters('ConnectedClusterName'))]"
}
]
}
Set the environment variables:
export TEMPLATE_FILE_NAME=<template-file-path>
export DEPLOYMENT_NAME=<desired-deployment-name>
Run this command to install the OSM extension:
az deployment group create --name $DEPLOYMENT_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --template-file $TEMPLATE_FILE_NAME
You should now be able to view the OSM resources and use the OSM extension in your cluster.
Install Azure Arc-enabled OSM using built-in policy
A built-in policy is available on Azure portal under the Kubernetes category: Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters should have the Open Service Mesh extension installed. This policy can be assigned at the scope of a subscription or a resource group.
The default action of this policy is Deploy if not exists. However, you can choose to audit the clusters for extension installations by changing the parameters during assignment. You're also prompted to specify the version you wish to install (v1.0.0-1 or higher) as a parameter.
Validate installation
Run the following command.
az k8s-extension show --cluster-type connectedClusters --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name osm
You should see a JSON output similar to:
{
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"configurationSettings": {},
"creationTime": "2021-04-29T19:22:00.7649729+00:00",
"errorInfo": {
"code": null,
"message": null
},
"extensionType": "microsoft.openservicemesh",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription-id>/resourceGroups/$RESOURCE_GROUP/providers/Microsoft.Kubernetes/connectedClusters/$CLUSTER_NAME/providers/Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions/osm",
"identity": null,
"installState": "Installed",
"lastModifiedTime": "2021-04-29T19:22:00.7649731+00:00",
"lastStatusTime": "2021-04-29T19:23:27.642+00:00",
"location": null,
"name": "osm",
"releaseTrain": "stable",
"resourceGroup": "$RESOURCE_GROUP",
"scope": {
"cluster": {
"releaseNamespace": "arc-osm-system"
},
"namespace": null
},
"statuses": [],
"type": "Microsoft.KubernetesConfiguration/extensions",
"version": "x.y.z"
}
For more commands that you can use to validate and troubleshoot the deployment of the Open Service Mesh (OSM) extension components on your cluster, see our troubleshooting guide
OSM controller configuration
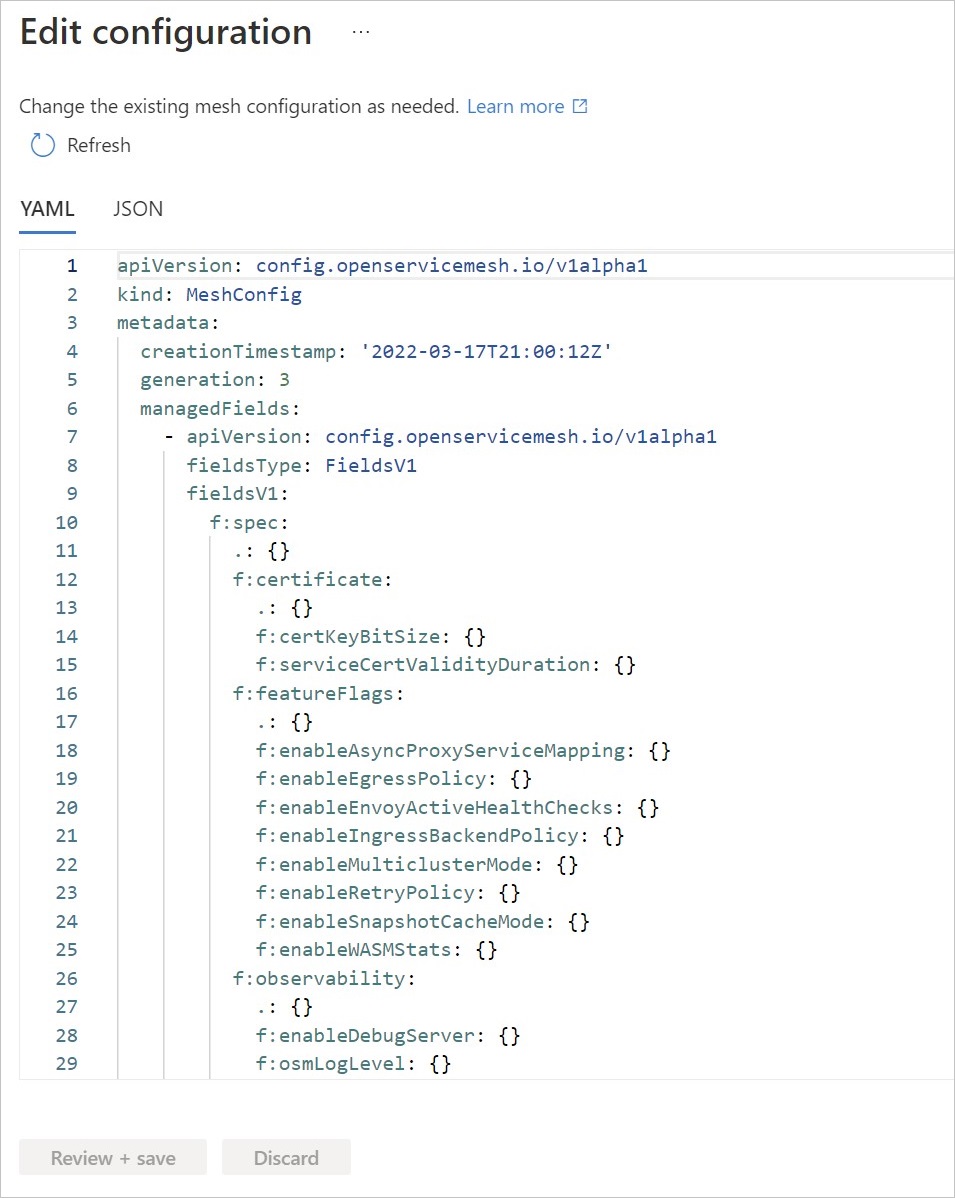
OSM deploys a MeshConfig resource osm-mesh-config as a part of its control plane in arc-osm-system namespace. The purpose of this MeshConfig is to provide the mesh owner/operator the ability to update some of the mesh configurations based on their needs. To view the default values, use the following command.
kubectl describe meshconfig osm-mesh-config -n arc-osm-system
The output shows the default values:
Certificate:
Cert Key Bit Size: 2048
Service Cert Validity Duration: 24h
Feature Flags:
Enable Async Proxy Service Mapping: false
Enable Egress Policy: true
Enable Envoy Active Health Checks: false
Enable Ingress Backend Policy: true
Enable Multicluster Mode: false
Enable Retry Policy: false
Enable Snapshot Cache Mode: false
Enable WASM Stats: true
Observability:
Enable Debug Server: false
Osm Log Level: info
Tracing:
Enable: false
Sidecar:
Config Resync Interval: 0s
Enable Privileged Init Container: false
Log Level: error
Resources:
Traffic:
Enable Egress: false
Enable Permissive Traffic Policy Mode: true
Inbound External Authorization:
Enable: false
Failure Mode Allow: false
Stat Prefix: inboundExtAuthz
Timeout: 1s
Inbound Port Exclusion List:
Outbound IP Range Exclusion List:
Outbound Port Exclusion List:
For more information, see the Config API reference. Notice that spec.traffic.enablePermissiveTrafficPolicyMode is set to true. When OSM is in permissive traffic policy mode, SMI traffic policy enforcement is bypassed. In this mode, OSM automatically discovers services that are a part of the service mesh and programs traffic policy rules on each Envoy proxy sidecar to be able to communicate with these services.
osm-mesh-config can also be viewed in the Azure portal by selecting Edit configuration in the cluster's Open Service Mesh section.
Making changes to OSM controller configuration
Note
Values in the MeshConfig osm-mesh-config are persisted across upgrades.
Changes to osm-mesh-config can be made using the kubectl patch command. In the following example, the permissive traffic policy mode is changed to false.
kubectl patch meshconfig osm-mesh-config -n arc-osm-system -p '{"spec":{"traffic":{"enablePermissiveTrafficPolicyMode":false}}}' --type=merge
If an incorrect value is used, validations on the MeshConfig CRD prevent the change with an error message explaining why the value is invalid. For example, this command shows what happens if we patch enableEgress to a non-boolean value:
kubectl patch meshconfig osm-mesh-config -n arc-osm-system -p '{"spec":{"traffic":{"enableEgress":"no"}}}' --type=merge
# Validations on the CRD will deny this change
The MeshConfig "osm-mesh-config" is invalid: spec.traffic.enableEgress: Invalid value: "string": spec.traffic.enableEgress in body must be of type boolean: "string"
Alternatively, to edit osm-mesh-config in Azure portal, select Edit configuration in the cluster's Open Service Mesh section.
Using Azure Arc-enabled OSM
To start using OSM capabilities, you need to first onboard the application namespaces to the service mesh. Download the OSM CLI from the OSM GitHub releases page. Once the namespaces are added to the mesh, you can configure the SMI policies to achieve the desired OSM capability.
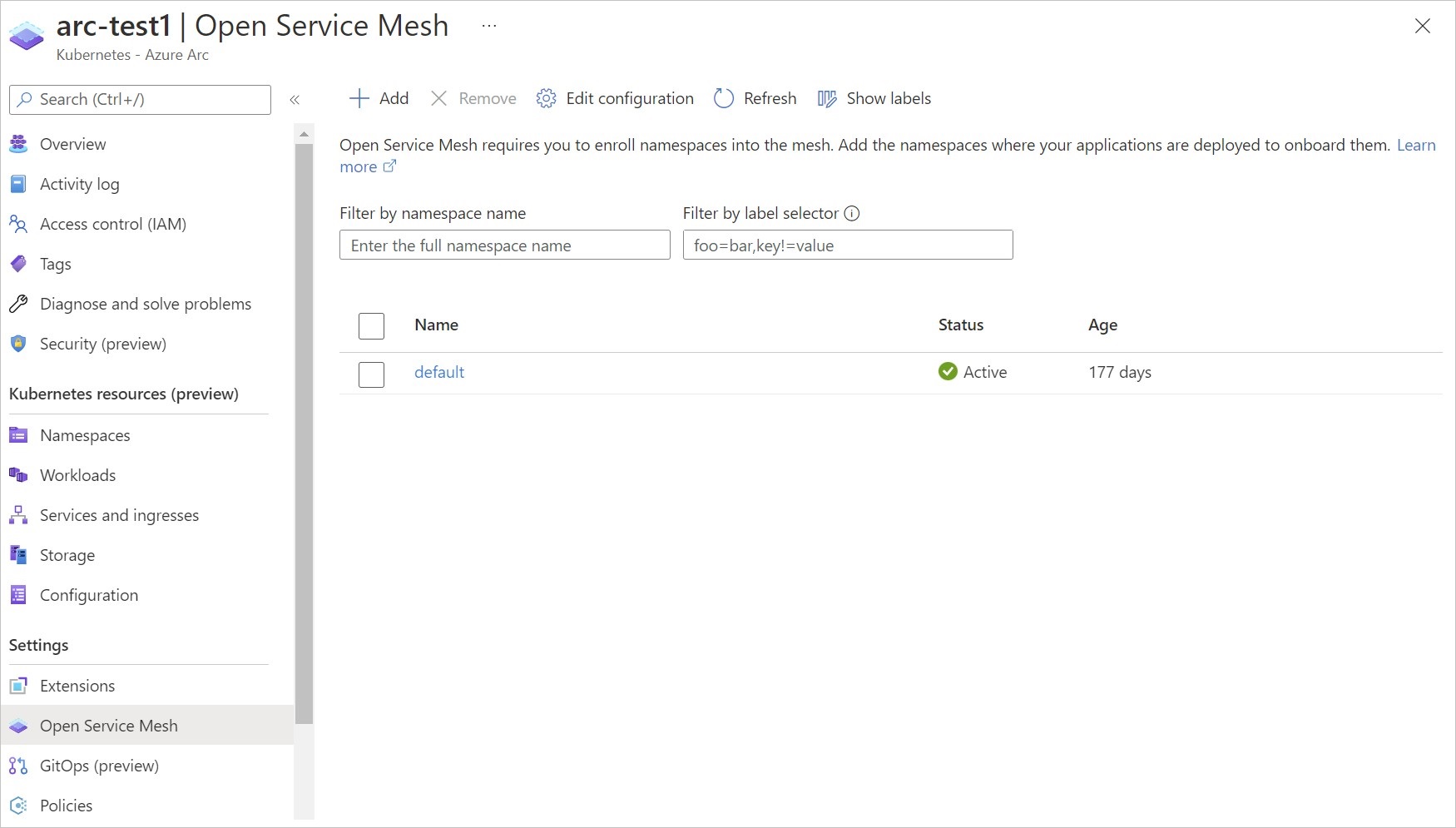
Onboard namespaces to the service mesh
Add namespaces to the mesh by running the following command:
osm namespace add <namespace_name>
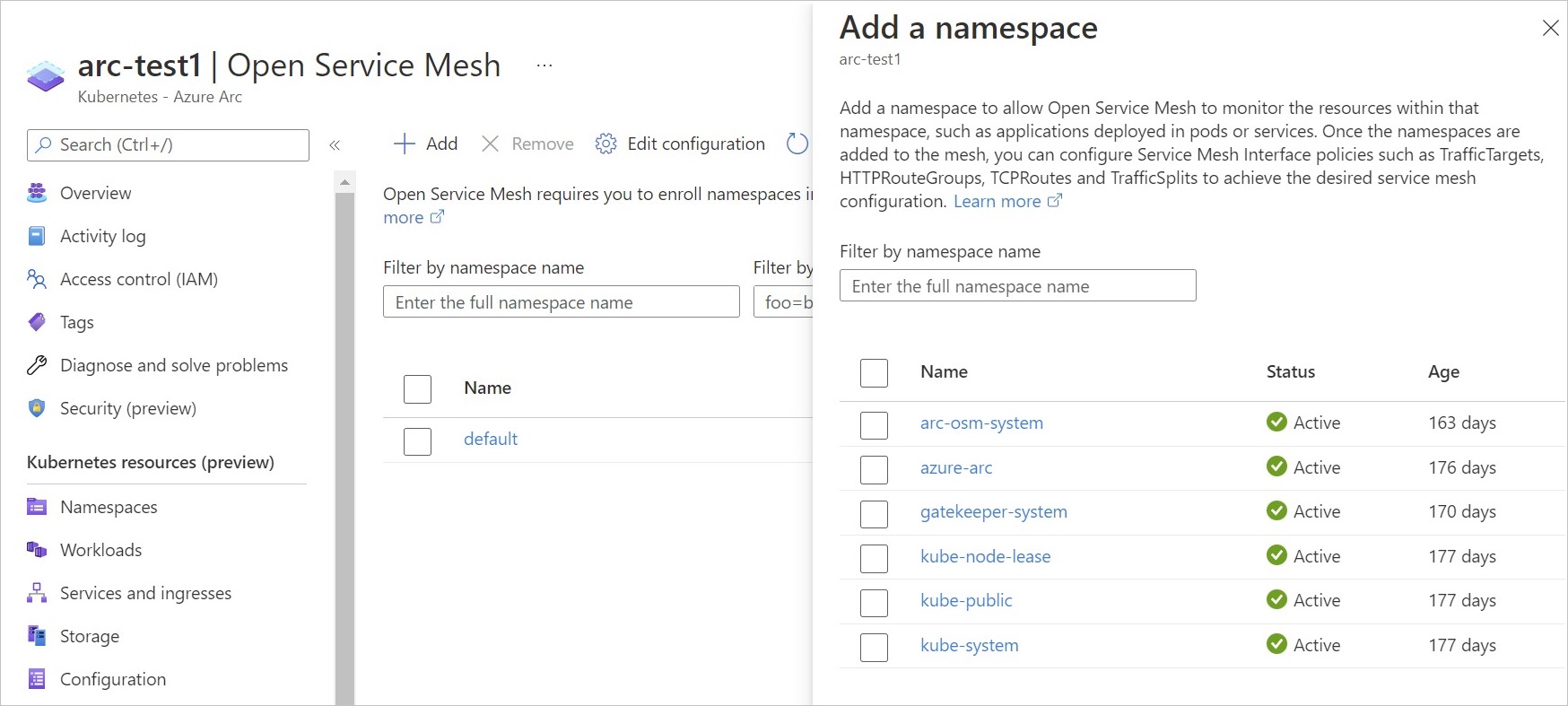
Namespaces can be onboarded from Azure portal as well by selecting +Add in the cluster's Open Service Mesh section.
For more information about onboarding services, see the Open Service Mesh documentation.
Configure OSM with Service Mesh Interface (SMI) policies
You can start with a sample application or use your test environment to try out SMI policies.
Note
If you use sample applications, ensure that their versions match the version of the OSM extension installed on your cluster. For example, if you are using v1.0.0 of the OSM extension, use the bookstore manifest from release-v1.0 branch of OSM upstream repository.
Configuring your own Jaeger, Prometheus and Grafana instances
The OSM extension doesn't install add-ons like Jaeger, Prometheus, Grafana and Flagger. You can integrate OSM with your own running instances of those tools instead. To integrate with your own instances, see the following documentation:
- BYO-Jaeger instance
- BYO-Prometheus instance
- BYO-Grafana dashboard
- OSM Progressive Delivery with Flagger
Note
Use the commands provided in the OSM GitHub documentation with caution. Ensure that you use the correct namespace name arc-osm-system when making changes to osm-mesh-config.
Monitoring application using Azure Monitor and Applications Insights (preview)
Both Azure Monitor and Azure Application Insights help you maximize the availability and performance of your applications and services by delivering a comprehensive solution for collecting, analyzing, and acting on telemetry from your cloud and on-premises environments. Azure Arc-enabled Open Service Mesh has deep integrations into both of these Azure services. This integration provides a seamless Azure experience for viewing and responding to critical KPIs provided by OSM metrics.
Important
Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes preview features are available on a self-service, opt-in basis. Previews are provided "as is" and "as available," and they're excluded from the service-level agreements and limited warranty. Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes previews are partially covered by customer support on a best-effort basis.
Follow these steps to allow Azure Monitor to scrape Prometheus endpoints for collecting application metrics.
Follow the guidance available here to ensure that the application namespaces that you wish to be monitored are onboarded to the mesh.
Expose the Prometheus endpoints for application namespaces.
osm metrics enable --namespace <namespace1> osm metrics enable --namespace <namespace2>Install the Azure Monitor extension using the guidance available here.
Create a Configmap in the
kube-systemnamespace that enables Azure Monitor to monitor your namespaces. For example, create acontainer-azm-ms-osmconfig.yamlwith the following to monitor<namespace1>and<namespace2>:kind: ConfigMap apiVersion: v1 data: schema-version: v1 config-version: ver1 osm-metric-collection-configuration: |- # OSM metric collection settings [osm_metric_collection_configuration] [osm_metric_collection_configuration.settings] # Namespaces to monitor monitor_namespaces = ["<namespace1>", "<namespace2>"] metadata: name: container-azm-ms-osmconfig namespace: kube-systemRun the following kubectl command
kubectl apply -f container-azm-ms-osmconfig.yaml
It may take up to 15 minutes for the metrics to show up in Log Analytics. You can try querying the InsightsMetrics table.
InsightsMetrics
| where Name contains "envoy"
| extend t=parse_json(Tags)
| where t.app == "namespace1"
Navigating the OSM dashboard
- Access your Arc connected Kubernetes cluster using this link.
- Go to Azure Monitor and navigate to the Reports tab to access the OSM workbook.
- Select the time-range & namespace to scope your services.
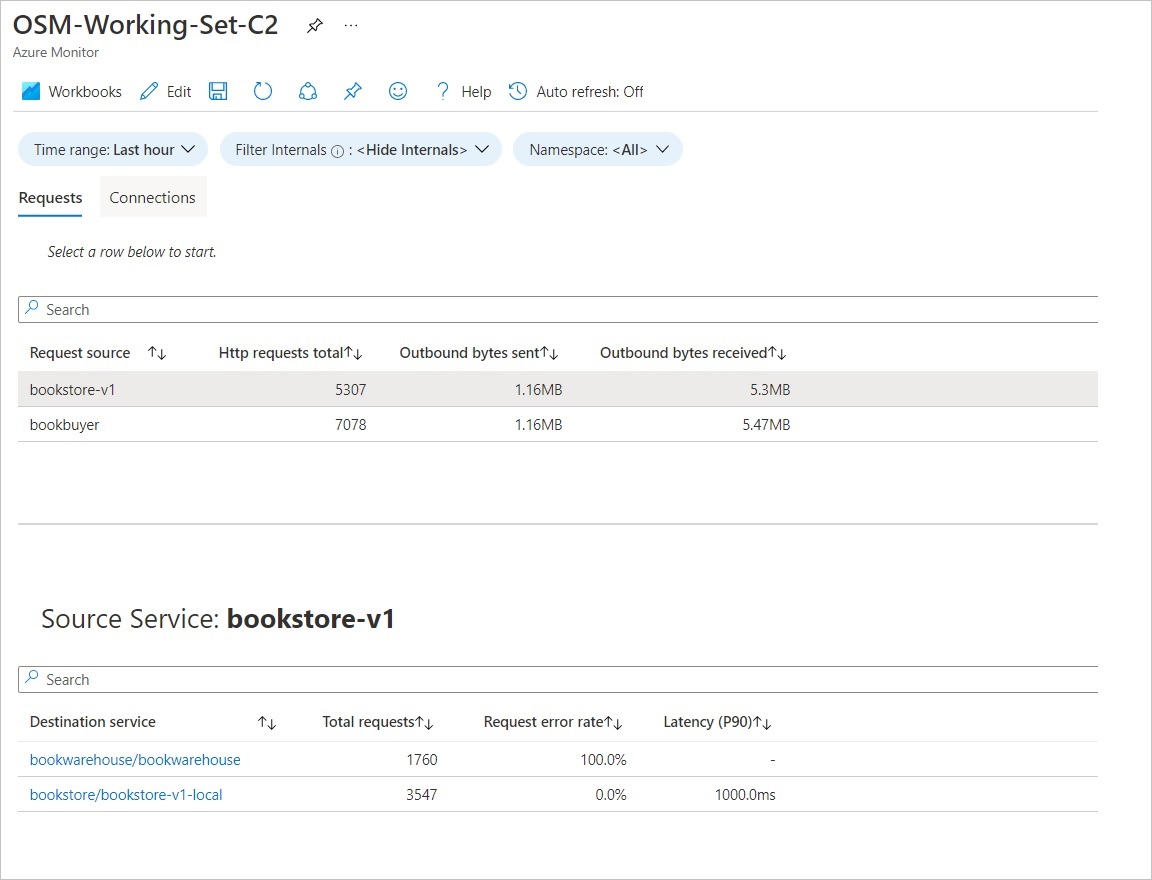
Requests tab
The Requests tab shows a summary of all the http requests sent via service to service in OSM.
- You can view all the services by selecting the service in the grid.
- You can view total requests, request error rate & P90 latency.
- You can drill down to destination and view trends for HTTP error/success code, success rate, pod resource utilization, and latencies at different percentiles.
Connections tab
The Connections tab shows a summary of all the connections between your services in Open Service Mesh.
- Outbound connections: total number of connections between Source and destination services.
- Outbound active connections: last count of active connections between source and destination in selected time range.
- Outbound failed connections: total number of failed connections between source and destination service.
Upgrade to a specific version of OSM
There may be some downtime of the control plane during upgrades. The data plane is only affected during CRD upgrades.
Supported upgrades
The OSM extension can be upgraded manually across minor and major versions. However, automatic upgrade (if enabled) only works across minor versions.
Upgrade to a specific OSM version manually
The following command upgrades the OSM-Arc extension to a specific version:
az k8s-extension update --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --cluster-type connectedClusters --release-train stable --name osm --version x.y.z
Enable automatic upgrades
If automatic upgrades aren't enabled by default, the following command can be run to enable them. The current value of --auto-upgrade-minor-version can be verified by running the az k8s-extension show command as detailed in the Validate installation step.
az k8s-extension update --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --cluster-type connectedClusters --release-train stable --name osm --auto-upgrade-minor-version true
Uninstall Azure Arc-enabled OSM
Use the following command:
az k8s-extension delete --cluster-type connectedClusters --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name osm -y
Verify that the extension instance has been deleted:
az k8s-extension list --cluster-type connectedClusters --cluster-name $CLUSTER_NAME --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP
This output should not include OSM. If you do not have any other extensions installed on your cluster, it's just an empty array.
When you use the az k8s-extension command to delete the OSM extension, the arc-osm-system namespace is not removed, and the actual resources within the namespace (like mutating webhook configuration and osm-controller pod) take around 10 minutes to delete.
Note
Use the az k8s-extension CLI to uninstall OSM components managed by Arc. Using the OSM CLI to uninstall is not supported by Arc and can result in undesirable behavior.
Next steps
- Just want to try things out? Get started quickly with an Azure Arc Jumpstart scenario using Cluster API.
- Get troubleshooting help for Azure Arc-enabled OSM.
-
- Explore other extensions for Arc-enabled Kubernetes.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for