Troubleshoot VM deployment in Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU
APPLIES TO:  Azure Stack Edge Pro - GPU
Azure Stack Edge Pro - GPU Azure Stack Edge Pro 2
Azure Stack Edge Pro 2 Azure Stack Edge Pro R
Azure Stack Edge Pro R Azure Stack Edge Mini R
Azure Stack Edge Mini R
This article describes how to troubleshoot common errors when deploying virtual machines on an Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU device. The article provides guidance for investigating the most common issues that cause VM provisioning timeouts and issues during network interface and VM creation.
To diagnose any VM provisioning failure, review guest logs for the failed virtual machine. For steps to collect VM guest logs and include them in a Support package, see Collect guest logs for VMs on Azure Stack Edge Pro.
For guidance on issues that prevent successful upload of a VM image before your VM deployment, see Troubleshoot virtual machine image uploads in Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU.
VM provisioning timeout
This section provides troubleshooting for most common causes of a VM provisioning timeout.
When VM provisioning times out, you see the following error:
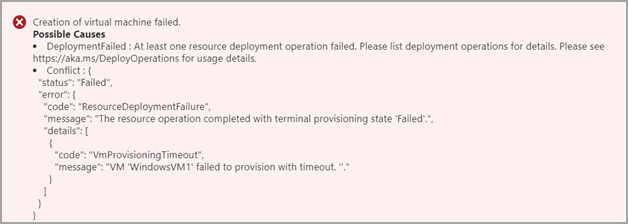
The following issues are the top causes of VM provisioning timeouts:
- The IP address that you assigned to the VM is already in use. Learn more
- The VM image that you used to deploy the VM wasn't prepared correctly. Learn more
- The default gateway and DNS server couldn't be reached from the guest VM. Learn more
- During a
cloud initinstallation,cloud initeither didn't run or there were issues while it was running. (Linux VMs only) Learn more - For a Linux VM deployed using a custom VM image, the Provisioning flags in the /etc/waagent.conf file aren't correct. (Linux VMs only) Learn more
- Primary network interface attached to a SRIOV enabled virtual switch Learn more
IP assigned to the VM is already in use
Error description: The VM was assigned a static IP address that is already in use, and VM provisioning failed. This error happens when the IP address is in use in the subnet on which the VM is deployed. When you deploy a VM via the Azure portal, the process checks for an existing IP address within your device but can't check IP addresses of other services or virtual machines that might also be on your subnet.
Suggested solution: Use a static IP address that isn't in use, or use a dynamic IP address provided by the DHCP server.
To check for a duplicate IP address:
Run the following
pingand Test-NetConnection (tnc) commands from any appliance on the same network:ping <IP address> tnc <IP address> tnc <IP address> -CommonTCPPort “RDP”
If you get a response, the IP address that you assigned to the new VM is already in use.
VM image not prepared correctly
Error description: To prepare a VM image for use on an Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU device, you must follow a specific workflow. You must create a gen1 virtual machine in Azure, customize the VM, generalize the VHD, and then download the OS VHD for that virtual machine. The prepared image must be a gen1 VHD with the "vhd" filename extension and the fixed type.
For an overview of requirements, see Create custom VM images for an Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU device. For guidance on resolving VM image issues, see Troubleshoot virtual machine image uploads in Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU.
Suggested solution: Complete the workflow for preparing your VM image. For guidance, see one of the following articles:
- Custom VM image workflows for Windows and Linux VMs
- Prepare a generalized image from a Windows VHD
- Prepare a generalized image using an ISO
- Use a specialized image to deploy VMs
Gateway, DNS server couldn't be reached from guest VM
Error description: If the default gateway and DNS server can't be reached during VM deployment, VM provisioning times out and the VM deployment fails.
Suggested solution: Verify that the default gateway and DNS server can be reached from the VM. Then repeat VM deployment.
To verify that the default gateway and DNS server can be reached from the VM, do the following steps:
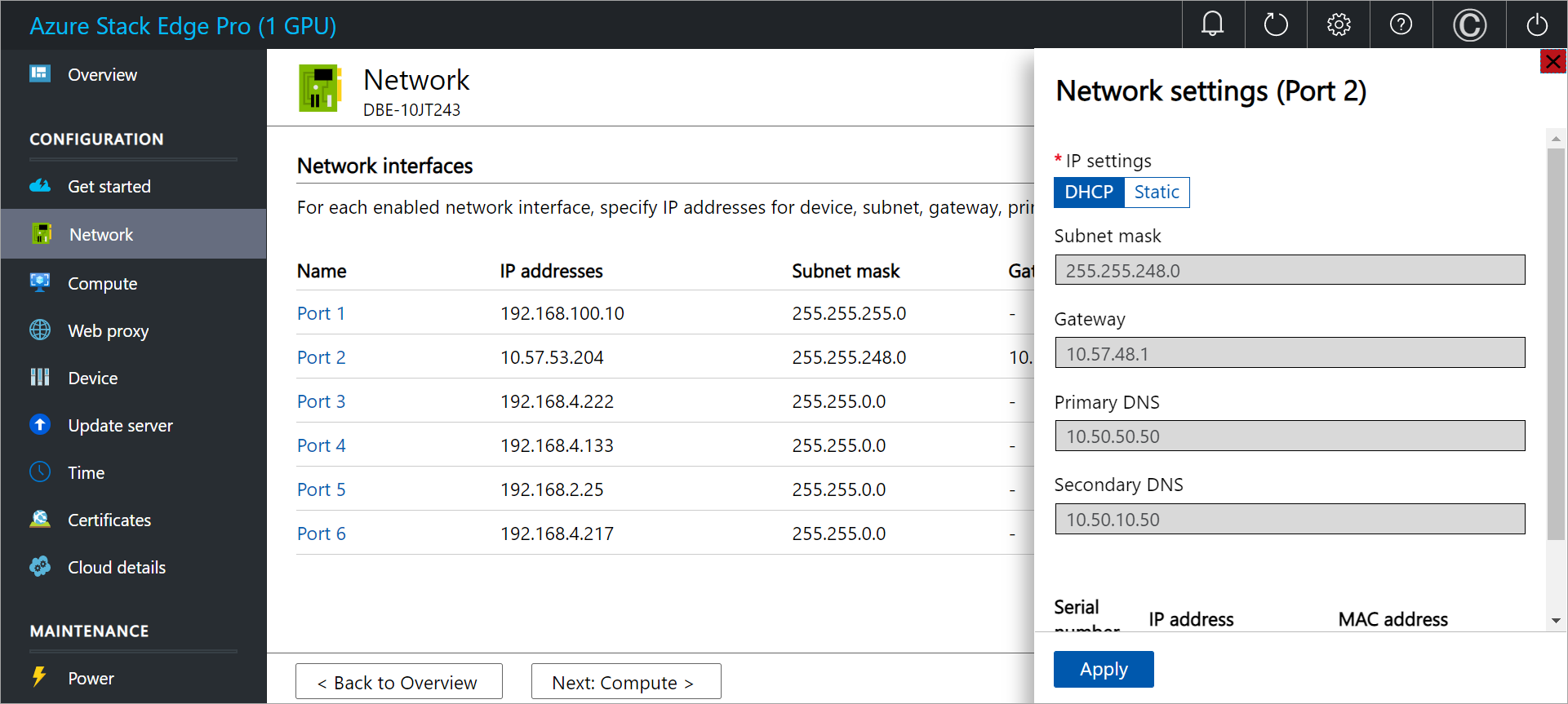
Run the following commands:
ping <default gateway IP address> ping <DNS server IP address>To find out the IP addresses for the default gateway and DNS servers, go to the local UI for your device. Select the port you're interested in, and view the network settings.
cloud init issues (Linux VMs)
Error description: cloud init didn't run, or there were issues while cloud init was running. cloud-init is used to customize a Linux VM when the VM boots for the first time. For more information, see cloud-init support for virtual machines in Azure.
Suggested solutions: To find issues that occurred when cloud init was run:
Check for
cloud initerrors in the following log files:- /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
- /var/log/cloud-init.log
- /var/log/waagent/log
To check for some of the most common issues that prevent cloud init from running successfully, do these steps:
Make sure the VM image is based on
cloud init. Run the following command:cloud-init --versionThe command should return the cloud init version number. If the image isn't
cloud init-based, the command won't return version information.To get help with
cloud initoptions, run the following command:cloud-init --helpMake sure the
cloud initinstance can run successfully with the data source set to Azure.When the data source is set to Azure, the entry in the cloud init logs looks similar to the following one.
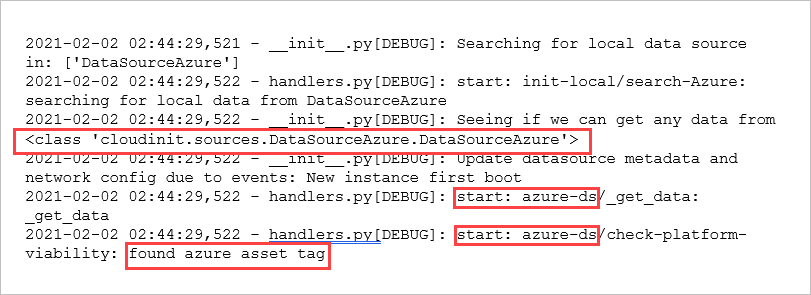
If the data source isn't set to Azure, you may need to revise your
cloud initscript. For more information, see Diving deeper into cloud-init.
Provisioning flags set incorrectly (Linux VMs)
Error description: To successfully deploy a Linux VM in Azure, provisioning must be disabled on the image, and provisioning using cloud init must be enabled. The Provisioning flags that set these values are configured correctly for standard VM images. If you use a custom VM image, you need to make sure they're correct.
Suggested solution: Make sure the Provisioning flags in the /etc/waagent.conf file have the following values:
| Capability | Required value |
|---|---|
| Enable provisioning | Provisioning.Enabled=n |
| Rely on cloud-init to provision | Provisioning.UseCloudInit=y |
Primary network interface attached to a SRIOV enabled virtual switch
Error description: The primary network interface attached to a single root I/O virtualization (SRIOV) interface-enabled virtual switch caused network traffic to bypass the Hyper-V, so the host couldn't receive DHCP requests from the VM, resulting in a provisioning timeout.
Suggested solutions:
Connect the VM primary network interface to a virtual switch without enabling accelerated networking.
On an Azure Stack Edge Pro 1 device, virtual switches created on Port 1 to Port 4 don't enable accelerated networking. On Port 5 or Port 6, virtual switches enable accelerated networking by default.
On an Azure Stack Edge Pro 2 device, virtual switches created on Port 1 or Port 2 don't enable accelerated networking. On Port 3 or Port 4, virtual switches enable accelerated networking by default.
Network interface creation issues
This section provides guidance for issues that cause network interface creation to fail during a VM deployment.
NIC creation timeout
Error description: Creation of the network interface on the VM didn't complete within the allowed timeout period. This failure can be caused by DHCP server issues in your environment.
To verify whether the network interface was created successfully, do these steps:
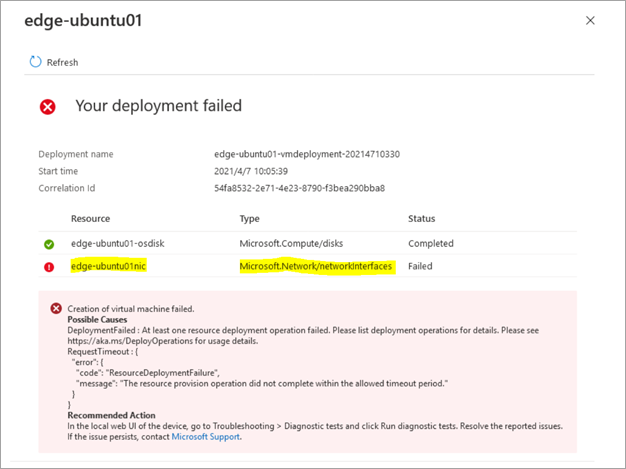
In the Azure portal, go to the Azure Stack Edge resource for your device (go to Edge Services > Virtual machines). Then select Deployments, and navigate to the VM deployment.
If a network interface wasn't created successfully, you see the following error.
Suggested solution: Create the VM again, and assign it a static IP address.
VM creation issues
This section covers common issues that occur during VM creation.
VM creation fails
Error description: If you have a Marketplace image created with Azure Stack Edge earlier than 2403 and then create a VM from the existing Marketplace image, your VM creation fails because Azure Stack Edge 2407 changed the download path for the Marketplace image.
Suggested solution: Use the following steps to delete the existing Marketplace image and then create a new Marketplace image from Azure portal.
From Azure portal, delete the existing Marketplace image.
List the ingestion and the BlobDownload ingestion job for the Marketplace image. Use these steps to Connect to Azure Resource Manager.
Run the following script to list ingestion jobs:
Specify the subscription ID in the following Uri:
$uri1 = "https://management.appliance name.DNS domain/subscriptions/sid/providers/Microsoft.AzureBridge/locations/DBELocal/ingestionJobs/?api-version=2022-03-01"
Function Get-AzCachedAccessToken() { $ErrorActionPreference = 'Stop' $azureRmProfile = [Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Common.Authentication.Abstractions.AzureRmProfileProvider]::Instance.Profile $currentAzureContext = Get-AzContext $profileClient = New-Object Microsoft.Azure.Commands.ResourceManager.Common.RMProfileClient($azureRmProfile) Write-Debug ("Getting access token for tenant" + $currentAzureContext.Subscription.TenantId) $token = $profileClient.AcquireAccessToken($currentAzureContext.Subscription.TenantId) $token.AccessToken } $token = Get-AzCachedAccessToken $headers = @{Authorization = "Bearer $token"; "Content-Type" = "application/json" } $v = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Uri $uri1 -Headers $headers v.valueFind the ingestion job name =
Marketplace image sku nameand kind =BlobDownload.Example: ingestion job name =
Ubuntu-18-04and kind =BlobDownload.
If the ingestion job is found in Step 1, use the following steps to delete the ingestion job and delete the image. For example, the ingestion job name in the example above is
ubuntu-18-04. Additionally,Subscription IDandResource groupname can be found in the example.$uri2 = "https://management.<appliance name>.<DNS domain>/subscriptions/sid/resourceGroups/rgname/providers/Microsoft.AzureBridge/locations/dbelocal/ingestionJobs/<ingestion job name>?api-version=2018-06-01"Invoke-RestMethod -Method DELETE -Uri $uri2 -Headers $headersFollow steps to Create a new VM image from Azure Marketplace.
Not enough memory to create the VM
Error description: When VM creation fails because of insufficient memory, you see the following error.
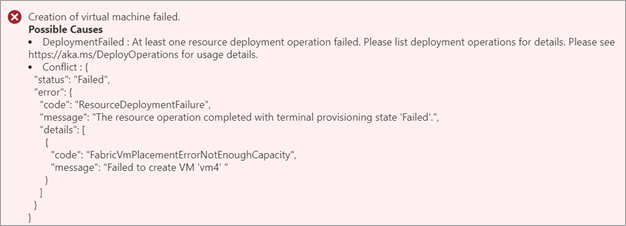
Suggested solution: Check the available memory on the device, and choose the VM size accordingly. For more information, see Supported virtual machine sizes on Azure Stack Edge.
The memory available for the deployment of a VM is constrained by several factors:
The amount of available memory on the device. For more information, see compute and memory specifications in Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU technical specifications and Azure Stack Edge Mini R technical specifications.
If Kubernetes is enabled, the compute memory required for Kubernetes and apps on the Kubernetes cluster.
The overhead for each virtual machine in Hyper-V.
Suggested solutions:
- Use a VM size that requires less memory.
- Stop any VMs that aren't in use from the portal before you deploy the new VM.
- Delete any VMs that are no longer in use.
Insufficient number of GPUs to create GPU VM
If you try to deploy a VM on a GPU device that already has Kubernetes enabled, no GPUs are available, and VM provisioning fails with the following error:
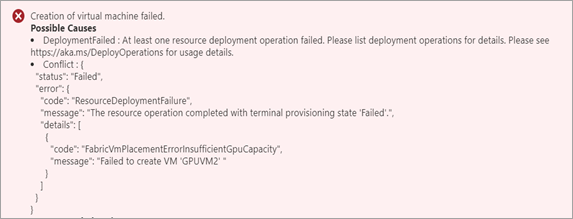
Possible causes: If Kubernetes is enabled before the VM is created, Kubernetes uses all the available GPUs, and you won’t be able to create any GPU-size VMs. You can create as many GPU-size VMs as the number of available GPUs. Your Azure Stack Edge device can be equipped with 1 or 2 GPUs.
Suggested solution: For VM deployment options on a 1-GPU or 2-GPU device with Kubernetes configured, see GPU VMs and Kubernetes.