Customize CMake build settings
Visual Studio uses a CMake configuration file to drive CMake generation and build. CMakePresets.json is supported by Visual Studio 2019 version 16.10 or later and is the recommended CMake configuration file. CMakePresets.json is supported directly by CMake and can be used to drive CMake generation and build from Visual Studio, from VS Code, in a Continuous Integration pipeline, and from the command line on Windows, Linux, and Mac. For more information on CMakePresets.json, see Configure and build with CMake Presets.
If you maintain projects that use a CMakeSettings.json file for CMake build configuration, Visual Studio 2019 and later versions provide a CMake settings editor. The editor lets you add CMake configurations and customize their settings easily. It's intended to be a simpler alternative to manually editing the CMakeSettings.json file. However, if you prefer to edit the file directly, you can select the Edit JSON link in the upper right of the editor.
To open the CMake settings editor, select the Configuration drop-down in the main toolbar and choose Manage Configurations.

Now you see the Settings Editor with the installed configurations on the left.
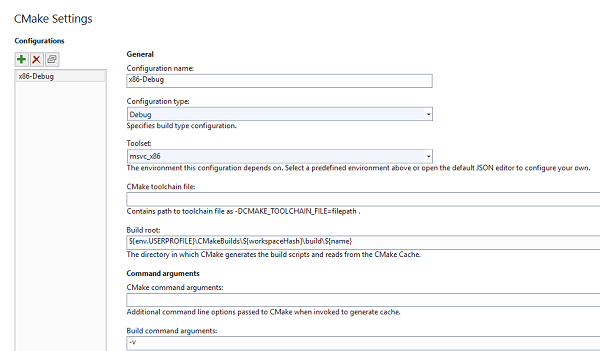
The left pane shows the installed configurations (x86-Debug). The right pane shows the settings for the selected configuration. The settings include the configuration name, configuration type (set to Debug), toolset (set to msvc_x86), CMake toolchain file (empty), build root (contains ${env:USERPROFILE}\CMakeBuilds\${workspaceHash}\build\${name}), CMake command arguments (empty), and build command arguments (-v).
Visual Studio provides one x64-Debug configuration by default. You can add more configurations by choosing the green plus sign. The settings that you see in the editor might vary depending on which configuration is selected.
The options that you choose in the editor are written to a file called CMakeSettings.json. This file provides command-line arguments and environment variables that are passed to CMake when you build the projects. Visual Studio never modifies CMakeLists.txt automatically; by using CMakeSettings.json you can customize the build through Visual Studio while leaving the CMake project files untouched so that others on your team can consume them with whatever tools they're using.
CMake General Settings
The following settings are available under the General heading:
Configuration name
Corresponds to the name setting. This name appears in the C++ configuration dropdown. You can use the ${name} macro to compose other property values such as paths.
Configuration type
Corresponds to the configurationType setting. Defines the build configuration type for the selected generator. Currently supported values are Debug, MinSizeRel, Release, and RelWithDebInfo. It maps to CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE.
Toolset
Corresponds to the inheritedEnvironments setting. Defines the compiler environment that's used to build the selected configuration. Supported values depend on the type of configuration. To create a custom environment, choose the Edit JSON link in the upper right corner of the Settings editor, and edit the CMakeSettings.json file directly.
CMake toolchain file
Path to the CMake toolchain file. This path is passed to CMake as "-DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE = <filepath>. Toolchain files specify locations of compilers and toolchain utilities, and other target platform and compiler-related information. By default, Visual Studio uses the vcpkg toolchain file if this setting is unspecified.
Build root
Corresponds to buildRoot. Maps to CMAKE_BINARY_DIR, and specifies where to create the CMake cache. The specified folder is created if it doesn't exist.
Command arguments
The following settings are available under the Command arguments heading:
CMake command arguments
Corresponds to cmakeCommandArgs. Specifies any more command-line options passed to CMake.
Build command arguments
Corresponds to buildCommandArgs. Specifies more switches to pass to the underlying build system. For example, passing -v when using the Ninja generator forces Ninja to output command lines.
CTest command arguments
Corresponds to ctestCommandArgs. Specifies more command-line options to pass to CTest when running tests.
General settings for remote builds
For configurations such as Linux that use remote builds, the following settings are also available:
rsync command arguments
Extra command-line options passed to rsync, a fast, versatile file-copying tool.
CMake variables and cache
These settings enable you to set CMake variables and save them in CMakeSettings.json. They're passed to CMake at build time, and override whatever values are in the CMakeLists.txt file. You can use this section in the same way that you might use the CMakeGUI to view a list of all the CMake variables available to edit. Choose the Save and generate cache button to view a list of all CMake variables available to edit, including advanced variables (per the CMakeGUI). You can filter the list by variable name.
Corresponds to variables. Contains a name-value pair of CMake variables passed as -D name=value to CMake. If your CMake project build instructions specify the addition of any variables directly to the CMake cache file, we recommend you add them here instead.
Advanced settings
CMake generator
Corresponds to generator. Maps to the CMake -G switch, and specifies the CMake generator to use. This property can also be used as a macro, ${generator}, when composing other property values. Visual Studio currently supports the following CMake generators:
- "Ninja"
- "Unix Makefiles"
- "Visual Studio 16 2019"
- "Visual Studio 16 2019 Win64"
- "Visual Studio 16 2019 ARM"
- "Visual Studio 15 2017"
- "Visual Studio 15 2017 Win64"
- "Visual Studio 15 2017 ARM"
- "Visual Studio 14 2015"
- "Visual Studio 14 2015 Win64"
- "Visual Studio 14 2015 ARM"
Because Ninja is designed for fast build speeds instead of flexibility and function, it's set as the default. However, some CMake projects might be unable to correctly build using Ninja. If that occurs, you can instruct CMake to generate a Visual Studio project instead.
IntelliSense mode
The IntelliSense mode used by the IntelliSense engine. If no mode is selected, Visual Studio inherits the mode from the specified toolset.
Install directory
The directory in which CMake installs targets. Maps to CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX.
CMake executable
The full path to the CMake program executable, including the file name and extension. It allows you to use a custom version of CMake with Visual Studio. For remote builds, specify the CMake location on the remote machine.
For configurations such as Linux that use remote builds, the following settings are also available:
Remote CMakeLists.txt root
The directory on the remote machine that contains the root CMakeLists.txt file.
Remote install root
The directory on the remote machine in which CMake installs targets. Maps to CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX.
Remote copy sources
Specifies whether to copy source files to the remote machine, and lets you specify whether to use rsync or sftp.
Directly edit CMakeSettings.json
You can also directly edit CMakeSettings.json to create custom configurations. The Settings Editor has an Edit JSON button in the upper right that opens the file for editing.
The following example shows a sample configuration, which you can use as a starting point:
{
"name": "x86-Debug",
"generator": "Ninja",
"configurationType": "Debug",
"inheritEnvironments": [ "msvc_x86" ],
"buildRoot": "${env.USERPROFILE}\\CMakeBuilds\\${workspaceHash}\\build\\${name}",
"installRoot": "${env.USERPROFILE}\\CMakeBuilds\\${workspaceHash}\\install\\${name}",
"cmakeCommandArgs": "",
"buildCommandArgs": "-v",
"ctestCommandArgs": ""
},
JSON IntelliSense helps you edit the CMakeSettings.json file:

The JSON editor also informs you when you choose incompatible settings.
For more information about each of the properties in the file, see CMakeSettings.json schema reference.
Visual Studio 2017 provides several CMake configurations that define how CMake is invoked to create the CMake cache for a given project. To add a new configuration, select the configuration drop-down in the toolbar and choose Manage Configurations:

You can choose from the list of predefined configurations:

The first time you select a configuration, Visual Studio creates a CMakeSettings.json file in your project's root folder. This file is used to re-create the CMake cache file, for example after a Clean operation.
To add another configuration, right-click CMakeSettings.json and choose Add Configuration.

You can also edit the file using the CMake Settings Editor. Right-click on CMakeSettings.json in Solution Explorer and choose Edit CMake Settings. Or, select Manage Configurations from the configuration drop-down at the top of the editor window.
You can also directly edit CMakeSettings.json to create custom configurations. The following example shows a sample configuration, which you can use as a starting point:
{
"name": "x86-Debug",
"generator": "Ninja",
"configurationType": "Debug",
"inheritEnvironments": [ "msvc_x86" ],
"buildRoot": "${env.USERPROFILE}\\CMakeBuilds\\${workspaceHash}\\build\\${name}",
"installRoot": "${env.USERPROFILE}\\CMakeBuilds\\${workspaceHash}\\install\\${name}",
"cmakeCommandArgs": "",
"buildCommandArgs": "-v",
"ctestCommandArgs": ""
},
JSON IntelliSense helps you edit the CMakeSettings.json file:

The JSON IntelliSense pop-up for "configurations" shows buildCommandArgs, buildRoot, cmakeCommandArgs, configurationType, among several others.
For more information about each of the properties in the file, see CMakeSettings.json schema reference.
See also
CMake Projects in Visual Studio
Configure a Linux CMake project
Connect to your remote Linux computer
Configure CMake debugging sessions
Deploy, run, and debug your Linux project
CMake predefined configuration reference