Configure Asana for automatic user provisioning
This tutorial describes the steps you need to do in both Asana and Microsoft Entra ID to configure automatic user provisioning. When configured, Microsoft Entra ID automatically provisions and deprovisions users and groups to Asana using the Microsoft Entra provisioning service. For important details on what this service does, how it works, and frequently asked questions, see Automate user provisioning and deprovisioning to SaaS applications with Microsoft Entra ID.
Capabilities supported
- Create users in Asana.
- Remove users in Asana when they do not require access anymore.
- Keep user attributes synchronized between Microsoft Entra ID and Asana.
- Provision groups and group memberships in Asana.
- Single sign-on to Asana (recommended).
Prerequisites
The scenario outlined in this tutorial assumes that you already have the following prerequisites:
- A Microsoft Entra tenant
- An Asana tenant with an Enterprise plan or better enabled
- A user account in Asana with admin permissions
Note
Microsoft Entra provisioning integration relies on the Asana API, which is available to Asana.
Step 1: Plan your provisioning deployment
- Learn about how the provisioning service works.
- Determine who will be in scope for provisioning.
- Determine what data to map between Microsoft Entra ID and Asana.
Step 2: Configure Asana to support provisioning with Microsoft Entra ID
Tip
To enable SAML-based single sign-on for Asana, follow the instructions provided. Single sign-on can be configured independently of automatic provisioning, although these two features complement each other.
Generate Service Account token in Asana
Sign in to Asana by using your admin account.
Select the profile photo from the top bar, and select Admin Console.
Select the Apps tab from with your admin console.
Select Service accounts.
Select Add Service Account and perform the following steps.

- Update Name and Description as needed.
- Under the Permission scopes section, select Scoped permissions and User provisioning (SCIM). Ensure the following permission scopes are selected:
- Users: Read
- Users: Create and modify
- Teams: Read
- Teams: Create and modify
- Select Save Changes.
Copy the token.
Step 3: Add Asana from the Microsoft Entra application gallery
Add Asana from the Microsoft Entra application gallery to start managing provisioning to Asana. If you have previously setup Asana for SSO, you can use the same application. However it's recommended that you create a separate app when testing out the integration initially. Learn more about adding an application from the gallery here.
Step 4: Define who will be in scope for provisioning
The Microsoft Entra provisioning service allows you to scope who will be provisioned based on assignment to the application and or based on attributes of the user / group. If you choose to scope who will be provisioned to your app based on assignment, you can use the following steps to assign users and groups to the application. If you choose to scope who will be provisioned based solely on attributes of the user or group, you can use a scoping filter as described here.
Start small. Test with a small set of users and groups before rolling out to everyone. When scope for provisioning is set to assigned users and groups, you can control this by assigning one or two users or groups to the app. When scope is set to all users and groups, you can specify an attribute based scoping filter.
If you need more roles, you can update the application manifest to add new roles.
Step 5: Configure automatic user provisioning to Asana
This section guides you through the steps to configure the Microsoft Entra provisioning service to create, update, and disable users and groups in Asana based on user and/or group assignments in Microsoft Entra ID.
To configure automatic user provisioning for Asana in Microsoft Entra ID:
Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Cloud Application Administrator.
Browse to Identity > Applications > Enterprise applications
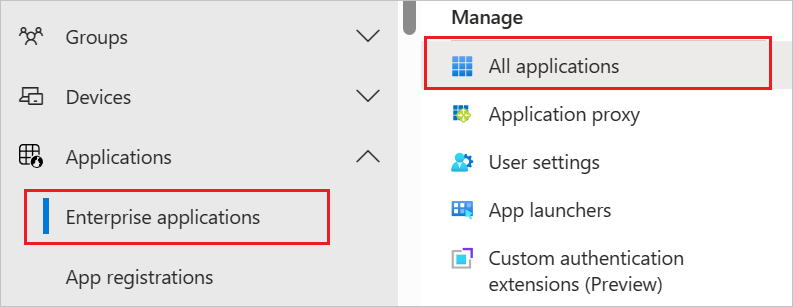
In the applications list, select Asana.
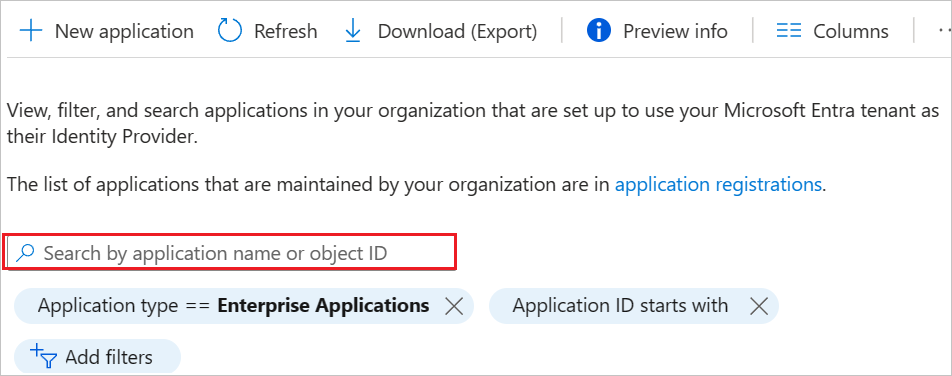
Select the Provisioning tab.
Set the Provisioning Mode to Automatic.

In the Admin Credentials section, input your Asana Tenant URL and Secret Token provided by Asana. Click Test Connection to ensure Microsoft Entra ID can connect to Asana. If the connection fails, contact Asana to check your account setup.

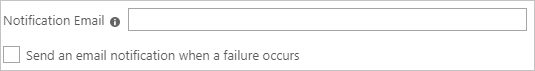
In the Notification Email field, enter the email address of a person or group who should receive the provisioning error notifications and select the Send an email notification when a failure occurs check box.
Select Save.
In the Mappings section, select Synchronize Microsoft Entra users to Asana.
Review the user attributes that are synchronized from Microsoft Entra ID to Asana in the Attribute-Mapping section. The attributes selected as Matching properties are used to match the user accounts in Asana for update operations. If you choose to change the matching target attribute, you need to ensure that the Asana API supports filtering users based on that attribute. Select the Save button to commit any changes.
Attribute Type Supported for filtering Required by Asana userName String ✓ ✓ active Boolean name.formatted String title String urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:department String urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:manager Reference addresses[type eq "work"].country String addresses[type eq "work"].region String addresses[type eq "work"].locality String phoneNumbers[type eq "work"].value String urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:employeeNumber String urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:costCenter String urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:organization String urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:division String Under the Mappings section, select Synchronize Microsoft Entra groups to Asana.
Review the group attributes that are synchronized from Microsoft Entra ID to Asana in the Attribute-Mapping section. The attributes selected as Matching properties are used to match the groups in Asana for update operations. Select the Save button to commit any changes.
Attribute Type Supported for filtering Required by Asana displayName String ✓ ✓ members Reference To configure scoping filters, refer to the following instructions provided in the Scoping filter tutorial.
To enable the Microsoft Entra provisioning service for Asana, change the Provisioning Status to On in the Settings section.

Define the users and groups that you would like to provision to Asana by choosing the appropriate values in Scope in the Settings section.
When you're ready to provision, click Save.

This operation starts the initial synchronization cycle of all users and groups defined in Scope in the Settings section. The initial cycle takes longer to execute than next cycles, which occur approximately every 40 minutes as long as the Microsoft Entra provisioning service is running.
Step 6: Monitor your deployment
Once you've configured provisioning, use the following resources to monitor your deployment:
- Use the provisioning logs to determine which users have been provisioned successfully or unsuccessfully
- Check the progress bar to see the status of the provisioning cycle and how close it's to completion
- If the provisioning configuration seems to be in an unhealthy state, the application goes into quarantine. Learn more about quarantine states here.
Change log
- 11/06/2021 - Dropped support for externalId, name.givenName and name.familyName. Added support for preferredLanguage , title and urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:department. Enabled Group Provisioning.
- 05/23/2023 - Dropped support for preferredLanguage Added support for urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:manager.
- 09/07/2023 - Added support for addresses[type eq "work"].locality, addresses[type eq "work"].region, addresses[type eq "work"].country, phoneNumbers[type eq "work"].value, urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:employeeNumber, urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:costCenter, urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:organization and urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User:division.
More resources
- Managing user account provisioning for Enterprise Apps
- What is application access and single sign-on with Microsoft Entra ID?