Xamarin.Forms and Azure Cognitive Services Introduction
Microsoft Cognitive Services are a set of APIs, SDKs, and services available to developers to make their applications more intelligent by adding features such as facial recognition, speech recognition, and language understanding. This article provides an introduction to the sample application that demonstrates how to invoke some of the Microsoft Cognitive Service APIs.
Overview
The accompanying sample is a todo list application that provides functionality to:
- View a list of tasks.
- Add and edit tasks through the soft keyboard, or by performing speech recognition with the Microsoft Speech API.
- Spell check tasks using the Bing Spell Check API. For more information, see Spell Checking using the Bing Spell Check API.
- Translate tasks from English to German using the Translator API. For more information, see Text Translation using the Translator API.
- Delete tasks.
- Set a task's status to 'done'.
Warning
The Bing Speech API has been deprecated in favor of the Azure Speech Service. For a sample dedicated to Azure Speech Service, see Speech recognition with the Speech Service API.
Tasks are stored in a local SQLite database. For more information about using a local SQLite database, see Working with a Local Database.
The TodoListPage is displayed when the application is launched. This page displays a list of any tasks stored in the local database, and allows the user to create a new task or to rate the application:
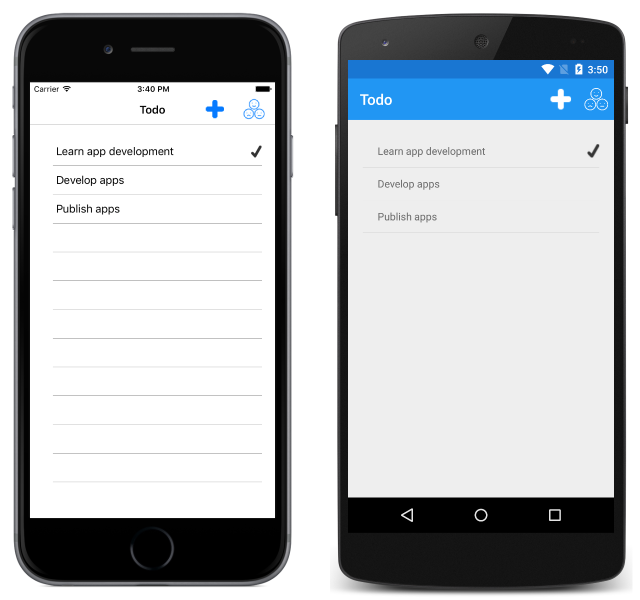
New items can be created by clicking on the + button, which navigates to the TodoItemPage. This page can also be navigated to by selecting a task:
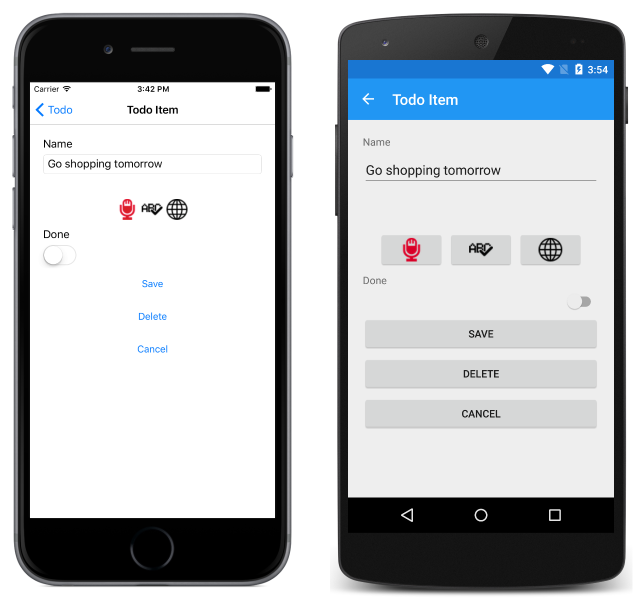
The TodoItemPage allows tasks to be created, edited, spell-checked, translated, saved, and deleted. Speech recognition can be used to create or edit a task. This is achieved by pressing the microphone button to start recording, and by pressing the same button a second time to stop recording, which sends the recording to the Bing Speech Recognition API.
Understand the application anatomy
The shared code project for the sample application consists of five main folders:
| Folder | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Models | Contains the data model classes for the application. This includes the TodoItem class, which models a single item of data used by the application. The folder also includes classes used to model JSON responses returned from different Microsoft Cognitive Service APIs. |
| Repositories | Contains the ITodoItemRepository interface and TodoItemRepository class that are used to perform database operations. |
| Services | Contains the interfaces and classes that are used to access different Microsoft Cognitive Service APIs, along with interfaces that are used by the DependencyService class to locate the classes that implement the interfaces in platform projects. |
| Utils | Contains the Timer class, which is used by the AuthenticationService class to renew a JWT access token every 9 minutes. |
| Views | Contains the pages for the application. |
The shared code project also contains some important files:
| File | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Constants.cs | The Constants class, which specifies the API keys and endpoints for the Microsoft Cognitive Service APIs that are invoked. The API key constants require updating to access the different Cognitive Service APIs. |
| App.xaml.cs | The App class is responsible for instantiating both the first page that will be displayed by the application on each platform, and the TodoManager class that is used to invoke database operations. |
NuGet packages
The sample application uses the following NuGet packages:
Newtonsoft.Json– provides a JSON framework for .NET.PCLStorage– provides a set of cross-platform local file IO APIs.sqlite-net-pcl– provides SQLite database storage.Xam.Plugin.Media– provides cross-platform photo taking and picking APIs.
In addition, these NuGet packages also install their own dependencies.
Model the data
The sample application uses the TodoItem class to model the data that is displayed and stored in the local SQLite database. The following code example shows the TodoItem class:
public class TodoItem
{
[PrimaryKey, AutoIncrement]
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool Done { get; set; }
}
The ID property is used to uniquely identify each TodoItem instance, and is decorated with SQLite attributes that make the property an auto-incrementing primary key in the database.
Invoke database operations
The TodoItemRepository class implements database operations, and an instance of the class can be accessed through the App.TodoManager property. The TodoItemRepository class provides the following methods to invoke database operations:
- GetAllItemsAsync – retrieves all of the items from the local SQLite database.
- GetItemAsync – retrieves a specified item from the local SQLite database.
- SaveItemAsync – creates or updates an item in the local SQLite database.
- DeleteItemAsync – deletes the specified item from the local SQLite database.
Platform project implementations
The Services folder in the shared code project contains the IFileHelper and IAudioRecorderService interfaces that are used by the DependencyService class to locate the classes that implement the interfaces in platform projects.
The IFileHelper interface is implemented by the FileHelper class in each platform project. This class consists of a single method, GetLocalFilePath, which returns a local file path for storing the SQLite database.
The IAudioRecorderService interface is implemented by the AudioRecorderService class in each platform project. This class consists of StartRecording, StopRecording, and supporting methods, which use platform APIs to record audio from the device's microphone and store it as a wav file. On iOS, the AudioRecorderService uses the AVFoundation API to record audio. On Android, the AudioRecordService uses the AudioRecord API to record audio. On the Universal Windows Platform (UWP), the AudioRecorderService uses the AudioGraph API to record audio.
Invoke cognitive services
The sample application invokes the following Microsoft Cognitive Services:
- Microsoft Speech API. For more information, see Speech Recognition using the Microsoft Speech API.
- Bing Spell Check API. For more information, see Spell Checking using the Bing Spell Check API.
- Translate API. For more information, see Text Translation using the Translator API.