Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this tutorial for C# development with ASP.NET Core, you create a C# ASP.NET Core web app in Visual Studio.
This tutorial shows you how to:
- Create a Visual Studio project
- Create a C# ASP.NET Core web app
- Make changes to the web app
- Explore IDE features
- Run the web app
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need:
- Visual Studio installed. Visit the Visual Studio downloads page for a free version. For more information about upgrading to the latest Visual Studio release, see Visual Studio updates.
- The ASP.NET and web development workload installed. To verify or install this workload in Visual Studio, select Tools > Get Tools and Features. For more information, see Change workloads or individual components.
Create a project
First, you create an ASP.NET Core project. The project type comes with all the template files you need to build a fully functional website.
On the start window, select Create a new project.
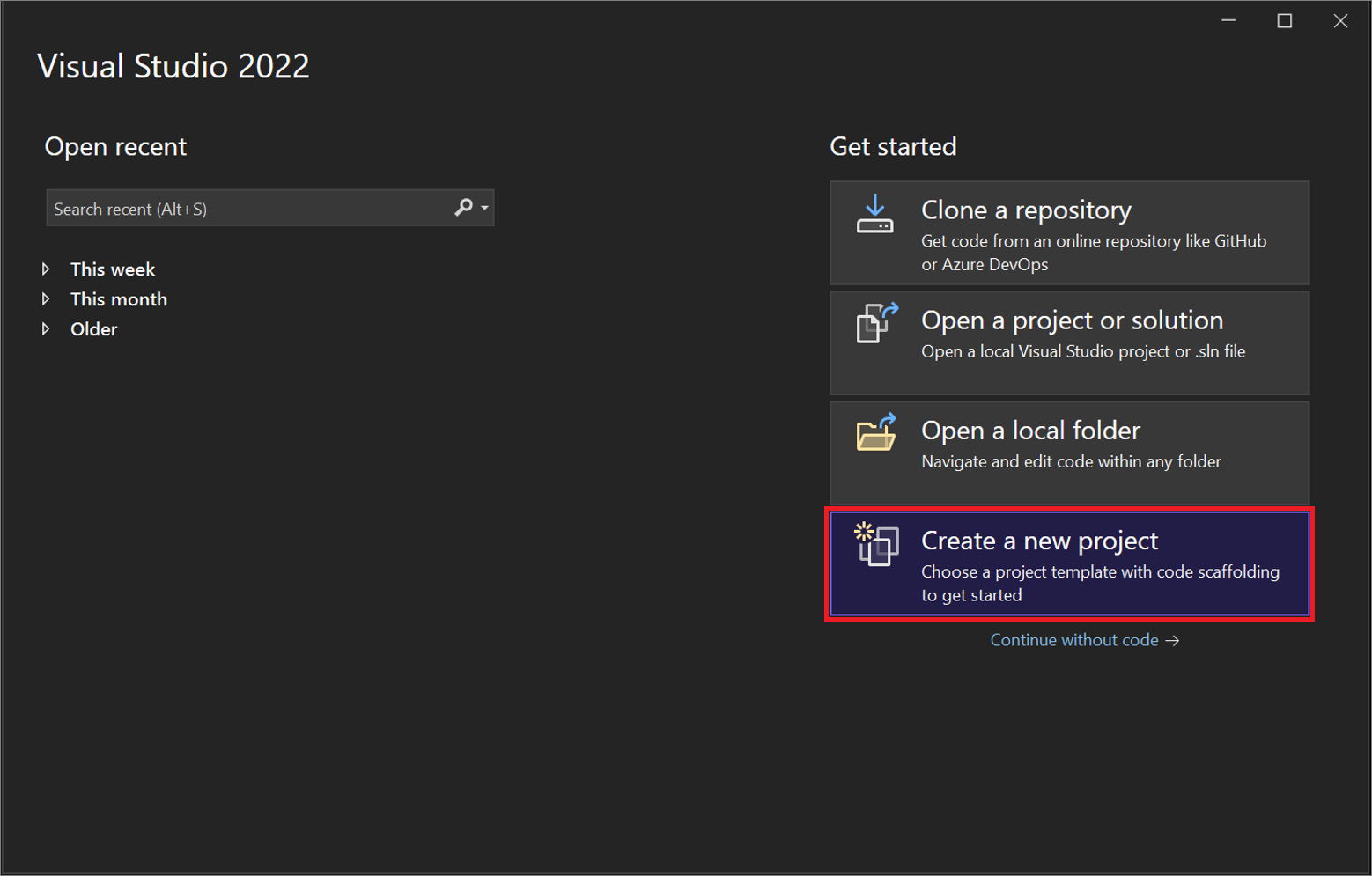
In the Create a new project window, select C# from the Language list. Next, select Windows from the All platforms list, and Web from the All project types list.
After you apply the language, platform, and project type filters, select the ASP.NET Core Web App (Razor Pages) template, and then select Next.
In the Configure your new project window, enter MyCoreApp in the Project name field. Then, select Next.
In the Additional information window, verify that .NET 8.0 appears in the Target Framework field.
From this window, you can enable container support and add authentication support. The drop-down menu for Authentication Type has the following four options:
- None: No authentication.
- Individual accounts: These authentications are stored in a local or Azure-based database.
- Microsoft identity platform: This option uses Microsoft Entra ID or Microsoft 365 for authentication.
- Windows: Suitable for intranet applications.
Leave the Enable container support box unchecked, and select None for Authentication Type.
Select Create.
Visual Studio opens your new project.
On the start window, select Create a new project.

In the Create a new project window, select C# from the Language list. Next, select Windows from the All platforms list, and Web from the All project types list.
After you apply the language, platform, and project type filters, select the ASP.NET Core Web App (Razor Pages) template, and then select Next.
In the Configure your new project window, enter MyCoreApp in the Project name field. Then, select Next.
In the Additional information window, verify that .NET 9.0 appears in the Framework field.
From this window, you can enable container support and add authentication support. The drop-down menu for Authentication Type has the following four options:
- None: No authentication.
- Individual accounts: These authentications are stored in a local or Azure-based database.
- Microsoft identity platform: This option uses Microsoft Entra ID or Microsoft 365 for authentication.
- Windows: Suitable for intranet applications.
Leave the Enable container support box unchecked, and select None for Authentication Type.
Select Create.
Visual Studio opens your new project.
About your solution
This solution follows the Razor Page design pattern. It's different than the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern in that it's streamlined to include the model and controller code within the Razor Page itself.
Tour your solution
The project template creates a solution with a single ASP.NET Core project named MyCoreApp. Select the Solution Explorer tab to view its contents.

Expand the Pages folder.

Select the Index.cshtml file, and view in the code editor.

Each .cshtml file has an associated code file. To open the code file in the editor, expand the Index.cshtml node in Solution Explorer, and select the Index.cshtml.cs file.

View the Index.cshtml.cs file in the code editor.

The project contains a wwwroot folder, which is the root for your website. Expand the folder to view its contents.

You can put static site content such as CSS, images, and JavaScript libraries directly in the paths where you want them.
The project also contains configuration files that manage the web app at run time. The default application configuration is stored in appsettings.json. However, you can override these settings by using appsettings.Development.json. Expand the appsettings.json file to view the appsettings.Development.json file.

Run, debug, and make changes
In the toolbar, select the https button to build and run the app in debug mode. Alternatively, press F5, or go to Debug > Start Debugging from the menu bar.

Note
You might also get a message that asks if you want to accept an ASP.NET Core SSL certificate. To view the code in a web browser, select Yes, and then select Yes if you receive a follow-up security warning message. Learn more about enforcing SSL in ASP.NET Core.
Visual Studio launches a browser window. You should then see Home and Privacy pages in the menu bar.
Select Privacy from the menu bar. The Privacy page in the browser renders the text that's set in the Privacy.cshtml file.

Return to Visual Studio, and then press Shift+F5 to stop debugging. This action closes the project in the browser window.
In Visual Studio, open Privacy.cshtml for editing. Next, delete the sentence, Use this page to detail your site's privacy policy and replace it with This page is under construction as of @ViewData["TimeStamp"].

Now, let's make a code change. Select Privacy.cshtml.cs. Then, clean up the
usingdirectives at the top of the file by selecting the following shortcut:Mouseover or select a greyed out
usingdirective. A Quick Actions light bulb appears below the caret or in the left margin. Select the light bulb, and then select the expand arrow next to Remove unnecessary usings.
Now select Preview changes to see what changes.

Select Apply. Visual Studio deletes the unnecessary
usingdirectives from the file.Next, create a string for the current date that's formatted for your culture or region by using the DateTime.ToString method.
- The first argument for the method specifies how the date should be displayed. This example uses the format specifier (
d) which indicates the short date format. - The second argument is the CultureInfo object that specifies the culture or region for the date. The second argument determines, among other things, the language of any words in the date, and the type of separators used.
Change the body of the
OnGet()method in Privacy.cshtml.cs to the following code:public void OnGet() { string dateTime = DateTime.Now.ToString("d", new CultureInfo("en-US")); ViewData["TimeStamp"] = dateTime; }- The first argument for the method specifies how the date should be displayed. This example uses the format specifier (
Notice that the following
usingdirective automatically gets added to the top of the file:using System.Globalization;System.Globalizationcontains the CultureInfo class.Press F5 to open your project in the web browser.
At the top of the web site, select Privacy to view your changes.

Close the web browser, press Shift+F5 to stop debugging.
Change your Home page
In the Solution Explorer, expand the Pages folder, and then select Index.cshtml.

The Index.cshtml file corresponds with your Home page in the web app, which runs in a web browser.

In the code editor, you see HTML code for the text that appears on the Home page.

Replace the Welcome text with Hello World!

Select https or press Ctrl+F5 to run the app and open it in a web browser.

In the web browser, you see your new changes on the Home page.

Close the web browser, press Shift+F5 to stop debugging, and save your project. You can now close Visual Studio.
Tour your solution
The project template creates a solution with a single ASP.NET Core project named MyCoreApp. Select the Solution Explorer tab to view its contents.

Expand the Pages folder.

Select the Index.cshtml file, and view in the code editor.

Each .cshtml file has an associated code file. To open the code file in the editor, expand the Index.cshtml node in Solution Explorer, and select the Index.cshtml.cs file.

View the Index.cshtml.cs file in the code editor.

The project contains a wwwroot folder, which is the root for your website. Expand the folder to view its contents.

You can put static site content such as CSS, images, and JavaScript libraries directly in the paths where you want them.
The project also contains configuration files that manage the web app at run time. The default application configuration is stored in appsettings.json. However, you can override these settings by using appsettings.Development.json. Expand the appsettings.json file to view the appsettings.Development.json file.

Run, debug, and make changes
In the toolbar, select the https button to build and run the app in debug mode. Alternatively, press F5, or go to Debug > Start Debugging from the menu bar.

Note
You might also get a message that asks if you want to accept an ASP.NET Core SSL certificate. To view the code in a web browser, select Yes, and then select Yes if you receive a follow-up security warning message. Learn more about enforcing SSL in ASP.NET Core.
Visual Studio launches a browser window. You should then see Home and Privacy pages in the menu bar.
Select Privacy from the menu bar. The Privacy page in the browser renders the text that's set in the Privacy.cshtml file.

Return to Visual Studio, and then press Shift+F5 to stop debugging. This action closes the project in the browser window.
In Visual Studio, open Privacy.cshtml for editing. Next, delete the sentence, Use this page to detail your site's privacy policy and replace it with This page is under construction as of @ViewData["TimeStamp"].

Now, let's make a code change. Select Privacy.cshtml.cs. Then, clean up the
usingdirectives at the top of the file by selecting the following shortcut:Mouseover or select a greyed out
usingdirective. A Quick Actions light bulb appears below the caret or in the left margin. Select the light bulb, and then select the expand arrow next to Remove unnecessary usings.
Now select Preview changes to see what changes.

Select Apply. Visual Studio deletes the unnecessary
usingdirectives from the file.Next, create a string for the current date that's formatted for your culture or region by using the DateTime.ToString method.
- The first argument for the method specifies how the date should be displayed. This example uses the format specifier (
d) which indicates the short date format. - The second argument is the CultureInfo object that specifies the culture or region for the date. The second argument determines, among other things, the language of any words in the date, and the type of separators used.
Change the body of the
OnGet()method in Privacy.cshtml.cs to the following code:public void OnGet() { string dateTime = DateTime.Now.ToString("d", new CultureInfo("en-US")); ViewData["TimeStamp"] = dateTime; }- The first argument for the method specifies how the date should be displayed. This example uses the format specifier (
Notice that the following
usingdirective automatically gets added to the top of the file:using System.Globalization;System.Globalizationcontains the CultureInfo class.Press F5 to open your project in the web browser.
At the top of the web site, select Privacy to view your changes.

Close the web browser, press Shift+F5 to stop debugging.
Change your Home page
In the Solution Explorer, expand the Pages folder, and then select Index.cshtml.

The Index.cshtml file corresponds with your Home page in the web app, which runs in a web browser.

In the code editor, you see HTML code for the text that appears on the Home page.

Replace the Welcome text with Hello World!

Select https or press Ctrl+F5 to run the app and open it in a web browser.

In the web browser, you see your new changes on the Home page.

Close the web browser, press Shift+F5 to stop debugging, and save your project. You can now close Visual Studio.
Next steps
Congratulations on completing this tutorial! We hope you enjoyed learning about C#, ASP.NET Core, and the Visual Studio IDE. To learn more about creating a web app or website with C# and ASP.NET, continue with the following tutorial:
Or, learn how to containerize your web app with Docker:





