Define unique keys for an Azure Cosmos DB container
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
This article presents the different ways to define unique keys when creating an Azure Cosmos DB container. It's currently possible to perform this operation either by using the Azure portal or through one of the SDKs.
Use the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Create a new Azure Cosmos DB account or select an existing one.
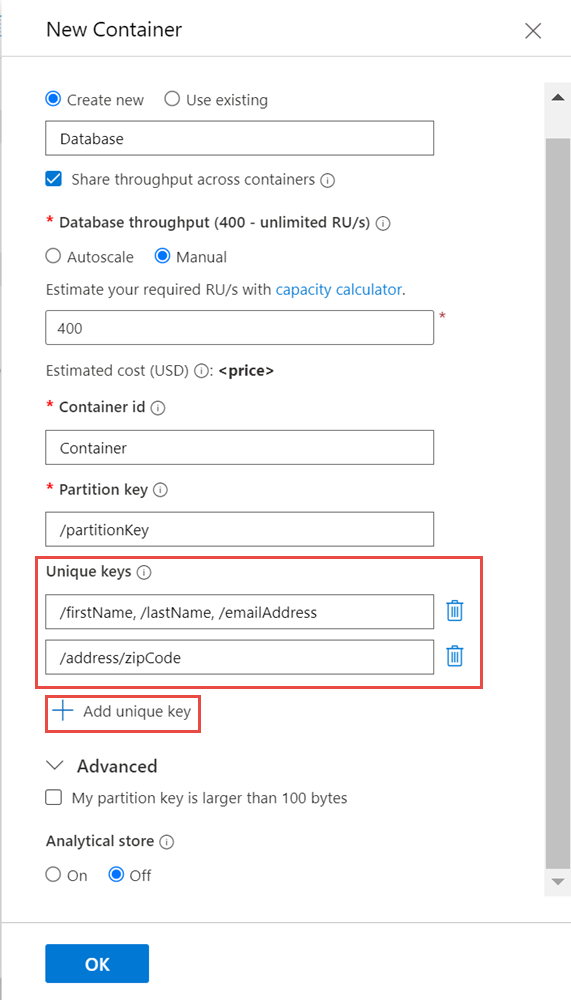
Open the Data Explorer pane and select the container that you want to work on.
Click on New Container.
In the Add Container dialog, click on + Add unique key to add a unique key entry.
Enter the path(s) of the unique key constraint
If needed, add more unique key entries by clicking on + Add unique key
Use PowerShell
To create a container with unique keys see, Create an Azure Cosmos DB container with unique key and TTL
Use the .NET SDK
When creating a new container using the .NET SDK v2, a UniqueKeyPolicy object can be used to define unique key constraints.
client.CreateDocumentCollectionAsync(UriFactory.CreateDatabaseUri("database"), new DocumentCollection
{
Id = "container",
PartitionKey = new PartitionKeyDefinition { Paths = new Collection<string>(new List<string> { "/myPartitionKey" }) },
UniqueKeyPolicy = new UniqueKeyPolicy
{
UniqueKeys = new Collection<UniqueKey>(new List<UniqueKey>
{
new UniqueKey { Paths = new Collection<string>(new List<string> { "/firstName", "/lastName", "/emailAddress" }) },
new UniqueKey { Paths = new Collection<string>(new List<string> { "/address/zipCode" }) }
})
}
});
Use the Java SDK
When creating a new container using the Java SDK, a UniqueKeyPolicy object can be used to define unique key constraints.
// create a new DocumentCollection object
DocumentCollection container = new DocumentCollection();
container.setId("container");
// create array of strings and populate them with the unique key paths
Collection<String> uniqueKey1Paths = new ArrayList<String>();
uniqueKey1Paths.add("/firstName");
uniqueKey1Paths.add("/lastName");
uniqueKey1Paths.add("/emailAddress");
Collection<String> uniqueKey2Paths = new ArrayList<String>();
uniqueKey2Paths.add("/address/zipCode");
// create UniqueKey objects and set their paths
UniqueKey uniqueKey1 = new UniqueKey();
UniqueKey uniqueKey2 = new UniqueKey();
uniqueKey1.setPaths(uniqueKey1Paths);
uniqueKey2.setPaths(uniqueKey2Paths);
// create a new UniqueKeyPolicy object and set its unique keys
UniqueKeyPolicy uniqueKeyPolicy = new UniqueKeyPolicy();
Collection<UniqueKey> uniqueKeys = new ArrayList<UniqueKey>();
uniqueKeys.add(uniqueKey1);
uniqueKeys.add(uniqueKey2);
uniqueKeyPolicy.setUniqueKeys(uniqueKeys);
// set the unique key policy
container.setUniqueKeyPolicy(uniqueKeyPolicy);
// create the container
client.createCollection(String.format("/dbs/%s", "database"), container, null);
Use the Node.js SDK
When creating a new container using the Node.js SDK, a UniqueKeyPolicy object can be used to define unique key constraints.
client.database('database').containers.create({
id: 'container',
uniqueKeyPolicy: {
uniqueKeys: [
{ paths: ['/firstName', '/lastName', '/emailAddress'] },
{ paths: ['/address/zipCode'] }
]
}
});
Use the Python SDK
When creating a new container using the Python SDK, unique key constraints can be specified as part of the dictionary passed as parameter.
client.CreateContainer('dbs/' + config['DATABASE'], {
'id': 'container',
'uniqueKeyPolicy': {
'uniqueKeys': [
{'paths': ['/firstName', '/lastName', '/emailAddress']},
{'paths': ['/address/zipCode']}
]
}
})
Next steps
- Learn more about partitioning
- Explore how indexing works