Enable Web Application Firewall using Azure PowerShell
You can restrict traffic on an application gateway with a Web Application Firewall (WAF). The WAF uses OWASP rules to protect your application. These rules include protection against attacks such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting attacks, and session hijacks.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Set up the network
- Create an application gateway with WAF enabled
- Create a virtual machine scale set
- Create a storage account and configure diagnostics
If you prefer, you can complete this article using the Azure portal or the Azure CLI.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. To get started, see Install Azure PowerShell. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
Azure Cloud Shell
Azure hosts Azure Cloud Shell, an interactive shell environment that you can use through your browser. You can use either Bash or PowerShell with Cloud Shell to work with Azure services. You can use the Cloud Shell preinstalled commands to run the code in this article, without having to install anything on your local environment.
To start Azure Cloud Shell:
| Option | Example/Link |
|---|---|
| Select Try It in the upper-right corner of a code or command block. Selecting Try It doesn't automatically copy the code or command to Cloud Shell. |  |
| Go to https://shell.azure.com, or select the Launch Cloud Shell button to open Cloud Shell in your browser. |  |
| Select the Cloud Shell button on the menu bar at the upper right in the Azure portal. |  |
To use Azure Cloud Shell:
Start Cloud Shell.
Select the Copy button on a code block (or command block) to copy the code or command.
Paste the code or command into the Cloud Shell session by selecting Ctrl+Shift+V on Windows and Linux, or by selecting Cmd+Shift+V on macOS.
Select Enter to run the code or command.
If you choose to install and use the PowerShell locally, this article requires the Azure PowerShell module version 1.0.0 or later. Run Get-Module -ListAvailable Az to find the version. If you need to upgrade, see Install Azure PowerShell module. If you're running PowerShell locally, you also need to run Login-AzAccount to create a connection with Azure.
Create a resource group
A resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed. Create an Azure resource group using New-AzResourceGroup.
$location = "eastus"
$rgname = New-AzResourceGroup -Name myResourceGroupAG -Location $location
Create network resources
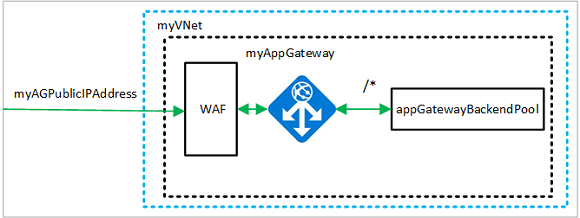
Create the subnet configurations named myBackendSubnet and myAGSubnet using New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig. Create the virtual network named myVNet using New-AzVirtualNetwork with the subnet configurations. And finally, create the public IP address named myAGPublicIPAddress using New-AzPublicIpAddress. These resources are used to provide network connectivity to the application gateway and its associated resources.
$backendSubnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig `
-Name myBackendSubnet `
-AddressPrefix 10.0.1.0/24
$agSubnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig `
-Name myAGSubnet `
-AddressPrefix 10.0.2.0/24
$vnet = New-AzVirtualNetwork `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Location eastus `
-Name myVNet `
-AddressPrefix 10.0.0.0/16 `
-Subnet $backendSubnetConfig, $agSubnetConfig
$pip = New-AzPublicIpAddress `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Location eastus `
-Name myAGPublicIPAddress `
-AllocationMethod Static `
-Sku Standard
Create an application gateway
In this section, you create resources that support the application gateway, and then finally create it and a WAF. The resources that you create include:
- IP configurations and frontend port - Associates the subnet that you previously created to the application gateway and assigns a port to use to access it.
- Default pool - All application gateways must have at least one backend pool of servers.
- Default listener and rule - The default listener listens for traffic on the port that was assigned and the default rule sends traffic to the default pool.
Create the IP configurations and frontend port
Associate myAGSubnet that you previously created to the application gateway using New-AzApplicationGatewayIPConfiguration. Assign myAGPublicIPAddress to the application gateway using New-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendIPConfig.
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myVNet
$subnet=$vnet.Subnets[1]
$gipconfig = New-AzApplicationGatewayIPConfiguration `
-Name myAGIPConfig `
-Subnet $subnet
$fipconfig = New-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendIPConfig `
-Name myAGFrontendIPConfig `
-PublicIPAddress $pip
$frontendport = New-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendPort `
-Name myFrontendPort `
-Port 80
Create the backend pool and settings
Create the backend pool named appGatewayBackendPool for the application gateway using New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPool. Configure the settings for the backend address pools using New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendHttpSettings.
$defaultPool = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPool `
-Name appGatewayBackendPool
$poolSettings = New-AzApplicationGatewayBackendHttpSettings `
-Name myPoolSettings `
-Port 80 `
-Protocol Http `
-CookieBasedAffinity Enabled `
-RequestTimeout 120
Create the default listener and rule
A listener is required to enable the application gateway to route traffic appropriately to the backend address pools. In this example, you create a basic listener that listens for traffic at the root URL.
Create a listener named mydefaultListener using New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener with the frontend configuration and frontend port that you previously created. A rule is required for the listener to know which backend pool to use for incoming traffic. Create a basic rule named rule1 using New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule.
$defaultlistener = New-AzApplicationGatewayHttpListener `
-Name mydefaultListener `
-Protocol Http `
-FrontendIPConfiguration $fipconfig `
-FrontendPort $frontendport
$frontendRule = New-AzApplicationGatewayRequestRoutingRule `
-Name rule1 `
-RuleType Basic `
-Priority 1000 `
-HttpListener $defaultlistener `
-BackendAddressPool $defaultPool `
-BackendHttpSettings $poolSettings
Create the application gateway with the WAF
Now that you created the necessary supporting resources, specify parameters for the application gateway using New-AzApplicationGatewaySku. Specify the Firewall Policy using New-AzApplicationGatewayFirewallPolicy. And then create the application gateway named myAppGateway using New-AzApplicationGateway.
$sku = New-AzApplicationGatewaySku `
-Name WAF_v2 `
-Tier WAF_v2 `
-Capacity 2
$policySetting = New-AzApplicationGatewayFirewallPolicySetting `
-Mode Prevention -State Enabled `
-MaxRequestBodySizeInKb 100 -MaxFileUploadInMb 256
$wafPolicy = New-AzApplicationGatewayFirewallPolicy -Name wafpolicyNew -ResourceGroup myResourceGroupAG `
-Location $location -PolicySetting $PolicySetting
$appgw = New-AzApplicationGateway `
-Name myAppGateway `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Location eastus `
-BackendAddressPools $defaultPool `
-BackendHttpSettingsCollection $poolSettings `
-FrontendIpConfigurations $fipconfig `
-GatewayIpConfigurations $gipconfig `
-FrontendPorts $frontendport `
-HttpListeners $defaultlistener `
-RequestRoutingRules $frontendRule `
-Sku $sku `
-FirewallPolicy $wafPolicy
Create a virtual machine scale set
In this example, you create a virtual machine scale set to provide servers for the backend pool in the application gateway. You assign the scale set to the backend pool when you configure the IP settings.
Replace <username> and <password> with your values before you run this script.
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myVNet
$appgw = Get-AzApplicationGateway `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myAppGateway
$backendPool = Get-AzApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPool `
-Name appGatewayBackendPool `
-ApplicationGateway $appgw
$ipConfig = New-AzVmssIpConfig `
-Name myVmssIPConfig `
-SubnetId $vnet.Subnets[0].Id `
-ApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPoolsId $backendPool.Id
$vmssConfig = New-AzVmssConfig `
-Location eastus `
-SkuCapacity 2 `
-SkuName Standard_DS2 `
-UpgradePolicyMode Automatic
Set-AzVmssStorageProfile $vmssConfig `
-ImageReferencePublisher MicrosoftWindowsServer `
-ImageReferenceOffer WindowsServer `
-ImageReferenceSku 2016-Datacenter `
-ImageReferenceVersion latest `
-OsDiskCreateOption FromImage
Set-AzVmssOsProfile $vmssConfig `
-AdminUsername <username> `
-AdminPassword "<password>" `
-ComputerNamePrefix myvmss
Add-AzVmssNetworkInterfaceConfiguration `
-VirtualMachineScaleSet $vmssConfig `
-Name myVmssNetConfig `
-Primary $true `
-IPConfiguration $ipConfig
New-AzVmss `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myvmss `
-VirtualMachineScaleSet $vmssConfig
Install IIS
$publicSettings = @{ "fileUris" = (,"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-docs-powershell-samples/master/application-gateway/iis/appgatewayurl.ps1");
"commandToExecute" = "powershell -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File appgatewayurl.ps1" }
$vmss = Get-AzVmss -ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG -VMScaleSetName myvmss
Add-AzVmssExtension -VirtualMachineScaleSet $vmss `
-Name "customScript" `
-Publisher "Microsoft.Compute" `
-Type "CustomScriptExtension" `
-TypeHandlerVersion 1.8 `
-Setting $publicSettings
Update-AzVmss `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myvmss `
-VirtualMachineScaleSet $vmss
Create a storage account and configure diagnostics
In this article, the application gateway uses a storage account to store data for detection and prevention purposes. You could also use Azure Monitor logs or Event Hub to record data.
Create the storage account
Create a storage account named myagstore1 using New-AzStorageAccount.
$storageAccount = New-AzStorageAccount `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myagstore1 `
-Location eastus `
-SkuName "Standard_LRS"
Configure diagnostics
Configure diagnostics to record data into the ApplicationGatewayAccessLog, ApplicationGatewayPerformanceLog, and ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog logs using Set-AzDiagnosticSetting.
$appgw = Get-AzApplicationGateway `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myAppGateway
$store = Get-AzStorageAccount `
-ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG `
-Name myagstore1
Set-AzDiagnosticSetting `
-ResourceId $appgw.Id `
-StorageAccountId $store.Id `
-Category ApplicationGatewayAccessLog, ApplicationGatewayPerformanceLog, ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog `
-Enabled $true `
-RetentionEnabled $true `
-RetentionInDays 30
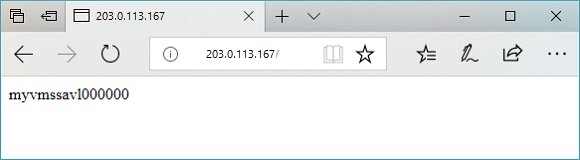
Test the application gateway
You can use Get-AzPublicIPAddress to get the public IP address of the application gateway. Copy the public IP address, and then paste it into the address bar of your browser.
Get-AzPublicIPAddress -ResourceGroupName myResourceGroupAG -Name myAGPublicIPAddress
Clean up resources
When no longer needed, remove the resource group, application gateway, and all related resources using Remove-AzResourceGroup.
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name myResourceGroupAG