MetaCacheDatabase (MCDB) setup
The MetaCacheDatabase (MCDB) feature is included in Exchange Server 2019. It allows a database availability group (DAG) to be accelerated by utilizing solid state disks (SSDs). Manage-MetaCacheDatabase.ps1 is an automation script created for Exchange Server administrators to set up and manage MCDB instances in their Exchange 2019 DAGs.
After installing Exchange Server 2019, you can find Manage-MetaCacheDatabase.ps1 here: drive:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\V15\Scripts. To make the Manage-MCDB CMDLet available in your Exchange Management Shell session, do the following:
cd $exscripts
. .\Manage-MetaCacheDatabase.ps1
You use this script to configure MCDB prerequisites on a properly configured DAG, to enable or disable MCDB, and to configure and repair MCDB on your servers.
SSD guidance
All SSDs used for MCDB need to be of the same capacity and type. A symmetrical configuration between servers is required, which means there needs to be an identical number of SSDs in each server, and the SSDs all need to be the same size.
Note
The Manage-MCDB cmdlet will only work with devices exposed as MediaType SSD by Windows.
It's recommended to target a 1:3 ratio between SSD and HDD devices per server. Therefore, deploy one SSD for every three HDDs. In order to avoid having to reduce the number of HDDs in the server, consider using M.2 form factor SSDs.
Providing 5% to 6% of SSD capacity relative to total HDD capacity is sufficient for on-premises deployments. For example, if your server contains 100 TB of HDD capacity for mailbox databases, an allocation of 5 TB to 6 TB for SSD capacity is enough.
The SSDs you use should qualify for "mixed use" and support one drive write per day (DWPD) or greater in terms of write endurance.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required for successful configuration and use of MCDB:
The DAG is configured for AutoReseed.
For more information, see the following topics:
RAW SSD drives are installed with the same SSD count and size for each server in the DAG. Make sure that all SSDs are completely empty, unformatted, and not write-protected. To verify this, you can use DiskPart or Clear-Disk.
Exchange Server 2019.
MCDB setup
The process of setting up MCDB can be broken down into four basic steps:
Set the correct values for the DAG you want to enable for MCDB.
Update Active Directory (AD) settings and wait for propagation (by running
ConfigureMCDBPrerequisite).Allow MCDB acceleration for each server of the DAG (by running
ServerAllowMCDB).Create the necessary infrastructure (Volumes, Mount Points) for MCDB on each server (by running
ConfigureMCDBOnServer).Let databases fail over to pick up the new settings.
After successful execution of all four steps, MCDB acceleration will begin for every database instance with a corresponding MCDB instance.
The following sections describe how to utilize the Manage-MetaCacheDatabase.ps1 script to achieve the above four steps.
Step 1: Configure proper values on the DAG you want to enable MCDB for
These DAG parameters are used to calculate the proper MCDB size on your SSD drives:
AutoDagTotalNumberOfDatabases: The number of databases in your DAG (for example, 50).
AutoDagDatabaseCopiesPerDatabase: The number of active and passive copies each individual database has.
AutoDagTotalNumberOfServers: The number of servers within your DAG, so between 2 and 16.
For example:
Set-DatabaseAvailabilityGroup testdag1 -AutoDagTotalNumberOfDatabases 20 -AutoDagDatabaseCopiesPerDatabase 4 -AutoDagTotalNumberOfServers 8
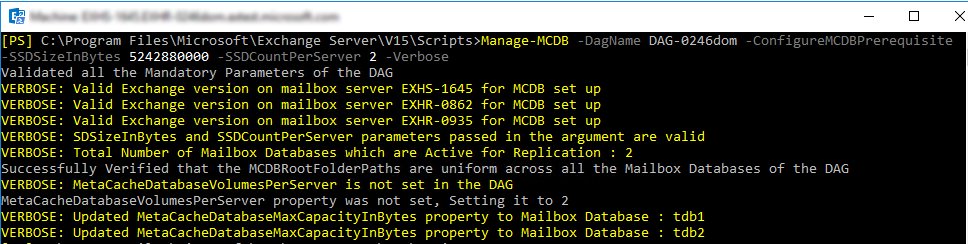
Step 2: Run Manage-MCDB -ConfigureMCDBPrerequisite
This parameter sets the Active Directory state for the DAG object. Full replication of the Active Directory state is required before MCDB can function properly on all servers.
ParameterSetIdentifier:
- ConfigureMCDBPrerequisite
Parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DagName | True | Name of the Database availability group. |
| SSDSizeInBytes | True | The capacity in bytes of each SSD in the server to be used for MCDB. |
| SSDCountPerServer | True | The count of SSD devices to be utilized for MCDB in each server. |
Scope:
- DAG: ConfigureMCDBPrerequisite operates on a DAG object.
Note
MCDB will utilize up to 95% of an SSD's physical capacity. The remaining 5% is kept free to account for file system and partition overhead, as well as for a small amount of additional buffer and over-provisioning.
Example:
Manage-MCDB -DagName TestDag1 -ConfigureMCDBPrerequisite -SSDSizeInBytes 5242880000 -SSDCountPerServer 2
Step 3: Run Manage-MCDB -ServerAllowMCDB
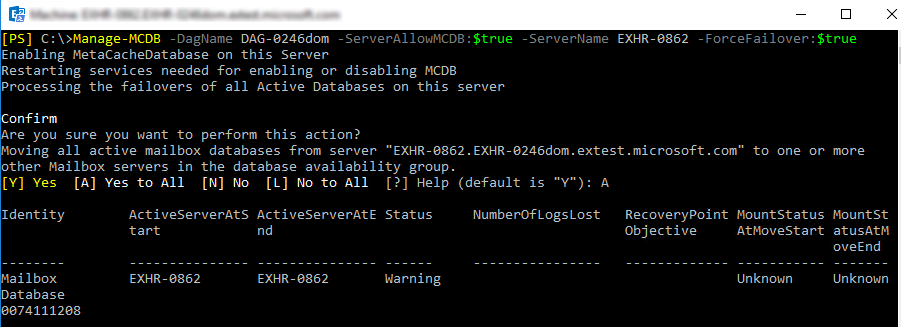
This command sets the local state on each DAG member to allow/disallow MCDB population and read acceleration.
ParameterSetIdentifier:
- ServerAllowMCDB
Parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DagName | True | Name of the Database availability group. |
| ServerName | True | Specifies the server to enable MetaCacheDatabase on. |
| ForceFailover | Optional | This Boolean switch can be utilized to cause all databases on a server to fail over. This is required to make all configuration changes take effect and to begin utilizing MCDB after mount points and database instances have been successfully created in Step 4: Run Manage-MCDB -ConfigureMCDBOnServer. It's also needed to disable SSD acceleration. |
Scope:
- Server: You need to run ServerAllowMCDB on each server in the DAG.
Examples:
Manage-MCDB -DagName TestDag1 -ServerAllowMCDB:$true -ServerName "exhs-5046"
Manage-MCDB -DagName TestDag1 -ServerAllowMCDB:$false -ServerName "exhs-5046" -ForceFailover $true
Step 4: Run Manage-MCDB -ConfigureMCDBOnServer
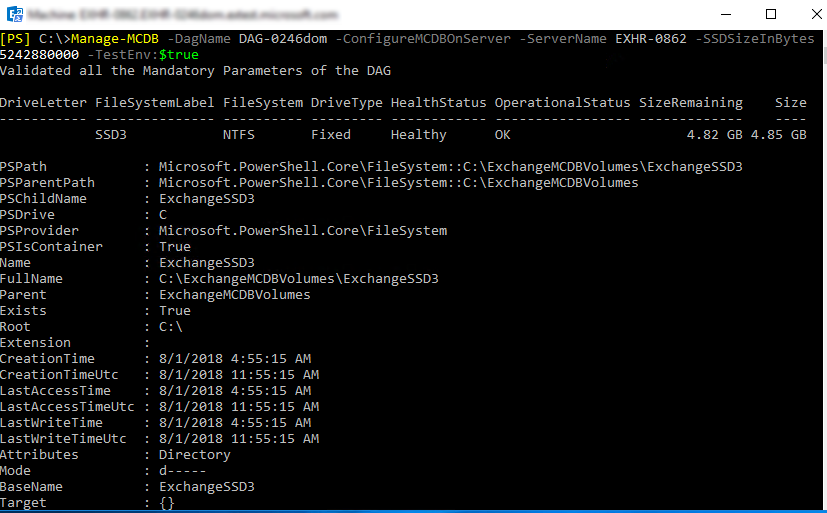
This command identifies unformatted SSD devices and formats them, and also creates the necessary mount points on a server for hosting MCDB instances. This parameter set can also be used to re-create mount points on a raw SSD that was added to replace a failed SSD.
ParameterSetIdentifier:
- ConfigureMCDBOnServer
Parameters:
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DagName | True | Name of the Database availability group. |
| ServerName | True | Specifies the server to identify unformatted SSD devices and create mount points on. |
| SSDSizeInBytes | True | This is the capacity, in bytes, of each SSD in the server to be used for MCDB. |
Scope:
- Server: You need to run ConfigureMCDBOnServer on each server in the DAG.
Example:
Manage-MCDB -DagName TestDag1 -ConfigureMCDBOnServer -ServerName "exhs-4056" -SSDSizeInBytes 5242880000
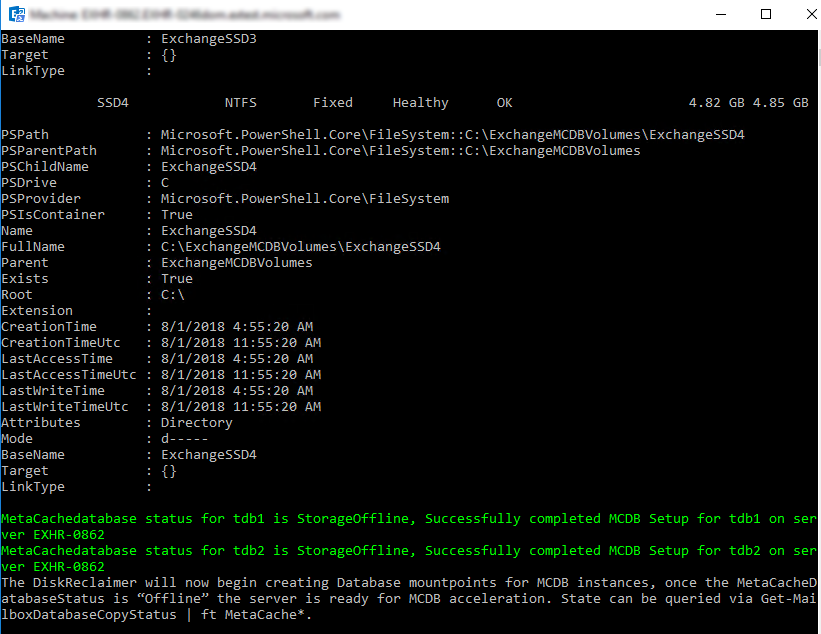
After performing the previous three steps (configuring ConfigureMCDBPrerequisite, ServerAllowMCDB, and ConfigureMCDBOnServer), the MCDB state will display as Storage Offline. This means that the environment is prepared and ready for MCDB instances to be created and populated. The next failover of the database instance causes the creation of the MCDB instance and enable acceleration. The instances transition through the health states shown in MCDB health states.
You can use the ServerAllowMCDB parameter set to cause fail overs of all DB instances present on a given server. Alternatively, you can use the Move-ActiveMailboxDatabase cmdlet to cause individual databases to fail over.
Manage-MCDB -DagName TestDag1 -ServerAllowMCDB:$true -ServerName "exhs-5046" -ForceFailover $true
MCDB health states
Use Get-MailboxDatabaseCopyStatus to query the state of the MCDB instances. There are five states that an MCDB instance can be in, as shown in the following table:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Disabled | MCDB is turned off. |
| StorageOffline | Basic infrastructure is missing or inaccessible, such as mount points or file paths. This is the state MCDB is in following an SSD failure. |
| Offline | Errors at the logical level, for example missing MCDB instances. |
| Initializing | Transient state, the system is determining what other state it should be in. |
| Healthy | Ready to serve requests. |