Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article provides information about the configuration steps that GitHub admins must complete for your organization to deploy the GitHub Server Pull Requests connector. When configured, the connector indexes pull request data from GitHub Enterprise Server so users can search, summarize, and retrieve PR information in Microsoft Search, Microsoft 365 Copilot, and Copilot Search.
This article applies to the GitHub Server Pull Requests connector. For information about how to deploy the connector, see Deploy the GitHub Server Pull Requests connector.
Setup checklist
The following checklist lists the steps involved in configuring the GitHub Server environment and setting up the connector prerequisites.
| Task | Role |
|---|---|
| Identify the organization name | GitHub admin |
| Ensure API access to the target GitHub instance | GitHub admin |
| Identify Microsoft Entra ID identity mapping rules | GitHub admin |
| Sign in to the GitHub account | GitHub admin |
| Configure a custom GitHub app for authentication | GitHub admin |
| Adjust GitHub Server API rate limit | GitHub admin |
| Configure firewall settings | Network admin |
Identify the organization name
Determine which GitHub Enterprise Server organization the connector will use for PR ingestion. The connector indexes only the content accessible to the GitHub App installed in the selected organization.
Ensure API access to the target GitHub instance
Confirm that your GitHub Enterprise Server instance is reachable via API. The connector requires API access to retrieve pull request metadata. Make sure that:
- The GitHub instance is accessible over HTTPS.
- Firewall or network restrictions allow inbound/outbound API requests.
- The Graph Connector Agent host device can reach the GitHub Enterprise Server domain.
Identify Microsoft Entra ID mapping rules
Define the Microsoft Entra ID mapping rules. Identity mapping ensures correct permissions enforcement when users access PR data in Copilot and search experiences.
Supported mapping strategies include:
- Email: Matches GitHub email addresses to Microsoft Entra ID properties.
- Login: Maps GitHub usernames to Microsoft Entra ID attributes.
- Name: Uses the GitHub profile name for mapping.
If identities don't match directly, you can use regular expressions (regex) to normalize data. For example: [a-zA-Z0-9]+
Users must share the required GitHub identity attributes, especially in Bring Your Own User (BYOU) environments.
Sign in to the GitHub account
If your organization uses single sign‑on (SSO), sign in to GitHub before configuring the connector. Currently, the GitHub Server Pull Requests connector doesn't support completing authentication flows that rely on SSO during connector configuration.
Use a custom GitHub app for authentication
For the most streamlined setup experience, use the GitHub app managed by Microsoft.
You can also choose to use your own GitHub app for authentication. If you choose this option, follow the steps in the following checklist to complete the setup.
| Task | Role |
|---|---|
| Create and configure the GitHub app | GitHub admin |
| Create credentials for the GitHub app | GitHub admin |
| Install the GitHub app | GitHub admin |
Create and configure the GitHub app
Verify that you have the right permissions assigned to configure the GitHub service. For more information, see Roles in an organization.
To create a GitHub app for use with the GitHub Server Pull Requests connector:
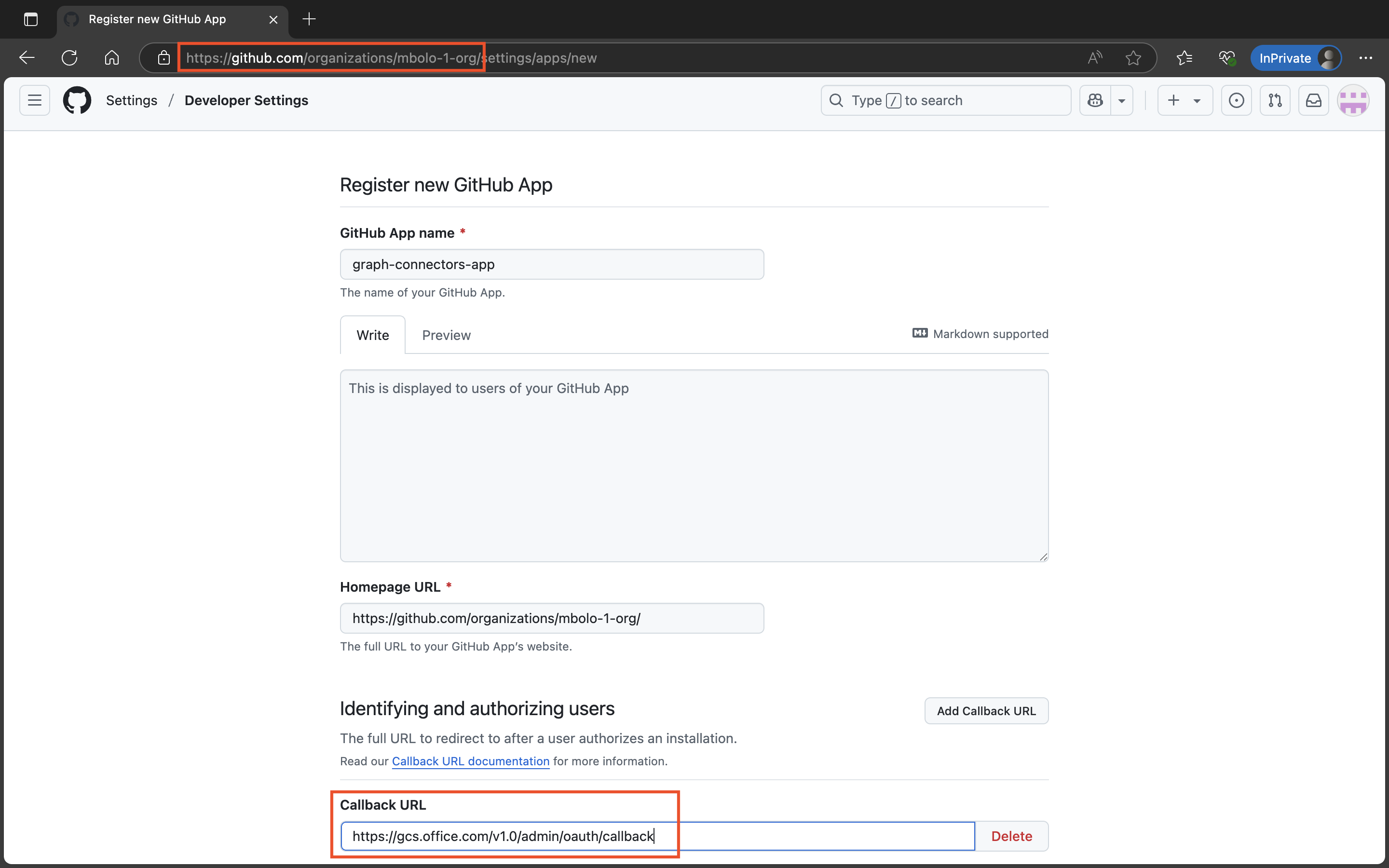
In GitHub, select your profile photo on the top right, select Organizations, and choose the organization the connector should pull data from.
On the organization overview page, select Settings.
In the left sidebar, scroll down to Developer settings and select GitHub Apps.
Select New GitHub App.
Configure the app:
- GitHub App name: Enter the name of your choice.
- Homepage URL: Copy the URL from your browser's address bar.
- Callback URL:
- For Microsoft 365 for enterprise:
https://gcs.office.com/v1.0/admin/oauth/callback - For Microsoft 365 Government:
https://gcsgcc.office.com/v1.0/admin/oauth/callback
- For Microsoft 365 for enterprise:
Uncheck the Webhook option.
Set the following permissions:
Repository permissions
- Contents - Read-only
- Metadata - Read-only
- Administration - Read-only
Organization permissions
- Members - Read-only
- Administration - Read-only
Account permissions
- Email addresses - Read-only
Under Where can this GitHub App be installed, select Any account, and then select Create GitHub App.
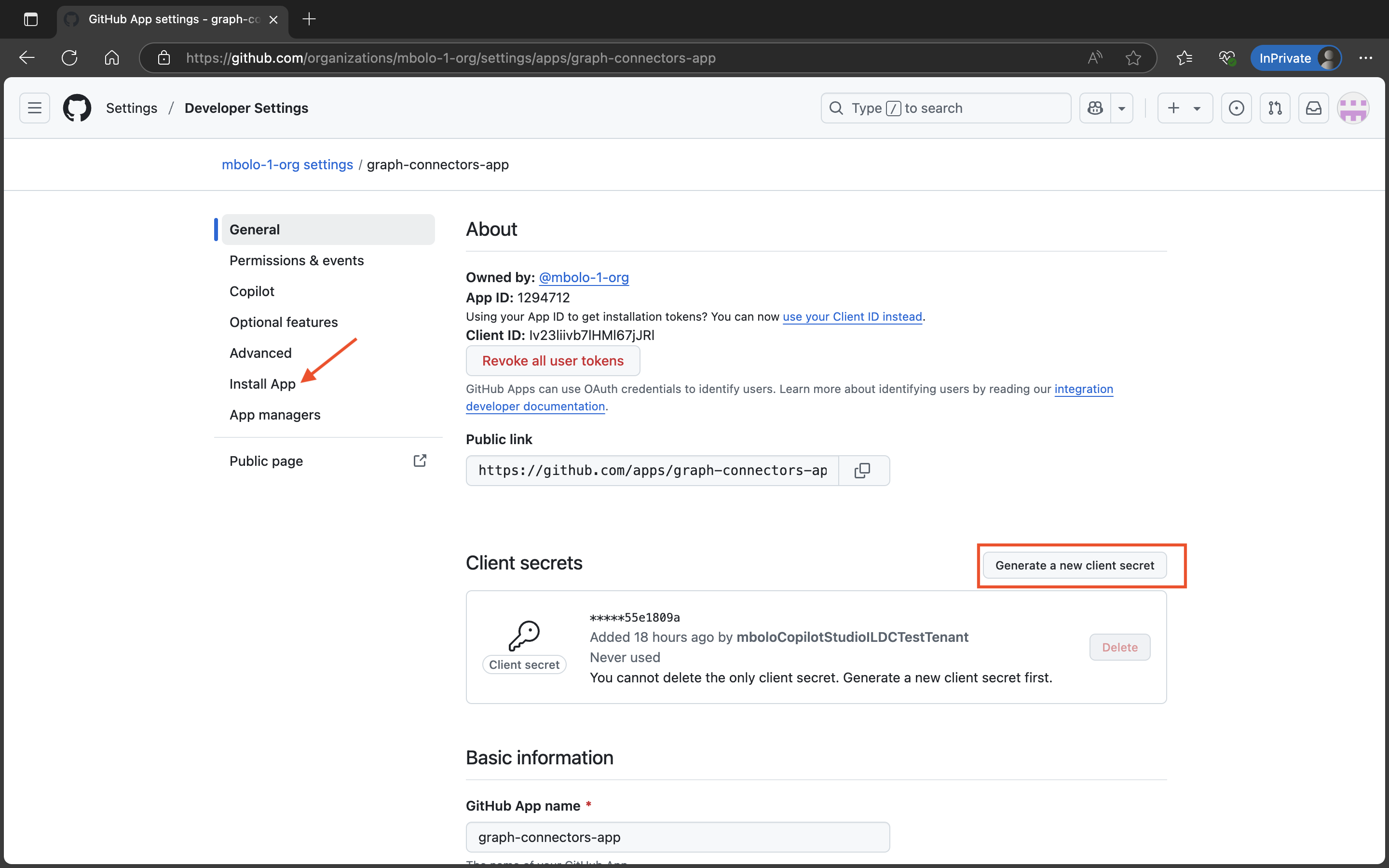
Create credentials for the GitHub app
On the General page of the GitHub app, select Generate a new client secret to generate and copy the client secret.
Install the GitHub app
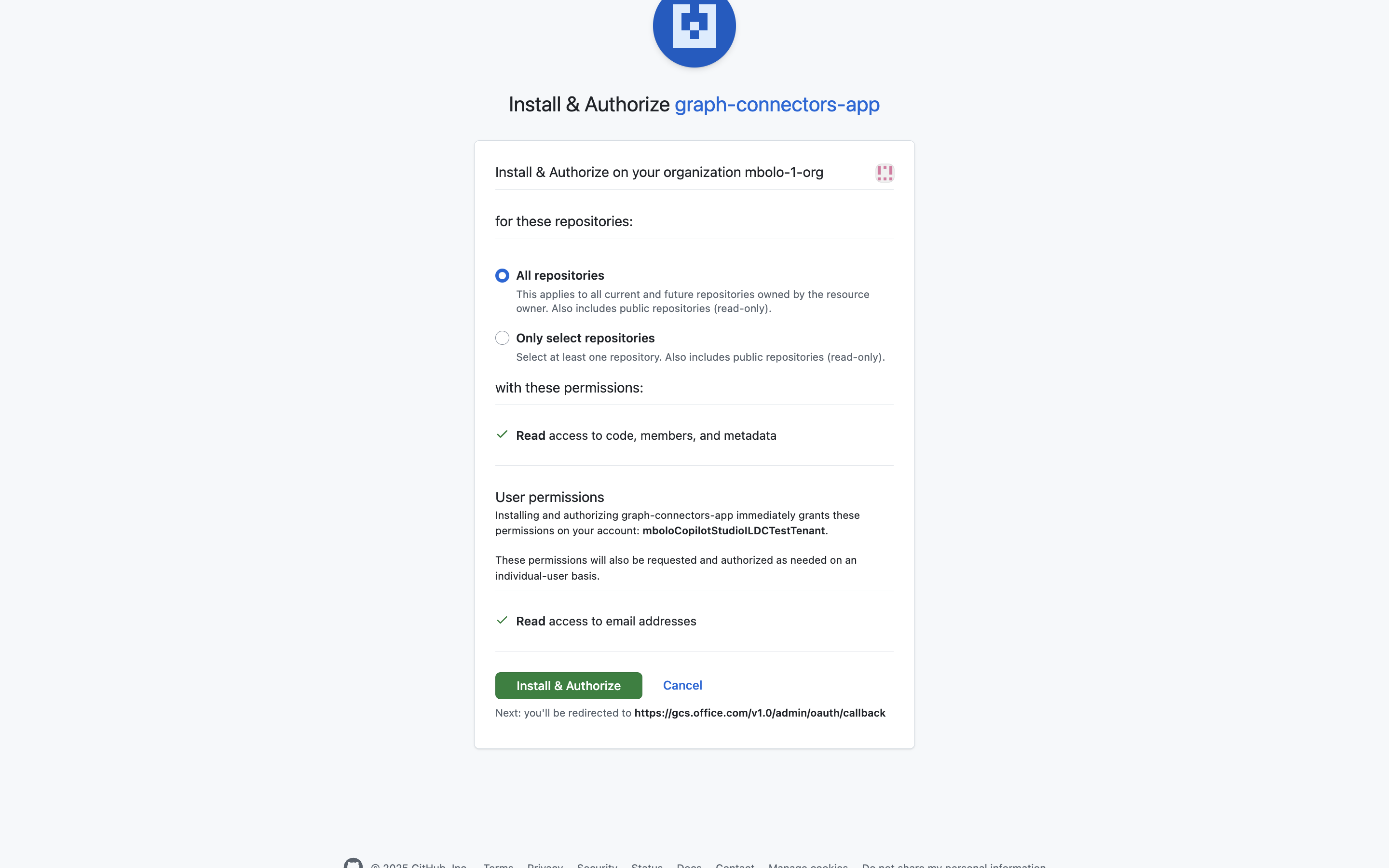
On the General page of the GitHub app, select Install App.
Select the organization where you want the app to be installed.
Adjust GitHub Server API rate limit
When you ingest large volumes of GitHub data—such as pull requests, issues, or knowledge files—the API rate‑limit configuration in your GitHub Server environment directly affects how quickly the ingestion process is completed. GitHub Server applies a default API limit of 15,000 authenticated requests per hour per user or token. This limit supports smaller datasets, but can slow ingestion when hundreds of thousands or millions of items are processed.
If your organization needs to increase throughput, you can raise the API rate limit. Higher limits allow the connector to retrieve items more quickly, but they also increase load on your GitHub Server infrastructure. Before you update rate‑limit settings, verify that your environment has adequate CPU capacity, storage I/O, and network bandwidth to support the increased request volume. After you update the limit, monitor system performance to ensure stable ingestion at higher throughput.
Rate-limit setting recommendations
Use the guidance in the following table to help you choose an appropriate rate‑limit setting based on the approximate number of pull requests in your GitHub environment.
| Approximate number of items | Recommended rate-limit setting | Approximate time to complete ingestion |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 100,000 | Use default rate‑limit settings (normal ingestion speed) | NA |
| 100,000 to 1,000,000 | Increase rate limit to 30,000 requests/hour | 2 days to 1 week |
| 1,000,000 or more | Use 30,000 requests/hour or higher (depending on server capacity) | 1–2 weeks (varies by environment load) |
Update the API rate-limit setting
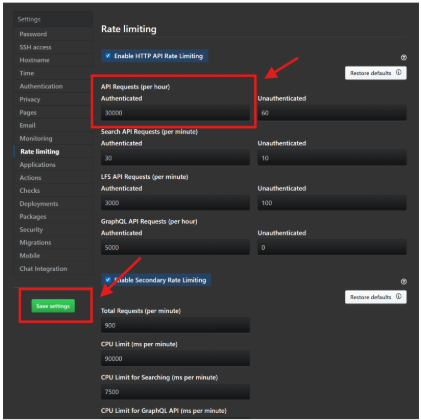
To increase the API request limit:
- Sign in to your GitHub Server instance with an admin account.
- In the upper‑right corner, select Site admin to enter administration mode. For more information, see Configuring rate limits.
- In the left pane, select Management Console (or Admin Console, depending on your version).
- Open the Rate limiting tab.
- Confirm that Enable HTTP API rate limiting is selected.
- Under API requests (per hour) – Authenticated, enter the rate‑limit value (for example, 30000).
- Select Save settings.
Note
When you save your changes, certain GitHub Server services might restart and cause a brief service interruption. After you save, allow time for the configuration to propagate across the instance.
Configure firewall settings
For added security, you can configure IP firewall rules for your Azure SQL Server or database. For more information, see IP firewall rules.
Add the following client IP ranges in the firewall settings.
| Region | Microsoft 365 Enterprise | Microsoft 365 Government |
|---|---|---|
| NAM | 52.250.92.252/30, 52.224.250.216/30 | 52.245.230.216/30, 20.141.117.64/30 |
| EUR | 20.54.41.208/30, 51.105.159.88/30 | NA |
| APC | 52.139.188.212/30, 20.43.146.44/30 | NA |
IP restrictions can cause the connector to stop working and lead to crawl failures. To resolve this issue, add the connector's IP address to the allowlist.