Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:  2013
2013  2016
2016  2019
2019  Subscription Edition
Subscription Edition  SharePoint in Microsoft 365
SharePoint in Microsoft 365
This article describes, step by step, how to use Excel 2016 to create a basic sales dashboard that contains several reports and a filter using an external data connection. The example dashboard described in this article resembles the following image:
Figure: Basic sales dashboard example
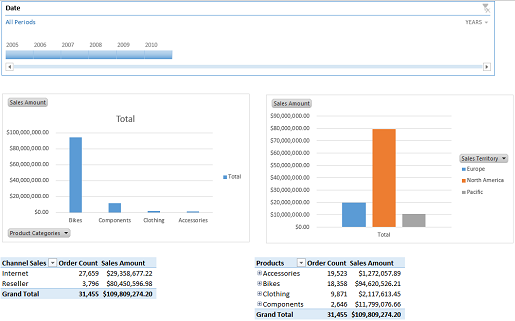
This article also describes how to publish the dashboard to SharePoint Server 2013 where others can view and use it. By following the steps in this article, you'll learn how to create and arrange different reports in a worksheet and connect a filter to those reports.
Before you begin
Before you begin this operation, review the following information about prerequisites:
Excel must be installed on the computer that you are using to create and publish the dashboard.
This scenario uses Adventure Works sample data and a Business Intelligence Center site in SharePoint Server 2013. If you do not have the sample data and a Business Intelligence Center site, have an IT administrator configure them for you using the instructions in Configure AdventureWorks for Business Intelligence solutions.
Excel Services must be configured in the SharePoint environment that you are using.
You must have some information about what authentication settings are used for Excel Services. User access can be provided using Windows Authentication with Kerberos delegation, the Secure Store Service, or, with OLAP data sources, the EffectiveUserName feature.
For information about how to configure Secure Store, see Plan the Secure Store Service in SharePoint Server and Configure the Secure Store Service in SharePoint Server. For information about how to configure the EffectiveUserName feature for OLAP data sources, see Use Analysis Services EffectiveUserName in SharePoint Server.
Plan the dashboard
Before you begin to create a dashboard, we recommend that you create a dashboard plan. The plan does not have to be extensive or complex. However, it should give you an idea of what you want to include in the dashboard. To help you prepare a dashboard plan, consider questions such as the following:
Who will use the dashboard?
What kinds of information do they want to see?
Does data exist that you can use to create the dashboard?
Our example dashboard is designed to be a prototype that you can use to learn how to create and publish Excel Services dashboards. To show how we might create a dashboard plan for a similar dashboard, see the following table.
Table: Basic plan for our example dashboard
| Question | Response |
|---|---|
| Who will use the dashboard? |
The dashboard is intended for use by sales representatives, sales managers, corporate executives, and other stakeholders who are interested in sales information for the fictitious company Adventure Works Cycles. |
| How will the dashboard be used? That is, what kinds of information do the dashboard consumers want to see? |
Sales representatives, managers, executives, and other dashboard consumers want to use the dashboard to view, explore, and analyze data. At a minimum, the dashboard consumers want to see the following kinds of information: Sales amounts for different product categories Sales amounts for different sales territories Sales for Internet and Reseller channels Dashboard consumers want to use the dashboard to view, explore, and analyze data to obtain answers to specific questions. The dashboard consumers also want to be able to use filters to focus on more specific information, such as sales for a particular period of time. |
| Does data exist that we can use to create the dashboard? |
Yes. The Adventure Works sample database contains the data that we want to use for the dashboard. Because this sample data is a multidimensional data cube, it will enable us to create interactive reports that dashboard users can use to explore data by viewing different levels of detail. |
| What items should the dashboard contain? |
Our example dashboard includes the following items: A data connection to SQL Server Analysis Services A report showing product sales information for different product categories A report showing sales information for different sales territories A report showing orders and sales information for different sales channels A report showing orders and sales across different product categories A filter that dashboard consumers can use to view information for a particular period of time or a range of time |
Now that we have created our dashboard plan, we can begin to create the dashboard.
Create the dashboard
To create the dashboard, we begin by creating a data connection. Then, we use that data connection to create the reports and the filter that we want to use. After that, we publish the workbook to SharePoint Server 2013.
Part 1: Create a data connection
Our example dashboard uses a single data connection to data that is stored in SQL Server 2012 Analysis Services. We'll use this data connection to create the reports and filter for the dashboard.
To create a connection to Analysis Services data
Open Microsoft Excel.
To create a workbook, select Blank workbook.
On the Data tab, select Get External Data group, then select From Other Sources, and then select From Analysis Services.
The Data Connection Wizard opens.
On the Connect to Database Server page, in the Server name box, specify the name of the server where the Analysis Services data that you want to use resides.
In the Log on credentials section, take one of the following steps:
If your organization is using Windows Authentication, select Use Windows Authentication, and then select Next.
If your organization is using specific user credentials, select Use the following User Name and Password, specify an appropriate user name and password, and then select Next.
Tip
If you don't know which option to choose, contact a SharePoint admin.
On the Select Database and Table page, select the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE database, then select the Adventure Works cube, and then select Next.
On the Save Data Connection File and Finish page, select Finish.
On the Import Data page, select the Only Create Connection option, and then select OK.
Keep Excel open.
At this point, we have created a connection to the Adventure Works cube in Analysis Services. By default, this data connection is saved in a My Data Sources folder in the Documents library on the computer and is embedded in the workbook. We'll use the ODC connection that is embedded in the workbook for the dashboard.
The next step is to create reports for the dashboard.
Part 2: Create reports
For our example dashboard, we'll create four reports, as described in the following table:
Table: Dashboard reports
| Report Type | Report Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PivotChart report |
ProductSales |
Bar chart report that shows sales amounts across different product categories. |
| PivotChart report |
GeoSales |
Bar chart report that shows sales amounts across different sales territories. |
| PivotTable report |
ChannelSales |
Table that shows order quantities and sales amounts across the Internet and Reseller channels. |
| PivotTable report |
OrderSales |
Table that shows order quantities and sales amounts across different product categories. |
We begin by creating the ProductSales report.
To create the ProductSales report
In Excel, on the Insert tab, in the Charts section, select PivotChart.
The Create PivotChart dialog appears.
In the Choose the data that you want to analyze section, select the Use an external data source option, and then select Choose Connection.
The Existing Connections dialog appears.
In the Connections in this Workbook section, select the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE data connection, and then select Open.
In the Create PivotChart dialog, select the Existing Worksheet option, and then select OK.
Chart1 opens for editing.
In the PivotChart Fields list, specify the following options:
In the Sales Summary section, select Sales Amount.
Sales Amount appears in the Values section, and the report updates to show a single bar.
In the Product section, select Product Categories.
Product Categories appears in the Axis section, and the report updates to show sales amounts across different product categories.
To sort the bars in descending order, take the following steps:
In the PivotChart Fields list, select the Product Categories dimension, and then select the down arrow that appears.
The Select field dialog appears.
To open the Sort (Category) dialog, select More Sort Options....
In the Sort options section, select the Descending (Z to A) by option, and then use the list to select Sales Amount.
Select OK.
To ensure that there is room for more reports, we'll move the PivotChart report closer to the upper-left corner of the worksheet. To do this, drag the report so that the upper-left corner aligns with the upper-left corner of cell B10 in the worksheet.
To avoid confusion about report names later, we'll specify a new name for the report. On the Analyze tab, in the PivotChart group, in the Chart Name box, delete the text that says Chart1, type ProductSales, and on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
Tip
Ensure that the name that you specify contains only alphanumeric characters (no spaces).
To ensure we don't encounter sizing issues later with the report, we'll specify size settings for the report. To do this, follow these steps:
In an empty section of the report, such as inside the upper-right corner of the report, right-click, and then select Format Chart Area.
The Format Chart Area list opens.
Below the Chart Options, select the Size and Properties toolbar command.
Expand the Size section, and then select the Lock aspect ratio option.
Expand the Properties section, select the Don't move or size with cells option, and verify that the Locked option is selected.
To optionally specify alternate text for the report, expand the Alt Text section, and then enter the text that you want to use for the report.
Close the Format Chart Area list.
Save the workbook by using a file name such as Adventure Works Sales.
Keep the workbook open.
At this point, we have created a PivotChart report. The next step is to create another PivotChart report and name it GeoSales that shows sales amounts across different geographical locations.
To create the GeoSales report
In Excel, on the same worksheet that was used to create the ProductSales report, select cell K10.
On the Insert tab, select PivotChart.
In the Choose the data that you want to analyze section, select the Use an external data source option, and then select Choose Connection.
The Existing Connections dialog appears.
In the Connections in this Workbook section, select the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE data connection, and then select Open.
In the Create PivotChart dialog, select the Existing Worksheet option, and then select OK.
Chart2 opens for editing.
Move the chart so that its upper-left corner aligns with the upper-left corner of cell J10 in the worksheet.
In the PivotChart Fields list, specify the following options:
In the Sales Summary section, select Sales Amount.
In the Sales Territory section, drag Sales Territory to the Legend section.
The report updates to display a bar chart showing sales amounts for Europe, North America, and Pacific.
Specify size settings for the report by following these steps:
In an empty section of the report, right-click, and then select the Format Chart Area option.
The Format Chart Area list opens.
Below the Chart Options, select the Size and Properties toolbar command.
Expand the Size section, and then select the Lock aspect ratio option.
Expand the Properties section, select the Don't move or size with cells option, and verify that Locked is selected.
To optionally specify alt text for the report, expand the Alt Text section, and then enter the text that you want to use for the report.
Close the Format Chart Area list.
Specify a new name for the report. On the Analyze tab, in the PivotChart group, in the Chart Name box, delete the text for Chart2, type GeoSales, and on your keyboard, and on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
On the File tab, select Save.
Keep the workbook open.
At this point, we have created two reports. The next step is to create the ChannelSales report.
To create the ChannelSales report
In Excel, on the same worksheet that was used to create the previous reports, select cell B26.
On the Insert tab, select PivotTable.
In the Choose the data that you want to analyze section, select the Use an external data source option, and then select Choose Connection.
The Existing Connections dialog appears.
In the Connections in this Workbook section, select the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE data connection, and then select Open.
Select the Existing Worksheet option, and then select OK.
PivotTable3 opens for editing.
In the PivotTable Fields list, specify the following options:
In the Sales Orders section, select Order Count.
In the Sales Summary section, select Sales Amount.
In the Sales Channel section, select Sales Channel.
The report updates to display a table showing order counts and sales amounts for the Internet and Reseller channels.
Select cell B26, and then, in the Formula bar, delete the text for Row Labels, and enter 'Channel Sales.' Then, on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
Specify a new name for the report. On the Analyze tab, in the PivotTable group, in the PivotTable Name box, delete the text for PivotTable3, type ChannelSales, and on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
On the File tab, select Save.
Keep the Excel workbook open.
At this point, we have created three reports using the same data source. The next step is to create the OrderSales report.
To create the OrderSales report
In Excel, on the same worksheet that was used to create the previous reports, select cell H26.
On the Insert tab, select PivotTable.
In the Choose the data that you want to analyze section, select the Use an external data source option, and then select Choose Connection.
The Existing Connections dialog appears.
In the Connections in this Workbook section, select the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE data connection, and then select Open.
Select the Existing Worksheet option, and then select OK.
PivotTable4 opens for editing.
In the PivotTable Fields list, specify the following options:
In the Sales Orders section, select Order Count.
In the Sales Summary section, select Sales Amount.
In the Product section, select Product Categories.
The report updates to display a table showing order counts and sales amounts for different product categories.
Select cell H26, and then, in the Formula bar, delete the default text for Row Labels, and then type Products. Then, on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
Specify a new name for the report. On the Analyze tab, in the PivotTable group, in the PivotTable Name box, delete the text for PivotTable4, type OrderSales, and on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
On the File tab, select Save.
Keep the workbook open.
At this point, we have created our four reports for our basic dashboard. The next step is to create a filter.
Part 3: Create a filter
Using Excel, there are several different kinds of filters we can create. For example, we can create a simple filter by putting a field in the Filter section of the Fields list. We can create a slicer, or, if we are using a multidimensional data source such as Analysis Services, we can create a timeline control. For this example dashboard, we'll create a timeline control. This filter will enable people to view information for a particular time.
To create a timeline control
In Excel, on the same worksheet that was used to create the reports, select cell B1.
On the Insert tab, in the Filter group, select Timeline.
The Existing Connections dialog appears.
In the Connections in this Workbook section, select the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE data connection, and then select Open.
The Insert Timelines dialog appears.
Select the Date option, and then select OK.
A timeline control opens.
Move the timeline control so that its upper-left corner aligns with the upper-left corner of cell B1.
To make the timeline control wider, use the resizing handles, and drag the sizing handle on the right side of the control to column M.
Select the timeline control, and on the Options tab, in the Timeline group, select the Report Connections toolbar command.
The Report Connections dialog appears.
Select ChannelSales, GeoSales, OrderSales, and ProductSales, and then select OK.
On the File tab, select Save.
Keep the Excel workbook open.
At this point, we have created a dashboard. The next step is to publish it to SharePoint Server 2013, where it can be used by others.
Publish the dashboard
To publish the workbook to SharePoint Server 2013, we'll follow a four-step process. First, we make some adjustments that affect how the workbook appears. Then, we specify Excel Services data authentication settings for the external data connection that we use. Next, we specify publish options for the workbook. Finally, we publish the workbook to SharePoint Server 2013.
We begin by making adjustments to the workbook. By default, our example dashboard displays gridlines on the worksheet that contains our dashboard. In addition, by default, the worksheet is called Sheet1. We can make some minor adjustments to improve how the dashboard appears.
To make minor display improvements to the workbook
In Excel, select the View tab.
To remove gridlines from the view, on the View tab, in the Show group, clear the Gridlines check box.
To remove row and column headings, on the View tab, in the Show group, clear the Headings check box.
To rename the worksheet, right-click its tab for Sheet1, and then select Rename. Enter a new name for the worksheet, such as SalesDashboard, and on your keyboard, press <Enter>.
On the File tab, select Save.
Keep the workbook open.
The workbook we created uses an external data connection that we want to keep active when we publish the workbook. To ensure that the data connection remains live so that data refresh is supported in Excel Services, we must specify authentication settings.
To specify authentication settings for the external data connection
In Excel, on the Data tab, select the Connections toolbar command.
The Workbook Connections dialog appears, and displays the AdventureWorksDW2012Multidimensional-EE data connection.
Select Properties.
In the Connection Properties dialog, on the Definition tab, next to Excel Services, select Authentication Settings....
In the Excel Services Authentication Settings dialog, take one of the following steps:
If Excel Services is configured to use Windows Authentication or the EffectiveUserName feature, select Use the authenticated user's account, and then select OK.
If Excel Services is configured to use Secure Store Service, select Use a stored account. In the Application ID box, specify the Secure Store target application ID, and then select OK.
If Excel Services is configured to use the unattended service account, select None, and then select OK.
Important
If you do not know which option to select, contact a SharePoint admin.
To close the Connection Properties dialog, select OK.
If you see a message that states that the connection in the workbook will no longer be identical to the connection that is defined in the external file, select Yes.
To close the Workbook Connections dialog, select Close.
When we created the reports for the dashboard, we gave each one a unique name and defined it as a named item in Excel. In addition to publishing the workbook to SharePoint Server 2013, we should publish the named items that we defined. This makes it possible to show a named item in its own SharePoint Web Part later. We do this by specifying publish options for the workbook.
Tip
This article does not describe how to display a named item in its own SharePoint Web Part. Therefore, the following procedure is optional. However, we recommend that, as a best practice, you perform the following procedure. This can save you from having to republish the workbook later.
To specify publish options for the workbook
On the File tab, select Info, and then select Browser View Options.
Select Browser View Options.
On the Show tab, use the list to select Items in the Workbook.
Select All Charts, then select All PivotTables, and then select OK.
On the File tab, select Save.
Keep the workbook open.
The next step is to publish the workbook to SharePoint Server 2013.
To publish the workbook to SharePoint Server
In Excel, on the File tab, select Save As, then select Computer, and then select Browse.
The Save As dialog appears.
In the address line, enter the SharePoint address to an Excel Services trusted file location.
Select Save.
The workbook is published in the SharePoint library that you specified.
Close the Excel workbook.
Now that we have created and published the dashboard, we can use it to explore data.
Use the dashboard
After the dashboard was published to SharePoint Server 2013, it is available for people to view and use it.
To open the dashboard
Open a web browser.
In the address bar, enter the address to the Business Intelligence Center site where the dashboard was published.
Select Site Contents, and then select Documents.
Select the Adventure Works Sales dashboard.
The dashboard opens for viewing.
Now that the dashboard is open for viewing, we can use it to obtain answers to specific questions, such as those that are described in the following table.
Table: Using the dashboard to obtain answers to specific questions
| Question | Action |
|---|---|
| Which product category has the largest number of orders? |
Using the OrderSales report, view the Order Count column for various product categories. You can see that Accessories has the largest number of orders. Also, Accessories also has the least total sales amount of all four product categories. |
| Does this company sell more merchandise through the Internet channel, or the Reseller channel? |
Using the ChannelSales report, you can see that, although the Internet channel has more orders, the Reseller channel has the highest sales amount. |
| Which year resulted in the highest total sales amount? |
Using the timeline control near the top of the screen, select the down arrow next to MONTHS, and select YEARS. Use the control to select one year at a time. The year 2007 has the highest sales amount. |
| Which sales territory has the highest sales amount for this company for all time? |
To clear the filter from the timeline control, in the upper-right corner of the timeline control, select the Clear Filter toolbar command. North America has the highest sales amount for this particular company. |
| Which subcategory of bikes has the highest overall sales? |
Using the ProductSales report, double-click the bar for Bikes. The report updates to show three subcategories: Mountain Bikes, Road Bikes, and Touring Bikes. The Mountain Bikes subcategory has the highest sales amount. |
See also
Concepts
Business intelligence capabilities in Excel Service (SharePoint Server 2013)
Create an Excel Services dashboard using a Data Model (SharePoint Server 2013)