Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this tutorial, we discuss how to leverage provided scripts and excel examples to understand the impact of applying either automatic or manual limits on version storage or impacted users. You will learn how to:
- Run impact analysis of setting Automatic limits.
- Run impact analysis of expiring versions older than specified days.
- Run impact analysis of storing version within specified count limits.
Before you begin
In the previous tutorial, you had generated a version storage usage report. This tutorial assumes that the report generation job has successfully completed and the report is fully populated.
Start by downloading the report file to your local computer. Use the scripts provided below to apply the desired setting on the file and analyze the impact.
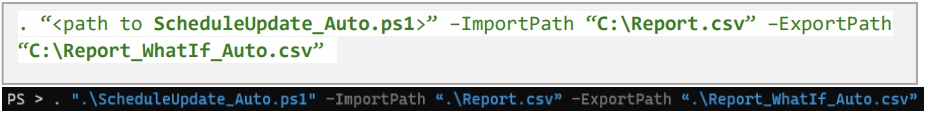
Run impact analysis of setting automatic version history limits
Here's an example of PowerShell script you could apply to generate a What-If Report file that applies the Automatic Expiration policy on the report file C:\Report.csv.
# save this file as ScheduleUpdate_Auto.ps1
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$ImportPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$ExportPath
)
$Schedule = Import-Csv -Path $ImportPath
$Schedule |
ForEach-Object {
$_.TargetExpirationDate = $_.AutomaticPolicyExpirationDate
}
$Schedule |
Export-Csv -Path $ExportPath -UseQuotes AsNeeded -NoTypeInformation
Note
Use PowerShell 7 to run the commands. You can install PowerShell 7 by following these instructions: Installing PowerShell on Windows - PowerShell | Microsoft Learn.
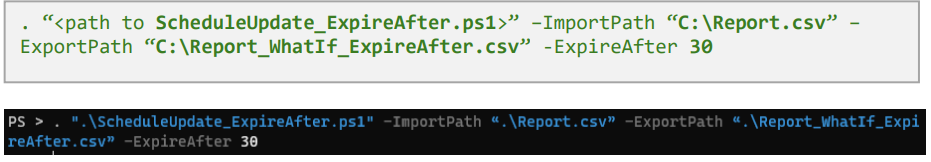
Run impact analysis of setting manual expiration limits
Here's an example of PowerShell script to generate a What-If Report file. It applies Manual Expiration with expire-after days set to 30 on the report file C:\Report.csv.
# save this file as ScheduleUpdate_ExpireAfter.ps1
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][string]$ImportPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][string]$ExportPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)][double]$ExpireAfter
)
function StringToDateTime($Value) { return [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Value) ? $null : [DateTime]::ParseExact($Value, "yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssK", $null) }
function DateTimeToString($Value) { return $null -eq $Value ? "" : $Value.ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssK") }
$Schedule = Import-Csv -Path $ImportPath
$Schedule |
ForEach-Object {
$SnapshotDate = StringToDateTime -Value $_.SnapshotDate
$TargetExpirationDate = $SnapshotDate.AddDays($ExpireAfter)
$_.TargetExpirationDate = DateTimeToString -Value $TargetExpirationDate
}
$Schedule |
Export-Csv -Path $ExportPath -UseQuotes AsNeeded -NoTypeInformation
Note
Use PowerShell 7 to run the commands. You can install PowerShell 7 by following these instructions: Installing PowerShell on Windows - PowerShell | Microsoft Learn.
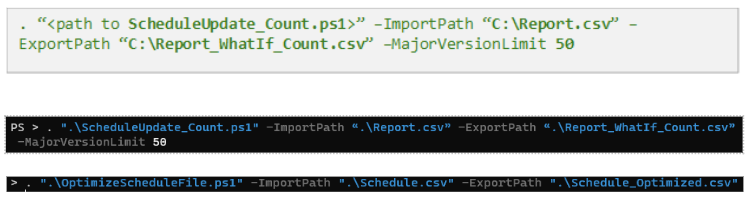
Run impact analysis of setting manual count limits
Here's an example of PowerShell script to generate a What-If report file. It applies a Manual with Count Limits policy with major version limit set to 50 on the report file C:\Report.csv.
# save this file as ScheduleUpdate_Count.ps1
param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$ImportPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$ExportPath,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)][int]$MajorVersionLimit
)
$Report = Import-Csv -Path $ImportPath
$PreviousWebId = [Guid]::Empty
$PreviousDocId = [Guid]::Empty
$PreviousWebUrl = [string]::Empty
$PreviousFileUrl = [string]::Empty
$PreviousModifiedByUserId = [string]::Empty
$PreviousModifiedByDisplayName = [string]::Empty
$FileToVersions = @{}
foreach ($Version in $Report)
{
$WebId = [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Version."WebId.Compact") ? $PreviousWebId : [Guid]::Parse($Version."WebId.Compact")
$DocId = [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Version."DocId.Compact") ? $PreviousDocId : [Guid]::Parse($Version."DocId.Compact")
$WebUrl = [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Version."WebUrl.Compact") ? $PreviousWebUrl : $Version."WebUrl.Compact"
$FileUrl = [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Version."FileUrl.Compact") ? $PreviousFileUrl : $Version."FileUrl.Compact"
$ModifiedByUserId = [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Version."ModifiedBy_UserId.Compact") ? $PreviousModifiedByUserId : $Version."ModifiedBy_UserId.Compact"
$ModifiedByDisplayName = [string]::IsNullOrEmpty($Version."ModifiedBy_DisplayName.Compact") ? $PreviousModifiedByDisplayName : $Version."ModifiedBy_DisplayName.Compact"
$PreviousWebId = $WebId
$PreviousDocId = $DocId
$PreviousWebUrl = $WebUrl
$PreviousFileUrl = $FileUrl
$PreviousModifiedByUserId = $ModifiedByUserId
$PreviousModifiedByDisplayName = $ModifiedByDisplayName
if (($PreviousWebId -eq [Guid]::Empty) -or ($WebId -eq [Guid]::Empty) -or
($PreviousDocId -eq [Guid]::Empty) -or ($DocId -eq [Guid]::Empty))
{
throw "Compact column error."
}
$Version."WebId.Compact" = $WebId
$Version."DocId.Compact" = $DocId
$Version."WebUrl.Compact" = $WebUrl
$Version."FileUrl.Compact" = $FileUrl
$Version."ModifiedBy_UserId.Compact" = $ModifiedByUserId
$Version."ModifiedBy_DisplayName.Compact" = $ModifiedByDisplayName
if ($null -eq $FileToVersions[$DocId])
{
$FileToVersions[$DocId] = [System.Collections.Generic.PriorityQueue[Object, Int32]]::new()
}
$VersionsQueue = $FileToVersions[$DocId]
$VersionNumber = [Int32]::Parse($Version.MajorVersion) * 512 + [Int32]::Parse($Version.MinorVersion)
$VersionsQueue.Enqueue($Version, -$VersionNumber)
}
$Schedule = [System.Collections.Generic.List[Object]]::new()
foreach ($FilesAndVersions in $FileToVersions.GetEnumerator())
{
$VersionsQueue = $FilesAndVersions.Value
$NumMajorVersionsSeen = 0
while ($VersionsQueue.Count -gt 0)
{
$Version = $VersionsQueue.Dequeue()
if ($NumMajorVersionsSeen -ge $MajorVersionLimit) {
$Version.TargetExpirationDate = [DateTime]::new(2000, 1, 1).ToString("yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssK")
}
if ([int]::Parse($Version.MinorVersion) -eq 0) { $NumMajorVersionsSeen++ }
$Schedule.Add($Version)
}
}
$Schedule |
Export-Csv -Path $ExportPath -UseQuotes AsNeeded -NoTypeInformation
Note
Use PowerShell 7 to run the commands. You can install PowerShell 7 by following these instructions: Installing PowerShell on Windows - PowerShell | Microsoft Learn.