Upgrading operating system of a virtual machine is essential for improving its performance and security. However, sometimes upgrade process can cause booting issues that prevent virtual machine from starting up. In this article, we will discuss some common reasons for booting issues after upgrading Linux virtual machines and how to troubleshoot them.
Reasons for Booting Issues After Upgrading Linux Virtual Machine
- Incompatibility with Virtual Machine Hardware Upgrading operating system of a virtual machine can cause incompatibility with hardware of virtual machine. This issue can occur if virtual machine's hardware is not compatible with new operating system version. For instance, if virtual machine has outdated hardware, upgrading to latest operating system version can cause compatibility issues that may prevent virtual machine from booting up.
- File System Issues Another common reason for booting issues after upgrading a Linux virtual machine is file system corruption. File system corruption can occur during upgrade process if there is a power outage, system crash, or any other unexpected event. file system may also become corrupted if upgrade process is interrupted or not completed successfully.
- Kernel Version Mismatch Upgrading operating system of a virtual machine can also cause kernel version mismatch. If kernel version of virtual machine is not compatible with new operating system version, virtual machine may fail to boot up. This issue can occur if virtual machine has an outdated kernel version or if new operating system version requires a newer kernel version.
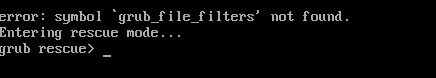
- Bootloader Issues bootloader is a program that loads operating system into memory during boot process. Upgrading operating system of a virtual machine can cause bootloader issues if new operating system version is not compatible with bootloader installed on virtual machine. This issue can occur if virtual machine's bootloader is outdated or if new operating system version requires a different bootloader.
Troubleshooting Booting Issues After Upgrading Linux Virtual Machine
- Check Virtual Machine Hardware Compatibility If virtual machine fails to boot up after upgrading operating system, first step is to check compatibility of virtual machine's hardware with new operating system version. You can check compatibility of hardware by reviewing system requirements of new operating system version. If hardware is not compatible, you may need to upgrade virtual machine's hardware to resolve issue.
- Check File System Integrity If virtual machine's file system becomes corrupted during upgrade process, it can cause booting issues. To check file system integrity, you can use "fsck" command in Linux. This command checks and repairs any errors in file system. To run "fsck" command, you need to boot virtual machine in recovery mode and then enter command in terminal.
- Update Kernel Version If virtual machine's kernel version is outdated or incompatible with new operating system version, you can update kernel version to resolve issue. To update kernel version, you can use package manager of Linux distribution installed on virtual machine. For instance, if virtual machine has Ubuntu installed, you can use "apt-get" command to update kernel version.
- Reinstall Bootloader If virtual machine's bootloader is outdated or incompatible with new operating system version, you can reinstall bootloader to resolve issue. To reinstall bootloader, you can use installation media of new operating system version. Boot virtual machine using installation media and select "Rescue mode" option. From there, you can reinstall bootloader using appropriate commands.
Examples of Booting Issues After Upgrading Linux Virtual Machine
Example 1: A virtual machine has Ubuntu 16.04 installed, and user decides to upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04. However, after upgrade process is completed, virtual machine fails to boot up.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Virtual Machine Hardware Compatibility: user reviews system requirements of Ubuntu 18.04 and discovers that virtual machine's hardware is not compatible. They upgrade virtual machine's hardware to meet system requirements of Ubuntu 18.04.
- Check File System Integrity: After upgrading virtual machine's hardware, user runs "fsck" command to check file system integrity. They discover that there are no file system errors.
- Update Kernel Version: user updates kernel version using "apt-get" command. They reboot virtual machine, and it boots up successfully.
Example 2: A virtual machine has CentOS 7 installed, and user decides to upgrade to CentOS 8. However, after upgrade process is completed, virtual machine fails to boot up.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Virtual Machine Hardware Compatibility: user reviews system requirements of CentOS 8 and discovers that virtual machine's hardware is compatible. They rule out hardware incompatibility as cause of booting issue.
- Check File System Integrity: user runs "fsck" command to check file system integrity. They discover that file system is corrupted and needs to be repaired.
- Update Kernel Version: user updates kernel version using package manager. They reboot virtual machine, but it still fails to boot up.
- Reinstall Bootloader: user boots virtual machine using installation media of CentOS 8 and selects "Rescue mode" option. They reinstall bootloader using appropriate commands. After reinstalling bootloader, virtual machine boots up successfully.
To know Linux boot process or booting sequence in detail please check this detailed explanation on Linux Boot Process.