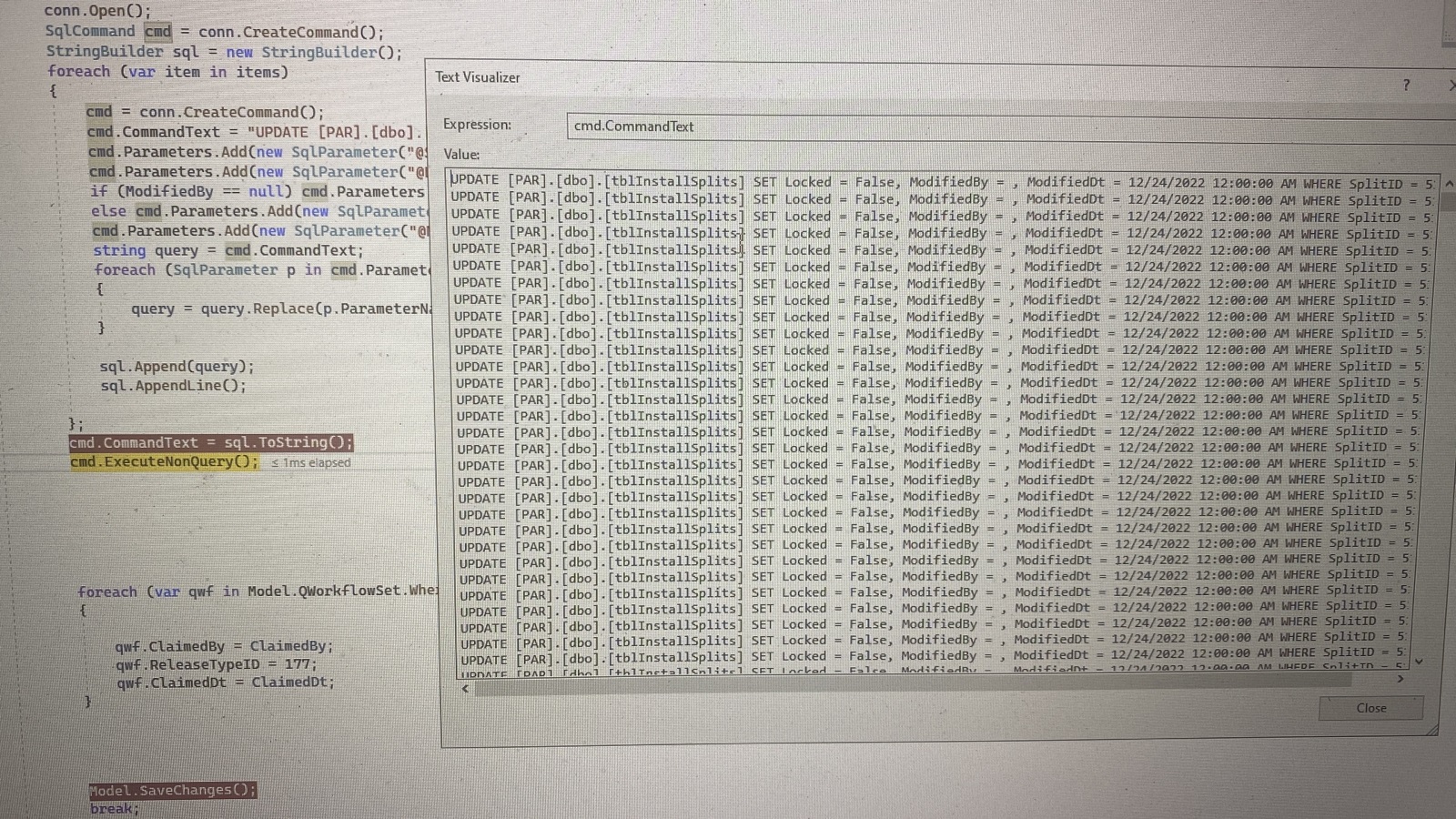
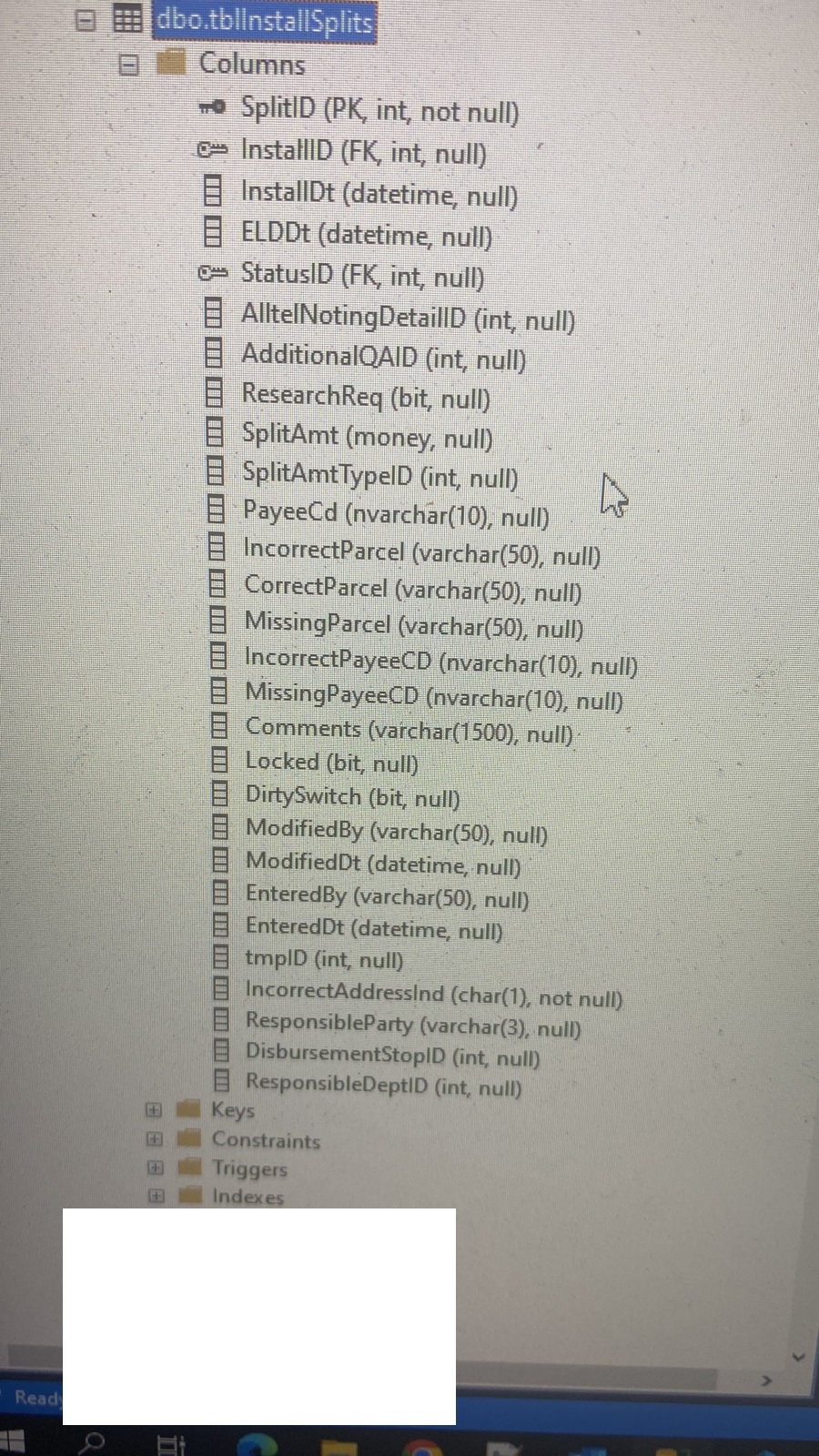
You could use MERGE with just the UPDATE option.
The following comes from the following code sample done with .NET Framework 4.8 and will work with .NET Core also. Here we have four columns to keep things simple.
namespace BulkCopyierLibrary
{
public class Exporter
{
public static (bool success, Exception exception) UpdateData(DataTable pDataTable)
{
string connectionString =
"Data Source=.\\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=BulkCopyDatabaseCodeSample;Integrated Security=True";
using (var cn = new SqlConnection() { ConnectionString = connectionString })
{
using (var cmd = new SqlCommand("", cn))
{
try
{
cn.Open();
cmd.CommandText = @"CREATE TABLE #TmpPersonTable(
[Id] [INT],
[FirstName] [TEXT] NULL,
[LastName] [TEXT] NULL,
[Gender] [INT] NULL,[BirthDay] [DATETIME2](7) NULL)";
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
using (var bulkCopy = new SqlBulkCopy(cn))
{
bulkCopy.BulkCopyTimeout = 660;
bulkCopy.DestinationTableName = "#TmpPersonTable";
bulkCopy.WriteToServer(pDataTable);
bulkCopy.Close();
}
cmd.CommandTimeout = 300;
cmd.CommandText = @"
MERGE INTO dbo.Person AS P
USING dbo.#TmpPersonTable AS S
ON P.Id = S.Id
WHEN MATCHED THEN
UPDATE SET P.FirstName = S.FirstName ,
P.LastName = S.LastName ,
P.Gender = S.Gender ,
P.BirthDay = S.BirthDay;
DROP TABLE #TmpPersonTable";
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return (false, ex);
}
finally
{
cn.Close();
}
return (true, null);
}
}
}
}
}