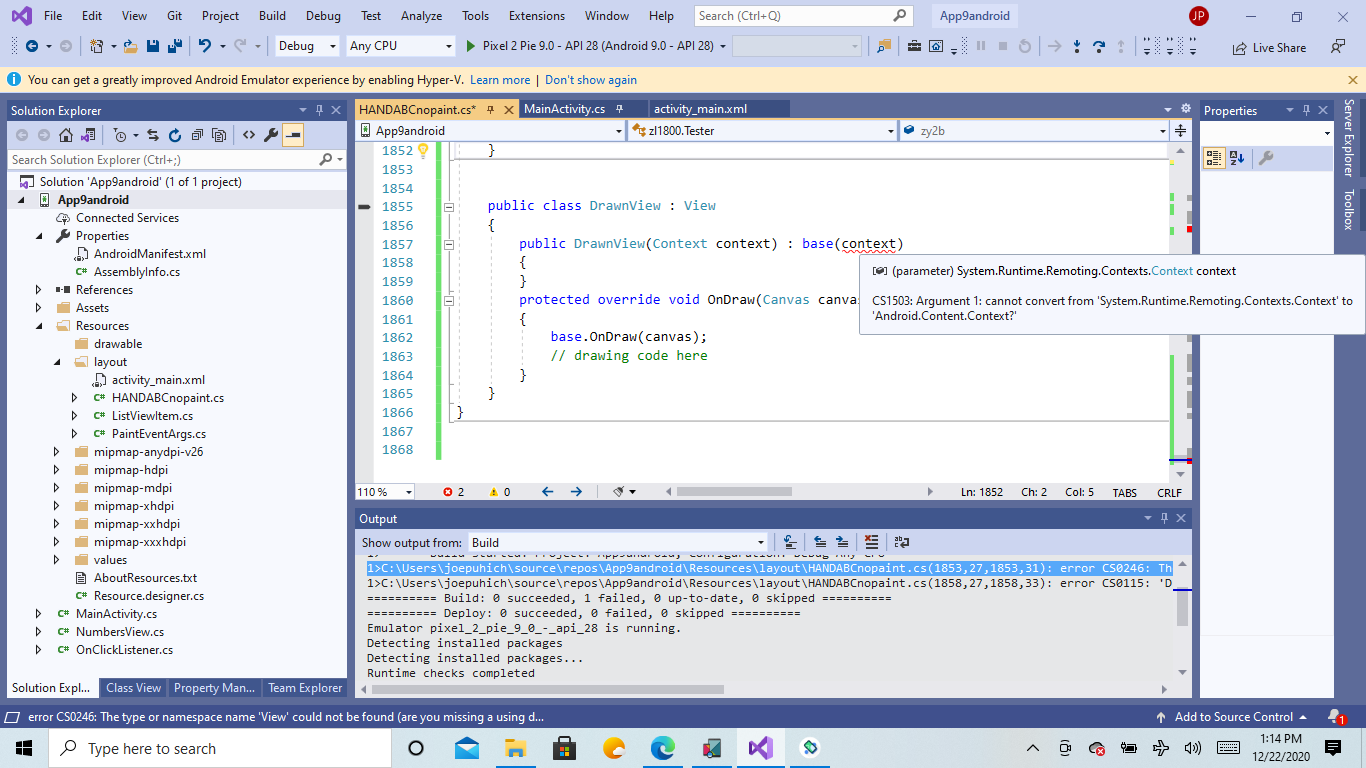
There are 2 types with name Context. Somewhere in that file you have a using statement that would be
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Contexts
Because of this, the Context in the
public DrawnView(Context context): base(context)
constructor is resolving to fully qualified System.Runtime.Remoting.Contexts.Context type, however the Android View constructor needs an Android.Content.Context, so in order to make that distinction, you will have to specify the fully qualified type name, e.g.:
public class DrawnView : View
{
public DrawnView(Android.Content.Context context): base(context)
{
}
protected override void OnDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
base.OnDraw(canvas);
// drawing code here
}
}
And when you call Invalidate(), you have to call it either from inside the DrawnView class, or on the instance of the DrawnView class that you want OnDraw to be called on, e.g.:
DrawnView drawnViewInstance = new DrawnView(context);
drawnViewInstance.Invalidate();
In the above, context is an Android.Content.Context, which can be the instance of your MainActivity (which is a subclass of Android.Content.Context). If the code above is in an Activity class, you can just pass in this for the context.
For a complete example, try this:
First start with a new template Xamarin.Android Single View app project.
Then add a new C# class file and create the DrawnView class with the OnDraw override:
using Android.Graphics;
using Android.Views;
namespace YourNamespace
{
public class DrawnView : View
{
public DrawnView(Android.Content.Context context) : base(context)
{
}
bool turnBlue = false;
protected override void OnDraw(Canvas canvas)
{
base.OnDraw(canvas);
if (turnBlue)
{
canvas.DrawColor(Color.Blue);
}
else
{
canvas.DrawColor(Color.Red);
}
turnBlue = !turnBlue;
}
}
}
The above will toggle itself to draw the background of the view as alternately blue or red every time OnDraw runs (i.e. when Invalidate() is called)
Then open the content_main.xml file in the Resources/layout folder and add an id to the RelativeLayout (leaving the other lines in place (...), i.e. just add the android:id):
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
...
android:id="@+id/relativeLayout1">
Then in MainActivity, create and add the DrawnView and change the FabOnClick method so that it invalidates the DrawnView (full code for MainActivity)
using System;
using Android.App;
using Android.Graphics;
using Android.OS;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Support.Design.Widget;
using Android.Support.V7.App;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Widget;
namespace YourNamespace
{
[Activity(Label = "@string/app_name", Theme = "@style/AppTheme.NoActionBar", MainLauncher = true)]
public class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity
{
DrawnView _drawnView;
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
base.OnCreate(savedInstanceState);
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.Init(this, savedInstanceState);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.activity_main);
Android.Support.V7.Widget.Toolbar toolbar = FindViewById<Android.Support.V7.Widget.Toolbar>(Resource.Id.toolbar);
SetSupportActionBar(toolbar);
FloatingActionButton fab = FindViewById<FloatingActionButton>(Resource.Id.fab);
fab.Click += FabOnClick;
// This is added code to get a reference to the layout and add the new DrawnView instance to it
RelativeLayout layout = FindViewById<RelativeLayout>(Resource.Id.relativeLayout1);
_drawnView = new DrawnView(this);
layout.AddView(_drawnView);
}
public override bool OnCreateOptionsMenu(IMenu menu)
{
MenuInflater.Inflate(Resource.Menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
public override bool OnOptionsItemSelected(IMenuItem item)
{
int id = item.ItemId;
if (id == Resource.Id.action_settings)
{
return true;
}
return base.OnOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
private void FabOnClick(object sender, EventArgs eventArgs)
{
// Invalidate the DrawnView so that it redraws with the new color
_drawnView.Invalidate();
}
public override void OnRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, string[] permissions, [GeneratedEnum] Android.Content.PM.Permission[] grantResults)
{
Xamarin.Essentials.Platform.OnRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
base.OnRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
}
}
}
Make sure that YourNamespace in the above code examples is changed to the actual namespace that your app is using.
Hope this helps. I would suggest you go through the Xamarin Android Getting Started docs to learn some fundamentals though:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/xamarin/android/get-started/