Azure Private DNS zones
Azure Private DNS manages and resolves domain names in the virtual network without the need to configure a custom DNS solution. By using private DNS zones, you can use your own custom domain name instead of the Azure-provided names during deployment.
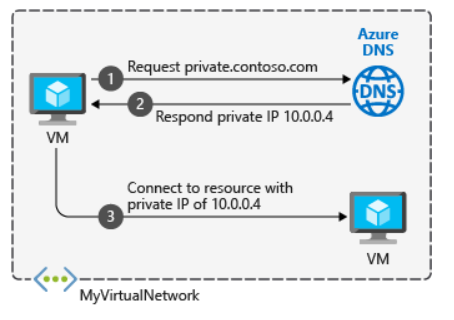
Private zones work along with virtual networks. You use them to manage domains for virtual machines or other resources within and across virtual networks. Internet connectivity isn't required for name resolution.
To resolve the records of a private DNS zone from your virtual network, you must link the virtual network with the zone. Linked virtual networks have full access and can resolve all DNS records published in the private zone. You can also enable autoregistration on a virtual network link. When you enable autoregistration on a virtual network link, the DNS records for the virtual machines in that virtual network are registered in the private zone. When autoregistration gets enabled, Azure DNS will update the zone record whenever a virtual machine gets created, changes its' IP address, or gets deleted.
Create an Azure private DNS zone using the Azure portal
DNS ZONES
A DNS zone is used to host the DNS records for a particular domain. To start hosting your domain in Azure DNS, you need to create a DNS zone for that domain name. Each DNS record for your domain is then created inside this DNS zone.
For example, the domain 'contoso.com' may contain several DNS records, such as 'mail.contoso.com' (for a mail server) and 'www.contoso.com' (for a web site).
Azure DNS supports all common DNS record types: A, AAAA, CAA, CNAME, MX, NS, PTR, SOA, SRV, and TXT.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dns/dns-zones-records
If the Answer is helpful, please click Accept Answer and up-vote, this can be beneficial to other community members.

