Hello @Hansli Tester ,
Thanks for reaching out and welcome to Microsoft Q&A forum community !!!
Yes, you are right but when you create an Azure AD DS managed domain (Ex: aaddscontoso.com) then Two Windows Server domain controllers (DCs) are deployed into your selected Azure region. This deployment of DCs is known as a replica set.
Azure Active Directory Domain Services (Azure AD DS) provides managed domain services with a subset of fully-compatible traditional AD DS features such as domain join, group policy, LDAP, and Kerberos / NTLM authentication.
Hence sharing file must work as long as Azure VMs are joined to Azure AD Domain Services ( not Azure AD joined which is different concept) and you can add new AADDS user to manage permission as shown below but when you use AADDS you don't have Domain Administrator or Enterprise Administrator permissions on a managed domain, these permissions are reserved by the service and aren't made available to users within the tenant.
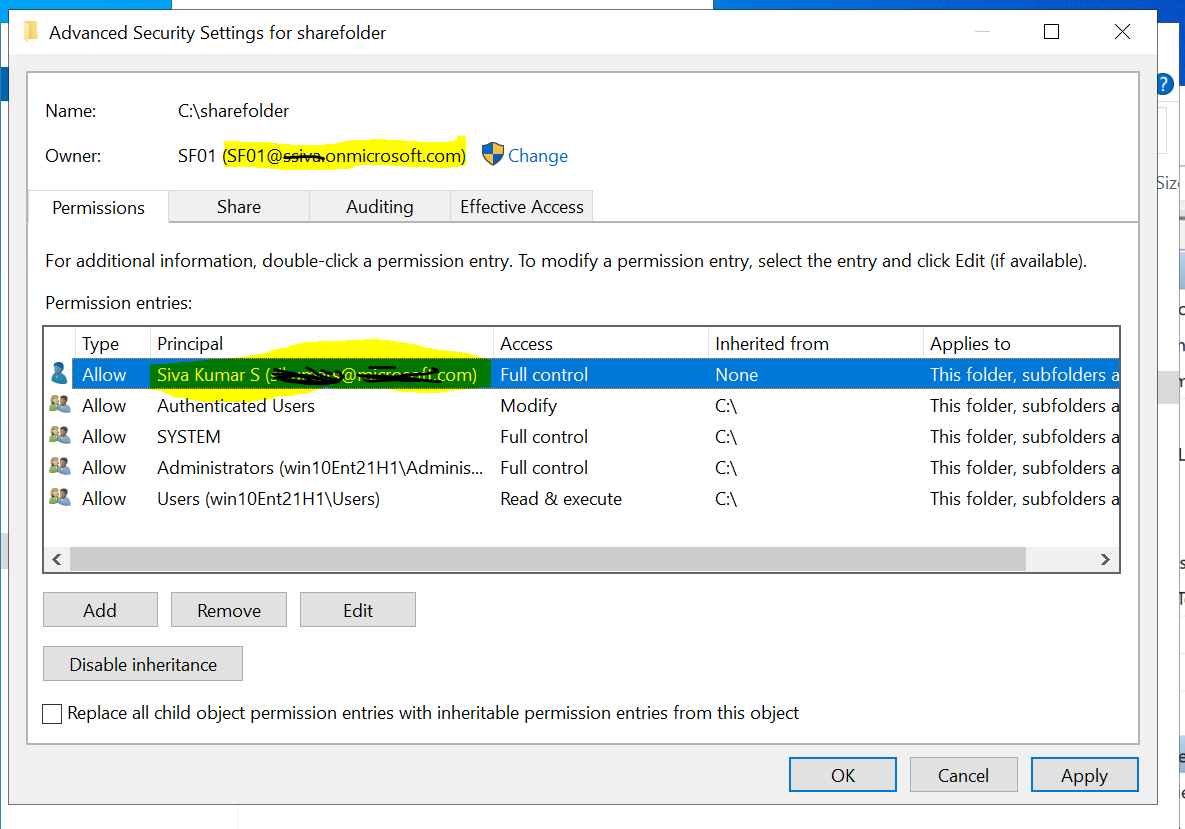
so with this scenario, AADDS lets you perform some privileged operations with file share permission for which "Domain Administrator" or "Enterprise Administrator" permissions doesn't require.
For example: lets say you had created a new share folder on VM which is part of AADDS joined and there are some NTFS permissions which is inherited by default to that folder so when you try "modifying/delete default inherited permissions" which require "Domain Administrator" or "Enterprise Administrator" access then with this scenario you may end-up in access denied due to less privileged access.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Azure Active Directory (AD) Domain Services
Alternatively, you could leverage Azure files and enabled Azure Active Directory Domain Services authentication which uses NTFS permissions over SMB for directories and files.
Hope this helps.
------
Please "Accept the answer" if the information helped you. This will help us and others in the community as well.
