Hello,
Thank you for posting here.
1.Check the value of Account lockout threshold under Default Domain Policy.
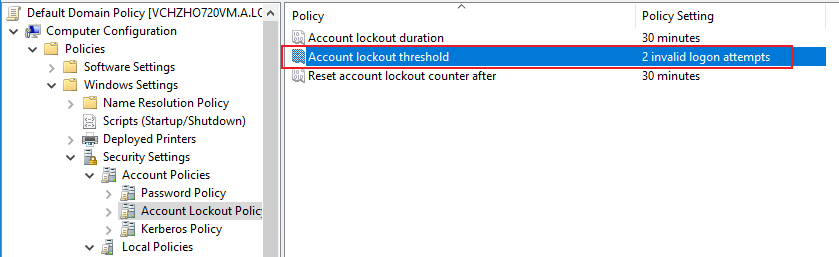
2.Check PDC in the doamin.
We can troubleshoot as below:
1.On the GPO: Default Domain Controller Policy
Legacy audit policy:
Computer Configuration\Windows settings\security settings\local policies\audit policy
Audit Account Logon Events – Failure (apply through Default Domain Controller Policy)
Audit Account Management - Success and Failure (apply through Default Domain Controller Policy)
Audit Logon Events – Failure (edit it through local group policy on server, we will say it later)
Or use advanced audit policies (advanced audit policies will overwrite traditional audit policies by default):
Computer Configuration\Windows settings\security settings\Advanced Audit Policy Configuration
on DCs(apply through Default Domain Controller Policy)
Account Logon:
Audit Kerberos Authentication Service - Failure
Audit Credential Validation – Failure
on DCs(apply through Default Domain Controller Policy)
Account Management:
Audit User Account Management – Success and Failure
on server or client (edit it through local group policy on server, we will say it later)
Logon/Logoff:
Audit Account Lockout – Failure
Audit Logon – Failure
2.We can run the following commands on the domain controller to force the refresh policy and check whether the related audit policy settings are enabled:
gpupdate /force
auditpol /get /category:*
3.After the accounts are locked again (we can choose 2-3 three accounts to check.), we can run lockoutstatus.exe tool to check the value of Bad Pwd Count are set on which DC.
Account Lockout Status (LockoutStatus.exe)
https://www.microsoft.com/en-sg/download/details.aspx?id=15201
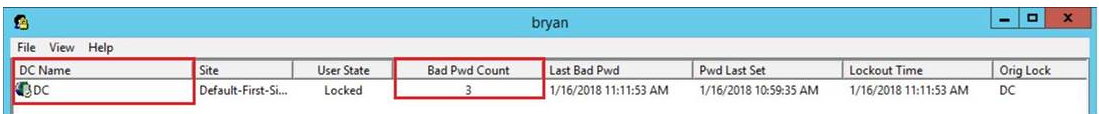
4.Then we check the security log from the domain controller whose Bad Pwd Count value is not 0. If the accounts are locked on multiple DCs, we can check the security log about this account on non-PDC.
5.Check if there are event IDs related to 4740, 4771 (error code 0X18) and 4776 (error code 0xc000006a) on DC security log. It seems that you can see 4740 and 4771 on DC.
6.Then check the Client Address or Source Workstation or Caller Computer Name through Event 4740 or Event 4771.
7.Maybe the account are locked on the machine (Client Address or Source Workstation or Caller Computer Name), we can enabled the following audit policy on source machine if we find it:
Computer Configuration\Windows settings\security settings\local policies\audit policy
Audit Logon Events – Failure (edit it through local group policy on server)
OR
Computer Configuration\Windows settings\security settings\Advanced Audit Policy Configuration
on server or client (edit it through local group policy on server)
Logon/Logoff:
Audit Account Lockout – Failure
Audit Logon – Failure
We can log in to the client to check:
• Check the credential management to see if there are cached user’s old credentials.
• Check if there is a wrong password to mount the network disk.
• Check whether the user has used the wrong password to start services, run scheduled tasks, etc.
• Are there other third-party programs that cache the user's wrong password.
Hope the information above is helpful. If anything is unclear, please feel free to let us know.
Best Regards,
Daisy Zhou