Hi Roger,
if a method is declared with the keyword async, an additional area is reserved in the stack. An instruction with await is started, the return information (CPU register, ...) for further work after the await is also stored in the stack (async area) and the control is returned to the caller without the further commands be processed after the await. Only when the waiting (await) has ended will the remaining commands of the method be processed after the await. The area in the stack created with async is used so that the runtime environment knows where to continue working in the interrupted method.
When executing with await on a task that executes a Sub (method with no return value) asynchronously, execution are not waited. When await is executed with a task that asynchronously processes a Function (method with return value), await waits for the result.
Try following demo:
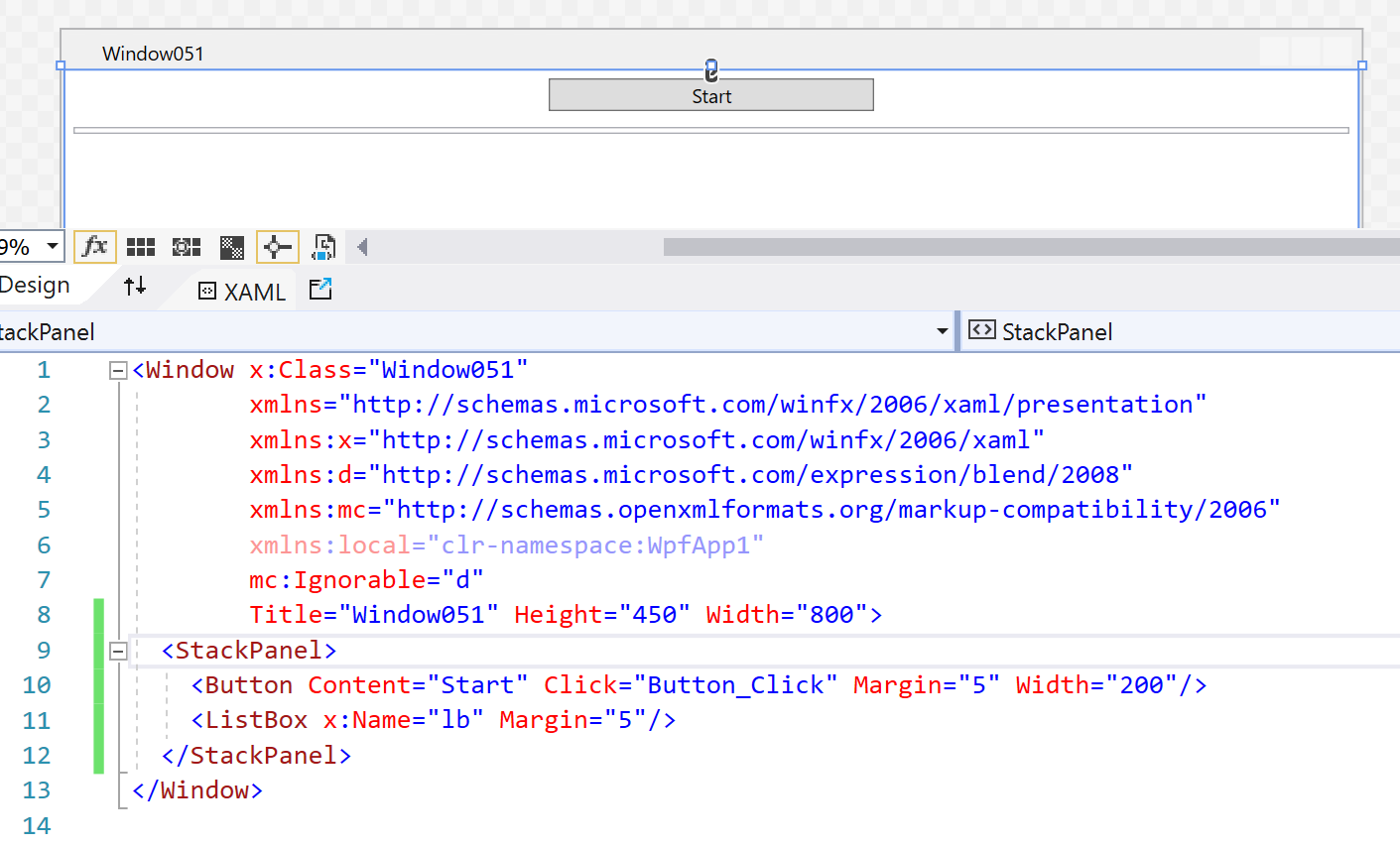
And CodeBehind:

Result: