Hi,
(1) In any doubt regarding performance of queries you should check the execution plan of the queries.
(2) The same query which executed on tables in two different database can behave totally different even if the table structure is the same. SQL Server might execute different execution plan depend on the data and other parameters (in addition to the table structure).
(3) A view is a virtual table defined by a query.
When we use the a view then SQL Server able to parse the view's query inline with the external query and not as a black box.
As a result for example in simple cases there is no impact to performance by using a simple view.
With that being said in many cases people build a view which make the combine query a lot more complex then needed. In such cases, the combine query does not provide the same performance as using a direct query simpler query which only uses the columns/data that is needed.
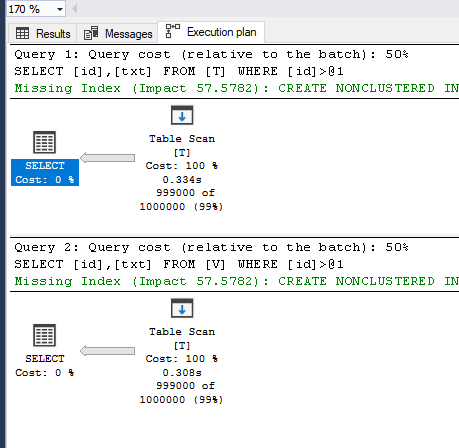
For example, in the following sample using view has no meaning and if you check the execution plan then you can see that the server does not even react to the view but uses the exact same execution plan directly on the original table
use tempdb
GO
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS T
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS V
GO
create table T(id int identity(1,1), txt nvarchar(100))
GO
INSERT T (txt)
SELECT top 1000000 NEWID()
from sys.all_objects t1
cross join sys.all_objects t2
GO
CREATE VIEW V as select id, txt from T
GO
-- Check Execution plan of these two execution
select id, txt from T where id>1000
select id, txt from V where id>1000
GO
As mentioned, there are cases where people are using a view in the wrong way, which result in poor performance when using the view. In these case the server will behave the same as using the view inline but the query of the view might make the combined query bad.
For example, several year ago I was asked to help a client that their DBA just finished an SQL Server course. In the course he learned about VIEW. As a result he decided to build a single view which JOIN all the tables (tens of tables using a single query!), since he did not have any understanding of what he learned. So in this case when he wanted to get data from a single table, then he used a SELECT from the view, which mad a JOIN of tens of table just in order to use a few columns from one table - obviously the performance of their system was poor and my payment goes up when they call me to fix their poor system :-)
Conclusion, using view in the wrong way can help the consultant when your system performance reduces, but using the right view in the right way should not cost any extra performance to direct execution AND IN FACT, IT CAN EVEN END WITH BETTER PERFORMENCE in some cases.
So... I mentioned that using view can end with better performance in some cases... for example, using index view or filtered view
Let's change the view a bit and use the same query and check the execution plan this time
CREATE OR ALTER VIEW V
WITH SCHEMABINDING -- needed to create the index
as select id, txt from dbo.T -- must use schema when use SCHEMABINDING
WHERE id > 1000
GO
CREATE UNIQUE CLUSTERED INDEX IDX_V ON V (id);
GO
select id, txt from T where id>1000
select id, txt from V where id>1000
GO
Notice the execution is totally different now! The query on the view used the index which we built.
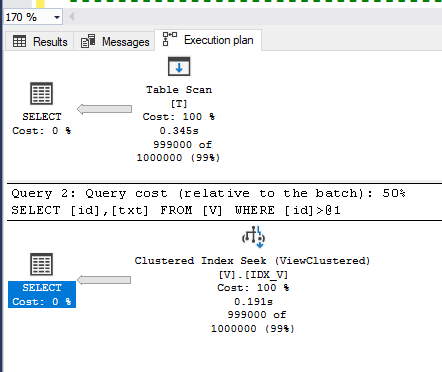
This is just a simple scenario to show different Execution Plan when suing the view. In this specific case, it might not end with different performance but represent the cases whcih might be more complex



