Hi @Mahdi Elahi ,
Access To User in AspNetUserRoles table
You can refer the following code to add User and Role navigation properties:
public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser
{
public int Age { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<ApplicationUserRole> UserRoles { get; set; }
}
public class ApplicationRole : IdentityRole
{
public string? RoleName { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<ApplicationUserRole> UserRoles { get; set; }
}
public class ApplicationUserRole : IdentityUserRole<string>
{
public virtual ApplicationUser User { get; set; }
public virtual ApplicationRole Role { get; set; }
}
ApplicationDbContext.cs:
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser, ApplicationRole, string,
IdentityUserClaim<string>, ApplicationUserRole, IdentityUserLogin<string>,
IdentityRoleClaim<string>, IdentityUserToken<string>>
{
public DbSet<ApplicationUser> ApplicationUsers { get; set; }
public DbSet<ApplicationRole> ApplicationRoles { get; set; }
public DbSet<ApplicationUserRole> ApplicationUserRoles { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>(b =>
{
// Each User can have many entries in the UserRole join table
b.HasMany(e => e.UserRoles)
.WithOne(e => e.User)
.HasForeignKey(ur => ur.UserId)
.IsRequired();
});
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationRole>(b =>
{
// Each Role can have many entries in the UserRole join table
b.HasMany(e => e.UserRoles)
.WithOne(e => e.Role)
.HasForeignKey(ur => ur.RoleId)
.IsRequired();
});
}
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
}
Then, in the controller, use the following code to access the AspNetUserRole table:
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _dbcontext;
private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _usermanager;
private readonly RoleManager<ApplicationRole> _roleManger;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger,
UserManager<ApplicationUser> userManager,
RoleManager<ApplicationRole> roleManager,
ApplicationDbContext applicationDbContext)
{
_logger = logger;
_dbcontext = applicationDbContext;
_usermanager = userManager;
_roleManger = roleManager;
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Index()
{
if (User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)
{
//get current user
var currentuser = await _usermanager.FindByNameAsync(User.Identity.Name);
//query the userrole table
//required using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
var userrole = _dbcontext.ApplicationUserRoles.Include(c=>c.User).Include(c=>c.Role).Where(c=>c.UserId == currentuser.Id).FirstOrDefault();
var user = userrole.User;
var role = userrole.Role;
}
return View();
}
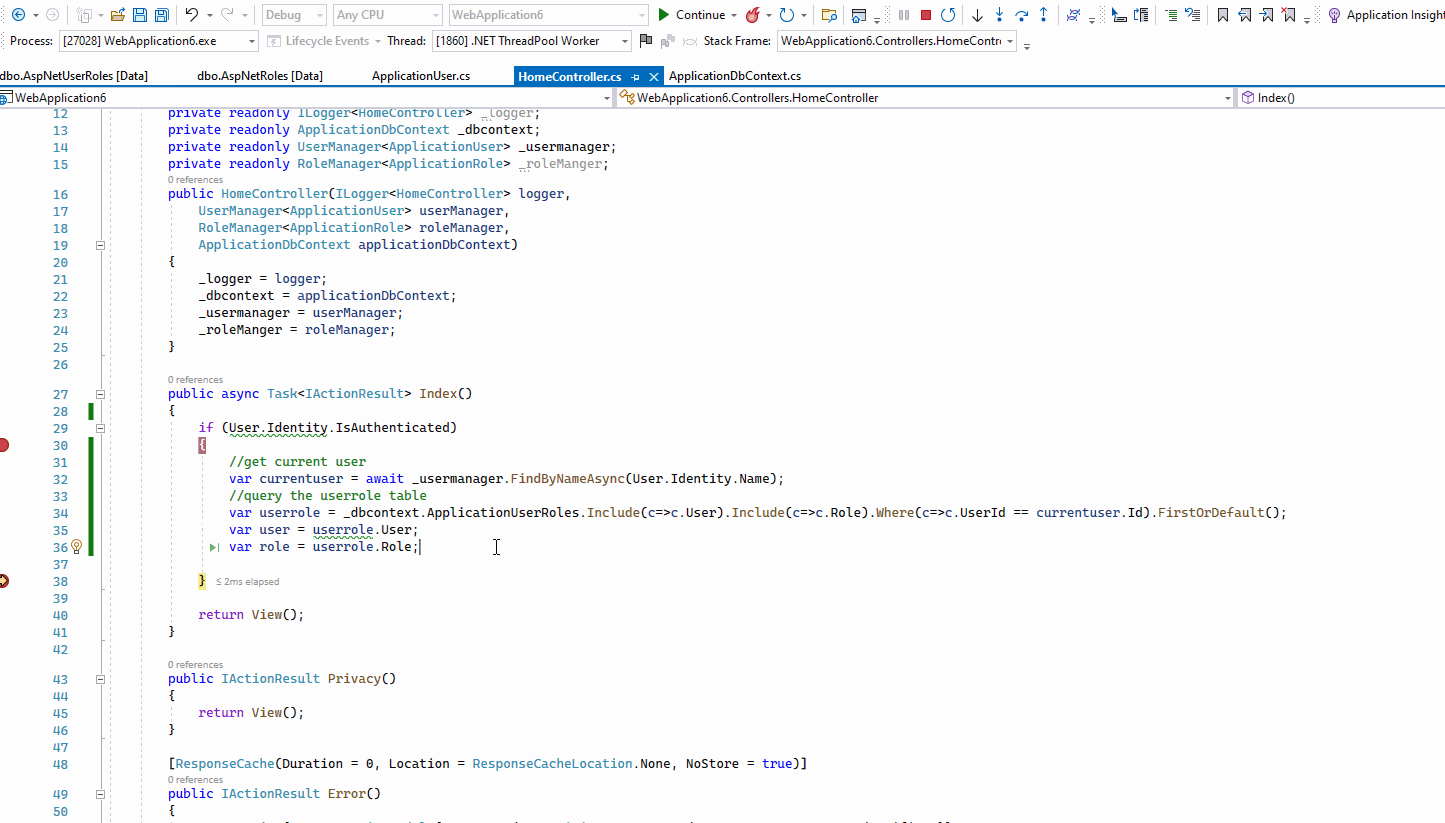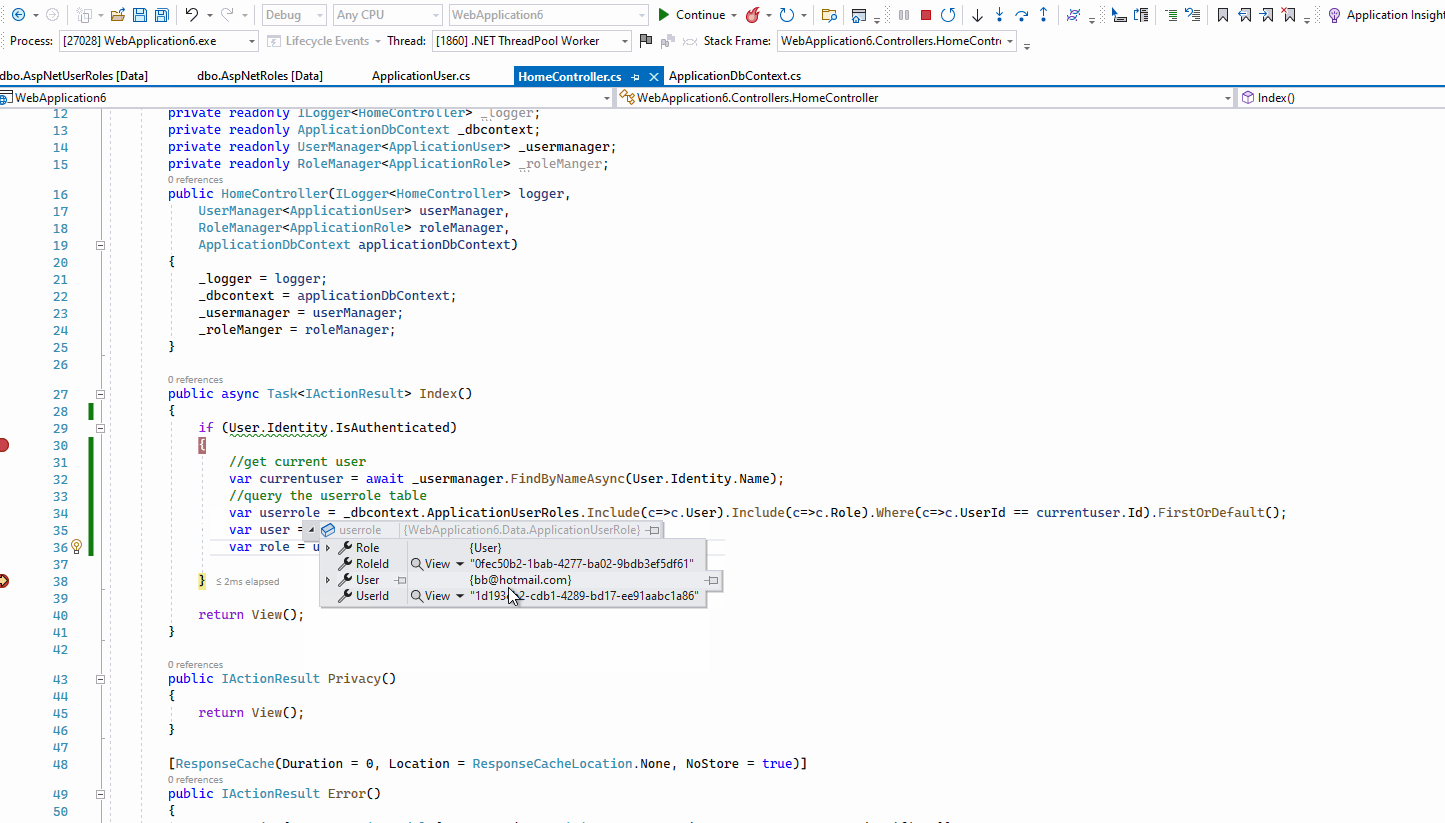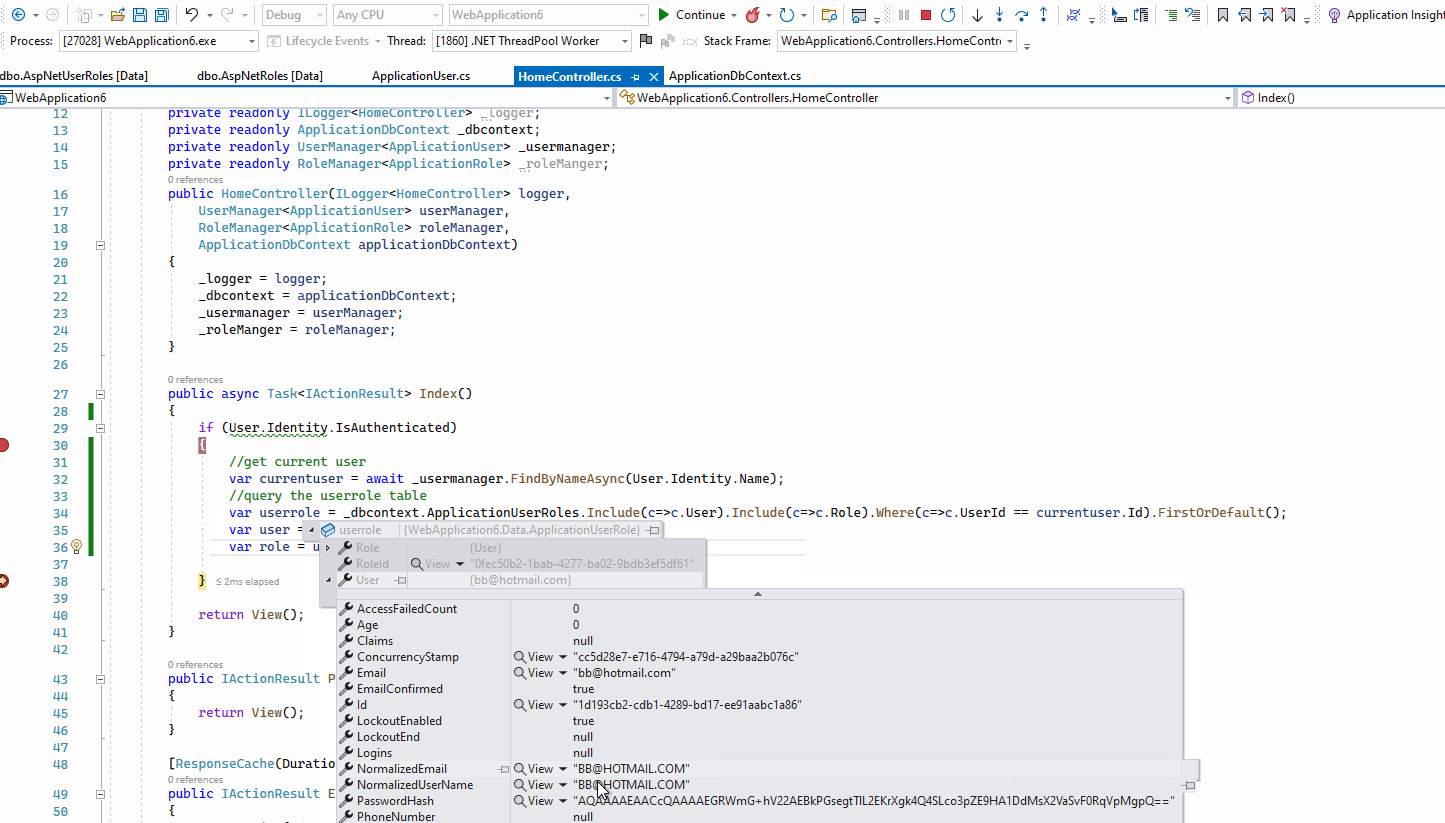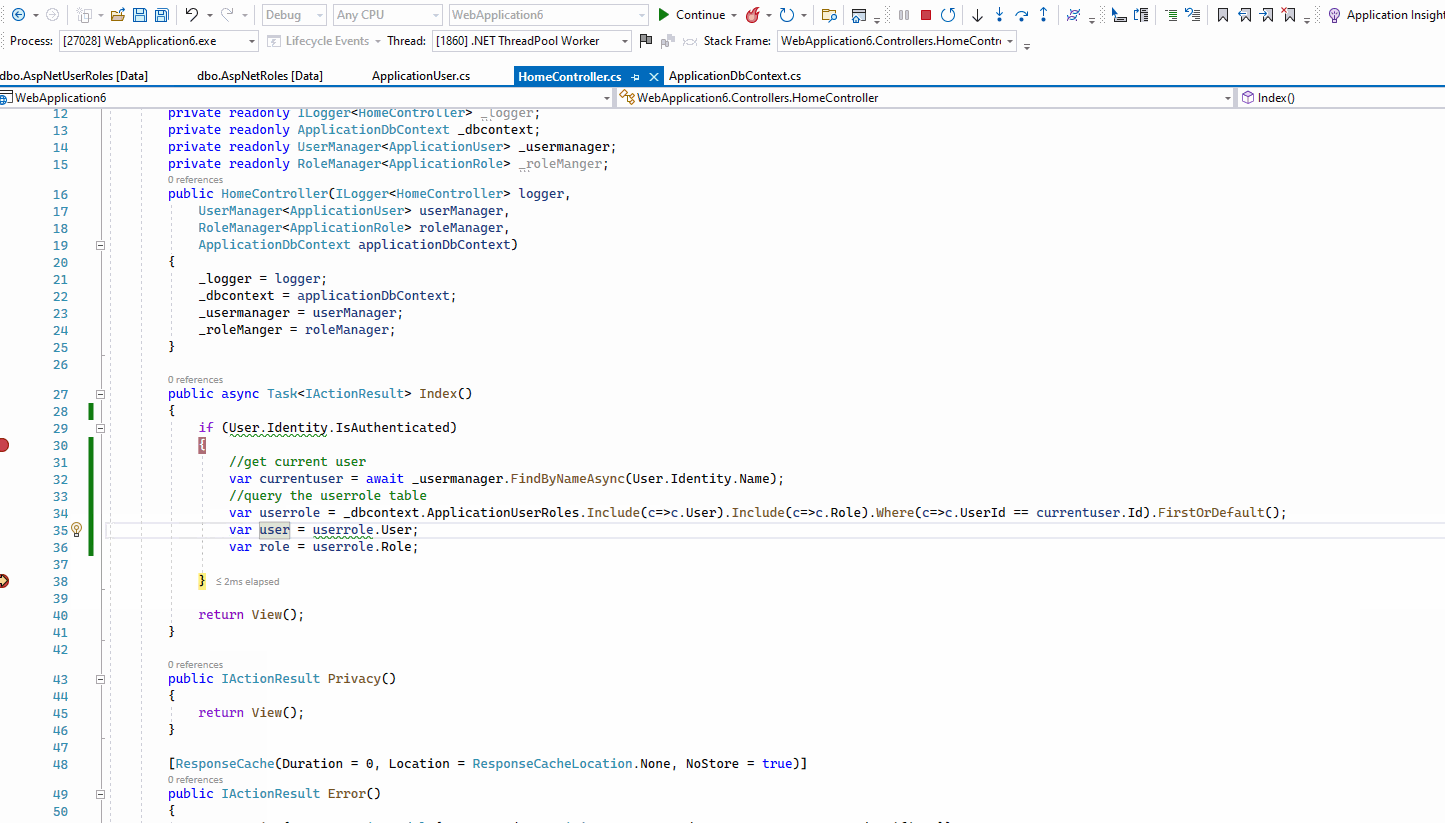
The result like this:
More detail information about customizing the Identity model, see Identity model customization in ASP.NET Core.
If the answer is the right solution, please click "Accept Answer" and kindly upvote it. If you have extra questions about this answer, please click "Comment".
Note: Please follow the steps in our documentation to enable e-mail notifications if you want to receive the related email notification for this thread.
Best regards,
Dillion