Loading GeoNames Data Into SQL Server 2008 (yet another way...)
In his post last year, Integrating Virtual Earth and GeoNames, Johannes described how to load the GeoNames database into SQL Server using the "Import Data" Wizard in SQL Server Management Studio. In his scenario, Johannes did not need to take advantage of the spatial type support in SQL Server 2008, since there were columns of latitude and longitude available for use by Virtual Earth. But what if you wanted to load the GeoNames locations into SQL Server Spatial and use the new geospatial features? This post describes how to do that in 6 easy steps...
- Download GeoNames data
- Prepare GeoNames data
- Create a database table for the GeoNames data
- Load the GeoNames data
- Add, update and index the spatial data column
- Sample spatial query
So, let's get started...
Download GeoNames Data
You can find GeoNames data organized by country (and a few other organizational categories) by browsing the GeoNames Download page. If you wanted to download the GeoNames data for the United States, you would choose US.zip. For this exercise, we are going to download the allCountries.zip file, containing the full worldwide GeoNames database. Unzipping the downloaded file will produce the file allCountries.txt.
Note: This version of GeoNames data was download on January 13, 2009 and contained 6,906,334 records.
Prepare GeoNames Data
The GeoNames data is available as a tab-delimited, UTF-8 encoded text file. Each record is terminated with newline character ('\n'). SQL Server 2008 does not support UTF-8, expecting such data in UTF-16 encoding with each record delimited with a carriage return, newline combination ('\r\n'). Additionally, it needs a Byte Order Marker (BOM) at the beginning of the file. Johannes introduced NAnt as a way to convert UTF-8 data to UTF-16. I chose another way. Using the Windows text editor, EditPad Pro, I converted the allCountries.txt file into a form compatible with SQL Server 2008. Here is the workflow I used with EditPad Pro:
Note: While this conversion could conceivably be done in Word 2007, Word cannot open and operate efficiently on files of this size. EditPad Pro can reasonably handle data of this magnitude.
a. Open allCountries.txt file in EditPad Pro.
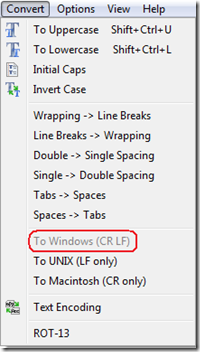
b. Set Record Delimiter. In the "Convert" menu (main menu), select "To Windows (CR LF)". This will set the record delimiter to '\r\n'.
This took several minutes to complete in EditPad Pro after the "To Windows (CR LF)" option was selected - presumably loading the file into memory and performing the requested operation...
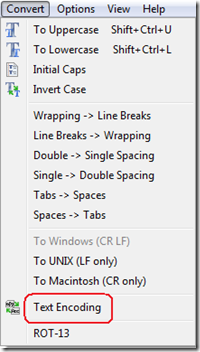
c. Set text encoding. While still in the "Convert" menu, choose "Text Encoding".
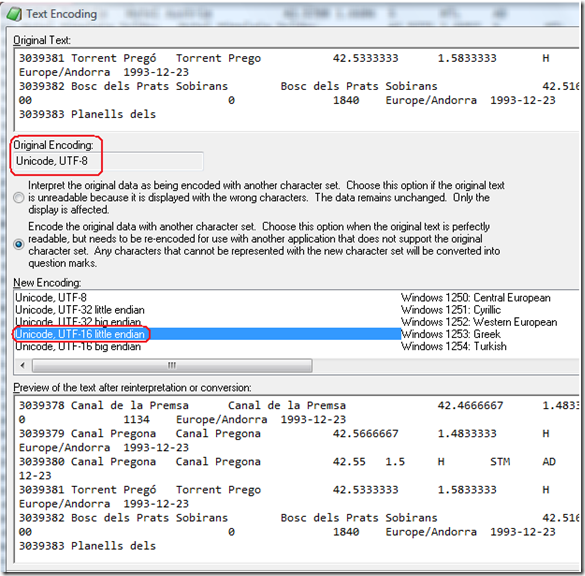
In the Text Encoding menu note the Original Encoding, set to Unicode, UTF-8. Select the "Encode the original data with another character set." button. Under New Encoding, choose "Unicode, UTF-16 little endian".
After hitting "OK", my humble dual proc machine with 2GB of RAM squawked about low virtual memory, but continued to process the file...
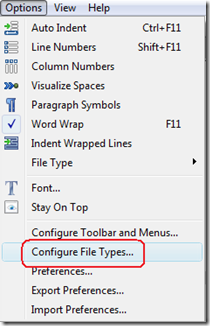
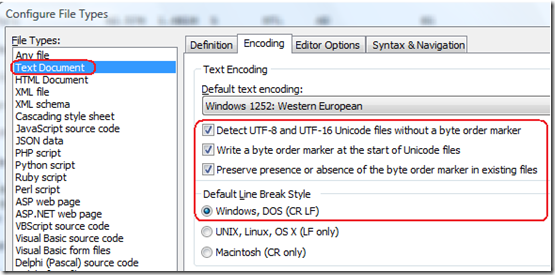
d. Set the Byte Order Marker (BOM). In the "Options" menu (main menu), select "Configure File Types...".
Choose the "Encoding" tab. Under File Types, make sure "Text Document" is selected. Make sure that the Text Encoding is set as follows:
Note on the Default Line Break Style: While it appears that the line break was already set under stop b. (above), it appears that setting the line break in both places is required, though it is not obvious, why...
Note on the Byte Order Marker (BOM): You can see the BOM as the FF FE bytes at the
start of the file by pressing Crtl+H in EditPad Pro (this switches EditPad Pro to hex display mode). If your file does not include the BOM, SQL Server will complain, when loading data, that the "...file does not have a Unicode signature."
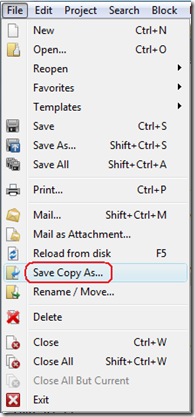
e. Create new file copy, correctly encoded for SQL Server 2008. In the "File" menu (main menu), select "Save Copy As...".
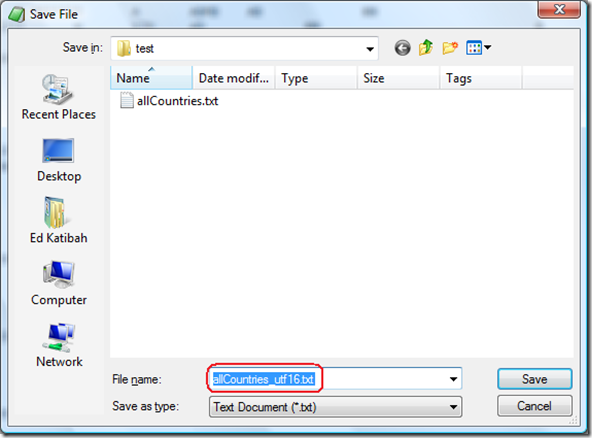
Save the file with the desired name (I used allCountries_utf16.txt):
The file, allCountries_utf16.txt, is now a Unicode UTF-16, BOM encoded text file with tab-delimited ('\t') fields and CR\LF row terminators ('\r\n'), ready for SQL Server 2008.
Before we leave this section, here are some statistics:
| FILE | SIZE | |
| allCountries.zip | 174,594 KB | |
| allCountries.txt | 783,093 KB | |
| allCountries_utf16.txt | 1,563,976 KB |
Create a database table for the GeoNames data
Here is the T-SQL to create a table called GeoNames...
CREATE TABLE GeoNames(
geonameid int NOT NULL,
name nvarchar(200) NULL,
asciiname nvarchar(200) NULL,
alternatenames nvarchar(max) NULL,
latitude float NULL,
longitude float NULL,
feature_class char(2) NULL,
feature_code nvarchar(10) NULL,
country_code char(3) NULL,
cc2 char(60) NULL,
admin1_code nvarchar(20) NULL,
admin2_code nvarchar(80) NULL,
admin3_code nvarchar(20) NULL,
admin4_code nvarchar(20) NULL,
population int NULL,
elevation int NULL,
gtopo30 int NULL,
timezone char(31) NULL,
modification_date date NULL
)
GO
Note on the alternatenames column: This column holds the GeoNames field which requires Unicode (UTF-8, UTF-16).
Load the GeoNames data
I used the BULK INSERT command to load the allCountries_utf16.txt file. Note the DATAFILETYPE = 'widechar' parameter - this is required for loading UTF-16 data.
BULK
INSERT GeoNames
FROM 'C:\temp\allCountries_utf16.txt'
WITH(
DATAFILETYPE = 'widechar',
FIELDTERMINATOR = '\t',
ROWTERMINATOR = '\n'
)
GO
--(6906334 rows(s) affected) (00:05:44)
Note on the ROWTERMINATOR: While I have changed the Row Terminator in the allCountries_utf16.txt file to '\r\n', SQL Server, curiously, requires the Row Terminator to be set to '\n'. There is no good explanation for this...
Add, update and index the spatial data column
The current table does not contain a column to hold native spatial data. Since the data is in WGS84 geographic coordinates, I used the geography data type for the new column:
ALTER TABLE GeoNames
ADD geog GEOGRAPHY NULL
GO
To populate the new geography column (geog), I used the STGeomFromText constructor to create a POINT feature for each GeoNames row. Since this is a text-based constructor, the longitude and latitude data, coming from columns of like name, will need to be converted into text using the CAST function. The SRID for the STGeomFromText constructor is set to 4326, the EPSG value for WGS84 coordinates.
UPDATE GeoNames
SET geog = GEOGRAPHY::STGeomFromText
('POINT(' + CAST(longitude AS CHAR(20))
+ ' ' + CAST(latitude AS CHAR(20)) + ')',4326)
GO
--(6906334 rows(s) affected) (00:09:40)
Note on coordinate order: Since this is an OGC-based operator, the WKT is formed as: 'POINT (<longitude> <latitude>)'.
In order to create a spatial index, the table must have a primary key. While I could have created the primary key in the CREATE TABLE DDL, this would have meant that the data was loaded into an existing index, slowing down the load process considerably.
ALTER TABLE GeoNames
ADD CONSTRAINT pk_geonames_geonameid
PRIMARY KEY (geonameid )
GO
Here is the DDL to create a spatial index on the geography column, geog:
CREATE SPATIAL INDEX geonames_mmmm16_sidx
ON GeoNames(geog)
USING GEOGRAPHY_GRID
WITH (
GRIDS = (MEDIUM, MEDIUM, MEDIUM, MEDIUM),
CELLS_PER_OBJECT = 16,
PAD_INDEX = ON
)
GO
--(00:10:30)
Sample spatial query
As an example of the type of queries which can now be supported using the GeoNames table, consider the following: "Find all place names within 1 kilometer of the Travis County (Texas) boundary line":
Note: the distance parameter for the STBuffer() method (geography data type) is in meters...
DECLARE @g GEOGRAPHY
DECLARE @h GEOGRAPHY
DECLARE @i GEOGRAPHY
DECLARE @j GEOGRAPHY
SELECT @g = geog FROM US_Counties WHERE NAME = 'Travis'
--SQL Server Execution Times: Elapsed time = 8 ms
SELECT @h = @g.STBuffer(1000) -- Positive buffer around Travis County
--SQL Server Execution Time: Elapsed time = 16 ms
SELECT @i = @g.STBuffer(-1000) -- Negative buffer around Travis County
--SQL Server Execution Time: Elapsed time = 16ms
SELECT @j = @h.STDifference(@i)-- Difference Polygon
--SQL Server Execution Time: Elapsed time = 4 ms
SELECT name FROM GeoNames WHERE geog.STIntersects(@j)=1
ORDER BY name ASC
--91 rows affected
--SQL Server Execution Time: Elapsed time = 823 ms.
Here is the list of place names returned by the query:
Anderson Mill Anderson Mill Elementary School Apple Spring Apple Spring Hollow Austin Air Ranch Airport Austin Raceway Park Balcones Country Club Balcones Country Club Lake Balcones Country Club Lake Dam Bear Creek Best Western Southgate Inn Ste Blessed Juan Diego Catholic Church Bonnet Cemetery Boultinghouse Mountain Bratton Cemetery Bridgeway Community Church Cambrian Creek Canyon Vista Middle School Canyon Vista Pool Cedar Park High School Center Union Church Chalk Knob Chalk Knob Branch Child Evangelism Fellowship Church Church of Christ - Pond Springs Clarence Washington Farm Dam Clarence Washington Farm Lake Cottonwood Branch Crestwood Suites - Austin Cypress Creek Baptist Church |
Cypress Elementary School Devils Hollow Esa Austin-Round Rock-South Fall Creek Cemetery Fitzhugh Fitzhugh Cemetery Garfield Pumping Station Gateway Community Church Gay Hollow Hamilton Hill Hammetts Crossing Hampton Inn Austin Round Rock Harris Branch Haynie Flat Cemetery Hilton Garden Inn Round Rock Hope Presbyterian Church Huddleston Cemetery Ingram Cemetery Jollyville Jollyville Cemetery Jollyville Elementary School KGTN-AM (Creedmoor) Koenig Ranch La Frontera in Round Rock La Quinta Inn & Suites Round Rock South Manchaca Optimist Youth Sports Complex Manchaca Springs Marriott Austin North Martin Hill McNeil |
McNeil High School Merrelltown Muleshoe Bend Muleshoe Bend Trail New Hope Community Church Niederwald Cemetery North Creek Park Pond Springs Presbyterian Church of the Hills Purple Sage Elementary School Rattan Creek Trail Red Bluff Creek Residence Inn By Marriott Austin Round Rock Rhodes Cemetery Rim Rock Trail Round Rock Korean Presbyterian Church Round Rock Opportunity Center Roy Creek Saint Vincent de Paul Catholic Church Shingle Hills Signal Hill Spicewood Elementary School Spillar Ranch Studio 6 Austin Northwest Tanglewood Spring Texas No Name Number 9 Dam The Marbridge School Turkey Bend Turkey Bend Trail Vasquez Cemetery Woods Hill |
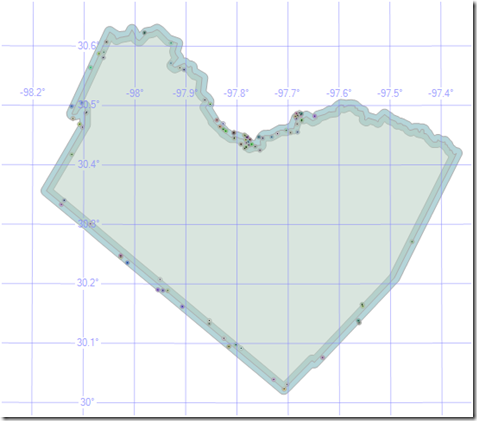
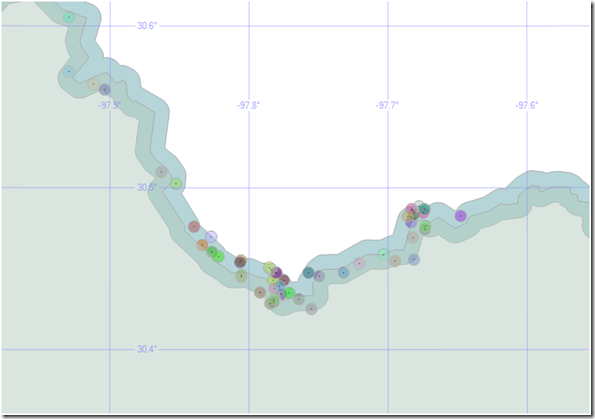
Here is the visual result of the place names locations, within the county boundary buffer, presented in Management Studio:
Here is a more detailed view (the actual point locations are represented by the block dots in the center of each point symbol):
And there you have it - sub-second performance against 6.9 million rows with a complex spatial object on a very modest machine...
Technorati Tags: GeoNames,Unicode,UTF-8,UTF-16,SQL Server,Spatial,Data Loading,EditPad
Comments
Anonymous
January 13, 2009
The comment has been removedAnonymous
January 13, 2009
Awesome post, will save people a lot of time and get a good quantity of data into the DB to play with.Anonymous
January 21, 2009
The comment has been removedAnonymous
January 21, 2009
out of interest how long did your windows conversion take - I am running 4gb ram 64bit Vista and its taking much longer than a few minutes :)Anonymous
January 23, 2009
The file conversion did take longer than a few minutes. I walked away from my machine during the conversion and was probably too cavalier in my time estimate. Take a look at my newest post. Using PowerShell, this conversion took 65 minutes.Anonymous
February 04, 2009
The comment has been removedAnonymous
February 04, 2009
Outstanding post, and exactly what I am looking for right now. Many thanks. I am not seeing any reference to the us_countries table used in the demo. Where would I find a copy of this?Anonymous
February 06, 2009
The comment has been removedAnonymous
February 18, 2009
EditPad Pro continues to give me Out of Memory errors an hour into running on my dual-core 4 GB RAM system running XP SP2. I am going to give TextPad a try.Anonymous
May 18, 2009
Be careful with your casts. CAST(longitude AS CHAR(20)) only gives me 3 digits after the decimal point, regardless of the precision of the float.... not sure why. I ended up using str(longitude, 14, 8) instead.Anonymous
December 06, 2009
Awesome post. If you have UltraEdit (file editor) and optimize it for large files (see ultraedit support site) you can perform the text file conversion in about 30 seconds or so. Also, this works for the update statement... same deal, but a little cleaner: UPDATE GeoNames SET Point = geography::Point(Latitude, Longitude, 4326)Anonymous
January 05, 2010
The comment has been removedAnonymous
January 29, 2010
Hi, I only get list of points from the last select statement, I dont see what you have in your example Shape of county, plus -/+ bounds, and points. What am I missing? select @city = geog from GEO_Counties where NAME = 'philadelphia' select CompanyName,Address, City, State, Zip, Phone, geography::Parse('Point('+ convert(varchar(50),lon) + ' ' + convert(varchar(50),lat) +')').STBuffer(8050) as VendorGeo from temp_Vendors where companyname like '%pizza%' and geography::Parse('Point('+ convert(varchar(50),lon) + ' ' + convert(varchar(50),lat) +')').STBuffer(8050).STIntersects(@city)=1Anonymous
February 25, 2010
Where did US_Counties come from?Anonymous
April 12, 2010
Mike C, you saved the day. I spent hours with EditPadPro. UE has always been a savior for me for years.Anonymous
July 28, 2010
Using a txt editor is a bad idea if you have big data. Even Ultra Edit will fail. Write your own conversion util by mbtowc(winapi)or GNU libiconv. And, for lazy man like me, Just get your self a Gnuwin32 pacvkage and fire out iconv: iconv -f utf-8 -t UTF-16LE YOURFILE.Anonymous
July 29, 2010
Hi, How can i get only Spatial enabled tables in sql server 2008 Thanks and Regard, VenkatAnonymous
July 29, 2010
Hi, How can i get only Spatial enabled tables in sql server 2008 Thanks and Regard, VenkatAnonymous
October 11, 2010
Why not using the import/export tool that comes with SQL Server?, this would be a much more direct approach to the problem of importing all this data.Anonymous
December 28, 2013
Hi Guys, I am getting following error on running Bulk statment Bulk load data conversion error (overflow) for row 8566408, column 15 (population). any idea?