SharePoint and SQL Clustering
What is Clustering?
Clustering In short can be defiled as a technology that automatically allows one physical server to take over the tasks and responsibilities of another physical server that has failed.
As we know we can’t expect all hardware and software to work always, there are always possibilities of their failure. But by having a proper DR solution in place we can ensure that user running mission-critical applications will have little or no downtime when such a failure occurs. Downtime can be very expensive.
The main benefits that clustering provides is the ability to recover from failed server hardware (excluding the shared disk) and failed software, such as failed services or a server lockup. It is not designed to protect data, to protect against a shared disk array from failing, to prevent hack attacks, to protect against network failure, or to prevent SQL Server from other potential disasters, such as power outages or acts of God.
Understanding Downtime
Acceptable uptime percentage |
Downtime per day |
Downtime per month |
Downtime per year |
95 |
72.00 minutes |
36 hours |
18.26 days |
99 (two nines) |
14.40 minutes |
7 hours |
3.65 days |
99.9 (three nines) |
86.40 seconds |
43 minutes |
8.77 hours |
99.99 (four nines) |
8.64 seconds |
4 minutes |
52.60 minutes |
99.999 (five nines) |
0.86 seconds |
26 seconds |
5.26 minutes |
At first we will discuss some theory of the crusting and finally we will configure a active passive SQL cluster with SharePoint.
· SQL clustering and SharePoint
· Infrastructure (Hardware & Software)
· Terminology
· What Are the Types of Clustering?
· Pros and Cons of Clustering
· Mirror or clustering.
· Let’s configure
1. SQL clustering and SharePoint
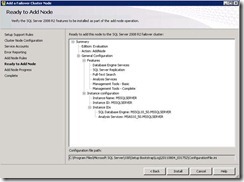
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) and Cumulative Update 2 failover clustering can be used to configure availability within a farm for Microsoft SharePoint Server 2010.
2. Infrastructure (Hardware & Software)
For this example I am using 4 hyper-v machines.
Hardware
· DC (Hyper-v with 2 Gb Ram )
· SPS 2010 (Hyper-v with 4 Gb Ram )
· SQL A (Hyper-v with 2 Gb Ram )
· SQL B (Hyper-v with 2 Gb Ram )
Software
· iSCSI Initiator https://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=18986
· iSCSI Target https://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=19867
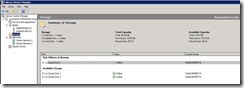
· SQL Server 2008
· SPS 2010
· Windows Sever 2008 R2
3. Terminology
Quorum
The cluster quorum maintains the definitive cluster configuration data and the current state of each node, each Services and Applications group, and each resource and network in the cluster. Furthermore, when each node reads the quorum data, depending on the information retrieved, the node determines if it should remain available, shut down the cluster, or activate any particular Services and Applications groups on the local node. To extend this even further, failover clusters can be configured to use one of four different cluster quorum models and essentially the quorum type chosen for a cluster defines the cluster. For example, a cluster that utilizes the Node and Disk Majority Quorum can be called a Node and Disk Majority cluster.
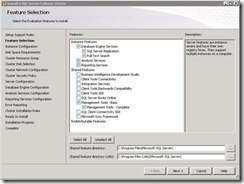
Cluster nodes can monitor the status of resources running on their local system, and can keep track of other nodes in the cluster through private network communication messages called heartbeats. Heartbeats determine the status of a node and send updates of cluster configuration changes to the cluster quorum resource
LUN
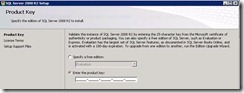
LUN stands for Logical Unit Number. A LUN is used to identify a disk or a disk volume that is presented to a host server or multiple hosts by a shared storage array or a SAN. LUNs provided by shared storage arrays and SANs must meet many requirements before they can be used with failover clusters but when they do, all active nodes in the cluster must have exclusive access to these LUNs.
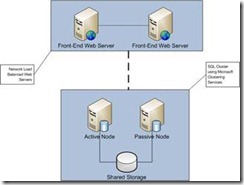
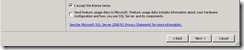
Shared storage.
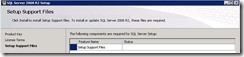
All nodes in the failover cluster must be able to access data on shared storage. The highly available workloads write their data to this shared storage. Therefore, if a node fails, when the resource is restarted on another node, the new node can read the same data from the shared storage that the previous node was accessing. Shared storage can be created with iSCSI, Serial Attached SCSI, or Fibre Channel, provided that it supports persistent reservations.
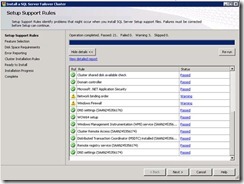
4. Pros and cons of SQL Server Clustering
Pros of SQL Server Clustering
· Reduces downtime to a bare minimum.
· Permits an automatic response to a failed server or software. No human intervention is required.
· It allows you to perform upgrades without forcing users off the system for extended periods of time.
· It allows you to reduce downtime due to routine server, network, or database maintenance.
· Clustering doesn’t require any servers to be renamed. So when failover occurs, it is relatively transparent to end-users.
· Failing back is quick, and can be done whenever the primary server if fixed and put back on-line.
· In some cases, clustering can be used to increase the scalability of an application. For example, if a current cluster is getting too busy, another server could be added to the cluster to expand the resources and help boost the performance of the application.
Cons of Clustering
· More expensive than other failover alternatives, such as log shipping or stand-by servers.
· Requires more set up time than other alternatives.
· Requires more on-going maintenance than other alternatives.
· Requires more experienced DBAs and network administrators.
5. Types of Clustering?
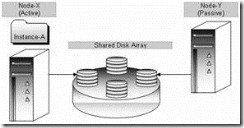
When you decide you want to cluster SQL Server, you have a choice of configuring what is called Active/Active or an Active/Passive cluster. Each has its own pros and cons. Let’s look at each, in the context of a two-node SQL Server cluster.
Active/Active
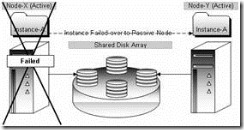
An Active/Active SQL Server cluster means that SQL Server is running on both nodes of a two-way cluster. Each copy of SQL Server acts independently, and users see two different SQL Servers. If one of the SQL Servers in the cluster should fail, then the failed instance of SQL Server will failover to the remaining server. This means that then both instances of SQL Server will be running on one physical server, instead of two.
As you can imagine, if two instances have to run on one physical server, performance can be affected, especially if the server’s have not been sized appropriately.
Active/Passive
An Active/Passive SQL Server cluster refers to a SQL Server cluster where only one instance of SQL Server is running on one of the physical servers in the cluster, and the other physical server does nothing, other than waiting to take over should the primary node should fail.
From a performance perspective, this is the better solution. On the other hand, this option makes less productive use of your physical hardware, which means this solution is more expensive.
Steps to configure.
- At first download ISCSI Target from https://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=19867 on your DC server (you can use any sever except two SQL servers).
- Install ISCSI Target with default settings
3. Now Start Microsoft iSCSI software target
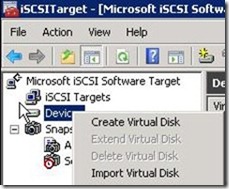
4. We will create new virtual disks.
5. We have to create total three.
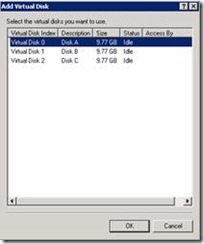
a. Disk-A.vhd (Quorum)
b. Disk-B.vhd (DTC)
c. Disk-C.vhd (Database storage)
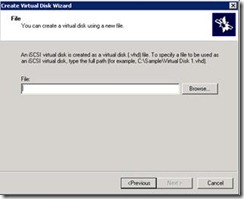
7. Provide a location (c:\data\ Disk-A.vhd). Repeat this three times to create three drives.
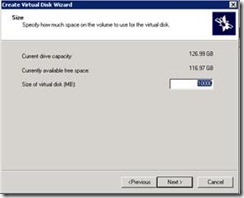
8. Provide space allocation for vhd, for Disk A and A we don’t need much. But disk c wills contain SQL data files to we have provide more.
9. For this lab I have there allocation.
a. Disk-A.vhd (1GB)
b. Disk-B.vhd (1GB)
c. Disk-C.vhd (10 GB)
10. It will ask for a target, at this time you can keep it empty hit next.
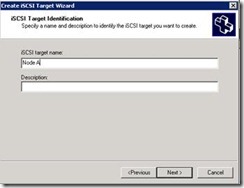
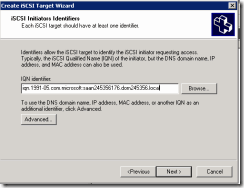
11. Now we have to create two targets as we have two nodes in cluster.
12. Let’s give name as Node A
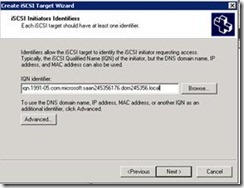
13. When you click next it will ask for iqn identifier
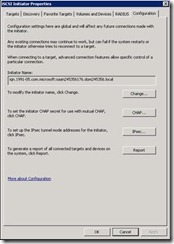
14. To get the IQN identifier login to SQL server A and SQL server B and in administrative programs start iSCSI initiator.
15. Now click on configuration and copy the “initiator Name”.
16. Login back to DC server paste the copied name in IQN identifier.
17. Repeat steps 11-16 and create second ISCSI and name it Node B, this time copy the IQN identifier from SQL server B.
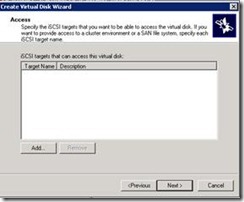
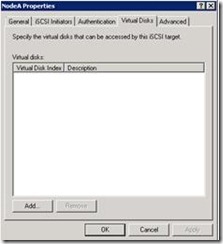
18. Right click on Node A and go to properties > Virtual Disks
19. Click add and select all three vhd which we created recently.
20. Repeat step 18-19 for Node B
21. Now log in to SQL A and from server features add failover clustering feature.
22. Repeat step 21 on SQL B server.
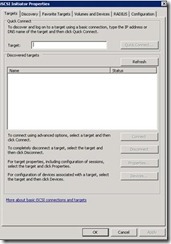
23. Now log on to SQL Server A and open iSCSI. Under target enter FQUD of the machine where we have iSCSI target running. In our case it is DC.
24. Now you have to connect to Node A created in iSCSI Target.
25. Repeat step 23 and 24 on SQL B server.
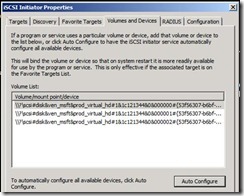
26. On SQL A open iSCSI and click on volumes and Devices Then click on auto configure.
27. You should see something like this.
28. Repeat step 26 on SQL B server.
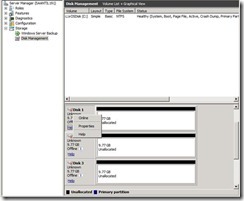
29. On sever SQL A open Disk manager and it will list three disks which you created earlier. Right click on each disk and select Online.
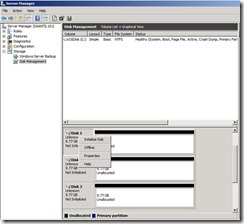
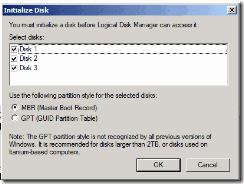
30. Now again right click and select initialize disk.
31. Select all three disk and hit ok.
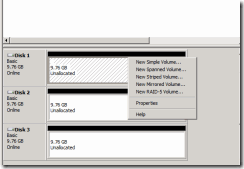
32. Now right click on Disk 1and select new simple volume.
33. Click next
34. Click next.
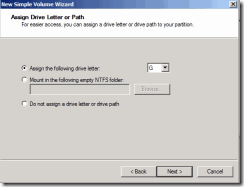
35. Assign a letter and select next.
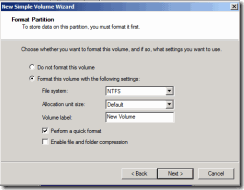
36. Select format option and click next.
37. Hit finish.
38. Repeat step 32 to 37 on Disk 2 and Disk 3.
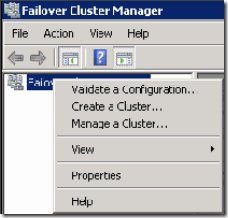
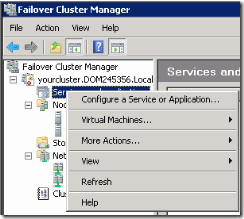
39. Now we will setup windows clustering services. For this login to SQL A go to administrative tools > Failover Cluster Manager
40. Now click create a cluster and click next.
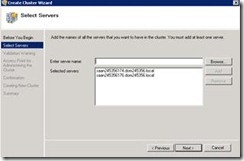
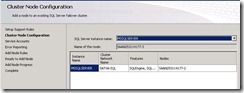
41. Add two SQL servers SQL A and SQL B as a part of cluster.
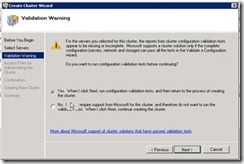
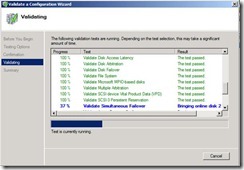
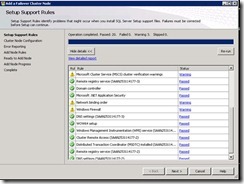
42. At this step select yes. It will run a validation test and update is any issue are there.
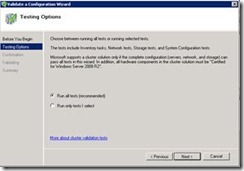
43. Select Run all test.
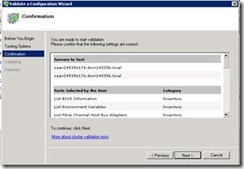
44. It will create a report and if any issue is there in report please fix those issues.
45. At this step validation check will run.
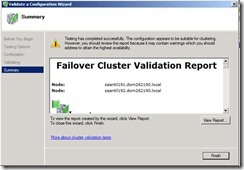
46. It will show report.
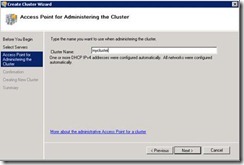
47. Here you can give any name to your cluster.
48. After the configuration is over it will show the two nodes with status “UP”
49. Just click one other option on left side and look for any issues.
50. Now right click on services and applications .
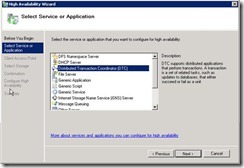
51. Click next
52. Select DTC .
53. Enter some name for DTC
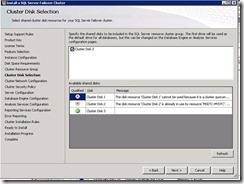
54. Select Cluster disk 2
55. Finally you will see DTC online
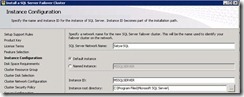
56. Now we have to start the SQL server installation. We will start from SQL A and we will select “New sql server failover cluster installation”
57. It’s a normal sql server installation stage, once its done Just click next.
58. Enter you key
59. Accept License.
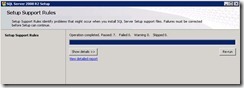
60. It will install setup support files.
61. Now it will run rules and show as if any issues are there.
62. Select the components you want to install.
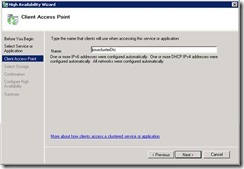
63. Here you have to specify the network name of the sql server. I have specified Satya-SQL
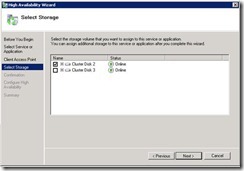
64. We have to select the drive where we want to store our databases.
a. We used Disk1 for quorum.
b. We used Disk2 for DTC
c. Disk3 will be used to store databases.
So select Disk3
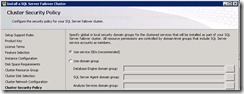
65. Select use services SIDs
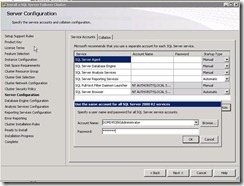
66. Provide credentials.
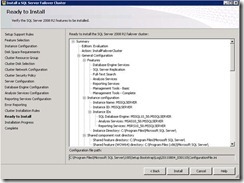
67. It will show all setting which we specified. Click install and it will install first node of the SQL cluster on SQL A
68. Now move to SQL B and select add node to a sql server failover cluster.
69. Again it will run support rules.
70. Select the serve instance name.
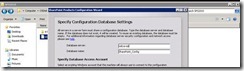
71. Now click on configuration .
72. Now when run Psconfig wizard on sharepoint server specify network name of the sql server. In our case it is Satya-sql.
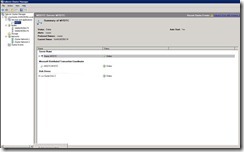
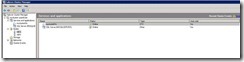
73. When I click on SQL A it shows that it is holding two resources.
74. But when I click on SQL B it shows nothing. That mean he is available but in passive mode.
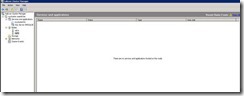
75. To test the automatic failover I just switch off my SQL A. Now SQL B will take over the resource.
76. Now as you can see my SQL B server is the owner of resources.
Comments
Anonymous
January 01, 2003
شات دردشةشات صوتي دردشة صوتية سعودي لولسعودي انحراف سعودي كول شات سعودي دردشة سعودية شات سعودي لولدردشة سعودي لول سعودي لول شات سعودي لولدردشة سعودي لول سعودي لول شات سعودي لولدردشة سعودي لول لول شات لول شات سعودي دردشة سعوديةدردشة لول سعودي كول شات سعودي كولدردشة سعودي كولسعودي انحراف شات سعودي انحراف دردشة سعودي انحراف شات انحرافدردشة انحراف انحراف سعودي كام شات سعودي كامدردشة سعودي كام شات كام شات سعودياتشات صوتي دردشة صوتية صدى قلبي #Anonymous
December 12, 2013
Although i would agree that SharePoint defiles SQL, i think the word you are looking for in that first sentence is define.Anonymous
May 11, 2015
The comment has been removedAnonymous
May 11, 2015
The comment has been removedAnonymous
May 25, 2015
The comment has been removedAnonymous
May 25, 2015
http://www.khaberfalastine.tk/">تحميل برنامجAnonymous
May 25, 2015
http://www.khaberfalastine.tk/2015/05/download-program-ears.html">تحميل برنامج الاذانAnonymous
May 25, 2015
http://www.khaberfalastine.tk/2015/05/matches-role-16-league-champions-asia.html">مباريات دور 16 في دوري ابطال اسياAnonymous
May 25, 2015
http://www.khaberfalastine.tk/2015/05/fish.html">title="<الطريقة الصحيحة لقلي السمك>"Anonymous
October 20, 2015
http://www.gamesyoum7.com/ العابAnonymous
October 28, 2015
شكرا لك موضوع جميل وشرح مميز مع تحيات شات بنات الضفة http://bnat-west.com/Anonymous
October 28, 2015
http://bnat-west.com/ title="بنات الضفة">شاتAnonymous
October 28, 2015
The comment has been removedAnonymous
October 28, 2015
http://bnat-west.com/vb/ title="بنات الضفة">منتدياتAnonymous
October 28, 2015
http://bnat-west.com/">
بنات الضفة thnx manAnonymous
October 28, 2015
The comment has been removedAnonymous
October 28, 2015
http://www.bnat-west.com/vb/forumdisplay.php?f=192">
http://www.bnat-west.com/vb/forumdisplay.php?f=185">
http://www.bnat-west.com/vb/forumdisplay.php?f=7">Anonymous
October 28, 2015
i like it .. nice nice good man
http://www.bnat-west.com/chat-bnat-tulkarm.html شات بنات طولكرمAnonymous
December 03, 2015
ادخل هنا واتعرف على بنات مصر
http://mostafaelgamal.blogspot.com.eg/Anonymous
April 25, 2016
ادخل هنا وانتا تعرف
http://www.egypetroleum.com/