Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In SQL Server 2005, 2008 and 2008 R2 Database Mirroring works at the individual database level. One challenge to using database mirroring is to keep your important SQL Agent jobs enabled or disabled depending on a database's current mirroring role. If a database is acting as a Principal, you will want the SQL Agent jobs associated with that database to be enabled, while if it is acting as a Mirror, you will want to disable the SQL Agent jobs associated with that database. This does not happen automatically without a little bit of preparation.
Any SQL Agent job that tries to access a database while it is acting as a Mirror will fail. It is a common best practice to script out database specific SQL Agent jobs from the instance where your databases normally run in the Principal role, and then create the same jobs on the instance where your databases are mirrored to, keeping them disabled until they are needed. If you have a planned or unplanned database mirroring failover you should consider having an automated method of enabling the Agent jobs on the Principal side of the mirror and disabling the Agent jobs on the Mirror side of the mirror.
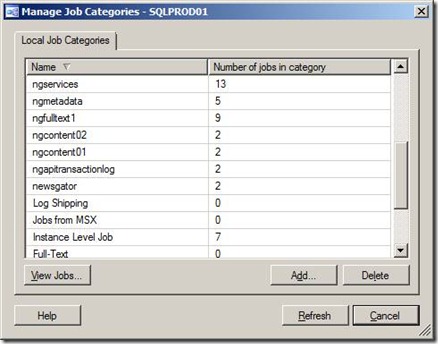
One way to help facilitate this is to add your own custom job categories for SQL Agent Jobs, so you can group SQL Agent jobs by database. SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) has a GUI that lets you add or delete job categories. You can get to this by right-clicking on "Jobs" under SQL Server Agent, and selecting "Manage Job Categories".
For this article, a customer environment is used. That customer is NewsGator (www.newsgator.com).
Information about SQL Agent jobs is stored in the msdb system database. Inside of the msdb database, you will find job information in the sysjobs table and category information in the syscategories table. You can look at your current job and category information with this query:
-- Get Agent jobs and Category information
SELECT sj.name AS [JobName], [enabled], sj.category_id,
sc.name AS [CategoryName]
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs AS sj
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.syscategories AS sc
ON sj.category_id = sc.category_id
ORDER BY sj.name;
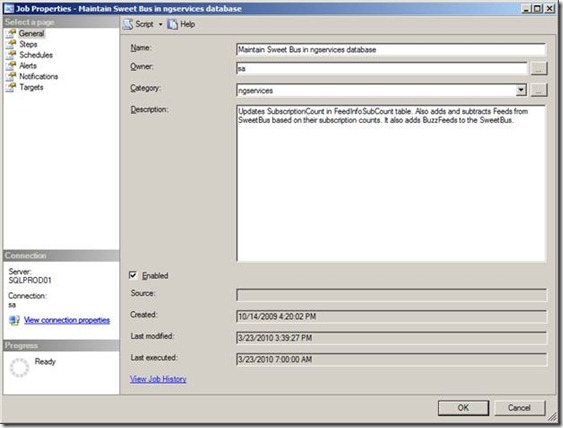
It is a best practice to create a custom Job Category that has the same name as each user database that is mirrored. You should also create a Job Category called "Instance Level Job" for any Agent jobs that are not database specific. After you have created the new Job Categories, you need to assign each Agent job to the correct category. You can do this by right-clicking on a job and selecting "Properties". You can select the correct category in the Categories combo-box. You will want assign each database specific Agent job to the correct category. Don't forget user database backup jobs (both full and transaction log), because even though they operate in the context of the master database, they will fail if they are run against a database that is in the mirror role.
Another best practice is to create a database called ServerMonitor on each SQL Server instance. This is a database that can be used to run things like instance level DMV queries. This database is not mirrored by design, since we want a database that will always be available on the instance, regardless of the mirroring role status of the other user databases.
Add a stored procedure to the ServerMonitor database called DBAdminCheckMirroringStatus. This stored procedure checks the mirroring_role for each mirrored database, and then calls another stored procedure called DBAdminChangeJobStatus that either enables or disables the SQL Agent jobs that are assigned to that databases job category. Then have another SQL Agent job run this DBAdminCheckMirroringStatus stored procedure every minute (or less often, depending on your business requirements). This will take care of keeping your SQL Agent jobs enabled on the Principal side of the mirror as needed. The important thing to remember is that these stored procedure need to be run on both servers. It is equally important to turn on the jobs on the new principal when the failover occurs as well as turn off all the jobs on the original principal.
USE [ServerMonitor]
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
GO
/* DBAdminChangeJobStatus =============================================================================
Description : Change Agent job status for all jobs in a Category
Used By: Only used to monitor the database instance
Last Modified Developer Description
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
===========================================================================*/
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[DBAdminChangeJobStatus]
(@CategoryID int,
@CurrentEnabledValue tinyint,
@NewEnabledValue tinyint)
AS
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @JobName nvarchar(128);
-- Declare cursor
DECLARE curJobNameList CURSOR
FAST_FORWARD
FOR
SELECT [name]
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs
WHERE category_id = @CategoryID
AND [enabled] = @CurrentEnabledValue;
OPEN curJobNameList;
FETCH NEXT
FROM curJobNameList
INTO @JobName;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_name = @JobName, @enabled = @NewEnabledValue;
FETCH NEXT
FROM curJobNameList
INTO @JobName;
END
CLOSE curJobNameList;
DEALLOCATE curJobNameList;
RETURN;
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS OFF
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
GO
/* DBAdminCheckMirroringStatus ==========================================================================
Description : Get database mirroring status for all mirrored databases and change Agent job status if needed
Used By: Only used to monitor the database instance
Last Modified Developer Description
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
=============================================================================
*/
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[DBAdminCheckMirroringStatus]
AS
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @DatabaseName nvarchar(128);
DECLARE @MirroringRole tinyint = 0;
DECLARE @CategoryID int = 0;
DECLARE curDatabaseNameList CURSOR
FAST_FORWARD
FOR
-- Get list of all mirrored databases
SELECT DB_NAME(database_id) AS [DatabaseName]
FROM sys.database_mirroring
WHERE database_id > 4
AND NOT mirroring_role IS NULL;
OPEN curDatabaseNameList;
FETCH NEXT
FROM curDatabaseNameList
INTO @DatabaseName;
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Get the CategoryID for the CategoryName that matches the DatabaseName
SET @CategoryID = (SELECT TOP(1) sj.category_id
FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs AS sj
INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.syscategories AS sc
ON sj.category_id = sc.category_id
WHERE sc.name = @DatabaseName
ORDER BY sj.category_id);
IF @CategoryID > 0
BEGIN
-- Get mirroring role for database
SET @MirroringRole =
(SELECT mirroring_role
FROM sys.database_mirroring
WHERE DB_NAME(database_id) =
@DatabaseName);
IF @MirroringRole = 1 -- Principal
BEGIN
-- Enable all jobs in this Category that are disabled
EXEC dbo.DBAdminChangeJobStatus
@CategoryID, 0, 1;
END
IF @MirroringRole = 2 -- Mirror
BEGIN
-- Disable all jobs in this Category that are enabled
EXEC dbo.DBAdminChangeJobStatus
@CategoryID, 1, 0;
END
END
SET @CategoryID = 0;
FETCH NEXT
FROM curDatabaseNameList
INTO @DatabaseName;
END
CLOSE curDatabaseNameList;
DEALLOCATE curDatabaseNameList;
RETURN;
GO
AUTHORS: Glenn Berry, Newsgator; Kevin Cox SQLCAT
Reviewers: Kun Cheng
Comments
Anonymous
December 15, 2010
Another approach worth considering: keep all jobs always enabled both on Mirror and Principal - this way switching will require less steps: Add new step to each job as a very first step: check if database is currently in mirror mode (I don't recall exactly how this is done but I saw a fairly simple query in MSDN forums). If it is - quit the job, otherwise continue to the next step.Anonymous
September 13, 2011
Suprise, you guys come to the rescue again.Anonymous
October 06, 2011
I beleive that this is not correct: "Any SQL Agent job that tries to access a database while it is acting as a Mirror will fail". If you create a job and set the database to the database which is mirrored (primary), and then the primary fails to the mirror, the job on the original primary server will still access the database now at the mirror. So the jobs are mirror aware. Jobs are not mirror aware if you simply reference the database in your SQL from another DB. JeffAnonymous
October 18, 2016
The comment has been removed