Events
Power BI DataViz World Championships
Feb 14, 4 PM - Mar 31, 4 PM
With 4 chances to enter, you could win a conference package and make it to the LIVE Grand Finale in Las Vegas
Learn moreThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
By Mitch Denny
ASP.NET Core 8.0 introduces support for .NET native ahead-of-time (AOT).
For Blazor WebAssembly Native AOT guidance, which adds to or supersedes the guidance in this article, see ASP.NET Core Blazor WebAssembly build tools and ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation.
Publishing and deploying a Native AOT app provides the following benefits:
The template app was run in our benchmarking lab to compare performance of an AOT published app, a trimmed runtime app, and an untrimmed runtime app. The following chart shows the results of the benchmarking:
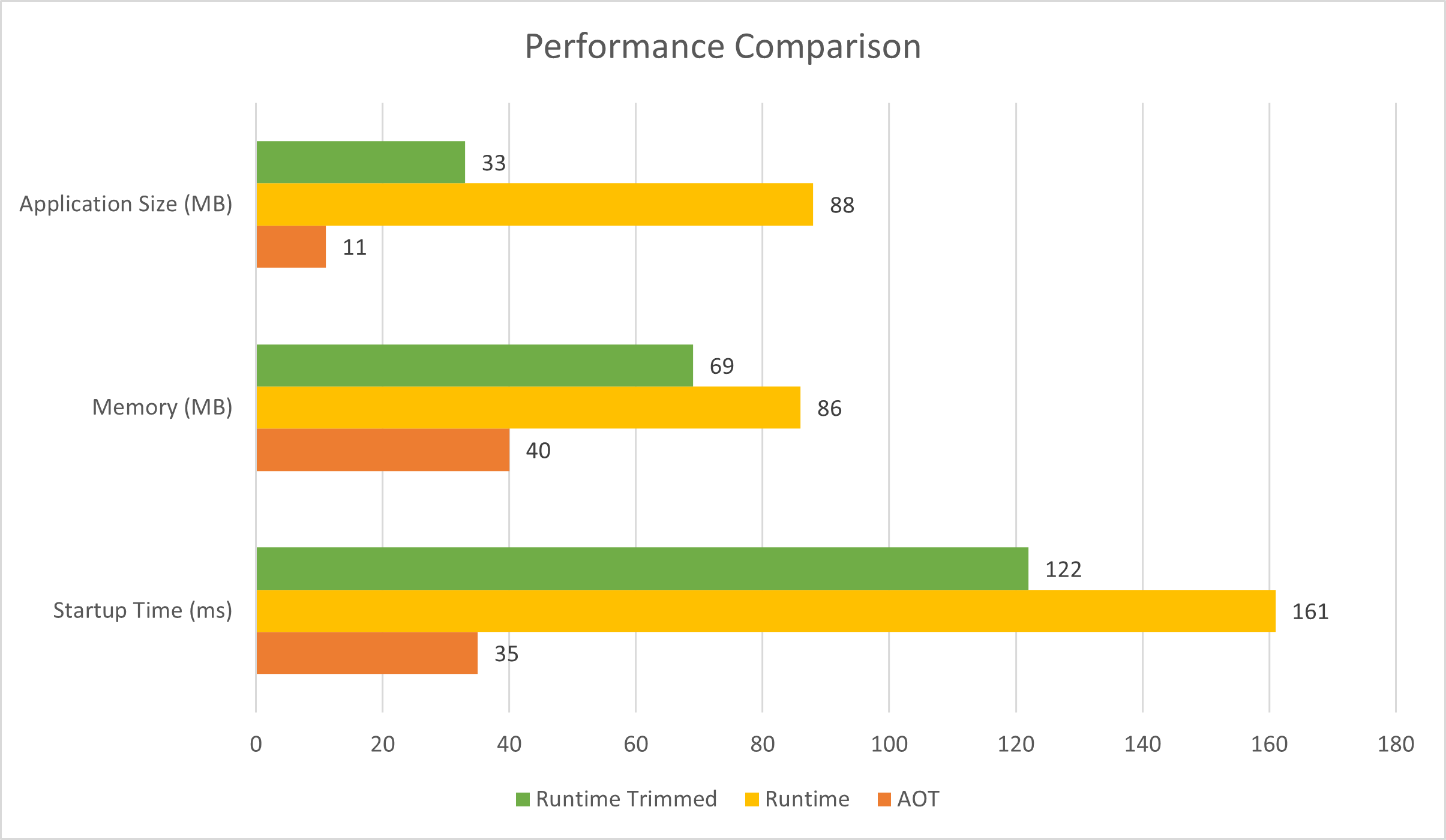
The preceding chart shows that Native AOT has lower app size, memory usage, and startup time.
Not all features in ASP.NET Core are currently compatible with Native AOT. The following table summarizes ASP.NET Core feature compatibility with Native AOT:
| Feature | Fully Supported | Partially Supported | Not Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| gRPC | Fully supported | ||
| Minimal APIs | Partially supported | ||
| MVC | Not supported | ||
| Blazor Server | Not supported | ||
| SignalR | Partially supported | ||
| JWT Authentication | Fully supported | ||
| Other Authentication | Not supported | ||
| CORS | Fully supported | ||
| HealthChecks | Fully supported | ||
| HttpLogging | Fully supported | ||
| Localization | Fully supported | ||
| OutputCaching | Fully supported | ||
| RateLimiting | Fully supported | ||
| RequestDecompression | Fully supported | ||
| ResponseCaching | Fully supported | ||
| ResponseCompression | Fully supported | ||
| Rewrite | Fully supported | ||
| Session | Not supported | ||
| Spa | Not supported | ||
| StaticFiles | Fully supported | ||
| WebSockets | Fully supported |
For more information on limitations, see:
It's important to test an app thoroughly when moving to a Native AOT deployment model. The AOT deployed app should be tested to verify functionality hasn't changed from the untrimmed and JIT-compiled app. When building the app, review and correct AOT warnings. An app that issues AOT warnings during publishing may not work correctly. If no AOT warnings are issued at publish time, the published AOT app should work the same as the untrimmed and JIT-compiled app.
Native AOT is enabled with the PublishAot MSBuild property. The following example shows how to enable Native AOT in a project file:
<PropertyGroup>
<PublishAot>true</PublishAot>
</PropertyGroup>
This setting enables Native AOT compilation during publish and enables dynamic code usage analysis during build and editing. A project that uses Native AOT publishing uses JIT compilation when running locally. An AOT app has the following differences from a JIT-compiled app:
Native AOT analysis includes all of the app's code and the libraries the app depends on. Review Native AOT warnings and take corrective steps. It's a good idea to publish apps frequently to discover issues early in the development lifecycle.
In .NET 8, Native AOT is supported by the following ASP.NET Core app types:
The ASP.NET Core Web API (Native AOT) template (short name webapiaot) creates a project with AOT enabled. The template differs from the Web API project template in the following ways:
.http file configured with sample HTTP requests that can be sent to the app's endpoints.Todo API instead of the weather forecast sample.PublishAot to the project file, as shown earlier in this article.The following example shows the code added to the Program.cs file to support JSON serialization source generation:
using MyFirstAotWebApi;
+using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
-var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder();
+var builder = WebApplication.CreateSlimBuilder(args);
+builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
+{
+ options.SerializerOptions.TypeInfoResolverChain.Insert(0, AppJsonSerializerContext.Default);
+});
var app = builder.Build();
var sampleTodos = TodoGenerator.GenerateTodos().ToArray();
var todosApi = app.MapGroup("/todos");
todosApi.MapGet("/", () => sampleTodos);
todosApi.MapGet("/{id}", (int id) =>
sampleTodos.FirstOrDefault(a => a.Id == id) is { } todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound());
app.Run();
+[JsonSerializable(typeof(Todo[]))]
+internal partial class AppJsonSerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext
+{
+
+}
Without this added code, System.Text.Json uses reflection to serialize and deserialize JSON. Reflection isn't supported in Native AOT.
For more information, see:
The launchSettings.json file created by the Web API (Native AOT) template has the iisSettings section and IIS Express profile removed:
{
"$schema": "http://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.json",
- "iisSettings": {
- "windowsAuthentication": false,
- "anonymousAuthentication": true,
- "iisExpress": {
- "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:11152",
- "sslPort": 0
- }
- },
"profiles": {
"http": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"launchUrl": "todos",
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5102",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
- "IIS Express": {
- "commandName": "IISExpress",
- "launchBrowser": true,
- "launchUrl": "todos",
- "environmentVariables": {
- "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
- }
- }
}
}
The template uses the CreateSlimBuilder() method instead of the CreateBuilder() method.
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using MyFirstAotWebApi;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateSlimBuilder(args);
builder.Logging.AddConsole();
builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.SerializerOptions.TypeInfoResolverChain.Insert(0, AppJsonSerializerContext.Default);
});
var app = builder.Build();
var sampleTodos = TodoGenerator.GenerateTodos().ToArray();
var todosApi = app.MapGroup("/todos");
todosApi.MapGet("/", () => sampleTodos);
todosApi.MapGet("/{id}", (int id) =>
sampleTodos.FirstOrDefault(a => a.Id == id) is { } todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound());
app.Run();
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Todo[]))]
internal partial class AppJsonSerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext
{
}
The CreateSlimBuilder method initializes the WebApplicationBuilder with the minimum ASP.NET Core features necessary to run an app.
As noted earlier, the CreateSlimBuilder method doesn't include support for HTTPS or HTTP/3. These protocols typically aren't required for apps that run behind a TLS termination proxy. For example, see TLS termination and end to end TLS with Application Gateway. HTTPS can be enabled by calling
builder.WebHost.UseKestrelHttpsConfiguration HTTP/3 can be enabled by calling builder.WebHost.UseQuic.
The CreateSlimBuilder method doesn't support the following features that are supported by the CreateBuilder method:
The CreateSlimBuilder method includes the following features needed for an efficient development experience:
appsettings.json and appsettings.{EnvironmentName}.json.For a builder that omits the preceding features, see The CreateEmptyBuilder method.
Including minimal features has benefits for trimming as well as AOT. For more information, see Trim self-contained deployments and executables.
For more detailed information, see Comparing WebApplication.CreateBuilder to CreateSlimBuilder
Because unused code is trimmed during publishing for Native AOT, the app can't use unbounded reflection at runtime. Source generators are used to produce code that avoids the need for reflection. In some cases, source generators produce code optimized for AOT even when a generator isn't required.
To view the source code that is generated, add the EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles property to an app's .csproj file, as shown in the following example:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<!-- Other properties omitted for brevity -->
<EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>true</EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
Run the dotnet build command to see the generated code. The output includes an obj/Debug/net8.0/generated/ directory that contains all the generated files for the project.
The dotnet publish command also compiles the source files and generates files that are compiled. In addition, dotnet publish passes the generated assemblies to a native IL compiler. The IL compiler produces the native executable. The native executable contains the native machine code.
Many of the popular libraries used in ASP.NET Core projects currently have some compatibility issues when used in a project targeting Native AOT, such as:
Libraries using these dynamic features need to be updated in order to work with Native AOT. They can be updated using tools like Roslyn source generators.
Library authors hoping to support Native AOT are encouraged to:
The Minimal API framework is optimized for receiving and returning JSON payloads using System.Text.Json. System.Text.Json:
System.Text.Json source generator.All types that are transmitted as part of the HTTP body or returned from request delegates in Minimal APIs apps must be configured on a JsonSerializerContext that is registered via ASP.NET Core’s dependency injection:
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using MyFirstAotWebApi;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateSlimBuilder(args);
builder.Logging.AddConsole();
builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.SerializerOptions.TypeInfoResolverChain.Insert(0, AppJsonSerializerContext.Default);
});
var app = builder.Build();
var sampleTodos = TodoGenerator.GenerateTodos().ToArray();
var todosApi = app.MapGroup("/todos");
todosApi.MapGet("/", () => sampleTodos);
todosApi.MapGet("/{id}", (int id) =>
sampleTodos.FirstOrDefault(a => a.Id == id) is { } todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound());
app.Run();
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Todo[]))]
internal partial class AppJsonSerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext
{
}
In the preceding highlighted code:
JsonSerializerContext is annotated with the [JsonSerializable] attribute to enable source generated JSON serializer code for the ToDo type.A parameter on the delegate that isn't bound to the body and does not need to be serializable. For example, a query string parameter that is a rich object type and implements IParsable<T>.
public class Todo
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string? Title { get; set; }
public DateOnly? DueBy { get; set; }
public bool IsComplete { get; set; }
}
static class TodoGenerator
{
private static readonly (string[] Prefixes, string[] Suffixes)[] _parts = new[]
{
(new[] { "Walk the", "Feed the" }, new[] { "dog", "cat", "goat" }),
(new[] { "Do the", "Put away the" }, new[] { "groceries", "dishes", "laundry" }),
(new[] { "Clean the" }, new[] { "bathroom", "pool", "blinds", "car" })
};
// Remaining code omitted for brevity.
See this GitHub issue to report or review issues with Native AOT support in ASP.NET Core.
WebApplication.CreateBuilder to CreateSlimBuilder[LogProperties] and the new telemetry logging source generatorASP.NET Core 8.0 introduces support for .NET native ahead-of-time (AOT).
Publishing and deploying a Native AOT app provides the following benefits:
The template app was run in our benchmarking lab to compare performance of an AOT published app, a trimmed runtime app, and an untrimmed runtime app. The following chart shows the results of the benchmarking:

The preceding chart shows that Native AOT has lower app size, memory usage, and startup time.
Not all features in ASP.NET Core are currently compatible with Native AOT. The following table summarizes ASP.NET Core feature compatibility with Native AOT:
| Feature | Fully Supported | Partially Supported | Not Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| gRPC | Fully supported | ||
| Minimal APIs | Partially supported | ||
| MVC | Not supported | ||
| Blazor Server | Not supported | ||
| SignalR | Not supported | ||
| JWT Authentication | Fully supported | ||
| Other Authentication | Not supported | ||
| CORS | Fully supported | ||
| HealthChecks | Fully supported | ||
| HttpLogging | Fully supported | ||
| Localization | Fully supported | ||
| OutputCaching | Fully supported | ||
| RateLimiting | Fully supported | ||
| RequestDecompression | Fully supported | ||
| ResponseCaching | Fully supported | ||
| ResponseCompression | Fully supported | ||
| Rewrite | Fully supported | ||
| Session | Not supported | ||
| Spa | Not supported | ||
| StaticFiles | Fully supported | ||
| WebSockets | Fully supported |
For more information on limitations, see:
It's important to test an app thoroughly when moving to a Native AOT deployment model. The AOT deployed app should be tested to verify functionality hasn't changed from the untrimmed and JIT-compiled app. When building the app, review and correct AOT warnings. An app that issues AOT warnings during publishing may not work correctly. If no AOT warnings are issued at publish time, the published AOT app should work the same as the untrimmed and JIT-compiled app.
Native AOT is enabled with the PublishAot MSBuild property. The following example shows how to enable Native AOT in a project file:
<PropertyGroup>
<PublishAot>true</PublishAot>
</PropertyGroup>
This setting enables Native AOT compilation during publish and enables dynamic code usage analysis during build and editing. A project that uses Native AOT publishing uses JIT compilation when running locally. An AOT app has the following differences from a JIT-compiled app:
Native AOT analysis includes all of the app's code and the libraries the app depends on. Review Native AOT warnings and take corrective steps. It's a good idea to publish apps frequently to discover issues early in the development lifecycle.
In .NET 8, Native AOT is supported by the following ASP.NET Core app types:
The ASP.NET Core Web API (Native AOT) template (short name webapiaot) creates a project with AOT enabled. The template differs from the Web API project template in the following ways:
.http file configured with sample HTTP requests that can be sent to the app's endpoints.Todo API instead of the weather forecast sample.PublishAot to the project file, as shown earlier in this article.The following example shows the code added to the Program.cs file to support JSON serialization source generation:
using MyFirstAotWebApi;
+using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
-var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder();
+var builder = WebApplication.CreateSlimBuilder(args);
+builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
+{
+ options.SerializerOptions.TypeInfoResolverChain.Insert(0, AppJsonSerializerContext.Default);
+});
var app = builder.Build();
var sampleTodos = TodoGenerator.GenerateTodos().ToArray();
var todosApi = app.MapGroup("/todos");
todosApi.MapGet("/", () => sampleTodos);
todosApi.MapGet("/{id}", (int id) =>
sampleTodos.FirstOrDefault(a => a.Id == id) is { } todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound());
app.Run();
+[JsonSerializable(typeof(Todo[]))]
+internal partial class AppJsonSerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext
+{
+
+}
Without this added code, System.Text.Json uses reflection to serialize and deserialize JSON. Reflection isn't supported in Native AOT.
For more information, see:
The launchSettings.json file created by the Web API (Native AOT) template has the iisSettings section and IIS Express profile removed:
{
"$schema": "http://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.json",
- "iisSettings": {
- "windowsAuthentication": false,
- "anonymousAuthentication": true,
- "iisExpress": {
- "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:11152",
- "sslPort": 0
- }
- },
"profiles": {
"http": {
"commandName": "Project",
"dotnetRunMessages": true,
"launchBrowser": true,
"launchUrl": "todos",
"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5102",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
},
- "IIS Express": {
- "commandName": "IISExpress",
- "launchBrowser": true,
- "launchUrl": "todos",
- "environmentVariables": {
- "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
- }
- }
}
}
The template uses the CreateSlimBuilder() method instead of the CreateBuilder() method.
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using MyFirstAotWebApi;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateSlimBuilder(args);
builder.Logging.AddConsole();
builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.SerializerOptions.TypeInfoResolverChain.Insert(0, AppJsonSerializerContext.Default);
});
var app = builder.Build();
var sampleTodos = TodoGenerator.GenerateTodos().ToArray();
var todosApi = app.MapGroup("/todos");
todosApi.MapGet("/", () => sampleTodos);
todosApi.MapGet("/{id}", (int id) =>
sampleTodos.FirstOrDefault(a => a.Id == id) is { } todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound());
app.Run();
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Todo[]))]
internal partial class AppJsonSerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext
{
}
The CreateSlimBuilder method initializes the WebApplicationBuilder with the minimum ASP.NET Core features necessary to run an app.
As noted earlier, the CreateSlimBuilder method doesn't include support for HTTPS or HTTP/3. These protocols typically aren't required for apps that run behind a TLS termination proxy. For example, see TLS termination and end to end TLS with Application Gateway. HTTPS can be enabled by calling builder.WebHost.UseKestrelHttpsConfiguration HTTP/3 can be enabled by calling builder.WebHost.UseQuic.
The CreateSlimBuilder method doesn't support the following features that are supported by the CreateBuilder method:
The CreateSlimBuilder method includes the following features needed for an efficient development experience:
appsettings.json and appsettings.{EnvironmentName}.json.For a builder that omits the preceding features, see The CreateEmptyBuilder method.
Including minimal features has benefits for trimming as well as AOT. For more information, see Trim self-contained deployments and executables.
For more detailed information, see Comparing WebApplication.CreateBuilder to CreateSlimBuilder
Because unused code is trimmed during publishing for Native AOT, the app can't use unbounded reflection at runtime. Source generators are used to produce code that avoids the need for reflection. In some cases, source generators produce code optimized for AOT even when a generator isn't required.
To view the source code that is generated, add the EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles property to an app's .csproj file, as shown in the following example:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<!-- Other properties omitted for brevity -->
<EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>true</EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>
Run the dotnet build command to see the generated code. The output includes an obj/Debug/net8.0/generated/ directory that contains all the generated files for the project.
The dotnet publish command also compiles the source files and generates files that are compiled. In addition, dotnet publish passes the generated assemblies to a native IL compiler. The IL compiler produces the native executable. The native executable contains the native machine code.
Many of the popular libraries used in ASP.NET Core projects currently have some compatibility issues when used in a project targeting Native AOT, such as:
Libraries using these dynamic features need to be updated in order to work with Native AOT. They can be updated using tools like Roslyn source generators.
Library authors hoping to support Native AOT are encouraged to:
The Minimal API framework is optimized for receiving and returning JSON payloads using System.Text.Json. System.Text.Json:
System.Text.Json source generator.All types that are transmitted as part of the HTTP body or returned from request delegates in Minimal APIs apps must be configured on a JsonSerializerContext that is registered via ASP.NET Core’s dependency injection:
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using MyFirstAotWebApi;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateSlimBuilder(args);
builder.Logging.AddConsole();
builder.Services.ConfigureHttpJsonOptions(options =>
{
options.SerializerOptions.TypeInfoResolverChain.Insert(0, AppJsonSerializerContext.Default);
});
var app = builder.Build();
var sampleTodos = TodoGenerator.GenerateTodos().ToArray();
var todosApi = app.MapGroup("/todos");
todosApi.MapGet("/", () => sampleTodos);
todosApi.MapGet("/{id}", (int id) =>
sampleTodos.FirstOrDefault(a => a.Id == id) is { } todo
? Results.Ok(todo)
: Results.NotFound());
app.Run();
[JsonSerializable(typeof(Todo[]))]
internal partial class AppJsonSerializerContext : JsonSerializerContext
{
}
In the preceding highlighted code:
JsonSerializerContext is annotated with the [JsonSerializable] attribute to enable source generated JSON serializer code for the ToDo type.A parameter on the delegate that isn't bound to the body and does not need to be serializable. For example, a query string parameter that is a rich object type and implements IParsable<T>.
public class Todo
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string? Title { get; set; }
public DateOnly? DueBy { get; set; }
public bool IsComplete { get; set; }
}
static class TodoGenerator
{
private static readonly (string[] Prefixes, string[] Suffixes)[] _parts = new[]
{
(new[] { "Walk the", "Feed the" }, new[] { "dog", "cat", "goat" }),
(new[] { "Do the", "Put away the" }, new[] { "groceries", "dishes", "laundry" }),
(new[] { "Clean the" }, new[] { "bathroom", "pool", "blinds", "car" })
};
// Remaining code omitted for brevity.
See this GitHub issue to report or review issues with Native AOT support in ASP.NET Core.
WebApplication.CreateBuilder to CreateSlimBuilder[LogProperties] and the new telemetry logging source generatorASP.NET Core feedback
ASP.NET Core is an open source project. Select a link to provide feedback:
Events
Power BI DataViz World Championships
Feb 14, 4 PM - Mar 31, 4 PM
With 4 chances to enter, you could win a conference package and make it to the LIVE Grand Finale in Las Vegas
Learn moreTraining
Learning path
Create cloud-native apps and services with .NET and ASP.NET Core - Training
Create independently deployable, highly scalable, and resilient apps and services using the free and open-source .NET platform. With .NET you can use popular microservice technology like Docker, Kubernetes, Dapr, Azure Container Registry, and more for .NET and ASP.NET Core applications and services.