Create a web API with ASP.NET Core and MongoDB
Note
This isn't the latest version of this article. For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
Warning
This version of ASP.NET Core is no longer supported. For more information, see the .NET and .NET Core Support Policy. For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
Important
This information relates to a pre-release product that may be substantially modified before it's commercially released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
By Pratik Khandelwal and Scott Addie
This tutorial creates a web API that runs Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations on a MongoDB NoSQL database.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure MongoDB
- Create a MongoDB database
- Define a MongoDB collection and schema
- Perform MongoDB CRUD operations from a web API
- Customize JSON serialization
Prerequisites
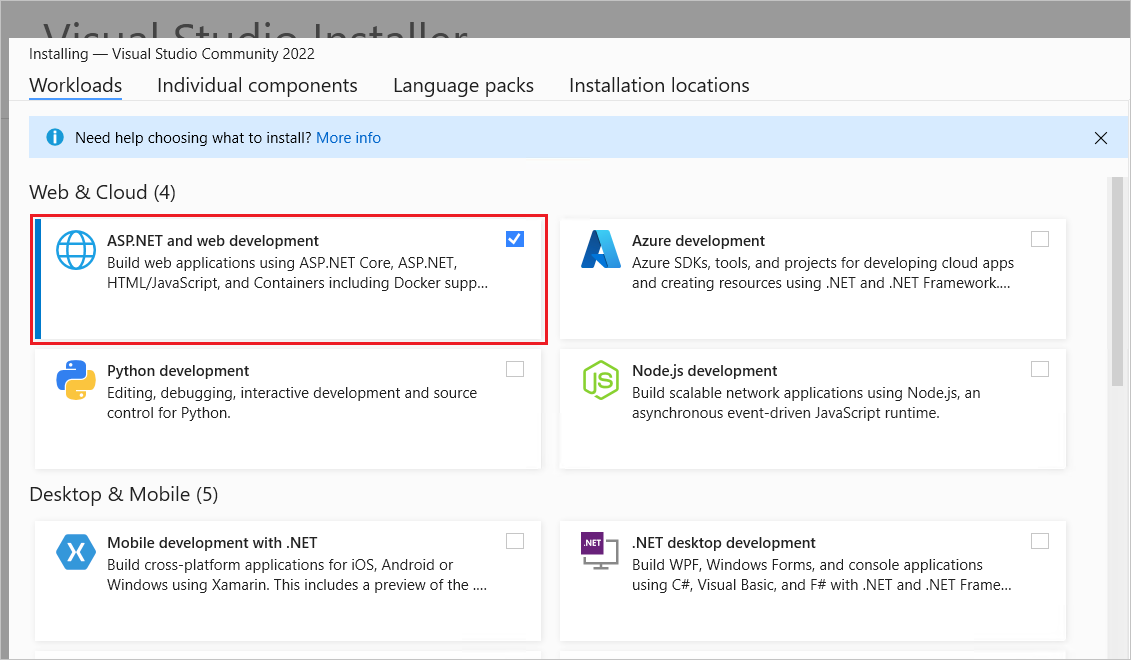
Visual Studio 2022 with the ASP.NET and web development workload.
Configure MongoDB
Enable MongoDB and MongoDB Shell access from anywhere on the development machine (Windows/Linux/macOS):
Download and Install MongoDB Shell:
- macOS/Linux: Choose a directory to extract the MongoDB Shell to. Add the resulting path for
mongoshto thePATHenvironment variable. - Windows: MongoDB Shell (mongosh.exe) is installed at C:\Users<user>\AppData\Local\Programs\mongosh. Add the resulting path for
mongosh.exeto thePATHenvironment variable.
- macOS/Linux: Choose a directory to extract the MongoDB Shell to. Add the resulting path for
Download and Install MongoDB:
- macOS/Linux: Verify the directory that MongoDB was installed at, usually in /usr/local/mongodb. Add the resulting path for
mongodbto thePATHenvironment variable. - Windows: MongoDB is installed at C:\Program Files\MongoDB by default. Add C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\<version_number>\bin to the
PATHenvironment variable.
- macOS/Linux: Verify the directory that MongoDB was installed at, usually in /usr/local/mongodb. Add the resulting path for
Choose a Data Storage Directory: Select a directory on your development machine for storing data. Create the directory if it doesn't exist. The MongoDB Shell doesn't create new directories:
- macOS/Linux: For example,
/usr/local/var/mongodb. - Windows: For example,
C:\\BooksData.
- macOS/Linux: For example,
In the OS command shell (not the MongoDB Shell), use the following command to connect to MongoDB on default port 27017. Replace
<data_directory_path>with the directory chosen in the previous step.mongod --dbpath <data_directory_path>
Use the previously installed MongoDB Shell in the following steps to create a database, make collections, and store documents. For more information on MongoDB Shell commands, see mongosh.
Open a MongoDB command shell instance by launching
mongosh.exe.In the command shell, connect to the default test database by running the following command:
mongoshRun the following command in the command shell:
use BookStoreA database named BookStore is created if it doesn't already exist. If the database does exist, its connection is opened for transactions.
Create a
Bookscollection using following command:db.createCollection('Books')The following result is displayed:
{ "ok" : 1 }Define a schema for the
Bookscollection and insert two documents using the following command:db.Books.insertMany([{ "Name": "Design Patterns", "Price": 54.93, "Category": "Computers", "Author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "Name": "Clean Code", "Price": 43.15, "Category": "Computers","Author": "Robert C. Martin" }])A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedIds" : [ ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52") ] }Note
The
ObjectIds shown in the preceding result won't match those shown in the command shell.View the documents in the database using the following command:
db.Books.find().pretty()A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), "Name" : "Design Patterns", "Price" : 54.93, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Ralph Johnson" } { "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52"), "Name" : "Clean Code", "Price" : 43.15, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Robert C. Martin" }The schema adds an autogenerated
_idproperty of typeObjectIdfor each document.
Create the ASP.NET Core web API project
- Go to File > New > Project.
- Select the ASP.NET Core Web API project type, and select Next.
- Name the project BookStoreApi, and select Next.
- In the Additional information dialog:
- Confirm the Framework is .NET 9.0 (Standard Term Support).
- Confirm the checkbox for Use controllers is checked.
- Confirm the checkbox for Enable OpenAPI support is checked.
- Select Create.
In the Package Manager Console window, navigate to the project root. Run the following command to install the .NET driver for MongoDB:
Install-Package MongoDB.Driver
Add an entity model
Add a Models directory to the project root.
Add a
Bookclass to the Models directory with the following code:using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class Book { [BsonId] [BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)] public string? Id { get; set; } [BsonElement("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!; public decimal Price { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } = null!; public string Author { get; set; } = null!; }In the preceding class, the
Idproperty is:- Required for mapping the Common Language Runtime (CLR) object to the MongoDB collection.
- Annotated with
[BsonId]to make this property the document's primary key. - Annotated with
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]to allow passing the parameter as typestringinstead of an ObjectId structure. Mongo handles the conversion fromstringtoObjectId.
The
BookNameproperty is annotated with the[BsonElement]attribute. The attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the MongoDB collection.
Add a configuration model
Add the following database configuration values to
appsettings.json:{ "BookStoreDatabase": { "ConnectionString": "mongodb://localhost:27017", "DatabaseName": "BookStore", "BooksCollectionName": "Books" }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", "Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" }Add a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass to the Models directory with the following code:namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class BookStoreDatabaseSettings { public string ConnectionString { get; set; } = null!; public string DatabaseName { get; set; } = null!; public string BooksCollectionName { get; set; } = null!; }The preceding
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass is used to store theappsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabaseproperty values. The JSON and C# property names are named identically to ease the mapping process.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase"));In the preceding code, the configuration instance to which the
appsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabasesection binds is registered in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. For example, theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsobject'sConnectionStringproperty is populated with theBookStoreDatabase:ConnectionStringproperty inappsettings.json.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsreference:using BookStoreApi.Models;
Add a CRUD operations service
Add a Services directory to the project root.
Add a
BooksServiceclass to the Services directory with the following code:using BookStoreApi.Models; using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; using MongoDB.Driver; namespace BookStoreApi.Services; public class BooksService { private readonly IMongoCollection<Book> _booksCollection; public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); } public async Task<List<Book>> GetAsync() => await _booksCollection.Find(_ => true).ToListAsync(); public async Task<Book?> GetAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.Find(x => x.Id == id).FirstOrDefaultAsync(); public async Task CreateAsync(Book newBook) => await _booksCollection.InsertOneAsync(newBook); public async Task UpdateAsync(string id, Book updatedBook) => await _booksCollection.ReplaceOneAsync(x => x.Id == id, updatedBook); public async Task RemoveAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.DeleteOneAsync(x => x.Id == id); }In the preceding code, a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsinstance is retrieved from DI via constructor injection. This technique provides access to theappsettings.jsonconfiguration values that were added in the Add a configuration model section.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>();In the preceding code, the
BooksServiceclass is registered with DI to support constructor injection in consuming classes. The singleton service lifetime is most appropriate becauseBooksServicetakes a direct dependency onMongoClient. Per the official Mongo Client reuse guidelines,MongoClientshould be registered in DI with a singleton service lifetime.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBooksServicereference:using BookStoreApi.Services;
The BooksService class uses the following MongoDB.Driver members to run CRUD operations against the database:
MongoClient: Reads the server instance for running database operations. The constructor of this class is provided in the MongoDB connection string:
public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); }IMongoDatabase: Represents the Mongo database for running operations. This tutorial uses the generic GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) method on the interface to gain access to data in a specific collection. Run CRUD operations against the collection after this method is called. In the
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection)method call:collectionrepresents the collection name.TDocumentrepresents the CLR object type stored in the collection.
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) returns a MongoCollection object representing the collection. In this tutorial, the following methods are invoked on the collection:
- DeleteOneAsync: Deletes a single document matching the provided search criteria.
- Find<TDocument>: Returns all documents in the collection matching the provided search criteria.
- InsertOneAsync: Inserts the provided object as a new document in the collection.
- ReplaceOneAsync: Replaces the single document matching the provided search criteria with the provided object.
Add a controller
Add a BooksController class to the Controllers directory with the following code:
using BookStoreApi.Models;
using BookStoreApi.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BookStoreApi.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class BooksController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly BooksService _booksService;
public BooksController(BooksService booksService) =>
_booksService = booksService;
[HttpGet]
public async Task<List<Book>> Get() =>
await _booksService.GetAsync();
[HttpGet("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Book>> Get(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return book;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post(Book newBook)
{
await _booksService.CreateAsync(newBook);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), new { id = newBook.Id }, newBook);
}
[HttpPut("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Update(string id, Book updatedBook)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
updatedBook.Id = book.Id;
await _booksService.UpdateAsync(id, updatedBook);
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
await _booksService.RemoveAsync(id);
return NoContent();
}
}
The preceding web API controller:
- Uses the
BooksServiceclass to run CRUD operations. - Contains action methods to support GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE HTTP requests.
- Calls CreatedAtAction in the
Createaction method to return an HTTP 201 response. Status code 201 is the standard response for an HTTP POST method that creates a new resource on the server.CreatedAtActionalso adds aLocationheader to the response. TheLocationheader specifies the URI of the newly created book.
Test the web API
Build and run the app.
Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books, where<port>is the automatically assigned port number for the app, to test the controller's parameterlessGetaction method, select Try it out > Execute. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:[ { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51", "bookName": "Design Patterns", "price": 54.93, "category": "Computers", "author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" } ]Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books/{id here}to test the controller's overloadedGetaction method. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:{ "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" }
Configure JSON serialization options
There are two details to change about the JSON responses returned in the Test the web API section:
- The property names' default camel casing should be changed to match the Pascal casing of the CLR object's property names.
- The
bookNameproperty should be returned asName.
To satisfy the preceding requirements, make the following changes:
In
Program.cs, chain the following highlighted code on to theAddControllersmethod call:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>(); builder.Services.AddControllers() .AddJsonOptions( options => options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null);With the preceding change, property names in the web API's serialized JSON response match their corresponding property names in the CLR object type. For example, the
Bookclass'sAuthorproperty serializes asAuthorinstead ofauthor.In
Models/Book.cs, annotate theBookNameproperty with the[JsonPropertyName]attribute:[BsonElement("Name")] [JsonPropertyName("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!;The
[JsonPropertyName]attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the web API's serialized JSON response.Add the following code to the top of
Models/Book.csto resolve the[JsonProperty]attribute reference:using System.Text.Json.Serialization;Repeat the steps defined in the Test the web API section. Notice the difference in JSON property names.
Add authentication support to a web API
ASP.NET Core Identity adds user interface (UI) login functionality to ASP.NET Core web apps. To secure web APIs and SPAs, use one of the following:
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C)
- Duende Identity Server
Duende Identity Server is an OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 framework for ASP.NET Core. Duende Identity Server enables the following security features:
- Authentication as a Service (AaaS)
- Single sign-on/off (SSO) over multiple application types
- Access control for APIs
- Federation Gateway
Important
Duende Software might require you to pay a license fee for production use of Duende Identity Server. For more information, see Migrate from ASP.NET Core 5.0 to 6.0.
For more information, see the Duende Identity Server documentation (Duende Software website).
Additional resources
This tutorial creates a web API that runs Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations on a MongoDB NoSQL database.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure MongoDB
- Create a MongoDB database
- Define a MongoDB collection and schema
- Perform MongoDB CRUD operations from a web API
- Customize JSON serialization
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2022 with the ASP.NET and web development workload.

Configure MongoDB
Enable MongoDB and MongoDB Shell access from anywhere on the development machine (Windows/Linux/macOS):
Download and Install MongoDB Shell:
- macOS/Linux: Choose a directory to extract the MongoDB Shell to. Add the resulting path for
mongoshto thePATHenvironment variable. - Windows: MongoDB Shell (mongosh.exe) is installed at C:\Users<user>\AppData\Local\Programs\mongosh. Add the resulting path for
mongosh.exeto thePATHenvironment variable.
- macOS/Linux: Choose a directory to extract the MongoDB Shell to. Add the resulting path for
Download and Install MongoDB:
- macOS/Linux: Verify the directory that MongoDB was installed at, usually in /usr/local/mongodb. Add the resulting path for
mongodbto thePATHenvironment variable. - Windows: MongoDB is installed at C:\Program Files\MongoDB by default. Add C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\<version_number>\bin to the
PATHenvironment variable.
- macOS/Linux: Verify the directory that MongoDB was installed at, usually in /usr/local/mongodb. Add the resulting path for
Choose a Data Storage Directory: Select a directory on your development machine for storing data. Create the directory if it doesn't exist. The MongoDB Shell doesn't create new directories:
- macOS/Linux: For example,
/usr/local/var/mongodb. - Windows: For example,
C:\\BooksData.
- macOS/Linux: For example,
In the OS command shell (not the MongoDB Shell), use the following command to connect to MongoDB on default port 27017. Replace
<data_directory_path>with the directory chosen in the previous step.mongod --dbpath <data_directory_path>
Use the previously installed MongoDB Shell in the following steps to create a database, make collections, and store documents. For more information on MongoDB Shell commands, see mongosh.
Open a MongoDB command shell instance by launching
mongosh.exe.In the command shell, connect to the default test database by running the following command:
mongoshRun the following command in the command shell:
use BookStoreA database named BookStore is created if it doesn't already exist. If the database does exist, its connection is opened for transactions.
Create a
Bookscollection using following command:db.createCollection('Books')The following result is displayed:
{ "ok" : 1 }Define a schema for the
Bookscollection and insert two documents using the following command:db.Books.insertMany([{ "Name": "Design Patterns", "Price": 54.93, "Category": "Computers", "Author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "Name": "Clean Code", "Price": 43.15, "Category": "Computers","Author": "Robert C. Martin" }])A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedIds" : [ ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52") ] }Note
The
ObjectIds shown in the preceding result won't match those shown in the command shell.View the documents in the database using the following command:
db.Books.find().pretty()A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), "Name" : "Design Patterns", "Price" : 54.93, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Ralph Johnson" } { "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52"), "Name" : "Clean Code", "Price" : 43.15, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Robert C. Martin" }The schema adds an autogenerated
_idproperty of typeObjectIdfor each document.
Create the ASP.NET Core web API project
Go to File > New > Project.
Select the ASP.NET Core Web API project type, and select Next.
Name the project BookStoreApi, and select Next.
Select the .NET 8.0 (Long Term support) framework and select Create.
In the Package Manager Console window, navigate to the project root. Run the following command to install the .NET driver for MongoDB:
Install-Package MongoDB.Driver
Add an entity model
Add a Models directory to the project root.
Add a
Bookclass to the Models directory with the following code:using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class Book { [BsonId] [BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)] public string? Id { get; set; } [BsonElement("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!; public decimal Price { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } = null!; public string Author { get; set; } = null!; }In the preceding class, the
Idproperty is:- Required for mapping the Common Language Runtime (CLR) object to the MongoDB collection.
- Annotated with
[BsonId]to make this property the document's primary key. - Annotated with
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]to allow passing the parameter as typestringinstead of an ObjectId structure. Mongo handles the conversion fromstringtoObjectId.
The
BookNameproperty is annotated with the[BsonElement]attribute. The attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the MongoDB collection.
Add a configuration model
Add the following database configuration values to
appsettings.json:{ "BookStoreDatabase": { "ConnectionString": "mongodb://localhost:27017", "DatabaseName": "BookStore", "BooksCollectionName": "Books" }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", "Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" }Add a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass to the Models directory with the following code:namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class BookStoreDatabaseSettings { public string ConnectionString { get; set; } = null!; public string DatabaseName { get; set; } = null!; public string BooksCollectionName { get; set; } = null!; }The preceding
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass is used to store theappsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabaseproperty values. The JSON and C# property names are named identically to ease the mapping process.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase"));In the preceding code, the configuration instance to which the
appsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabasesection binds is registered in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. For example, theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsobject'sConnectionStringproperty is populated with theBookStoreDatabase:ConnectionStringproperty inappsettings.json.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsreference:using BookStoreApi.Models;
Add a CRUD operations service
Add a Services directory to the project root.
Add a
BooksServiceclass to the Services directory with the following code:using BookStoreApi.Models; using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; using MongoDB.Driver; namespace BookStoreApi.Services; public class BooksService { private readonly IMongoCollection<Book> _booksCollection; public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); } public async Task<List<Book>> GetAsync() => await _booksCollection.Find(_ => true).ToListAsync(); public async Task<Book?> GetAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.Find(x => x.Id == id).FirstOrDefaultAsync(); public async Task CreateAsync(Book newBook) => await _booksCollection.InsertOneAsync(newBook); public async Task UpdateAsync(string id, Book updatedBook) => await _booksCollection.ReplaceOneAsync(x => x.Id == id, updatedBook); public async Task RemoveAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.DeleteOneAsync(x => x.Id == id); }In the preceding code, a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsinstance is retrieved from DI via constructor injection. This technique provides access to theappsettings.jsonconfiguration values that were added in the Add a configuration model section.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>();In the preceding code, the
BooksServiceclass is registered with DI to support constructor injection in consuming classes. The singleton service lifetime is most appropriate becauseBooksServicetakes a direct dependency onMongoClient. Per the official Mongo Client reuse guidelines,MongoClientshould be registered in DI with a singleton service lifetime.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBooksServicereference:using BookStoreApi.Services;
The BooksService class uses the following MongoDB.Driver members to run CRUD operations against the database:
MongoClient: Reads the server instance for running database operations. The constructor of this class is provided in the MongoDB connection string:
public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); }IMongoDatabase: Represents the Mongo database for running operations. This tutorial uses the generic GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) method on the interface to gain access to data in a specific collection. Run CRUD operations against the collection after this method is called. In the
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection)method call:collectionrepresents the collection name.TDocumentrepresents the CLR object type stored in the collection.
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) returns a MongoCollection object representing the collection. In this tutorial, the following methods are invoked on the collection:
- DeleteOneAsync: Deletes a single document matching the provided search criteria.
- Find<TDocument>: Returns all documents in the collection matching the provided search criteria.
- InsertOneAsync: Inserts the provided object as a new document in the collection.
- ReplaceOneAsync: Replaces the single document matching the provided search criteria with the provided object.
Add a controller
Add a BooksController class to the Controllers directory with the following code:
using BookStoreApi.Models;
using BookStoreApi.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BookStoreApi.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class BooksController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly BooksService _booksService;
public BooksController(BooksService booksService) =>
_booksService = booksService;
[HttpGet]
public async Task<List<Book>> Get() =>
await _booksService.GetAsync();
[HttpGet("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Book>> Get(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return book;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post(Book newBook)
{
await _booksService.CreateAsync(newBook);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), new { id = newBook.Id }, newBook);
}
[HttpPut("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Update(string id, Book updatedBook)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
updatedBook.Id = book.Id;
await _booksService.UpdateAsync(id, updatedBook);
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
await _booksService.RemoveAsync(id);
return NoContent();
}
}
The preceding web API controller:
- Uses the
BooksServiceclass to run CRUD operations. - Contains action methods to support GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE HTTP requests.
- Calls CreatedAtAction in the
Createaction method to return an HTTP 201 response. Status code 201 is the standard response for an HTTP POST method that creates a new resource on the server.CreatedAtActionalso adds aLocationheader to the response. TheLocationheader specifies the URI of the newly created book.
Test the web API
Build and run the app.
Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books, where<port>is the automatically assigned port number for the app, to test the controller's parameterlessGetaction method, select Try it out > Execute. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:[ { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51", "bookName": "Design Patterns", "price": 54.93, "category": "Computers", "author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" } ]Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books/{id here}to test the controller's overloadedGetaction method. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:{ "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" }
Configure JSON serialization options
There are two details to change about the JSON responses returned in the Test the web API section:
- The property names' default camel casing should be changed to match the Pascal casing of the CLR object's property names.
- The
bookNameproperty should be returned asName.
To satisfy the preceding requirements, make the following changes:
In
Program.cs, chain the following highlighted code on to theAddControllersmethod call:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>(); builder.Services.AddControllers() .AddJsonOptions( options => options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null);With the preceding change, property names in the web API's serialized JSON response match their corresponding property names in the CLR object type. For example, the
Bookclass'sAuthorproperty serializes asAuthorinstead ofauthor.In
Models/Book.cs, annotate theBookNameproperty with the[JsonPropertyName]attribute:[BsonElement("Name")] [JsonPropertyName("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!;The
[JsonPropertyName]attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the web API's serialized JSON response.Add the following code to the top of
Models/Book.csto resolve the[JsonProperty]attribute reference:using System.Text.Json.Serialization;Repeat the steps defined in the Test the web API section. Notice the difference in JSON property names.
Add authentication support to a web API
ASP.NET Core Identity adds user interface (UI) login functionality to ASP.NET Core web apps. To secure web APIs and SPAs, use one of the following:
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C)
- Duende Identity Server
Duende Identity Server is an OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 framework for ASP.NET Core. Duende Identity Server enables the following security features:
- Authentication as a Service (AaaS)
- Single sign-on/off (SSO) over multiple application types
- Access control for APIs
- Federation Gateway
Important
Duende Software might require you to pay a license fee for production use of Duende Identity Server. For more information, see Migrate from ASP.NET Core 5.0 to 6.0.
For more information, see the Duende Identity Server documentation (Duende Software website).
Additional resources
This tutorial creates a web API that runs Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations on a MongoDB NoSQL database.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure MongoDB
- Create a MongoDB database
- Define a MongoDB collection and schema
- Perform MongoDB CRUD operations from a web API
- Customize JSON serialization
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2022 with the ASP.NET and web development workload.

Configure MongoDB
Enable MongoDB and Mongo DB Shell access from anywhere on the development machine:
On Windows, MongoDB is installed at C:\Program Files\MongoDB by default. Add C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\<version_number>\bin to the
PATHenvironment variable.Download the MongoDB Shell and choose a directory to extract it to. Add the resulting path for
mongosh.exeto thePATHenvironment variable.Choose a directory on the development machine for storing the data. For example, C:\BooksData on Windows. Create the directory if it doesn't exist. The mongo Shell doesn't create new directories.
In the OS command shell (not the MongoDB Shell), use the following command to connect to MongoDB on default port 27017. Replace
<data_directory_path>with the directory chosen in the previous step.mongod --dbpath <data_directory_path>
Use the previously installed MongoDB Shell in the following steps to create a database, make collections, and store documents. For more information on MongoDB Shell commands, see mongosh.
Open a MongoDB command shell instance by launching
mongosh.exe.In the command shell connect to the default test database by running the following command:
mongoshRun the following command in the command shell:
use BookStoreA database named BookStore is created if it doesn't already exist. If the database does exist, its connection is opened for transactions.
Create a
Bookscollection using following command:db.createCollection('Books')The following result is displayed:
{ "ok" : 1 }Define a schema for the
Bookscollection and insert two documents using the following command:db.Books.insertMany([{ "Name": "Design Patterns", "Price": 54.93, "Category": "Computers", "Author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "Name": "Clean Code", "Price": 43.15, "Category": "Computers","Author": "Robert C. Martin" }])A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedIds" : [ ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52") ] }Note
The
ObjectIds shown in the preceding result won't match those shown in the command shell.View the documents in the database using the following command:
db.Books.find().pretty()A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), "Name" : "Design Patterns", "Price" : 54.93, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Ralph Johnson" } { "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52"), "Name" : "Clean Code", "Price" : 43.15, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Robert C. Martin" }The schema adds an autogenerated
_idproperty of typeObjectIdfor each document.
Create the ASP.NET Core web API project
Go to File > New > Project.
Select the ASP.NET Core Web API project type, and select Next.
Name the project BookStoreApi, and select Next.
Select the .NET 7.0 (Standard Term Support) framework and select Create.
From the Tools menu, select NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console.
In the Package Manager Console window, navigate to the project root. Run the following command to install the .NET driver for MongoDB:
Install-Package MongoDB.Driver
Add an entity model
Add a Models directory to the project root.
Add a
Bookclass to the Models directory with the following code:using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class Book { [BsonId] [BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)] public string? Id { get; set; } [BsonElement("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!; public decimal Price { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } = null!; public string Author { get; set; } = null!; }In the preceding class, the
Idproperty is:- Required for mapping the Common Language Runtime (CLR) object to the MongoDB collection.
- Annotated with
[BsonId]to make this property the document's primary key. - Annotated with
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]to allow passing the parameter as typestringinstead of an ObjectId structure. Mongo handles the conversion fromstringtoObjectId.
The
BookNameproperty is annotated with the[BsonElement]attribute. The attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the MongoDB collection.
Add a configuration model
Add the following database configuration values to
appsettings.json:{ "BookStoreDatabase": { "ConnectionString": "mongodb://localhost:27017", "DatabaseName": "BookStore", "BooksCollectionName": "Books" }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", "Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" }Add a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass to the Models directory with the following code:namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class BookStoreDatabaseSettings { public string ConnectionString { get; set; } = null!; public string DatabaseName { get; set; } = null!; public string BooksCollectionName { get; set; } = null!; }The preceding
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass is used to store theappsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabaseproperty values. The JSON and C# property names are named identically to ease the mapping process.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase"));In the preceding code, the configuration instance to which the
appsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabasesection binds is registered in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. For example, theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsobject'sConnectionStringproperty is populated with theBookStoreDatabase:ConnectionStringproperty inappsettings.json.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsreference:using BookStoreApi.Models;
Add a CRUD operations service
Add a Services directory to the project root.
Add a
BooksServiceclass to the Services directory with the following code:using BookStoreApi.Models; using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; using MongoDB.Driver; namespace BookStoreApi.Services; public class BooksService { private readonly IMongoCollection<Book> _booksCollection; public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); } public async Task<List<Book>> GetAsync() => await _booksCollection.Find(_ => true).ToListAsync(); public async Task<Book?> GetAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.Find(x => x.Id == id).FirstOrDefaultAsync(); public async Task CreateAsync(Book newBook) => await _booksCollection.InsertOneAsync(newBook); public async Task UpdateAsync(string id, Book updatedBook) => await _booksCollection.ReplaceOneAsync(x => x.Id == id, updatedBook); public async Task RemoveAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.DeleteOneAsync(x => x.Id == id); }In the preceding code, a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsinstance is retrieved from DI via constructor injection. This technique provides access to theappsettings.jsonconfiguration values that were added in the Add a configuration model section.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>();In the preceding code, the
BooksServiceclass is registered with DI to support constructor injection in consuming classes. The singleton service lifetime is most appropriate becauseBooksServicetakes a direct dependency onMongoClient. Per the official Mongo Client reuse guidelines,MongoClientshould be registered in DI with a singleton service lifetime.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBooksServicereference:using BookStoreApi.Services;
The BooksService class uses the following MongoDB.Driver members to run CRUD operations against the database:
MongoClient: Reads the server instance for running database operations. The constructor of this class is provided the MongoDB connection string:
public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); }IMongoDatabase: Represents the Mongo database for running operations. This tutorial uses the generic GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) method on the interface to gain access to data in a specific collection. Run CRUD operations against the collection after this method is called. In the
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection)method call:collectionrepresents the collection name.TDocumentrepresents the CLR object type stored in the collection.
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) returns a MongoCollection object representing the collection. In this tutorial, the following methods are invoked on the collection:
- DeleteOneAsync: Deletes a single document matching the provided search criteria.
- Find<TDocument>: Returns all documents in the collection matching the provided search criteria.
- InsertOneAsync: Inserts the provided object as a new document in the collection.
- ReplaceOneAsync: Replaces the single document matching the provided search criteria with the provided object.
Add a controller
Add a BooksController class to the Controllers directory with the following code:
using BookStoreApi.Models;
using BookStoreApi.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BookStoreApi.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class BooksController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly BooksService _booksService;
public BooksController(BooksService booksService) =>
_booksService = booksService;
[HttpGet]
public async Task<List<Book>> Get() =>
await _booksService.GetAsync();
[HttpGet("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Book>> Get(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return book;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post(Book newBook)
{
await _booksService.CreateAsync(newBook);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), new { id = newBook.Id }, newBook);
}
[HttpPut("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Update(string id, Book updatedBook)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
updatedBook.Id = book.Id;
await _booksService.UpdateAsync(id, updatedBook);
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
await _booksService.RemoveAsync(id);
return NoContent();
}
}
The preceding web API controller:
- Uses the
BooksServiceclass to run CRUD operations. - Contains action methods to support GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE HTTP requests.
- Calls CreatedAtAction in the
Createaction method to return an HTTP 201 response. Status code 201 is the standard response for an HTTP POST method that creates a new resource on the server.CreatedAtActionalso adds aLocationheader to the response. TheLocationheader specifies the URI of the newly created book.
Test the web API
Build and run the app.
Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books, where<port>is the automatically assigned port number for the app, to test the controller's parameterlessGetaction method. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:[ { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51", "bookName": "Design Patterns", "price": 54.93, "category": "Computers", "author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" } ]Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books/{id here}to test the controller's overloadedGetaction method. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:{ "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" }
Configure JSON serialization options
There are two details to change about the JSON responses returned in the Test the web API section:
- The property names' default camel casing should be changed to match the Pascal casing of the CLR object's property names.
- The
bookNameproperty should be returned asName.
To satisfy the preceding requirements, make the following changes:
In
Program.cs, chain the following highlighted code on to theAddControllersmethod call:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>(); builder.Services.AddControllers() .AddJsonOptions( options => options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null);With the preceding change, property names in the web API's serialized JSON response match their corresponding property names in the CLR object type. For example, the
Bookclass'sAuthorproperty serializes asAuthorinstead ofauthor.In
Models/Book.cs, annotate theBookNameproperty with the[JsonPropertyName]attribute:[BsonElement("Name")] [JsonPropertyName("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!;The
[JsonPropertyName]attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the web API's serialized JSON response.Add the following code to the top of
Models/Book.csto resolve the[JsonProperty]attribute reference:using System.Text.Json.Serialization;Repeat the steps defined in the Test the web API section. Notice the difference in JSON property names.
Add authentication support to a web API
ASP.NET Core Identity adds user interface (UI) login functionality to ASP.NET Core web apps. To secure web APIs and SPAs, use one of the following:
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C)
- Duende Identity Server
Duende Identity Server is an OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 framework for ASP.NET Core. Duende Identity Server enables the following security features:
- Authentication as a Service (AaaS)
- Single sign-on/off (SSO) over multiple application types
- Access control for APIs
- Federation Gateway
Important
Duende Software might require you to pay a license fee for production use of Duende Identity Server. For more information, see Migrate from ASP.NET Core 5.0 to 6.0.
For more information, see the Duende Identity Server documentation (Duende Software website).
Additional resources
This tutorial creates a web API that runs Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations on a MongoDB NoSQL database.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure MongoDB
- Create a MongoDB database
- Define a MongoDB collection and schema
- Perform MongoDB CRUD operations from a web API
- Customize JSON serialization
Prerequisites
- Visual Studio 2022 with the ASP.NET and web development workload.
- .NET 6.0 SDK
Configure MongoDB
Enable MongoDB and Mongo DB Shell access from anywhere on the development machine:
On Windows, MongoDB is installed at C:\Program Files\MongoDB by default. Add C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\<version_number>\bin to the
PATHenvironment variable.Download the MongoDB Shell and choose a directory to extract it to. Add the resulting path for
mongosh.exeto thePATHenvironment variable.Choose a directory on the development machine for storing the data. For example, C:\BooksData on Windows. Create the directory if it doesn't exist. The mongo Shell doesn't create new directories.
In the OS command shell (not the MongoDB Shell), use the following command to connect to MongoDB on default port 27017. Replace
<data_directory_path>with the directory chosen in the previous step.mongod --dbpath <data_directory_path>
Use the previously installed MongoDB Shell in the following steps to create a database, make collections, and store documents. For more information on MongoDB Shell commands, see mongosh.
Open a MongoDB command shell instance by launching
mongosh.exe.In the command shell connect to the default test database by running the following command:
mongoshRun the following command in the command shell:
use BookStoreA database named BookStore is created if it doesn't already exist. If the database does exist, its connection is opened for transactions.
Create a
Bookscollection using following command:db.createCollection('Books')The following result is displayed:
{ "ok" : 1 }Define a schema for the
Bookscollection and insert two documents using the following command:db.Books.insertMany([{ "Name": "Design Patterns", "Price": 54.93, "Category": "Computers", "Author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "Name": "Clean Code", "Price": 43.15, "Category": "Computers","Author": "Robert C. Martin" }])A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedIds" : [ ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52") ] }Note
The
ObjectIds shown in the preceding result won't match those shown in the command shell.View the documents in the database using the following command:
db.Books.find().pretty()A result similar to the following is displayed:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51"), "Name" : "Design Patterns", "Price" : 54.93, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Ralph Johnson" } { "_id" : ObjectId("61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52"), "Name" : "Clean Code", "Price" : 43.15, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Robert C. Martin" }The schema adds an autogenerated
_idproperty of typeObjectIdfor each document.
Create the ASP.NET Core web API project
Go to File > New > Project.
Select the ASP.NET Core Web API project type, and select Next.
Name the project BookStoreApi, and select Next.
Select the .NET 6.0 (Long-term support) framework and select Create.
In the Package Manager Console window, navigate to the project root. Run the following command to install the .NET driver for MongoDB:
Install-Package MongoDB.Driver
Add an entity model
Add a Models directory to the project root.
Add a
Bookclass to the Models directory with the following code:using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class Book { [BsonId] [BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)] public string? Id { get; set; } [BsonElement("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!; public decimal Price { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } = null!; public string Author { get; set; } = null!; }In the preceding class, the
Idproperty is:- Required for mapping the Common Language Runtime (CLR) object to the MongoDB collection.
- Annotated with
[BsonId]to make this property the document's primary key. - Annotated with
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]to allow passing the parameter as typestringinstead of an ObjectId structure. Mongo handles the conversion fromstringtoObjectId.
The
BookNameproperty is annotated with the[BsonElement]attribute. The attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the MongoDB collection.
Add a configuration model
Add the following database configuration values to
appsettings.json:{ "BookStoreDatabase": { "ConnectionString": "mongodb://localhost:27017", "DatabaseName": "BookStore", "BooksCollectionName": "Books" }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", "Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" }Add a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass to the Models directory with the following code:namespace BookStoreApi.Models; public class BookStoreDatabaseSettings { public string ConnectionString { get; set; } = null!; public string DatabaseName { get; set; } = null!; public string BooksCollectionName { get; set; } = null!; }The preceding
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsclass is used to store theappsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabaseproperty values. The JSON and C# property names are named identically to ease the mapping process.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase"));In the preceding code, the configuration instance to which the
appsettings.jsonfile'sBookStoreDatabasesection binds is registered in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. For example, theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsobject'sConnectionStringproperty is populated with theBookStoreDatabase:ConnectionStringproperty inappsettings.json.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBookStoreDatabaseSettingsreference:using BookStoreApi.Models;
Add a CRUD operations service
Add a Services directory to the project root.
Add a
BooksServiceclass to the Services directory with the following code:using BookStoreApi.Models; using Microsoft.Extensions.Options; using MongoDB.Driver; namespace BookStoreApi.Services; public class BooksService { private readonly IMongoCollection<Book> _booksCollection; public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); } public async Task<List<Book>> GetAsync() => await _booksCollection.Find(_ => true).ToListAsync(); public async Task<Book?> GetAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.Find(x => x.Id == id).FirstOrDefaultAsync(); public async Task CreateAsync(Book newBook) => await _booksCollection.InsertOneAsync(newBook); public async Task UpdateAsync(string id, Book updatedBook) => await _booksCollection.ReplaceOneAsync(x => x.Id == id, updatedBook); public async Task RemoveAsync(string id) => await _booksCollection.DeleteOneAsync(x => x.Id == id); }In the preceding code, a
BookStoreDatabaseSettingsinstance is retrieved from DI via constructor injection. This technique provides access to theappsettings.jsonconfiguration values that were added in the Add a configuration model section.Add the following highlighted code to
Program.cs:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>();In the preceding code, the
BooksServiceclass is registered with DI to support constructor injection in consuming classes. The singleton service lifetime is most appropriate becauseBooksServicetakes a direct dependency onMongoClient. Per the official Mongo Client reuse guidelines,MongoClientshould be registered in DI with a singleton service lifetime.Add the following code to the top of
Program.csto resolve theBooksServicereference:using BookStoreApi.Services;
The BooksService class uses the following MongoDB.Driver members to run CRUD operations against the database:
MongoClient: Reads the server instance for running database operations. The constructor of this class is provided the MongoDB connection string:
public BooksService( IOptions<BookStoreDatabaseSettings> bookStoreDatabaseSettings) { var mongoClient = new MongoClient( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.ConnectionString); var mongoDatabase = mongoClient.GetDatabase( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.DatabaseName); _booksCollection = mongoDatabase.GetCollection<Book>( bookStoreDatabaseSettings.Value.BooksCollectionName); }IMongoDatabase: Represents the Mongo database for running operations. This tutorial uses the generic GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) method on the interface to gain access to data in a specific collection. Run CRUD operations against the collection after this method is called. In the
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection)method call:collectionrepresents the collection name.TDocumentrepresents the CLR object type stored in the collection.
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) returns a MongoCollection object representing the collection. In this tutorial, the following methods are invoked on the collection:
- DeleteOneAsync: Deletes a single document matching the provided search criteria.
- Find<TDocument>: Returns all documents in the collection matching the provided search criteria.
- InsertOneAsync: Inserts the provided object as a new document in the collection.
- ReplaceOneAsync: Replaces the single document matching the provided search criteria with the provided object.
Add a controller
Add a BooksController class to the Controllers directory with the following code:
using BookStoreApi.Models;
using BookStoreApi.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace BookStoreApi.Controllers;
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class BooksController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly BooksService _booksService;
public BooksController(BooksService booksService) =>
_booksService = booksService;
[HttpGet]
public async Task<List<Book>> Get() =>
await _booksService.GetAsync();
[HttpGet("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<Book>> Get(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return book;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post(Book newBook)
{
await _booksService.CreateAsync(newBook);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), new { id = newBook.Id }, newBook);
}
[HttpPut("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Update(string id, Book updatedBook)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
updatedBook.Id = book.Id;
await _booksService.UpdateAsync(id, updatedBook);
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id:length(24)}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(string id)
{
var book = await _booksService.GetAsync(id);
if (book is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
await _booksService.RemoveAsync(id);
return NoContent();
}
}
The preceding web API controller:
- Uses the
BooksServiceclass to run CRUD operations. - Contains action methods to support GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE HTTP requests.
- Calls CreatedAtAction in the
Createaction method to return an HTTP 201 response. Status code 201 is the standard response for an HTTP POST method that creates a new resource on the server.CreatedAtActionalso adds aLocationheader to the response. TheLocationheader specifies the URI of the newly created book.
Test the web API
Build and run the app.
Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books, where<port>is the automatically assigned port number for the app, to test the controller's parameterlessGetaction method. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:[ { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f51", "bookName": "Design Patterns", "price": 54.93, "category": "Computers", "author": "Ralph Johnson" }, { "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" } ]Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books/{id here}to test the controller's overloadedGetaction method. A JSON response similar to the following is displayed:{ "id": "61a6058e6c43f32854e51f52", "bookName": "Clean Code", "price": 43.15, "category": "Computers", "author": "Robert C. Martin" }
Configure JSON serialization options
There are two details to change about the JSON responses returned in the Test the web API section:
- The property names' default camel casing should be changed to match the Pascal casing of the CLR object's property names.
- The
bookNameproperty should be returned asName.
To satisfy the preceding requirements, make the following changes:
In
Program.cs, chain the following highlighted code on to theAddControllersmethod call:var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add services to the container. builder.Services.Configure<BookStoreDatabaseSettings>( builder.Configuration.GetSection("BookStoreDatabase")); builder.Services.AddSingleton<BooksService>(); builder.Services.AddControllers() .AddJsonOptions( options => options.JsonSerializerOptions.PropertyNamingPolicy = null);With the preceding change, property names in the web API's serialized JSON response match their corresponding property names in the CLR object type. For example, the
Bookclass'sAuthorproperty serializes asAuthorinstead ofauthor.In
Models/Book.cs, annotate theBookNameproperty with the[JsonPropertyName]attribute:[BsonElement("Name")] [JsonPropertyName("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } = null!;The
[JsonPropertyName]attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the web API's serialized JSON response.Add the following code to the top of
Models/Book.csto resolve the[JsonProperty]attribute reference:using System.Text.Json.Serialization;Repeat the steps defined in the Test the web API section. Notice the difference in JSON property names.
Add authentication support to a web API
ASP.NET Core Identity adds user interface (UI) login functionality to ASP.NET Core web apps. To secure web APIs and SPAs, use one of the following:
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C)
- Duende Identity Server
Duende Identity Server is an OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 framework for ASP.NET Core. Duende Identity Server enables the following security features:
- Authentication as a Service (AaaS)
- Single sign-on/off (SSO) over multiple application types
- Access control for APIs
- Federation Gateway
Important
Duende Software might require you to pay a license fee for production use of Duende Identity Server. For more information, see Migrate from ASP.NET Core 5.0 to 6.0.
For more information, see the Duende Identity Server documentation (Duende Software website).
Additional resources
This tutorial creates a web API that runs Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations on a MongoDB NoSQL database.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure MongoDB
- Create a MongoDB database
- Define a MongoDB collection and schema
- Perform MongoDB CRUD operations from a web API
- Customize JSON serialization
View or download sample code (how to download)
Prerequisites
- .NET Core SDK 3.0 or later
- Visual Studio 2019 with the ASP.NET and web development workload
- MongoDB
Configure MongoDB
If using Windows, MongoDB is installed at C:\Program Files\MongoDB by default. Add C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\<version_number>\bin to the Path environment variable. This change enables MongoDB access from anywhere on your development machine.
Use the mongo Shell in the following steps to create a database, make collections, and store documents. For more information on mongo Shell commands, see Working with the mongo Shell.
Choose a directory on your development machine for storing the data. For example, C:\BooksData on Windows. Create the directory if it doesn't exist. The mongo Shell doesn't create new directories.
Open a command shell. Run the following command to connect to MongoDB on default port 27017. Remember to replace
<data_directory_path>with the directory you chose in the previous step.mongod --dbpath <data_directory_path>Open another command shell instance. Connect to the default test database by running the following command:
mongoRun the following command in a command shell:
use BookstoreDbA database named BookstoreDb is created if it doesn't already exist. If the database does exist, its connection is opened for transactions.
Create a
Bookscollection using following command:db.createCollection('Books')The following result is displayed:
{ "ok" : 1 }Define a schema for the
Bookscollection and insert two documents using the following command:db.Books.insertMany([{'Name':'Design Patterns','Price':54.93,'Category':'Computers','Author':'Ralph Johnson'}, {'Name':'Clean Code','Price':43.15,'Category':'Computers','Author':'Robert C. Martin'}])The following result is displayed:
{ "acknowledged" : true, "insertedIds" : [ ObjectId("5bfd996f7b8e48dc15ff215d"), ObjectId("5bfd996f7b8e48dc15ff215e") ] }Note
The ID's shown in this article will not match the IDs when you run this sample.
View the documents in the database using the following command:
db.Books.find({}).pretty()The following result is displayed:
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5bfd996f7b8e48dc15ff215d"), "Name" : "Design Patterns", "Price" : 54.93, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Ralph Johnson" } { "_id" : ObjectId("5bfd996f7b8e48dc15ff215e"), "Name" : "Clean Code", "Price" : 43.15, "Category" : "Computers", "Author" : "Robert C. Martin" }The schema adds an autogenerated
_idproperty of typeObjectIdfor each document.
The database is ready. You can start creating the ASP.NET Core web API.
Create the ASP.NET Core web API project
Go to File > New > Project.
Select the ASP.NET Core Web Application project type, and select Next.
Name the project BooksApi, and select Create.
Select the .NET Core target framework and ASP.NET Core 3.0. Select the API project template, and select Create.
Visit the NuGet Gallery: MongoDB.Driver to determine the latest stable version of the .NET driver for MongoDB. In the Package Manager Console window, navigate to the project root. Run the following command to install the .NET driver for MongoDB:
Install-Package MongoDB.Driver -Version {VERSION}
Add an entity model
Add a Models directory to the project root.
Add a
Bookclass to the Models directory with the following code:using MongoDB.Bson; using MongoDB.Bson.Serialization.Attributes; namespace BooksApi.Models { public class Book { [BsonId] [BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)] public string Id { get; set; } [BsonElement("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; } public decimal Price { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public string Author { get; set; } } }In the preceding class, the
Idproperty is:- Required for mapping the Common Language Runtime (CLR) object to the MongoDB collection.
- Annotated with
[BsonId]to make this property the document's primary key. - Annotated with
[BsonRepresentation(BsonType.ObjectId)]to allow passing the parameter as typestringinstead of an ObjectId structure. Mongo handles the conversion fromstringtoObjectId.
The
BookNameproperty is annotated with the[BsonElement]attribute. The attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the MongoDB collection.
Add a configuration model
Add the following database configuration values to
appsettings.json:{ "BookstoreDatabaseSettings": { "BooksCollectionName": "Books", "ConnectionString": "mongodb://localhost:27017", "DatabaseName": "BookstoreDb" }, "Logging": { "IncludeScopes": false, "Debug": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } }, "Console": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } } } }Add a
BookstoreDatabaseSettings.csfile to the Models directory with the following code:namespace BooksApi.Models { public class BookstoreDatabaseSettings : IBookstoreDatabaseSettings { public string BooksCollectionName { get; set; } public string ConnectionString { get; set; } public string DatabaseName { get; set; } } public interface IBookstoreDatabaseSettings { string BooksCollectionName { get; set; } string ConnectionString { get; set; } string DatabaseName { get; set; } } }The preceding
BookstoreDatabaseSettingsclass is used to store theappsettings.jsonfile'sBookstoreDatabaseSettingsproperty values. The JSON and C# property names are named identically to ease the mapping process.Add the following highlighted code to
Startup.ConfigureServices:public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // requires using Microsoft.Extensions.Options services.Configure<BookstoreDatabaseSettings>( Configuration.GetSection(nameof(BookstoreDatabaseSettings))); services.AddSingleton<IBookstoreDatabaseSettings>(sp => sp.GetRequiredService<IOptions<BookstoreDatabaseSettings>>().Value); services.AddControllers(); }In the preceding code:
- The configuration instance to which the
appsettings.jsonfile'sBookstoreDatabaseSettingssection binds is registered in the Dependency Injection (DI) container. For example, aBookstoreDatabaseSettingsobject'sConnectionStringproperty is populated with theBookstoreDatabaseSettings:ConnectionStringproperty inappsettings.json. - The
IBookstoreDatabaseSettingsinterface is registered in DI with a singleton service lifetime. When injected, the interface instance resolves to aBookstoreDatabaseSettingsobject.
- The configuration instance to which the
Add the following code to the top of
Startup.csto resolve theBookstoreDatabaseSettingsandIBookstoreDatabaseSettingsreferences:using BooksApi.Models;
Add a CRUD operations service
Add a Services directory to the project root.
Add a
BookServiceclass to the Services directory with the following code:using BooksApi.Models; using MongoDB.Driver; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; namespace BooksApi.Services { public class BookService { private readonly IMongoCollection<Book> _books; public BookService(IBookstoreDatabaseSettings settings) { var client = new MongoClient(settings.ConnectionString); var database = client.GetDatabase(settings.DatabaseName); _books = database.GetCollection<Book>(settings.BooksCollectionName); } public List<Book> Get() => _books.Find(book => true).ToList(); public Book Get(string id) => _books.Find<Book>(book => book.Id == id).FirstOrDefault(); public Book Create(Book book) { _books.InsertOne(book); return book; } public void Update(string id, Book bookIn) => _books.ReplaceOne(book => book.Id == id, bookIn); public void Remove(Book bookIn) => _books.DeleteOne(book => book.Id == bookIn.Id); public void Remove(string id) => _books.DeleteOne(book => book.Id == id); } }In the preceding code, an
IBookstoreDatabaseSettingsinstance is retrieved from DI via constructor injection. This technique provides access to theappsettings.jsonconfiguration values that were added in the Add a configuration model section.Add the following highlighted code to
Startup.ConfigureServices:public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.Configure<BookstoreDatabaseSettings>( Configuration.GetSection(nameof(BookstoreDatabaseSettings))); services.AddSingleton<IBookstoreDatabaseSettings>(sp => sp.GetRequiredService<IOptions<BookstoreDatabaseSettings>>().Value); services.AddSingleton<BookService>(); services.AddControllers(); }In the preceding code, the
BookServiceclass is registered with DI to support constructor injection in consuming classes. The singleton service lifetime is most appropriate becauseBookServicetakes a direct dependency onMongoClient. Per the official Mongo Client reuse guidelines,MongoClientshould be registered in DI with a singleton service lifetime.Add the following code to the top of
Startup.csto resolve theBookServicereference:using BooksApi.Services;
The BookService class uses the following MongoDB.Driver members to run CRUD operations against the database:
MongoClient: Reads the server instance for running database operations. The constructor of this class is provided the MongoDB connection string:
public BookService(IBookstoreDatabaseSettings settings) { var client = new MongoClient(settings.ConnectionString); var database = client.GetDatabase(settings.DatabaseName); _books = database.GetCollection<Book>(settings.BooksCollectionName); }IMongoDatabase: Represents the Mongo database for running operations. This tutorial uses the generic GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) method on the interface to gain access to data in a specific collection. Run CRUD operations against the collection after this method is called. In the
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection)method call:collectionrepresents the collection name.TDocumentrepresents the CLR object type stored in the collection.
GetCollection<TDocument>(collection) returns a MongoCollection object representing the collection. In this tutorial, the following methods are invoked on the collection:
- DeleteOne: Deletes a single document matching the provided search criteria.
- Find<TDocument>: Returns all documents in the collection matching the provided search criteria.
- InsertOne: Inserts the provided object as a new document in the collection.
- ReplaceOne: Replaces the single document matching the provided search criteria with the provided object.
Add a controller
Add a BooksController class to the Controllers directory with the following code:
using BooksApi.Models;
using BooksApi.Services;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace BooksApi.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class BooksController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly BookService _bookService;
public BooksController(BookService bookService)
{
_bookService = bookService;
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult<List<Book>> Get() =>
_bookService.Get();
[HttpGet("{id:length(24)}", Name = "GetBook")]
public ActionResult<Book> Get(string id)
{
var book = _bookService.Get(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return book;
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult<Book> Create(Book book)
{
_bookService.Create(book);
return CreatedAtRoute("GetBook", new { id = book.Id.ToString() }, book);
}
[HttpPut("{id:length(24)}")]
public IActionResult Update(string id, Book bookIn)
{
var book = _bookService.Get(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_bookService.Update(id, bookIn);
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id:length(24)}")]
public IActionResult Delete(string id)
{
var book = _bookService.Get(id);
if (book == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_bookService.Remove(id);
return NoContent();
}
}
}
The preceding web API controller:
- Uses the
BookServiceclass to run CRUD operations. - Contains action methods to support GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE HTTP requests.
- Calls CreatedAtRoute in the
Createaction method to return an HTTP 201 response. Status code 201 is the standard response for an HTTP POST method that creates a new resource on the server.CreatedAtRoutealso adds aLocationheader to the response. TheLocationheader specifies the URI of the newly created book.
Test the web API
Build and run the app.
Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/booksto test the controller's parameterlessGetaction method. The following JSON response is displayed:[ { "id":"5bfd996f7b8e48dc15ff215d", "bookName":"Design Patterns", "price":54.93, "category":"Computers", "author":"Ralph Johnson" }, { "id":"5bfd996f7b8e48dc15ff215e", "bookName":"Clean Code", "price":43.15, "category":"Computers", "author":"Robert C. Martin" } ]Navigate to
https://localhost:<port>/api/books/{id here}to test the controller's overloadedGetaction method. The following JSON response is displayed:{ "id":"{ID}", "bookName":"Clean Code", "price":43.15, "category":"Computers", "author":"Robert C. Martin" }
Configure JSON serialization options
There are two details to change about the JSON responses returned in the Test the web API section:
- The property names' default camel casing should be changed to match the Pascal casing of the CLR object's property names.
- The
bookNameproperty should be returned asName.
To satisfy the preceding requirements, make the following changes:
Json.NET has been removed from ASP.NET shared framework. Add a package reference to
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.NewtonsoftJson.In
Startup.ConfigureServices, chain the following highlighted code on to theAddControllersmethod call:public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.Configure<BookstoreDatabaseSettings>( Configuration.GetSection(nameof(BookstoreDatabaseSettings))); services.AddSingleton<IBookstoreDatabaseSettings>(sp => sp.GetRequiredService<IOptions<BookstoreDatabaseSettings>>().Value); services.AddSingleton<BookService>(); services.AddControllers() .AddNewtonsoftJson(options => options.UseMemberCasing()); }With the preceding change, property names in the web API's serialized JSON response match their corresponding property names in the CLR object type. For example, the
Bookclass'sAuthorproperty serializes asAuthor.In
Models/Book.cs, annotate theBookNameproperty with the following[JsonProperty]attribute:[BsonElement("Name")] [JsonProperty("Name")] public string BookName { get; set; }The
[JsonProperty]attribute's value ofNamerepresents the property name in the web API's serialized JSON response.Add the following code to the top of
Models/Book.csto resolve the[JsonProperty]attribute reference:using Newtonsoft.Json;Repeat the steps defined in the Test the web API section. Notice the difference in JSON property names.
Add authentication support to a web API
ASP.NET Core Identity adds user interface (UI) login functionality to ASP.NET Core web apps. To secure web APIs and SPAs, use one of the following:
- Microsoft Entra ID
- Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C)
- Duende IdentityServer. Duende IdentityServer is 3rd party product.
Duende IdentityServer is an OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0 framework for ASP.NET Core. Duende IdentityServer enables the following security features:
- Authentication as a Service (AaaS)
- Single sign-on/off (SSO) over multiple application types
- Access control for APIs
- Federation Gateway
For more information, see Overview of Duende IdentityServer.
For more information on other authentication providers, see Community OSS authentication options for ASP.NET Core
Next steps
For more information on building ASP.NET Core web APIs, see the following resources:
ASP.NET Core
