Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
This isn't the latest version of this article. For the current release, see the .NET 10 version of this article.
Warning
This version of ASP.NET Core is no longer supported. For more information, see the .NET and .NET Core Support Policy. For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
By Joe Audette
The RazorPagesMovieContext object handles the task of connecting to the database and mapping Movie objects to database records. The database context is registered with the Dependency Injection container in Program.cs:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
The ASP.NET Core Configuration system reads the ConnectionString key. For local development, configuration gets the connection string from the appsettings.json file.
The generated connection string is similar to the following JSON:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RazorPagesMovieContext": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=RazorPagesMovieContext-f2e0482c-952d-4b1c-afe9-a1a3dfe52e55;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Warning
This article uses a local database that doesn't require the user to be authenticated. Production apps should use the most secure authentication flow available. For more information on authentication for deployed test and production apps, see Secure authentication flows.
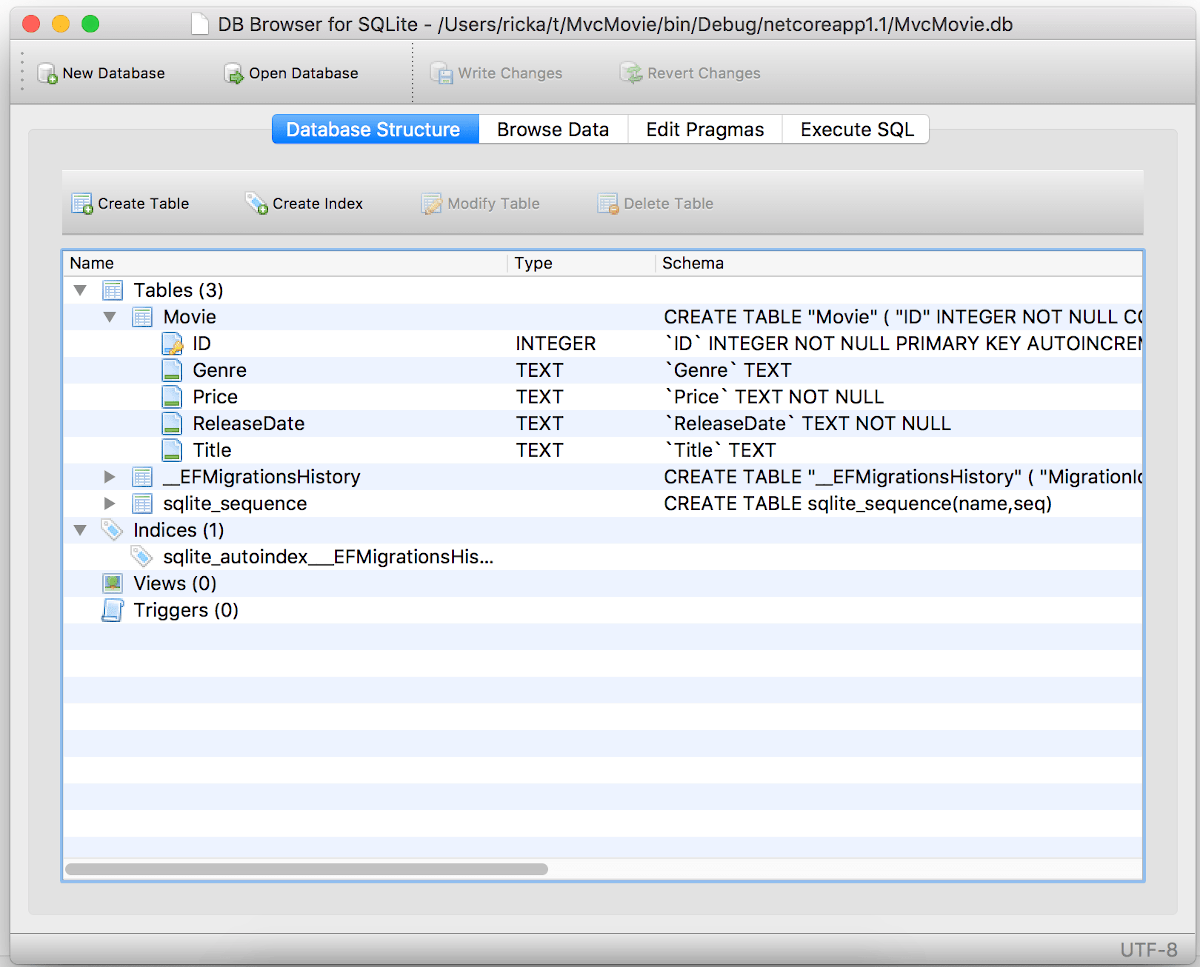
SQL Server Express LocalDB
LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express database engine that's targeted for program development. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB database creates *.mdf files in the C:\Users\<user>\ directory.
From the View menu, open SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX).

Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Designer:

Note the key icon next to
ID. By default, EF creates a property namedIDfor the primary key.Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Data:
Seed the database
Create a new class named SeedData in the Models folder with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Models;
public static class SeedData
{
public static void Initialize(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var context = new RazorPagesMovieContext(
serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<
DbContextOptions<RazorPagesMovieContext>>()))
{
if (context == null || context.Movie == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("Null RazorPagesMovieContext");
}
// Look for any movies.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return; // DB has been seeded
}
context.Movie.AddRange(
new Movie
{
Title = "When Harry Met Sally",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1989-2-12"),
Genre = "Romantic Comedy",
Price = 7.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters ",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1984-3-13"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 8.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters 2",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1986-2-23"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 9.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Rio Bravo",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1959-4-15"),
Genre = "Western",
Price = 3.99M
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
If there are any movies in the database, the seed initializer returns and no movies are added.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return;
}
Add the seed initializer
Update the Program.cs with the following highlighted code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
SeedData.Initialize(services);
}
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapStaticAssets();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
In the previous code, Program.cs has been modified to do the following:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection (DI) container.
- Call the
seedData.Initializemethod, passing to it the database context instance. - Dispose the context when the seed method completes. The using statement ensures the context is disposed.
The following exception occurs when Update-Database has not been run:
SqlException: Cannot open database "RazorPagesMovieContext-" requested by the login. The login failed.Login failed for user 'user name'.
Test the app
Delete all the records in the database so the seed method will run. Stop and start the app to seed the database. If the database isn't seeded, put a breakpoint on if (context.Movie.Any()) and step through the code.
The app shows the seeded data:
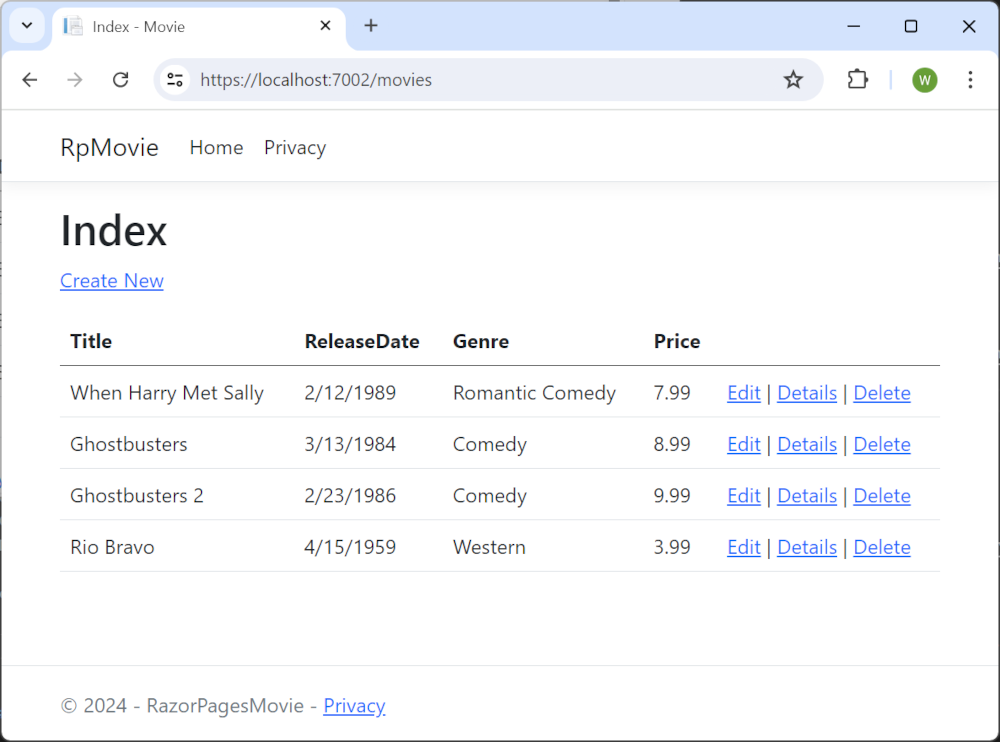
Next steps
The RazorPagesMovieContext object handles the task of connecting to the database and mapping Movie objects to database records. The database context is registered with the Dependency Injection container in Program.cs:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
The ASP.NET Core Configuration system reads the ConnectionString key. For local development, configuration gets the connection string from the appsettings.json file.
The generated connection string is similar to the following JSON:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RazorPagesMovieContext": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=RazorPagesMovieContext-bc;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Warning
This article uses a local database that doesn't require the user to be authenticated. Production apps should use the most secure authentication flow available. For more information on authentication for deployed test and production apps, see Secure authentication flows.
SQL Server Express LocalDB
LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express database engine that's targeted for program development. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB database creates *.mdf files in the C:\Users\<user>\ directory.
From the View menu, open SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX).
Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Designer: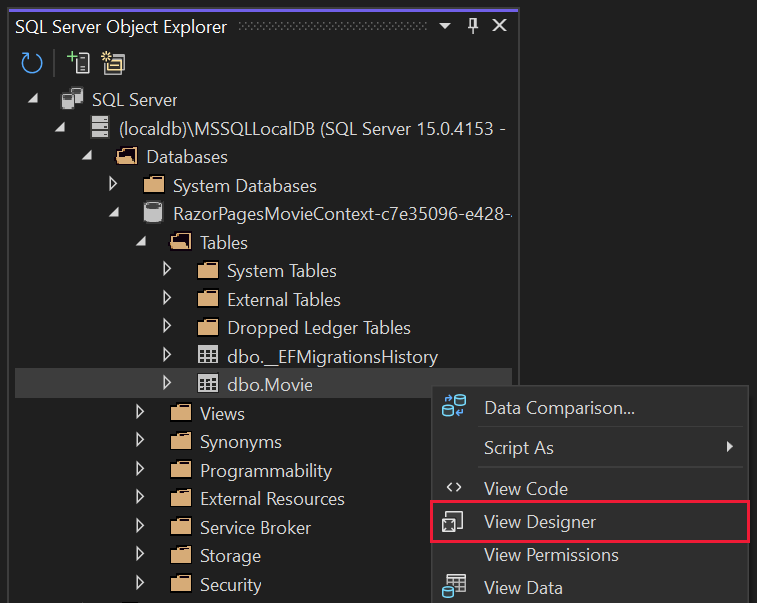
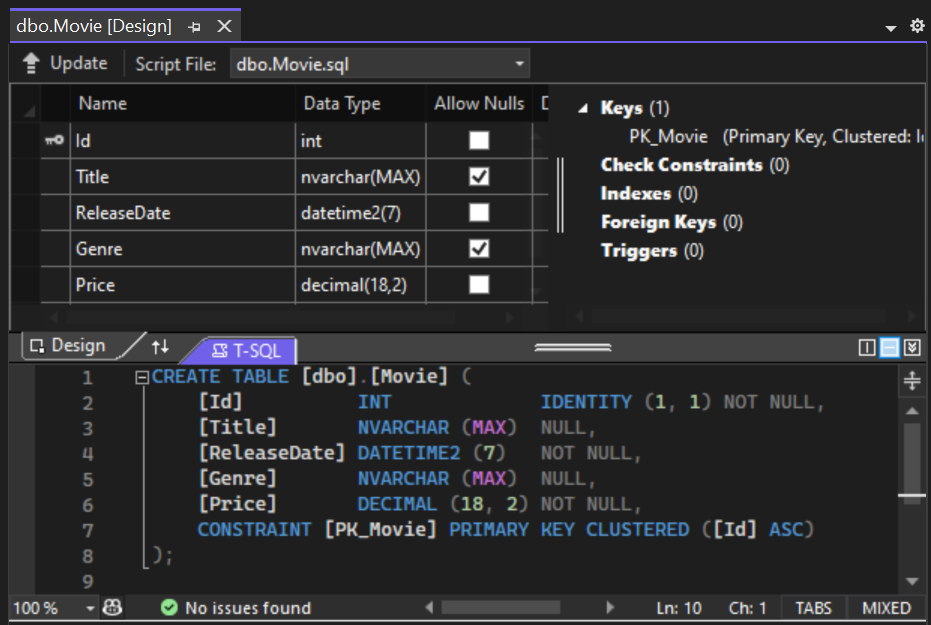
Note the key icon next to
ID. By default, EF creates a property namedIDfor the primary key.Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Data: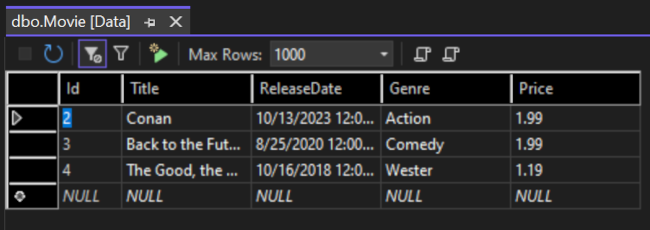
Seed the database
Create a new class named SeedData in the Models folder with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Models;
public static class SeedData
{
public static void Initialize(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var context = new RazorPagesMovieContext(
serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<
DbContextOptions<RazorPagesMovieContext>>()))
{
if (context == null || context.Movie == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("Null RazorPagesMovieContext");
}
// Look for any movies.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return; // DB has been seeded
}
context.Movie.AddRange(
new Movie
{
Title = "When Harry Met Sally",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1989-2-12"),
Genre = "Romantic Comedy",
Price = 7.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters ",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1984-3-13"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 8.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters 2",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1986-2-23"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 9.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Rio Bravo",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1959-4-15"),
Genre = "Western",
Price = 3.99M
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
If there are any movies in the database, the seed initializer returns and no movies are added.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return;
}
Add the seed initializer
Update the Program.cs with the following highlighted code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
SeedData.Initialize(services);
}
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
In the previous code, Program.cs has been modified to do the following:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection (DI) container.
- Call the
seedData.Initializemethod, passing to it the database context instance. - Dispose the context when the seed method completes. The using statement ensures the context is disposed.
The following exception occurs when Update-Database has not been run:
SqlException: Cannot open database "RazorPagesMovieContext-" requested by the login. The login failed.Login failed for user 'user name'.
Test the app
Delete all the records in the database so the seed method will run. Stop and start the app to seed the database. If the database isn't seeded, put a breakpoint on if (context.Movie.Any()) and step through the code.
The app shows the seeded data:
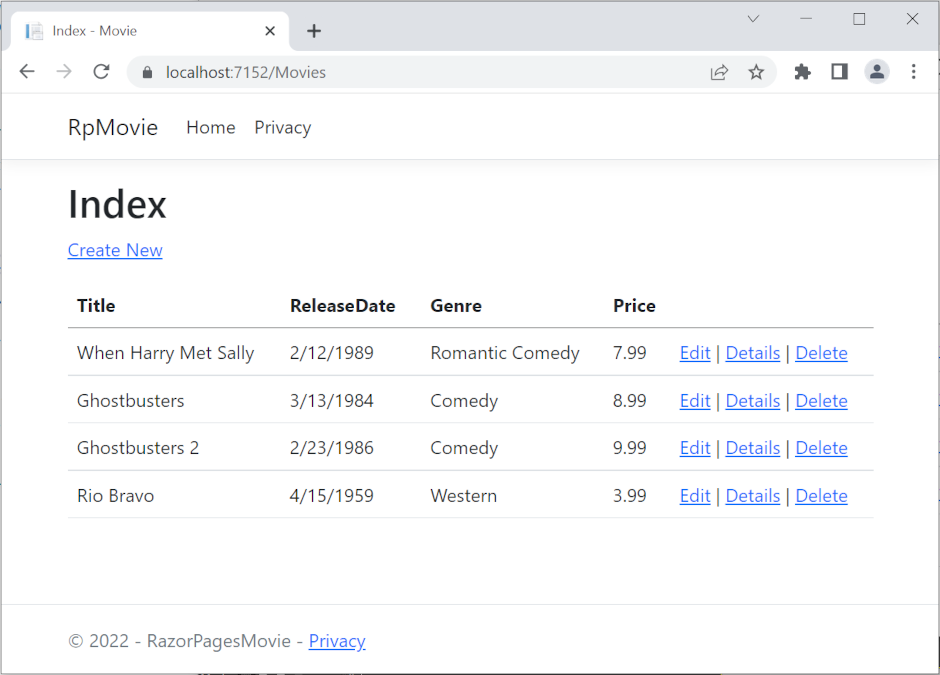
Next steps
The RazorPagesMovieContext object handles the task of connecting to the database and mapping Movie objects to database records. The database context is registered with the Dependency Injection container in Program.cs:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
The ASP.NET Core Configuration system reads the ConnectionString key. For local development, configuration gets the connection string from the appsettings.json file.
The generated connection string is similar to the following JSON:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RazorPagesMovieContext": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=RazorPagesMovieContext-bc;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Warning
This article uses a local database that doesn't require the user to be authenticated. Production apps should use the most secure authentication flow available. For more information on authentication for deployed test and production apps, see Secure authentication flows.
SQL Server Express LocalDB
LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express database engine that's targeted for program development. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB database creates *.mdf files in the C:\Users\<user>\ directory.
From the View menu, open SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX).
Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Designer: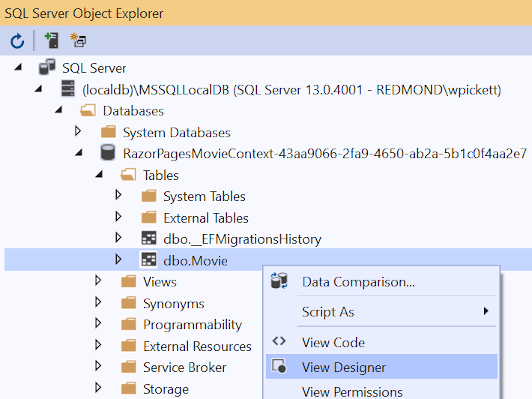
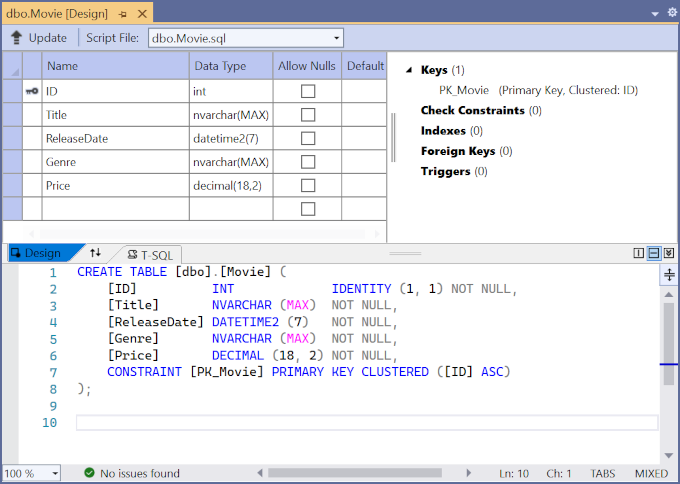
Note the key icon next to
ID. By default, EF creates a property namedIDfor the primary key.Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Data: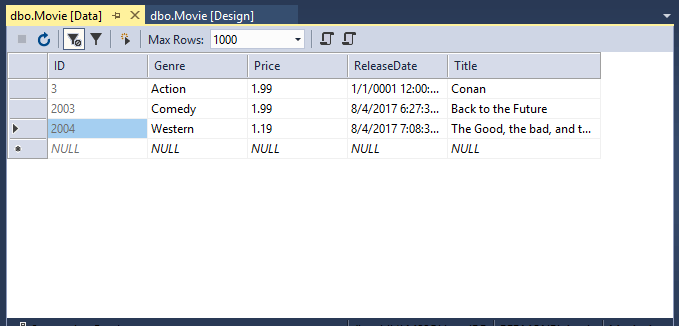
Seed the database
Create a new class named SeedData in the Models folder with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Models;
public static class SeedData
{
public static void Initialize(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var context = new RazorPagesMovieContext(
serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<
DbContextOptions<RazorPagesMovieContext>>()))
{
if (context == null || context.Movie == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("Null RazorPagesMovieContext");
}
// Look for any movies.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return; // DB has been seeded
}
context.Movie.AddRange(
new Movie
{
Title = "When Harry Met Sally",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1989-2-12"),
Genre = "Romantic Comedy",
Price = 7.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters ",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1984-3-13"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 8.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters 2",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1986-2-23"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 9.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Rio Bravo",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1959-4-15"),
Genre = "Western",
Price = 3.99M
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
If there are any movies in the database, the seed initializer returns and no movies are added.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return;
}
Add the seed initializer
Update the Program.cs with the following highlighted code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
SeedData.Initialize(services);
}
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
In the previous code, Program.cs has been modified to do the following:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection (DI) container.
- Call the
seedData.Initializemethod, passing to it the database context instance. - Dispose the context when the seed method completes. The using statement ensures the context is disposed.
The following exception occurs when Update-Database has not been run:
SqlException: Cannot open database "RazorPagesMovieContext-" requested by the login. The login failed.Login failed for user 'user name'.
Test the app
Delete all the records in the database so the seed method will run. Stop and start the app to seed the database. If the database isn't seeded, put a breakpoint on if (context.Movie.Any()) and step through the code.
The app shows the seeded data:

Next steps
The RazorPagesMovieContext object handles the task of connecting to the database and mapping Movie objects to database records. The database context is registered with the Dependency Injection container in Program.cs:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
The ASP.NET Core Configuration system reads the ConnectionString key. For local development, configuration gets the connection string from the appsettings.json file.
The generated connection string is similar to the following JSON:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RazorPagesMovieContext": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=RazorPagesMovieContext-bc;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Warning
This article uses a local database that doesn't require the user to be authenticated. Production apps should use the most secure authentication flow available. For more information on authentication for deployed test and production apps, see Secure authentication flows.
SQL Server Express LocalDB
LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express database engine that's targeted for program development. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB database creates *.mdf files in the C:\Users\<user>\ directory.
From the View menu, open SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX).

Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Designer:

Note the key icon next to
ID. By default, EF creates a property namedIDfor the primary key.Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Data:
Seed the database
Create a new class named SeedData in the Models folder with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Models
{
public static class SeedData
{
public static void Initialize(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var context = new RazorPagesMovieContext(
serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<
DbContextOptions<RazorPagesMovieContext>>()))
{
if (context == null || context.Movie == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("Null RazorPagesMovieContext");
}
// Look for any movies.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return; // DB has been seeded
}
context.Movie.AddRange(
new Movie
{
Title = "When Harry Met Sally",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1989-2-12"),
Genre = "Romantic Comedy",
Price = 7.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters ",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1984-3-13"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 8.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters 2",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1986-2-23"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 9.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Rio Bravo",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1959-4-15"),
Genre = "Western",
Price = 3.99M
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
}
If there are any movies in the database, the seed initializer returns and no movies are added.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return;
}
Add the seed initializer
Update the Program.cs with the following highlighted code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext") ?? throw new InvalidOperationException("Connection string 'RazorPagesMovieContext' not found.")));
var app = builder.Build();
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
SeedData.Initialize(services);
}
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.Run();
In the previous code, Program.cs has been modified to do the following:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection (DI) container.
- Call the
seedData.Initializemethod, passing to it the database context instance. - Dispose the context when the seed method completes. The using statement ensures the context is disposed.
The following exception occurs when Update-Database has not been run:
SqlException: Cannot open database "RazorPagesMovieContext-" requested by the login. The login failed.Login failed for user 'user name'.
Test the app
Delete all the records in the database so the seed method will run. Stop and start the app to seed the database. If the database isn't seeded, put a breakpoint on if (context.Movie.Any()) and step through the code.
The app shows the seeded data:

Next steps
View or download sample code (how to download).
The RazorPagesMovieContext object handles the task of connecting to the database and mapping Movie objects to database records. The database context is registered with the Dependency Injection container in the ConfigureServices method in Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext")));
}
The ASP.NET Core Configuration system reads the ConnectionString key. For local development, configuration gets the connection string from the appsettings.json file.
The generated connection string is similar to the following JSON:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RazorPagesMovieContext": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=RazorPagesMovieContext-bc;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Warning
This article uses a local database that doesn't require the user to be authenticated. Production apps should use the most secure authentication flow available. For more information on authentication for deployed test and production apps, see Secure authentication flows.
SQL Server Express LocalDB
LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express database engine that's targeted for program development. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB database creates *.mdf files in the C:\Users\<user>\ directory.
From the View menu, open SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX).

Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Designer:
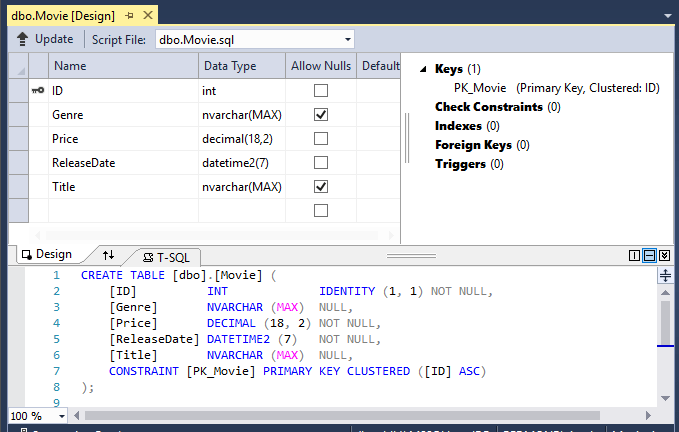
Note the key icon next to
ID. By default, EF creates a property namedIDfor the primary key.Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Data:
Seed the database
Create a new class named SeedData in the Models folder with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Models
{
public static class SeedData
{
public static void Initialize(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var context = new RazorPagesMovieContext(
serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<
DbContextOptions<RazorPagesMovieContext>>()))
{
// Look for any movies.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return; // DB has been seeded
}
context.Movie.AddRange(
new Movie
{
Title = "When Harry Met Sally",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1989-2-12"),
Genre = "Romantic Comedy",
Price = 7.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters ",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1984-3-13"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 8.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters 2",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1986-2-23"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 9.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Rio Bravo",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1959-4-15"),
Genre = "Western",
Price = 3.99M
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
}
If there are any movies in the database, the seed initializer returns and no movies are added.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return;
}
Add the seed initializer
Replace the contents of the Program.cs with the following code:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
using System;
namespace RazorPagesMovie
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build();
using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
try
{
SeedData.Initialize(services);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>();
logger.LogError(ex, "An error occurred seeding the DB.");
}
}
host.Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
}
}
In the previous code, the Main method has been modified to do the following:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection container.
- Call the
seedData.Initializemethod, passing to it the database context instance. - Dispose the context when the seed method completes. The using statement ensures the context is disposed.
The following exception occurs when Update-Database has not been run:
SqlException: Cannot open database "RazorPagesMovieContext-" requested by the login. The login failed.Login failed for user 'user name'.
Test the app
Delete all the records in the database. Use the delete links in the browser or from SSOX
Force the app to initialize by calling the methods in the
Startupclass, so the seed method runs. To force initialization, IIS Express must be stopped and restarted. Stop and restart IIS with any of the following approaches:Right-click the IIS Express system tray icon in the notification area and select Exit or Stop Site:

If the app is running in non-debug mode, press F5 to run in debug mode.
If the app in debug mode, stop the debugger and press F5.
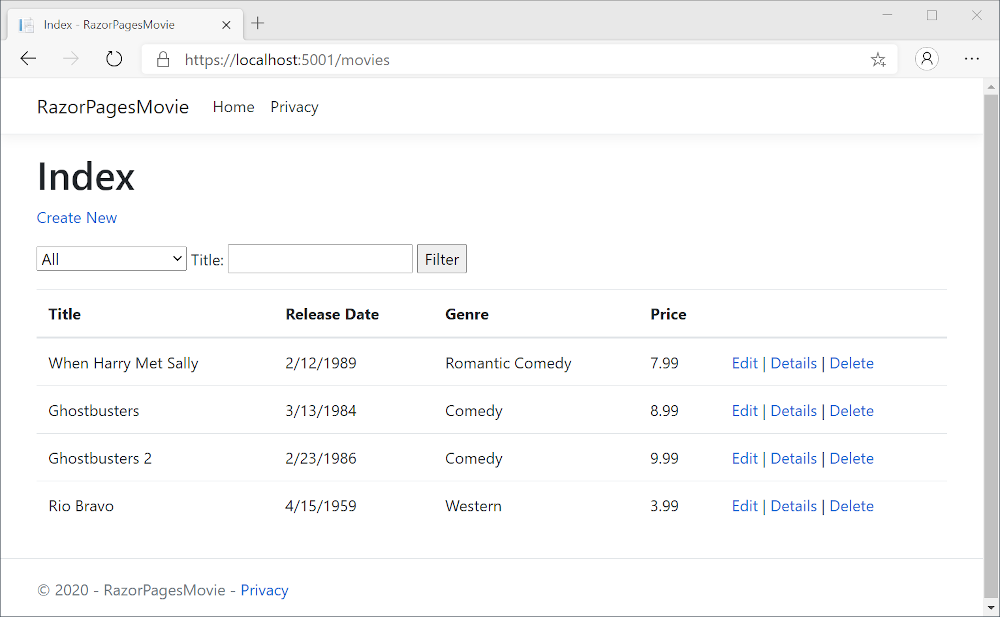
The app shows the seeded data:
Next steps
View or download sample code (how to download).
The RazorPagesMovieContext object handles the task of connecting to the database and mapping Movie objects to database records. The database context is registered with the Dependency Injection container in the ConfigureServices method in Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddDbContext<RazorPagesMovieContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("RazorPagesMovieContext")));
}
The ASP.NET Core Configuration system reads the ConnectionString key. For local development, configuration gets the connection string from the appsettings.json file.
The generated connection string will be similar to the following:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"RazorPagesMovieContext": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=RazorPagesMovieContext-bc;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
Warning
This article uses a local database that doesn't require the user to be authenticated. Production apps should use the most secure authentication flow available. For more information on authentication for deployed test and production apps, see Secure authentication flows.
SQL Server Express LocalDB
LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express database engine that's targeted for program development. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB database creates *.mdf files in the C:\Users\<user>\ directory.
From the View menu, open SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX).
Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Designer: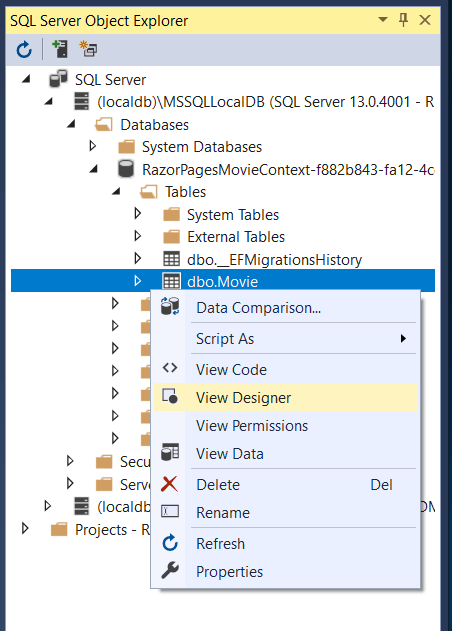

Note the key icon next to ID. By default, EF creates a property named ID for the primary key.
Right-click on the
Movietable and select View Data:
Seed the database
Create a new class named SeedData in the Models folder with the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using RazorPagesMovie.Data;
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace RazorPagesMovie.Models
{
public static class SeedData
{
public static void Initialize(IServiceProvider serviceProvider)
{
using (var context = new RazorPagesMovieContext(
serviceProvider.GetRequiredService<
DbContextOptions<RazorPagesMovieContext>>()))
{
// Look for any movies.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return; // DB has been seeded
}
context.Movie.AddRange(
new Movie
{
Title = "When Harry Met Sally",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1989-2-12"),
Genre = "Romantic Comedy",
Price = 7.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters ",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1984-3-13"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 8.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Ghostbusters 2",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1986-2-23"),
Genre = "Comedy",
Price = 9.99M
},
new Movie
{
Title = "Rio Bravo",
ReleaseDate = DateTime.Parse("1959-4-15"),
Genre = "Western",
Price = 3.99M
}
);
context.SaveChanges();
}
}
}
}
If there are any movies in the database, the seed initializer returns and no movies are added.
if (context.Movie.Any())
{
return;
}
Add the seed initializer
Replace the contents of the Program.cs with the following code:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
using System;
namespace RazorPagesMovie
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build();
using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
try
{
SeedData.Initialize(services);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>();
logger.LogError(ex, "An error occurred seeding the DB.");
}
}
host.Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
}
}
In the previous code, the Main method has been modified to do the following:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection container.
- Call the
seedData.Initializemethod, passing to it the database context instance. - Dispose the context when the seed method completes. The using statement ensures the context is disposed.
The following exception occurs when Update-Database has not been run:
SqlException: Cannot open database "RazorPagesMovieContext-" requested by the login. The login failed.Login failed for user 'user name'.
Test the app
Delete all the records in the database. Use the delete links in the browser or from SSOX.
Force the app to initialize by calling the methods in the
Startupclass, so the seed method runs. To force initialization, IIS Express must be stopped and restarted. Stop and restart IIS with any of the following approaches:Right-click the IIS Express system tray icon in the notification area and tap Exit or Stop Site:


- If the app is running in non-debug mode, press F5 to run in debug mode.
- If the app in debug mode, stop the debugger and press F5.
The app shows the seeded data:
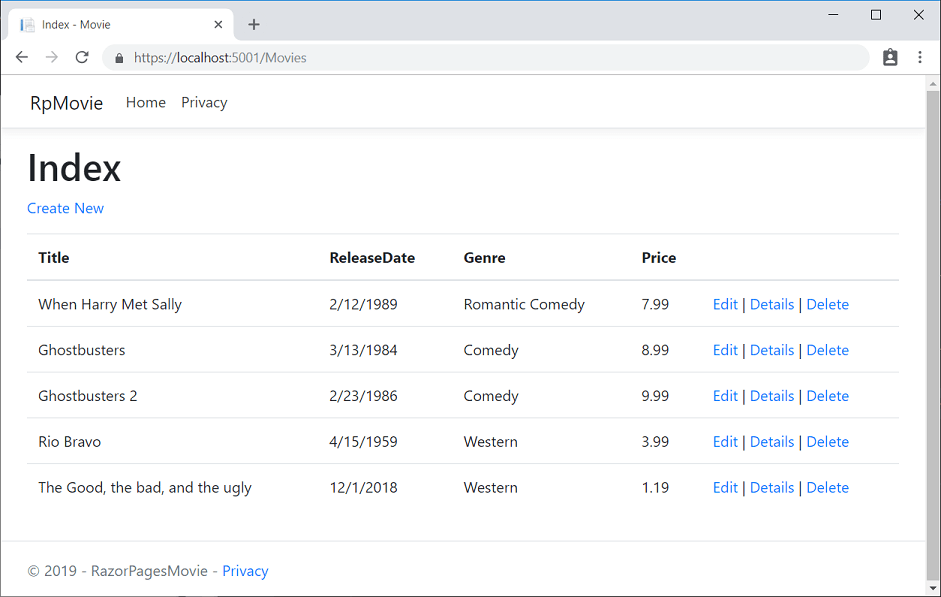
Next steps
ASP.NET Core