Sorting, paging, and filtering data with model binding and web forms
This tutorial series demonstrates basic aspects of using model binding with an ASP.NET Web Forms project. Model binding makes data interaction more straight-forward than dealing with data source objects (such as ObjectDataSource or SqlDataSource). This series starts with introductory material and moves to more advanced concepts in later tutorials.
This tutorial shows how to add sorting, paging, and filtering of the data through model binding.
This tutorial builds on the project created in the first part of the series.
You can download the complete project in C# or VB. The downloadable code works with either Visual Studio 2012 or Visual Studio 2013. It uses the Visual Studio 2012 template, which is slightly different than the Visual Studio 2013 template shown in this tutorial.
What you'll build
In this tutorial, you'll:
- Enable sorting and paging of the data
- Enable filtering of the data based on a selection by the user
Add sorting
Enabling sorting in the GridView is very easy. In the Student.aspx file, simply set AllowSorting to true in the GridView. You do not need to set a SortExpression value for each column as the DataField is automatically used. The GridView modifies the query to include ordering the data by the selected value. The highlighted code below shows the addition you need to make to enable sorting.
<asp:GridView runat="server" ID="studentsGrid"
ItemType="ContosoUniversity.Models.Student" DataKeyNames="StudentID"
SelectMethod="studentsGrid_GetData"
UpdateMethod="studentsGrid_UpdateItem" DeleteMethod="studentsGrid_DeleteItem"
AllowSorting="true"
AutoGenerateEditButton="true" AutoGenerateDeleteButton="true"
AutoGenerateColumns="false">
<Columns>
<asp:DynamicField DataField="StudentID" />
<asp:DynamicField DataField="LastName" />
<asp:DynamicField DataField="FirstName" />
<asp:DynamicField DataField="Year" />
<asp:TemplateField HeaderText="Total Credits">
<ItemTemplate>
<asp:Label Text="<%# Item.Enrollments.Sum(en => en.Course.Credits) %>"
runat="server" />
</ItemTemplate>
</asp:TemplateField>
</Columns>
</asp:GridView>
Run the web application, and test sorting student records by the values in different columns.
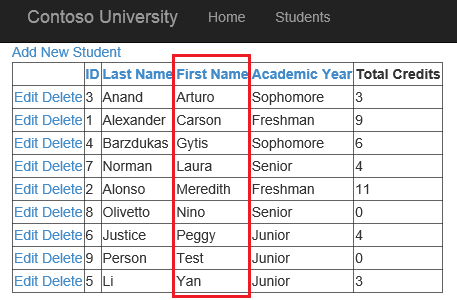
Add paging
Enabling paging is also very easy. In the GridView, set the AllowPaging property to true and set the PageSize property to the number of records you wish to display on each page. In this tutorial, you can set it to 4.
<asp:GridView runat="server" ID="studentsGrid"
ItemType="ContosoUniversity.Models.Student" DataKeyNames="StudentID"
SelectMethod="studentsGrid_GetData"
UpdateMethod="studentsGrid_UpdateItem" DeleteMethod="studentsGrid_DeleteItem"
AllowSorting="true" AllowPaging="true" PageSize="4"
AutoGenerateEditButton="true" AutoGenerateDeleteButton="true"
AutoGenerateColumns="false">
Run the web application, and notice that now the records are divided over multiple pages with no more than 4 records displayed on a single page.
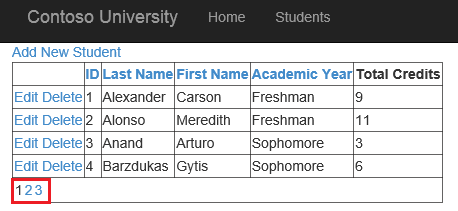
Deferred query execution improves the application efficiency. Instead of retrieving the entire data set, the GridView modifies the query to retrieve only the records for the current page.
Filter records by user selection
Model binding adds several attributes which enable you to designate how to set the value for a parameter in a model binding method. These attributes are in the System.Web.ModelBinding namespace. They include:
- Control
- Cookie
- Form
- Profile
- QueryString
- RouteData
- Session
- UserProfile
- ViewState
In this tutorial, you will use a control's value to filter which records are displayed in the GridView. You will add the Control attribute to the query method you had created earlier. In a later tutorial, you will apply the QueryString attribute to a parameter to specify that the parameter value comes from a query string value.
First, above the ValidationSummary, add a drop down list for filtering which students are shown.
<asp:HyperLink runat="server" NavigateUrl="~/AddStudent" Text="Add New Student" />
<br /><br />
<asp:Label runat="server" Text="Show:" />
<asp:DropDownList runat="server" AutoPostBack="true" ID="DisplayYear">
<asp:ListItem Text="All" Value="" />
<asp:ListItem Text="Freshman" />
<asp:ListItem Text="Sophomore" />
<asp:ListItem Text="Junior" />
<asp:ListItem Text="Senior" />
</asp:DropDownList>
<asp:ValidationSummary runat="server" ShowModelStateErrors="true"/>
In the code-behind file, modify the select method to receive a value from the control, and set the name of the parameter to the name of the control that provides the value.
You must add a using statement for the System.Web.ModelBinding namespace to resolve the Control attribute.
using System.Web.ModelBinding;
The following code shows the select method re-worked to filter the returned data based on the value of the drop down list. Adding a control attribute before a parameter specifies that the value for this parameter comes from a control with the same name.
public IQueryable<Student> studentsGrid_GetData([Control] AcademicYear? displayYear)
{
SchoolContext db = new SchoolContext();
var query = db.Students.Include(s => s.Enrollments.Select(e => e.Course));
if (displayYear != null)
{
query = query.Where(s => s.Year == displayYear);
}
return query;
}
Run the web application and select different values from the drop down list to filter the list of students.
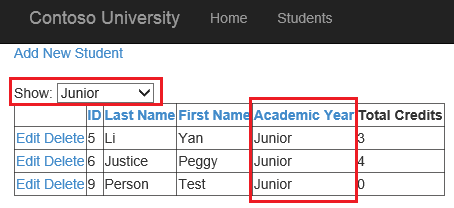
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you enabled sorting and paging of the data. You also enabled filtering the data by the value of a control.
In the next tutorial you will enhance the UI by integrating a JQuery UI widget into the dynamic data template.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for