Deploy an Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2 via Azure Resource Manager deployment template
Applies to: Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2
This article details how to use an Azure Resource Manager template in the Azure portal to deploy an Azure Stack HCI in your environment. The article also contains the prerequisites and the preparation steps required to begin the deployment.
Important
Azure Resource Manager template deployment of Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2 systems is targeted for deployments-at-scale. The intended audience for this deployment is IT administrators who have experience deploying Azure Stack HCI clusters. We recommend that you deploy a version 23H2 system via the Azure portal first, and then perform subsequent deployments via the Resource Manager template.
Prerequisites
- Completion of Register your servers with Azure Arc and assign deployment permissions. Make sure that:
- All the mandatory extensions are installed successfully. The mandatory extensions include: Azure Edge Lifecycle Manager, Azure Edge Device Management, Telemetry and Diagnostics, and Azure Edge Remote Support.
- All servers are running the same version of OS.
- All the servers have the same network adapter configuration.
Step 1: Prepare Azure resources
Follow these steps to prepare the Azure resources you need for the deployment:
Create a service principal and client secret
To authenticate your cluster, you need to create a service principal and a corresponding Client secret for Arc Resource Bridge (ARB).
Create a service principal for ARB
Follow the steps in Create a Microsoft Entra application and service principal that can access resources via Azure portal to create the service principal and assign the roles. Alternatively, use the PowerShell procedure to Create an Azure service principal with Azure PowerShell.
The steps are also summarized here:
Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Cloud Application Administrator. Browse to Identity > Applications > App registrations then select New registration.
Provide a Name for the application, select a Supported account type, and then select Register.
Once the service principal is created, go to the Enterprise applications page. Search for and select the SPN you created.
Under properties, copy the Application (client) ID and the Object ID for this service principal.
You use the Application (client) ID against the
arbDeploymentAppIDparameter and the Object ID against thearbDeploymentSPNObjectIDparameter in the Resource Manager template.
Create a client secret for ARB service principal
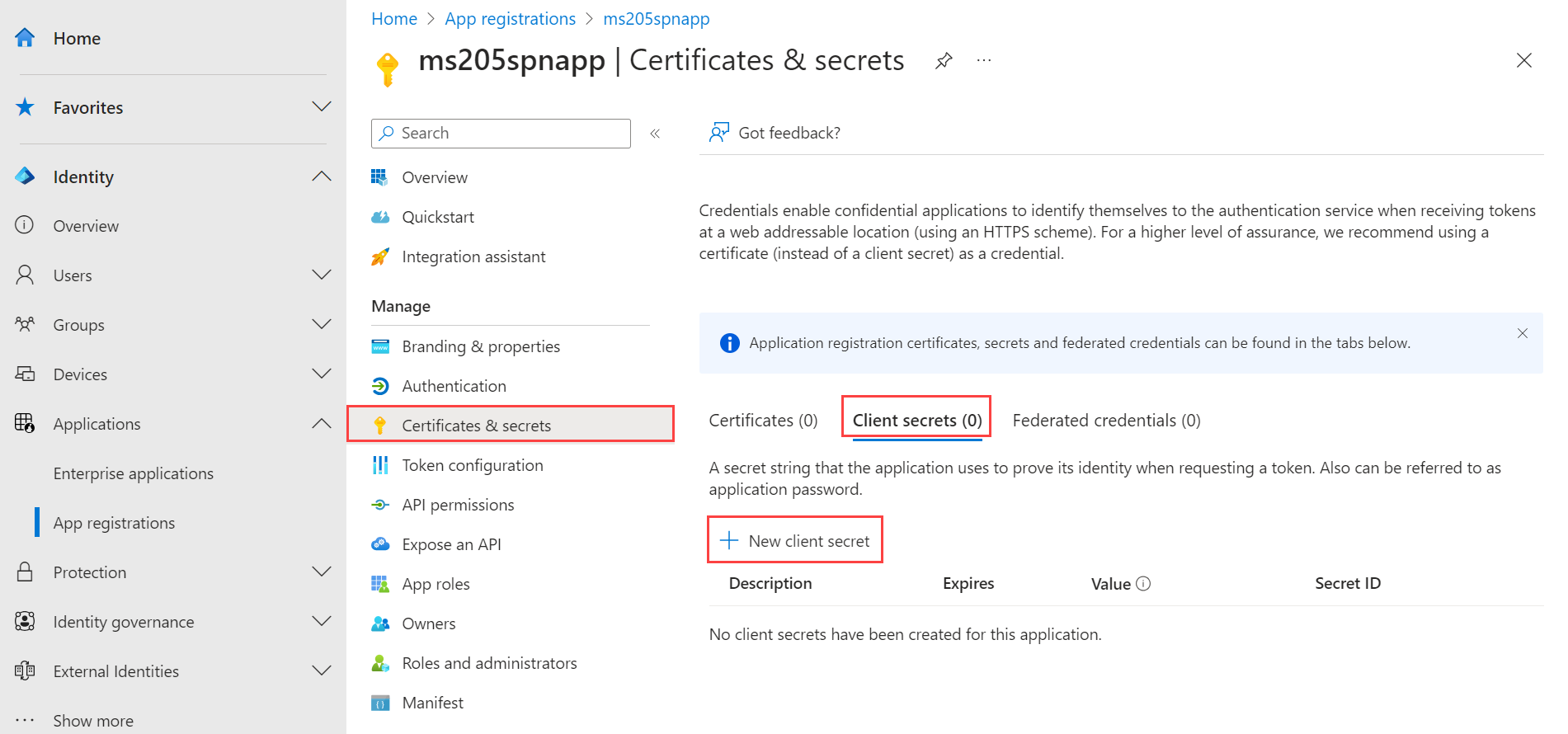
Go to the application registration that you created and browse to Certificates & secrets > Client secrets.
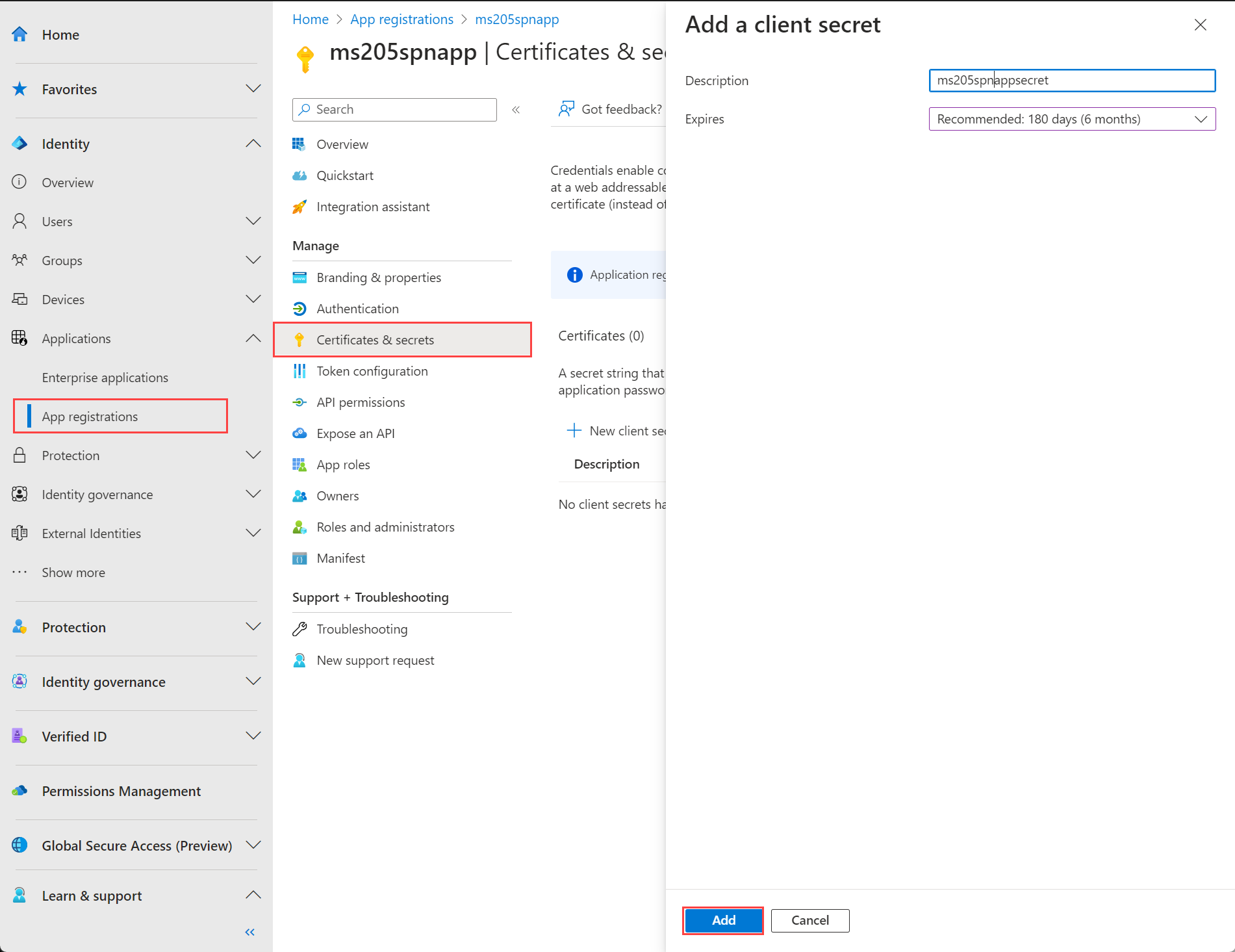
Select + New client secret.
Add a Description for the client secret and provide a timeframe when it Expires. Select Add.
Copy the client secret value as you use it later.
Note
For the application client ID, you will need it's secret value. Client secret values can't be viewed except for immediately after creation. Be sure to save this value when created before leaving the page.
You use the client secret value against the
arbDeploymentAppSecretparameter in the Resource Manager template.
Get the object ID for Azure Stack HCI Resource Provider
This object ID for the Azure Stack HCI RP is unique per Azure tenant.
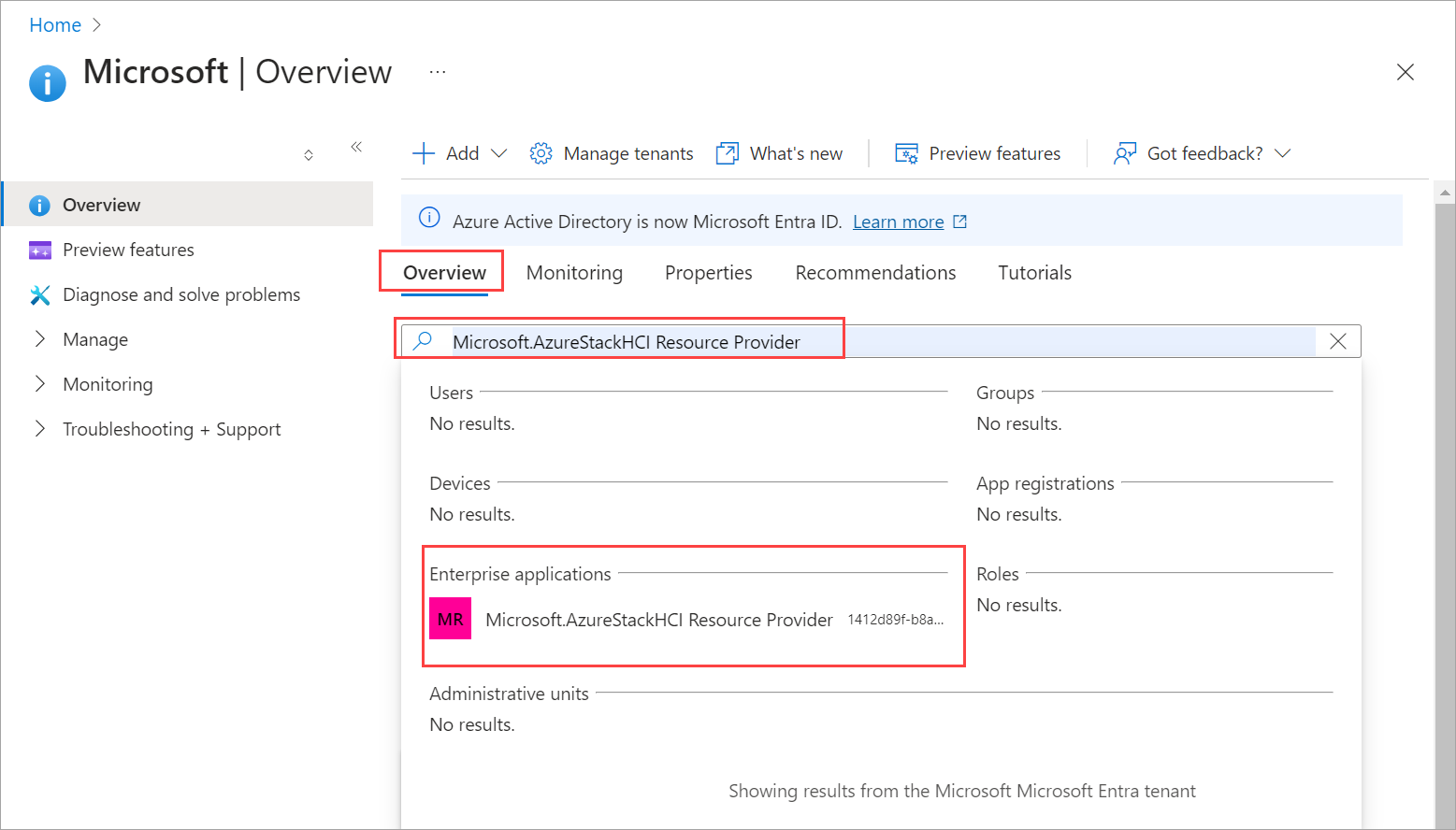
In the Azure portal, search for and go to Microsoft Entra ID.
Go to the Overview tab and search for Microsoft.AzureStackHCI Resource Provider.
Select the SPN that is listed and copy the Object ID.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to get the object ID of the Azure Stack HCI RP service principal. Run the following command in PowerShell:
Get-AzADServicePrincipal -DisplayName "Microsoft.AzureStackHCI Resource Provider"You use the Object ID against the
hciResourceProviderObjectIDparameter in the Resource Manager template.
Step 2: Deploy using Azure Resource Manager template
A Resource Manager template creates and assigns all the resource permissions required for deployment.
With all the prerequisite and preparation steps complete, you're ready to deploy using a known good and tested Resource Manager deployment template and corresponding parameters JSON file. Use the parameters contained in the JSON file to fill out all values, including the values generated previously.
Important
In this release, make sure that all the parameters contained in the JSON value are filled out including the ones that have a null value. If there are null values, then those need to be populated or the validation fails.
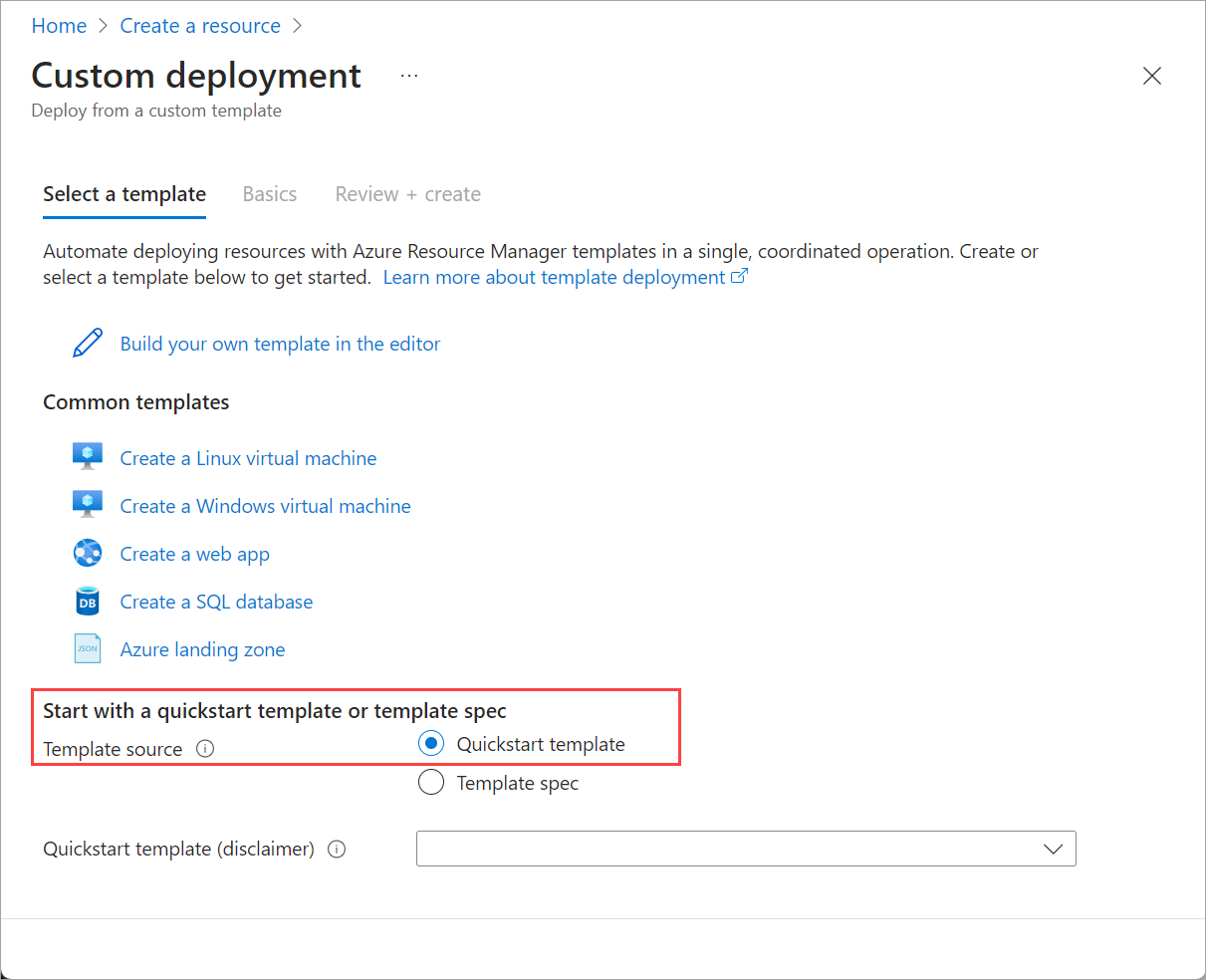
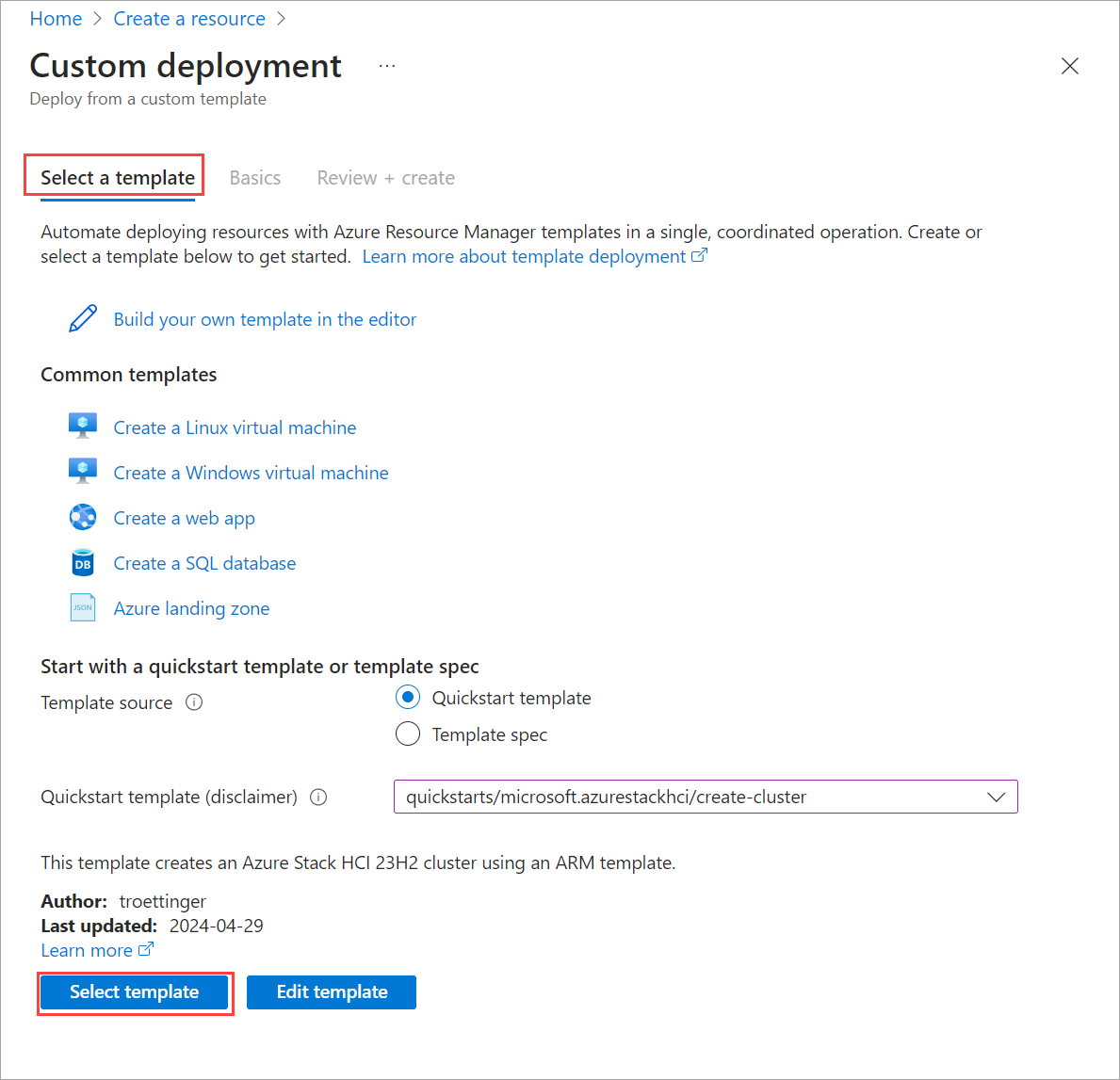
In the Azure portal, go to Home and select + Create a resource.
Select Create under Template deployment (deploy using custom templates).
Near the bottom of the page, find Start with a quickstart template or template spec section. Select Quickstart template option.
Use the Quickstart template (disclaimer) field to filter for the appropriate template. Type azurestackhci/create-cluster for the filter.
When finished, Select template.
On the Basics tab, you see the Custom deployment page. You can select the various parameters through the dropdown list or select Edit parameters.
Edit parameters such as network intent or storage network intent. Once the parameters are all filled out, Save the parameters file.
Select the appropriate resource group for your environment.
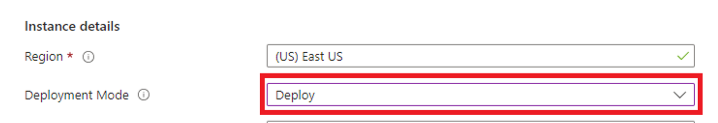
Scroll to the bottom, and confirm that Deployment Mode = Validate.
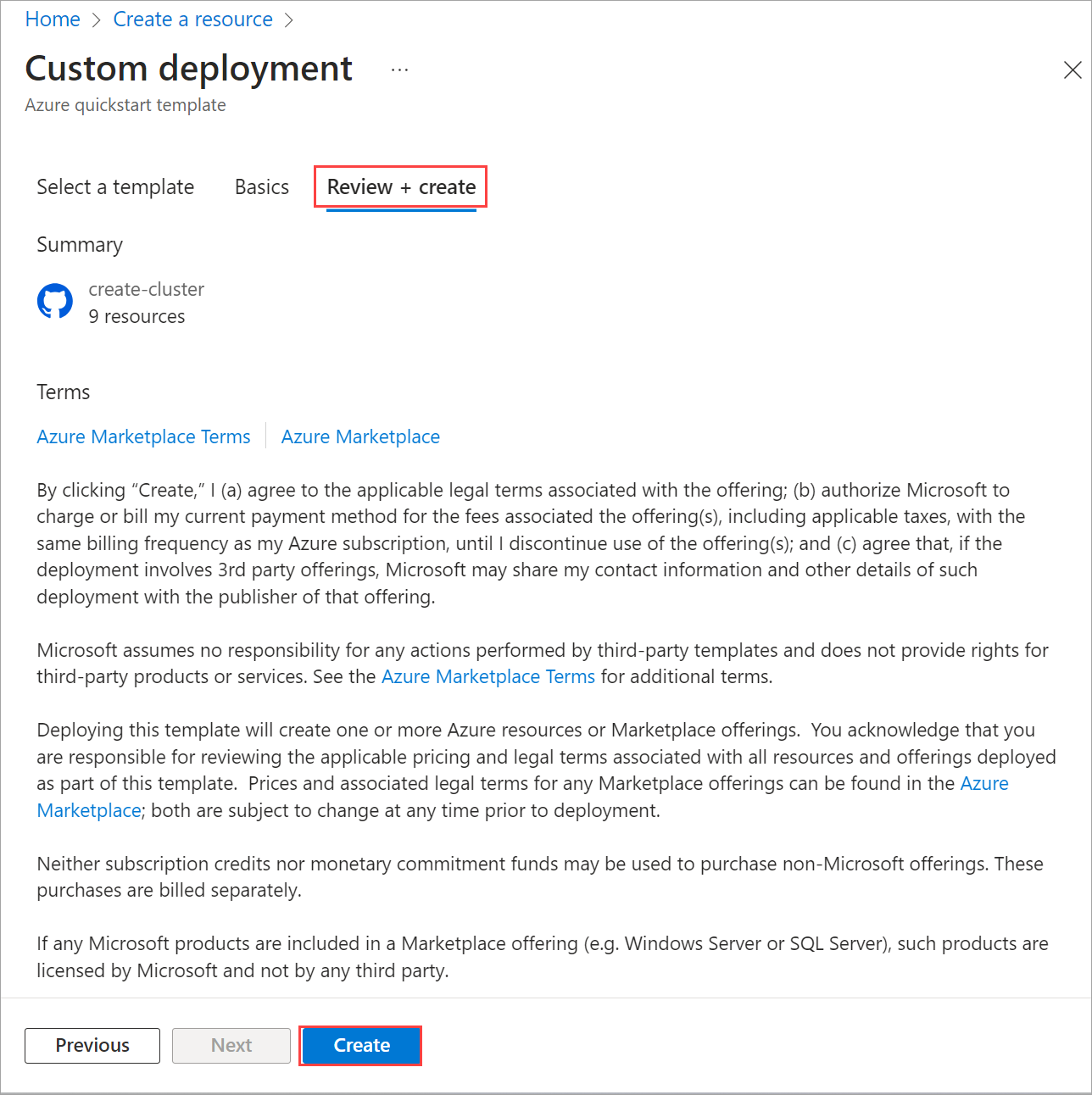
Select Review + create.
On the Review + Create tab, select Create. This creates the remaining prerequisite resources and validates the deployment. Validation takes about 10 minutes to complete.
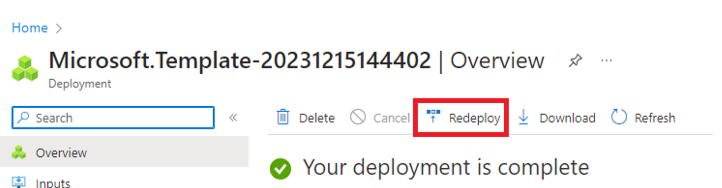
Once validation is complete, select Redeploy.
On the Custom deployment screen, select Edit parameters. Load up the previously saved parameters and select Save.
At the bottom of the workspace, change the final value in the JSON from Validate to Deploy, where Deployment Mode = Deploy.
Verify that all the fields for the Resource Manager deployment template are filled in by the Parameters JSON.
Select the appropriate resource group for your environment.
Scroll to the bottom, and confirm that Deployment Mode = Deploy.
Select Review + create.
Select Create. The deployment begins, using the existing prerequisite resources that were created during the Validate step.
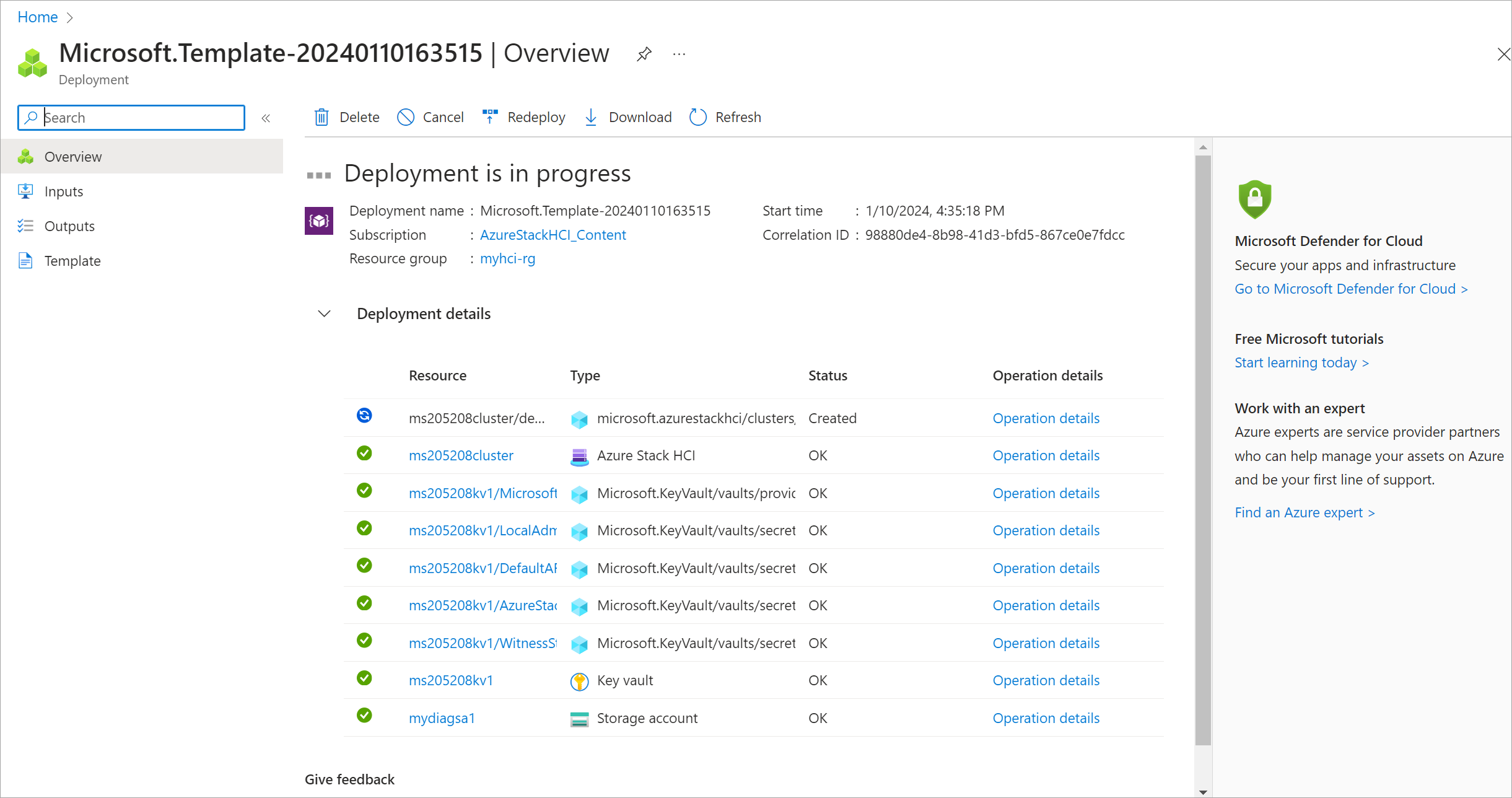
The Deployment screen cycles on the Cluster resource during deployment.
Once deployment initiates, there's a limited Environment Checker run, a full Environment Checker run, and cloud deployment starts. After a few minutes, you can monitor deployment in the portal.
In a new browser window, navigate to the resource group for your environment. Select the cluster resource.
Select Deployments.
Refresh and watch the deployment progress from the first server (also known as the seed server and is the first server where you deployed the cluster). Deployment takes between 2.5 and 3 hours. Several steps take 40-50 minutes or more.
The step in deployment that takes the longest is Deploy Moc and ARB Stack. This step takes 40-45 minutes.
Once complete, the task at the top updates with status and end time.
You can also check out this community sourced template to Deploy an Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2 cluster using Bicep.
Troubleshoot deployment issues
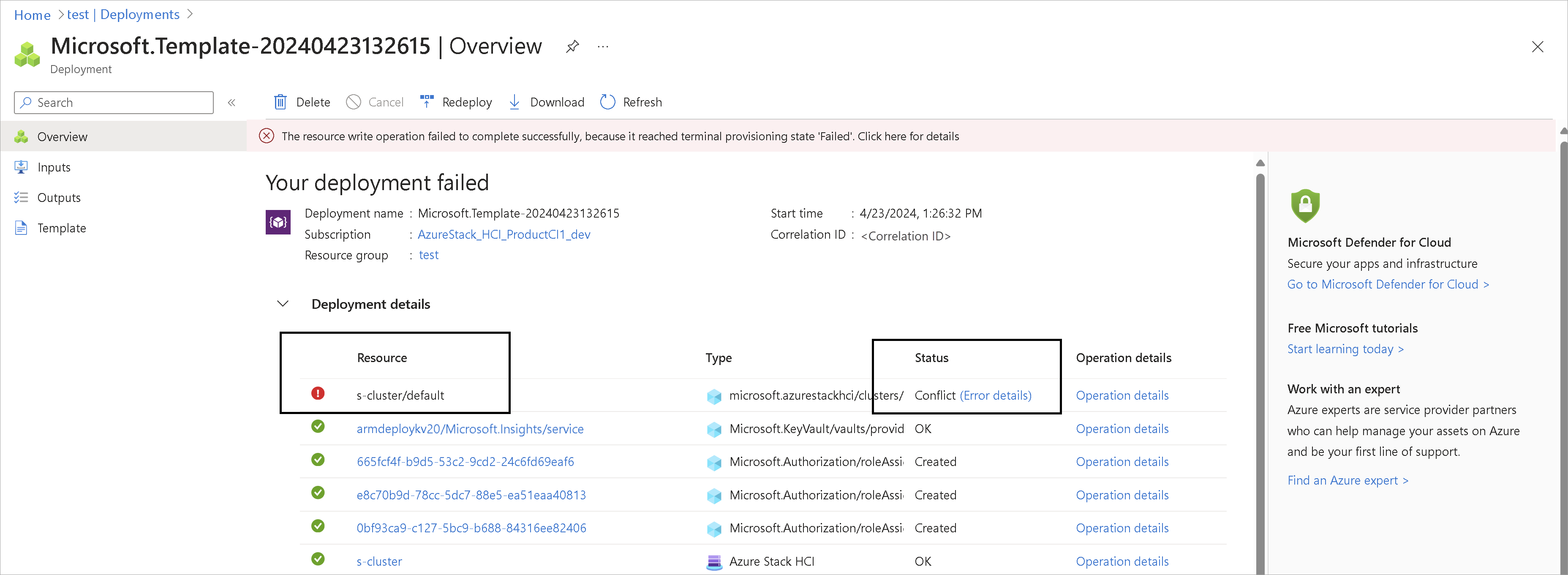
If the deployment fails, you should see an error message on the deployments page.
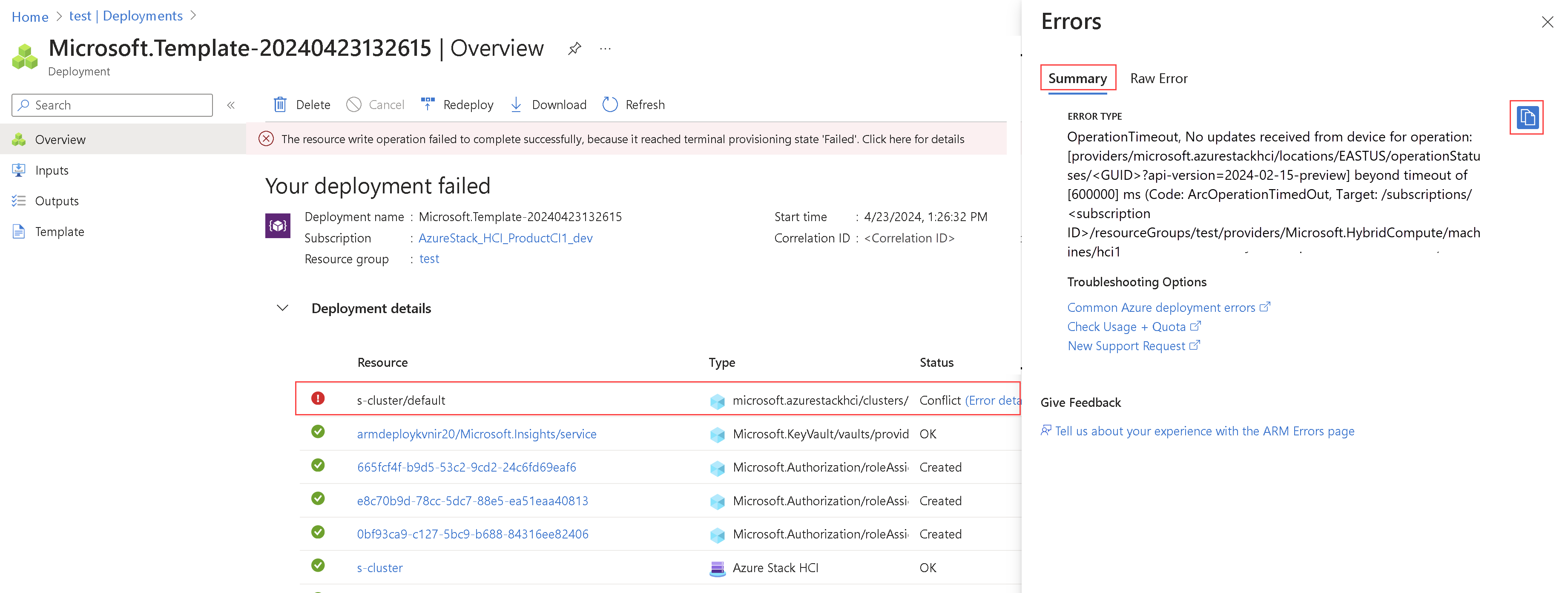
On the Deployment details, select the error details.
Copy the error message from the Errors blade. You can provide this error message to Microsoft support for further assistance.
Known issues for ARM template deployment
This section contains known issues and workarounds for ARM template deployment.
Role assignment already exists
Issue: In this release, you may see Role assignment already exists error. This error occurs if the Azure Stack HCI cluster deployment was attempted from the portal first and the same resource group was used for ARM template deployment. You see this error on the Overview > Deployment details page for the applicable resource. This error indicates that an equivalent role assignment was already done by another identity for the same resource group scope and the ARM template deployment is unable to perform role assignment.
Workaround: Although these errors can be disregarded and deployment can proceed via the ARM template, we strongly recommend that you don't interchange deployment modes between the portal and ARM template.
Tenant ID, application ID, principal ID, and scope aren't allowed to be updated
Issue: Role assignment fails with error Tenant ID, application ID, principal ID, and scope aren't allowed to be updated. You see this error on the Overview > Deployment details page for the applicable resource. This error could show up when there are zombie role assignments in the same resource group. For example, when a prior deployment was performed and the resources corresponding to that deployment were deleted but the role assignment resources were left around.
Workaround: To identify the zombie role assignments, go to Access control (IAM) > Role assignments > Type : Unknown tab. These assignments are listed as *Identity not found. Unable to find identity. Delete such role assignments and then retry ARM template deployment.
License sync issue
Issue: In this release, you may encounter license sync issue when using ARM template deployment.
Workaround: After the cluster completes the validation stage, we recommend that you don't initiate another ARM template deployment in Validate mode if your cluster is in Deployment failed state. Starting another deployment resets the cluster properties, which could result in license sync issues.