Optimize storage with ReFS deduplication and compression in Azure Stack HCI
Applies to: Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2
This article describes the Resilient File System (ReFS) deduplication and compression feature and how to use this feature in Azure Stack HCI to optimize storage.
What is ReFS deduplication and compression?
ReFS deduplication and compression is a storage optimization feature designed specifically for active workloads, such as Azure virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) on Azure Stack HCI. This feature helps optimize storage usage and reduce storage cost.
This feature uses ReFS block cloning to reduce data movement and enable metadata only operations. The feature operates at the data block level and uses fixed block size depending on the cluster size. The compression engine generates a heatmap to identify if a block should be eligible for compression, optimizing for CPU usage.
You can run ReFS deduplication and compression as a one-time job or automate it with scheduled jobs. This feature works with both all-flash and hybrid systems and supports various resiliency settings, such as two-way mirror, nested two-way mirror, three-way mirror, and mirror accelerated parity.
Benefits
Here are the benefits of using ReFS deduplication and compression:
- Storage savings for active workloads. Designed for active workloads, such as VDI, ensuring efficient performance in demanding environments.
- Multiple modes. Operates in three modes: deduplication only, compression only, and deduplication and compression (default mode), allowing optimization based on your needs.
- Incremental deduplication. Deduplicates only new or changed data as opposed to scanning the entire volume every time, optimizing job duration and reducing impact on system performance.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that the following prerequisites are completed:
- You have access to an Azure Stack HCI cluster that is deployed and registered.
- You have the cluster shared volume (CSV) created on the cluster and you have access to it.
- The CSV doesn't have the Windows Data Deduplication feature enabled already.
Use ReFS deduplication and compression
You can use ReFS deduplication and compression via Windows Admin Center or PowerShell. PowerShell allows both manual and automated jobs, whereas Windows Admin Center supports only scheduled jobs. Regardless of the method, you can customize job settings and utilize file change tracking for quicker subsequent runs.
Enable and run ReFS deduplication and compression
In Windows Admin Center, you can create a schedule for ReFS deduplication and compression to run on an existing volume or a new volume during volume creation.
Follow these steps to enable ReFS deduplication and compression via Windows Admin Center and set a schedule when it should run:
Connect to a cluster, and then on the Tools pane on the left, select Volumes.
On the Volumes page, select the Inventory tab, select the appropriate volume, and then select Settings. To turn on ReFS deduplication and compression for a new volume, select + Create.
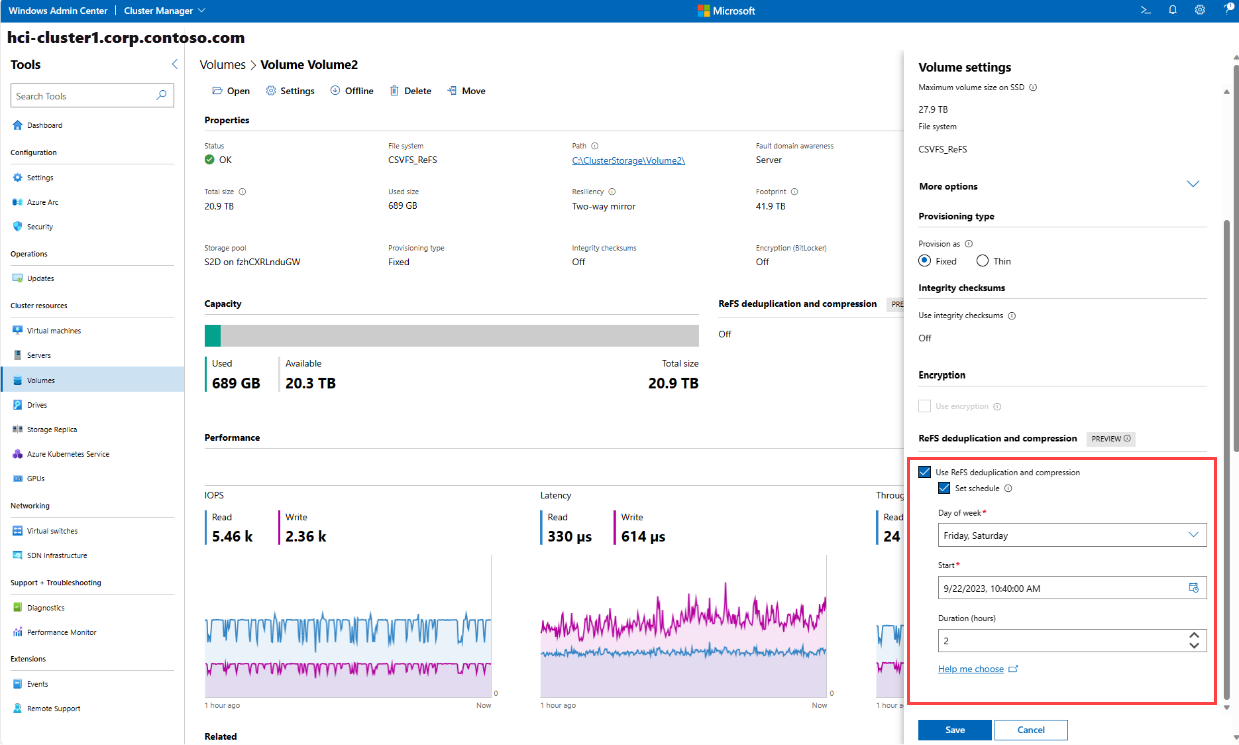
On the Volume settings pane on the right, under More options dropdown, select the Use ReFS deduplication and compression checkbox.
Select the days of the week when ReFS deduplication and compression should run, the time for a job to start running, and maximum duration (default is unlimited), and then select Save.
The following screenshot shows that ReFS deduplication and compression runs on Friday and Saturday at 10:40 AM with a maximum duration of 2 hours, starting from 9/22/2023. If the Start date was changed to 9/21/2023, the first run will still be 9/22/2023 10:40AM as that's the first Friday after 9/21/2023.
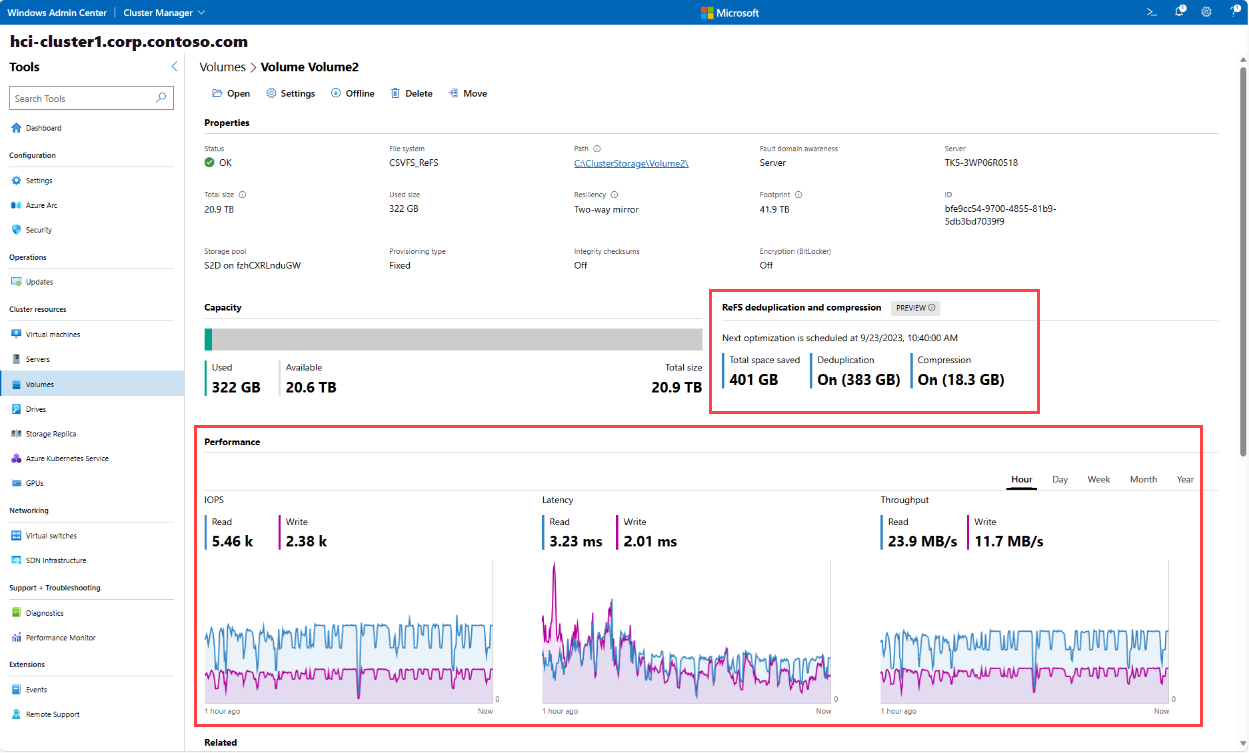
Verify the changes in the Properties section of the volume. The schedule appears under the Properties section and displays the savings breakdown and next scheduled run time. These savings are updated after each run, and you can observe the performance impact in the charts under the Performance section.
Suspend scheduled jobs
Suspending the schedule cancels any running jobs and stops scheduled runs in the future. This option retains ReFS deduplication and compression-related metadata and continues to track file changes for optimized future runs. You can resume the schedule at any time, with the schedule settings preserved.
Follow these steps to suspend scheduled jobs using Windows Admin Center:
Connect to a cluster, and then on the Tools pane on the left, select Volumes.
On the Volumes page, select the Inventory tab, select the appropriate volume, and then select Settings.
On the Volume settings pane on the right, under More options dropdown, deselect the Set Schedule checkbox, and then select Save.
Disable ReFS deduplication and compression on a volume
Disabling ReFS deduplication and compression on a volume stops any runs that are in progress and cancels future scheduled jobs. In addition, related volume metadata isn't retained, and file change tracking is stopped.
When you disable this feature, it doesn't undo deduplication or compression, as all the operations occur at the metadata layer. Over time, the data returns to its original state as the volume incurs reads and writes.
Note
You can perform decompression operations using ReFSUtil.
Follow these steps to disable the feature using Windows Admin Center:
Connect to a cluster, and then on the Tools pane on the left, select Volumes.
On the Volumes page, select the Inventory tab, select the appropriate volume, and then select Settings.
On the Volume settings pane on the right, under More options dropdown, deselect the Use ReFS deduplication and compression checkbox, and then select Save.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
This section answers frequently asked questions about ReFS deduplication and compression.
Is the ReFS deduplication and compression feature different from Windows Data Deduplication?
Yes, this feature is entirely different from the Windows Data Deduplication feature.
Important
We don't support enabling both ReFS deduplication and compression and Windows Data Deduplication simultaneously.
ReFS deduplication and compression is designed for active workloads, focusing on minimizing performance impact after optimization. Unlike Windows Data Deduplication, ReFS deduplication and compression doesn't use a chunk store to store deduped data, and there's no physical data movement involved. The feature relies on ReFS block cloning to enable metadata-only operations. Windows Data Deduplication might provide better storage savings due to its use of variable block sizes, it's also suitable for a broader range of workload types, such as General-purpose file servers (GPFS), backup targets, and more.
What are the phases of ReFS deduplication and compression?
The optimization process comprises the following phases that occur sequentially and depend on the specified mode. If an optimization run reaches a duration limit, then the compression might not run.
Initialization. In this phase, the storage volume is scanned to identify redundant blocks of data.
Data deduplication. In this phase, the redundant blocks are single-instanced and tracked using ReFS block cloning.
Compression. In this phase, a heatmap is generated to identify if a block should be eligible for compression. The default settings compress infrequently accessed or cold data to reduce their size. You can change the compression levels to adjust the range of blocks eligible for compression.
What happens when the duration limit is reached before the volume is fully optimized?
The duration limit is in place to prevent any performance impact on customer workloads caused by the optimization job during business hours. A deduplication service monitors the optimized parts of a volume and incoming file modifications. This data is utilized in future jobs to reduce optimization time. For example, if a volume is only 30% processed in the first run due to the duration limit, the subsequent run addresses the remaining 70% and any new data.
Known issues
The following section lists the known issues that currently exist with ReFS deduplication and compression.
When Compression is enabled, using the -FullRun parameter on jobs after the first optimization run might result in a deadlock in the system.
Status: Open.
Avoid using -FullRun in manually started jobs unless the Type is Dedup.
Follow these steps as a temporary workaround to mitigate this issue:
Disable ReFS deduplication and compression on the volume:
Disable-ReFSDedup -Volume <path>Decompress the volume using
refsutil:refsutil compression /c /f NONE <vol>Re-enable ReFS deduplication and compression with the
Deduponly mode, if needed:Enable-ReFSDedup -Volume <path> -Type Dedup
Scheduling jobs to run simultaneously on multiple CSVs within a single cluster can potentially trigger CSV movements and negatively impact performance.
Status: Open.
As a recommended best practice, consider staggering the start time of the jobs to avoid any overlap. However, if all jobs must run simultaneously, adjust the CPU allocation per job across all CSVs so that it amounts to less than 50% of the overall cluster CPU utilization. Keep in mind that imposing CPU limitations may result in longer job execution times.
ReFS deduplication and compression job completed (either successfully or was canceled) and storage savings aren't listed in Get-ReFSDedupStatus or Windows Admin Center.
Status: Resolved.
The temporary workaround for this issue is to initiate a one-time job and the results update immediately.
Start-ReFSDedupJob -Volume <path>
Sending stopped monitoring Event Tracing for Windows (ETW) events after disabling ReFS deduplication and compression on a volume.
Status: Resolved.
Once ReFS deduplication and compression is disabled on a volume, the ETW channel for ReFS deduplication logs repeated stopped monitoring events. However, we don't anticipate significant usage impact because of this issue.
Job failed event not logged if volume is moved to another node during compression.
Status: Resolved.
If the CSV is moved to another server of the cluster while compression is in progress, the job failed event isn't logged in the ReFS deduplication channel. However, we don't anticipate significant usage impact because of this issue.