Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Currently Conditional Access policies can be applied to all apps or to individual apps. Organizations with a large number of apps might find this process difficult to manage across multiple Conditional Access policies.
Application filters for Conditional Access allow organizations to tag service principals with custom attributes. These custom attributes are then added to their Conditional Access policies. Filters for applications are evaluated at token issuance runtime, not configuration.
In this document, you create a custom attribute set, assign a custom security attribute to your application, and create a Conditional Access policy to secure the application.
Assign roles
Custom security attributes are security sensitive and can only be managed by delegated users. One or more of the following roles should be assigned to the users who manage or report on these attributes.
| Role name | Description |
|---|---|
| Attribute Assignment Administrator | Assign custom security attribute keys and values to supported Microsoft Entra objects. |
| Attribute Assignment Reader | Read custom security attribute keys and values for supported Microsoft Entra objects. |
| Attribute Definition Administrator | Define and manage the definition of custom security attributes. |
| Attribute Definition Reader | Read the definition of custom security attributes. |
Assign the appropriate role to the users who manage or report on these attributes at the directory scope. For detailed steps, see Assign Microsoft Entra roles.
Important
By default, Global Administrator and other administrator roles do not have permissions to read, define, or assign custom security attributes.
Create custom security attributes
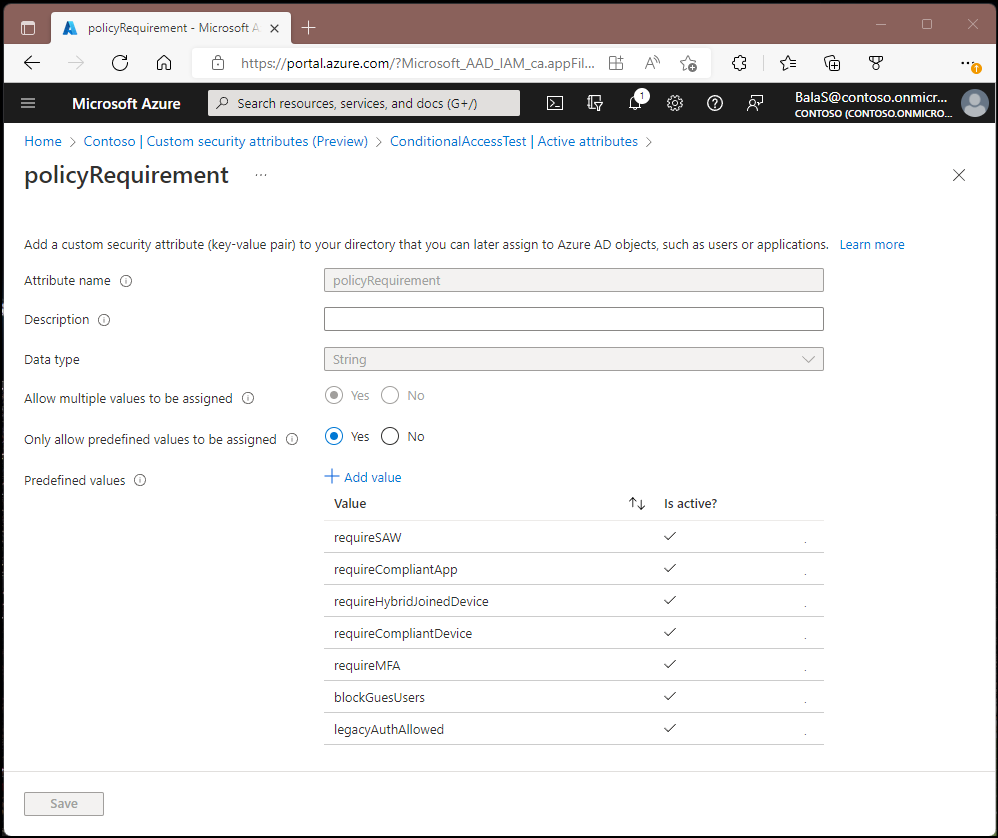
Follow the instructions in the article, Add or deactivate custom security attributes in Microsoft Entra ID to add the following Attribute set and New attributes.
- Create an Attribute set named ConditionalAccessTest.
- Create New attributes named policyRequirement that Allow multiple values to be assigned and Only allow predefined values to be assigned. We add the following predefined values:
- legacyAuthAllowed
- blockGuestUsers
- requireMFA
- requireCompliantDevice
- requireHybridJoinedDevice
- requireCompliantApp
Note
Conditional Access filters for applications only work with custom security attributes of type string. Custom Security Attributes support creation of Boolean data type but Conditional Access Policy only supports string.
Create a Conditional Access policy
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Conditional Access Administrator and Attribute Definition Reader.
- Browse to Entra ID > Conditional Access.
- Select New policy.
- Give your policy a name. We recommend that organizations create a meaningful standard for the names of their policies.
- Under Assignments, select Users or workload identities.
- Under Include, select All users.
- Under Exclude, select Users and groups and choose your organization's emergency access or break-glass accounts.
- Select Done.
- Under Target resources, select the following options:
- Select what this policy applies to Cloud apps.
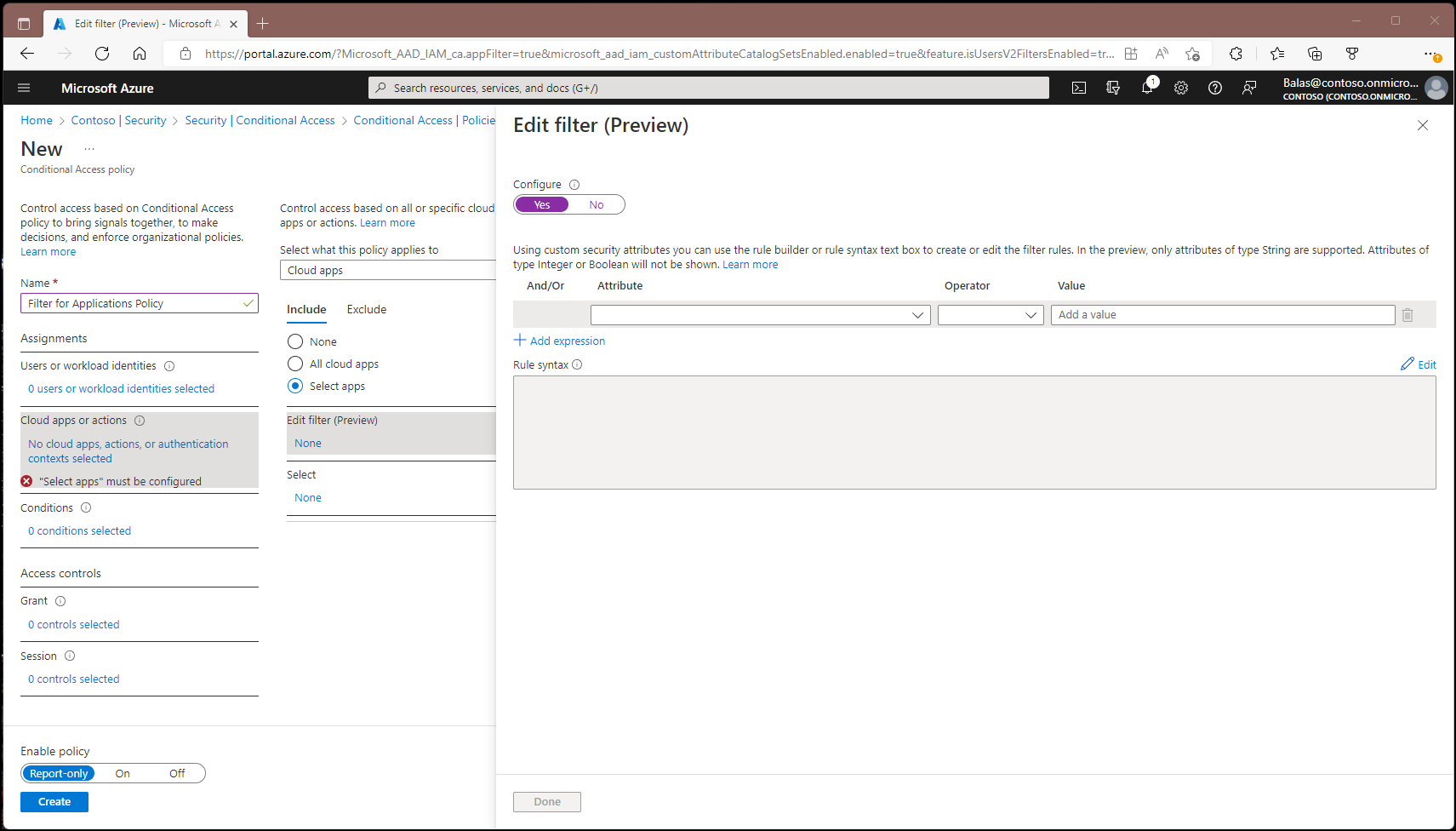
- Include Select resources.
- Select Edit filter.
- Set Configure to Yes.
- Select the Attribute we created earlier called policyRequirement.
- Set Operator to Contains.
- Set Value to requireMFA.
- Select Done.
- Under Access controls > Grant, select Grant access, Require multifactor authentication, and select Select.
- Confirm your settings and set Enable policy to Report-only.
- Select Create to create to enable your policy.
After confirming your settings using policy impact or report-only mode, move the Enable policy toggle from Report-only to On.
Configure custom attributes
Step 1: Set up a sample application
If you already have a test application that makes use of a service principal, you can skip this step.
Set up a sample application that, demonstrates how a job or a Windows service can run with an application identity, instead of a user's identity. Follow the instructions in the article Quickstart: Get a token and call the Microsoft Graph API by using a console app's identity to create this application.
Step 2: Assign a custom security attribute to an application
When you don't have a service principal listed in your tenant, it can't be targeted. The Office 365 suite is an example of one such service principal.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Conditional Access Administrator~/identity/role-based-access-control/permissions-reference.md#conditional-access-administrator) and Attribute Assignment Administrator.
- Browse to Entra ID > Enterprise apps.
- Select the service principal you want to apply a custom security attribute to.
- Under Manage > Custom security attributes, select Add assignment.
- Under Attribute set, select ConditionalAccessTest.
- Under Attribute name, select policyRequirement.
- Under Assigned values, select Add values, select requireMFA from the list, then select Done.
- Select Save.
Step 3: Test the policy
Sign in as a user who the policy would apply to and test to see that MFA is required when accessing the application.
Other scenarios
- Blocking legacy authentication
- Blocking external access to applications
- Requiring compliant device or Intune app protection policies
- Enforcing sign in frequency controls for specific applications
- Requiring a privileged access workstation for specific applications
- Require session controls for high risk users and specific applications
Related content
Determine effect using Conditional Access report-only mode
Use report-only mode for Conditional Access to determine the results of new policy decisions.