Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:  Workforce tenants
Workforce tenants  External tenants (learn more)
External tenants (learn more)
Note
Certain features described in this article are preview features. For more information about previews, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
To enhance security, you can limit what your users can access when they use an external account to sign in from your networks or devices. The tenant restrictions settings, included with cross-tenant access settings, let you create a policy to control access to external apps.
For example, suppose a user in your organization created a separate account in an unknown tenant, or an external organization gave your user an account that lets them sign in to their organization. You can use tenant restrictions to prevent the user from using some or all external apps while they're signed in with the external account on your network or devices.
The following diagram shows the steps that an example organization takes to prevent user access by using tenant restrictions v2.
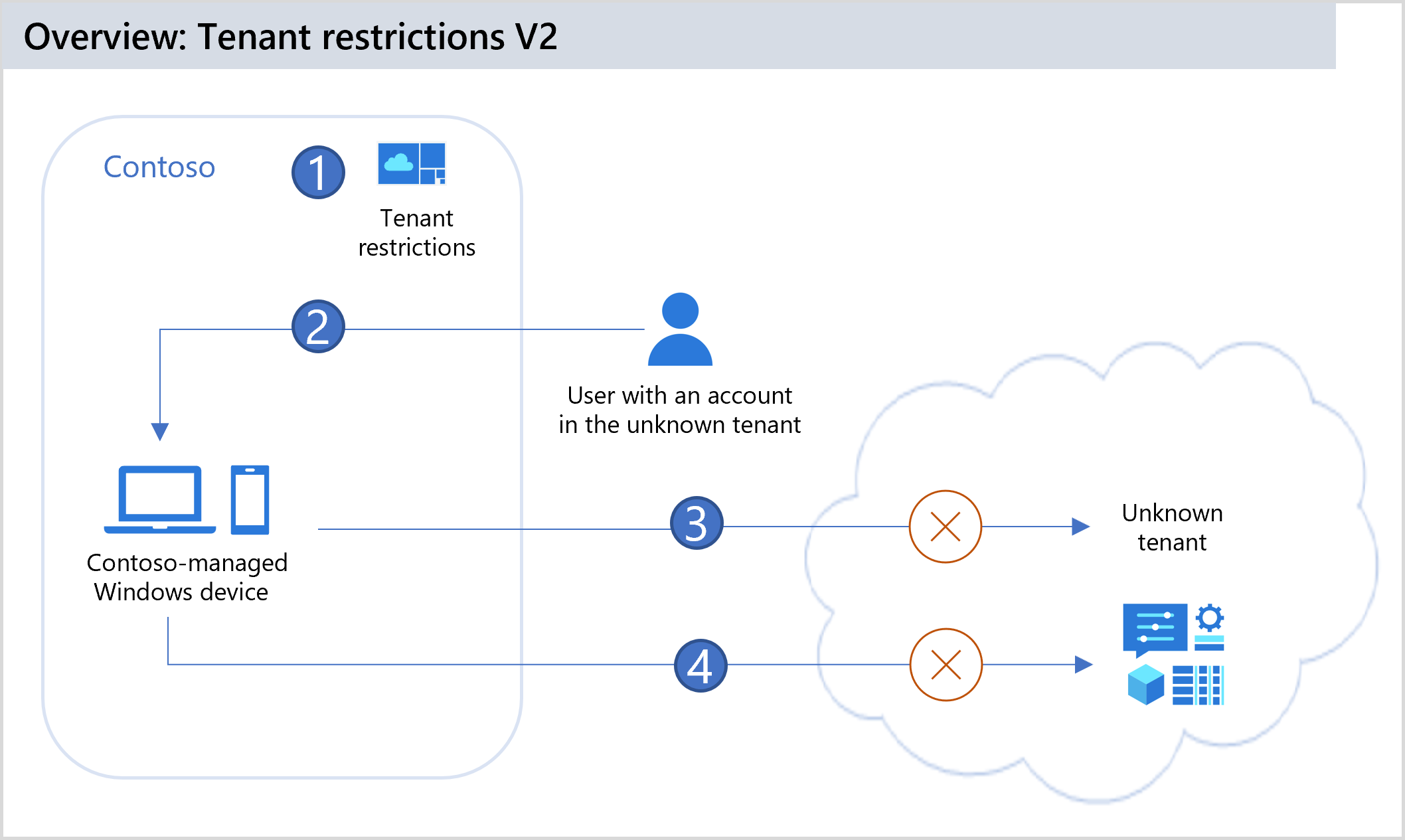
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Contoso configures tenant restrictions in its cross-tenant access settings to block all external accounts and external apps. Contoso adds enforcement signaling with the tenant restrictions v2 header via either universal tenant restrictions v2 or a corporate proxy. Microsoft Entra ID enforces the tenant restrictions v2 policy when the header is present on the request. |
| 2 | The user of a Contoso-managed device tries to sign in to an external app by using an account from an unknown tenant. The tenant restrictions v2 HTTP header, with Contoso's tenant ID and the policy ID for tenant restrictions, is added to the authentication request. |
| 3 | Authentication plane protection: Microsoft Entra ID enforces Contoso's tenant restrictions v2 policy and blocks external accounts from accessing external tenants during the authentication. |
| 4 | Data plane protection (preview): Microsoft Entra ID blocks any anonymous access to Microsoft Forms, SharePoint files, or Microsoft Teams meetings. Microsoft Entra ID also blocks user access to the resource with an infiltrated token. |
Tenant restrictions v2 provides options for both of these protection types:
Authentication plane protection refers to using a tenant restrictions v2 policy to block sign-ins that use external identities. For example, you can prevent a malicious insider from leaking data over external email by preventing the attacker from signing in to their malicious tenant. Authentication plane protection in tenant restrictions v2 is generally available.
Data plane protection refers to preventing attacks that bypass authentication. For example, an attacker might try to allow access to a malicious tenant's apps by anonymously joining a Teams meeting or anonymously accessing SharePoint files. Or the attacker might copy an access token from a device in a malicious tenant and import it to your organizational device. Data plane protection in tenant restrictions v2 forces the user to authenticate for attempts to access a resource. Data plane protection blocks access if authentication fails.
Tenant restrictions v1 provides authentication plane protection through a tenant allowlist configured on your corporate proxy. Tenant restrictions v2 gives you options for granular authentication and data plane protection, with or without a corporate proxy. If you're using a corporate proxy for header injection, options include only authentication plane protection.
Tenant restrictions v2 overview
In your organization's cross-tenant access settings, you can configure a tenant restrictions v2 policy. After you create the policy, there are three ways to apply the policy in your organization:
- Universal tenant restrictions. This option provides authentication plane protection without a corporate proxy. Universal tenant restrictions use Global Secure Access to tag all traffic no matter the operating system, browser, or device form factor. This option allows support for both client and remote network connectivity.
- Authentication plane. You can deploy a corporate proxy in your organization and configure the proxy to set tenant restrictions v2 signals on all traffic to Microsoft Entra ID and Microsoft accounts.
- Windows. For your corporate-owned Windows devices, you can enforce both authentication plane and data plane protection by enforcing tenant restrictions directly on devices. Tenant restrictions are enforced upon resource access to provide data path coverage and protection against token infiltration. A corporate proxy isn't required for policy enforcement. Devices can be Microsoft Entra ID managed, or they can be domain joined and managed via Group Policy.
Note
This article describes how to configure tenant restrictions v2 by using the Microsoft Entra admin center. You can also use the Microsoft Graph API for cross-tenant access settings to create these same tenant restrictions policies.
Supported scenarios
You can scope tenant restrictions v2 to specific users, groups, organizations, or external apps. Apps built on the networking stack for the Windows operating system are protected. The following scenarios are supported:
- All Office apps (all versions/release channels)
- Universal Windows Platform (UWP) .NET applications
- Authentication plane protection for all applications that authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID, including all Microsoft applications and any partner applications that use Microsoft Entra ID for authentication
- Data plane protection for SharePoint Online, Exchange Online, and Microsoft Graph
- Anonymous access protection for Forms, SharePoint Online, OneDrive, and Teams (with federation controls configured)
- Authentication and data plane protection for Microsoft tenant or consumer accounts
- When you use universal tenant restrictions in Global Secure Access, all browsers and platforms
- When you use Windows Group Policy, Microsoft Edge and all websites in Microsoft Edge
- Scenarios with device-based authentication (including custom applications integrated with Microsoft Graph)
Unsupported scenarios
- Anonymous blocking to consumer OneDrive accounts. You can work around this limitation at a proxy level by blocking
https://onedrive.live.com/. - When a user accesses a partner app, like Slack, by using an anonymous link or non-Microsoft Entra account.
- When a user copies a Microsoft Entra ID-issued token from a home machine to a work machine and uses it to access a third-party app like Slack.
- Per-user tenant restrictions for Microsoft accounts.
Compare tenant restrictions v1 and v2
The following table compares the features in each version.
| Feature | Tenant restrictions v1 | Tenant restrictions v2 |
|---|---|---|
| Policy enforcement | The corporate proxy enforces the tenant restrictions policy on the Microsoft Entra ID control plane. | Options: - Universal tenant restrictions in Global Secure Access provide authentication plane support on all platforms. - In corporate proxy header injection, the corporate proxy sets tenant restrictions v2 signals on all traffic. - Windows device management provides both authentication plane and data plane protection. Devices are configured to point Microsoft traffic to the tenant restrictions policy. The policy is enforced in the cloud. |
| Policy enforcement limitation | You can manage corporate proxies by adding tenants to the Microsoft Entra traffic allowlist. The character limit of the header value in Restrict-Access-To-Tenants: <allowed-tenant-list> limits the number of tenants that you can add. |
This feature is managed by a cloud policy in the cross-tenant access policy. A default policy is created at the tenant level, and a partner policy is created for each external tenant. |
| Malicious tenant requests | Microsoft Entra ID blocks malicious tenant authentication requests to provide authentication plane protection. | Microsoft Entra ID blocks malicious tenant authentication requests to provide authentication plane protection. |
| Granularity | This feature is limited to tenants and all Microsoft accounts. | This feature includes tenant, user, group, and application granularity. (User-level granularity isn't supported with Microsoft accounts.) |
| Anonymous access | Anonymous access to Teams meetings and file sharing is allowed. | Anonymous access to Teams meetings is blocked. Access to anonymously shared resources (anyone with the link) is blocked. Anonymous access to Forms is blocked. |
| Microsoft accounts | This feature uses a Restrict-MSA header to block access to consumer accounts. |
This feature allows control of Microsoft account authentication on both the identity and data planes. For example, if you enforce tenant restrictions by default, you can create a policy that allows users to access the following specific apps with their Microsoft accounts: Microsoft Learn (app ID 18fbca16-2224-45f6-85b0-f7bf2b39b3f3) or Microsoft Enterprise Skills Initiative (app ID 195e7f27-02f9-4045-9a91-cd2fa1c2af2f). |
| Proxy management | You can manage corporate proxies by adding tenants to the Microsoft Entra traffic allowlist. | For authentication plane protection on a corporate proxy, configure the proxy to set tenant restrictions v2 signals on all traffic. |
| Platform support | This feature is supported on all platforms. It provides only authentication plane protection. | Universal tenant restrictions in Global Secure Access support any operating system, browser, or device form factor. Authentication plane protection on a corporate proxy supports macOS, Chrome browser, and .NET applications. Windows device management supports Windows operating systems and Microsoft Edge. |
| Portal support | There's no user interface in the Microsoft Entra admin center for configuring the policy. | A user interface is available in the Microsoft Entra admin center for setting up the cloud policy. |
| Unsupported apps | Not applicable. | Block unsupported app use with Microsoft endpoints by using App Control for Business in Windows (formerly Windows Defender Application Control [WDAC]) or Windows Firewall (for example, for Chrome or Firefox). See Block Chrome, Firefox, and .NET applications like PowerShell later in this article. |
Migrate tenant restrictions v1 policies to v2 on the proxy
Migrating tenant restrictions policies from v1 to v2 is a one-time operation. After migration, no client-side changes are required. You can make any subsequent server-side policy changes via the Microsoft Entra admin center.
When you enable tenant restrictions v2 on a proxy, you can enforce tenant restrictions v2 only on the authentication plane. To enable tenant restrictions v2 on both the authentication and data planes, you should enable client-side signaling for tenant restrictions v2 by using a Windows Group Policy Object (GPO).
Step 1: Configure an allowed list of partner tenants
Tenant restrictions v1 lets you create an allowlist of tenant IDs and/or Microsoft sign-in endpoints to ensure that users access external tenants that your organization authorizes. Tenant restrictions v1 achieved the allowlist by adding the Restrict-Access-To-Tenants: <allowed-tenant-list> header on the proxy. For example: Restrict-Access-To-Tenants: "contoso.com, fabrikam.com, northwindtraders.com". Learn more about tenant restrictions v1.
With tenant restrictions v2, the configuration is moved to the server-side cloud policy. There's no need for the tenant restrictions v1 header, so remove this header from your corporate proxy. For each tenant in the allowed-tenant-list header, create a partner tenant policy. Follow these guidelines:
- Keep the tenant restrictions v2 default policy that blocks all external tenant access from foreign identities (for example,
user@<externaltenant>.com). - Create a partner tenant policy for each tenant listed in your tenant restrictions v1 allowlist by following the steps at Step 2: Configure tenant restrictions v2 for specific partners later in this article.
- Allow only specific users to access specific applications. This design increases your security posture by limiting access to necessary users only.
Step 2: Block consumer account or Microsoft account tenants
To not allow users to sign in to consumer applications, tenant restrictions v1 needs the sec-Restrict-Tenant-Access-Policy header to be injected into traffic visiting login.live.com, like sec-Restrict-Tenant-Access-Policy: restrict-msa.
With tenant restrictions v2, the configuration is moved to the server-side cloud policy. There's no need for the tenant restrictions v1 header. On your corporate proxy, remove tenant the restrictions v1 header sec-Restrict-Tenant-Access-Policy: restrict-msa.
Create a partner tenant policy for the Microsoft account tenant by following Step 2: Configure tenant restrictions v2 for specific partners later in this article. Because user-level assignment isn't available for Microsoft account tenants, the policy applies to all users of Microsoft accounts. However, application-level granularity is available. You should limit the applications that Microsoft accounts or consumer accounts can access to only necessary applications.
Note
Blocking the Microsoft account tenant doesn't block device traffic from sources other than users, including:
- Traffic for Autopilot, Windows Update, and organizational data collection.
- Business-to-business (B2B) authentication of consumer accounts, or passthrough authentication, where Azure apps and Office.com apps use Microsoft Entra ID to sign in consumer users in a consumer context.
Step 3: Enable tenant restrictions v2 on the corporate proxy
You can configure the corporate proxy to enable client-side tagging of the tenant restrictions v2 header by using the following corporate proxy setting: sec-Restrict-Tenant-Access-Policy: <DirectoryID>:<policyGUID>.
In that setting, replace <DirectoryID> with your Microsoft Entra tenant ID. Replace <policyGUID> with the object ID for your cross-tenant access policy.
Tenant restrictions vs. inbound and outbound settings
Although tenant restrictions are configured along with your cross-tenant access settings, they operate separately from inbound and outbound access settings. Cross-tenant access settings give you control when users sign in with an account from your organization. By contrast, tenant restrictions give you control when users are using an external account. Your inbound and outbound settings for B2B collaboration and B2B direct connections don't affect (and are unaffected by) your tenant restrictions settings.
Think of the access settings this way:
- Inbound settings control external account access to your internal apps.
- Outbound settings control internal account access to external apps.
- Tenant restrictions control external account access to external apps.
Tenant restrictions vs. B2B collaboration
When your users need access to external organizations and apps, we recommend that you enable tenant restrictions to block external accounts and use B2B collaboration instead. B2B collaboration gives you the ability to:
- Use Conditional Access and force multifactor authentication for B2B collaboration users.
- Manage inbound and outbound access.
- Terminate sessions and credentials when a B2B collaboration user's employment status changes or their credentials are breached.
- Use sign-in logs to view details about B2B collaboration users.
Prerequisites
To configure tenant restrictions, you need:
- Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2.
- An account with a role of at least Security Administrator to configure a tenant restrictions v2 policy.
- For Windows GPO configuration, Windows devices running Windows 10 or Windows 11 with the latest updates.
Configure a server-side cloud policy for tenant restrictions v2
Step 1: Configure default tenant restrictions
Settings for tenant restrictions v2 are located in the Microsoft Entra admin center, under Cross-tenant access settings. First, configure the default tenant restrictions that you want to apply to all users, groups, apps, and organizations. If you need partner-specific configurations, you can add a partner's organization and customize any settings that differ from your defaults.
To configure default tenant restrictions:
Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Security Administrator.
Browse to Entra ID > External Identities > Cross-tenant access settings.
Select the Default settings tab.
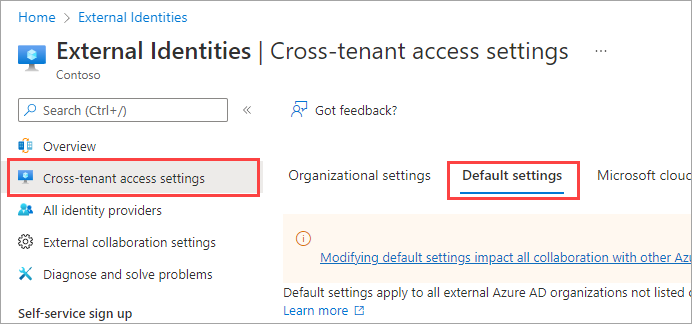
Scroll to the Tenant restrictions section.
Select the Edit tenant restrictions defaults link.
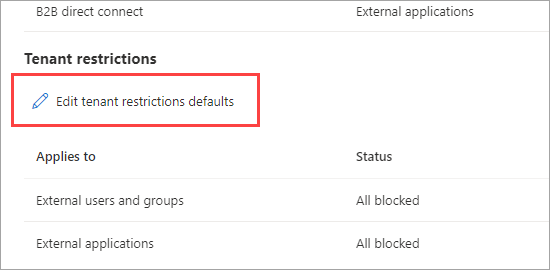
If a default policy doesn't exist yet in the tenant, a Create policy link appears next to Policy ID. Select this link.
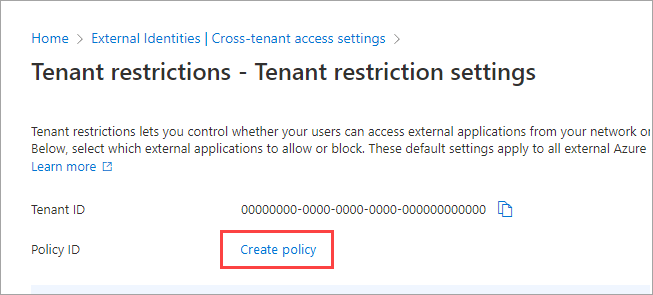
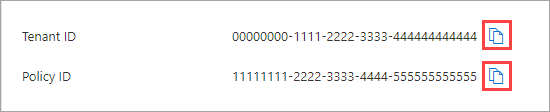
The Tenant restrictions pane displays both your Tenant ID value and your Policy ID value for tenant restrictions. Use the copy icons to copy both of these values. You'll use them later when you configure Windows clients to enable tenant restrictions.
Select the External users and groups tab. Under Access status, choose one of the following options:
- Allow access: Allows all users who are signed in with external accounts to access external apps (specified on the External applications tab).
- Block access: Blocks all users who are signed in with external accounts from accessing external apps (specified on the External applications tab).
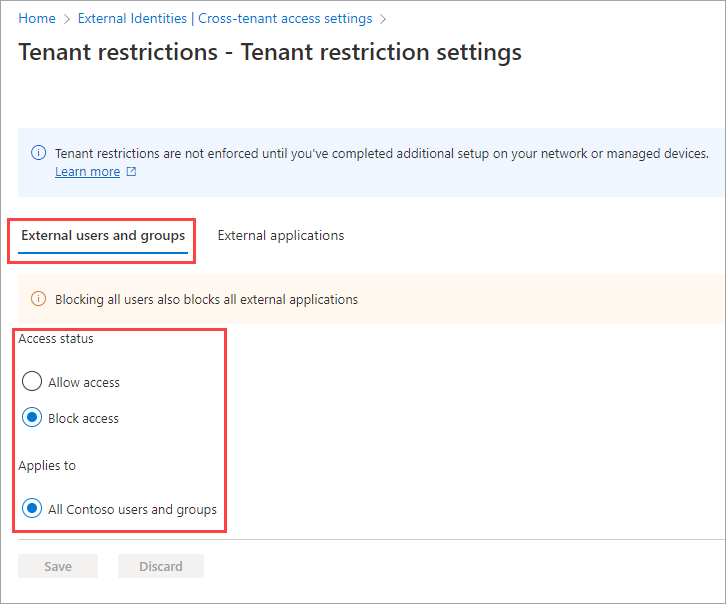
Note
Default settings can't be scoped to individual accounts or groups, so Applies to always equals All <your tenant> users and groups. Be aware that if you block access for all users and groups, you also need to block access to all external applications (on the External applications tab).
Select the External applications tab. Under Access status, choose one of the following options:
- Allow access: Allows all users who are signed in with external accounts to access the apps specified in the Applies to section.
- Block access: Blocks all users who are signed in with external accounts from accessing the apps specified in the Applies to section.
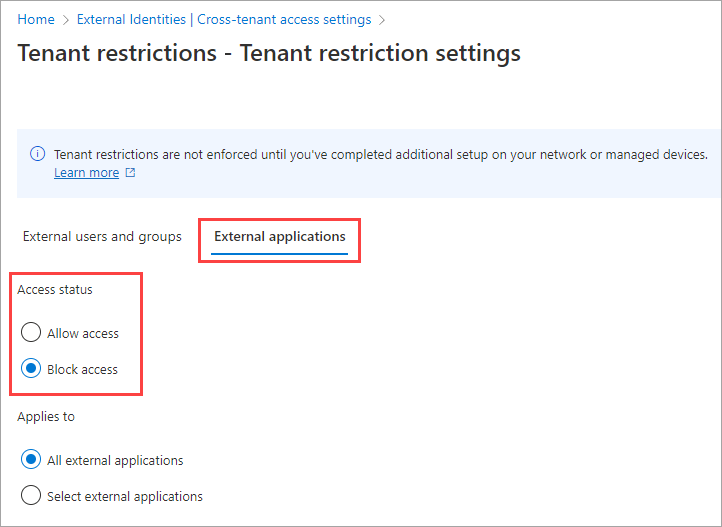
Under Applies to, select one of the following options:
All external applications: Applies the action that you chose under Access status to all external applications. If you block access to all external applications, you also need to block access for all of your users and groups (on the External users and groups tab).
Select external applications: Lets you choose the external applications that you want the action under Access status to apply to.
To select applications, choose Add Microsoft applications or Add other applications. Then search by the application name or the application ID (either the client app ID or the resource app ID), and select the app. (See a list of IDs for commonly used Microsoft applications.) If you want to add more apps, use the Add button. When you finish, select Submit.
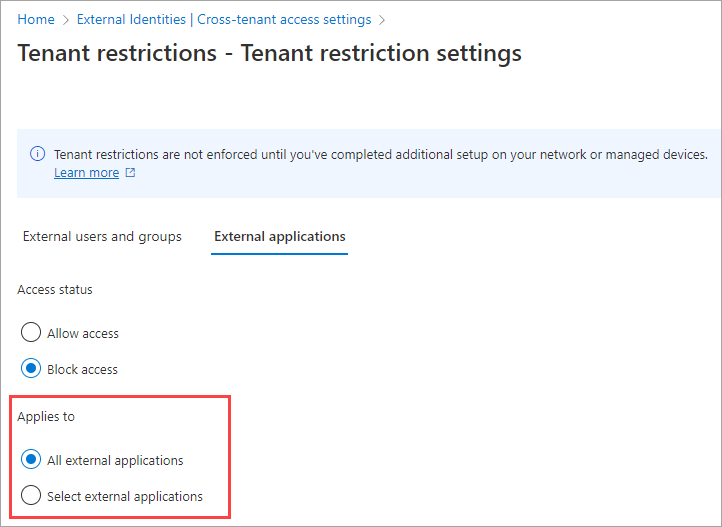
Select Save.
Step 2: Configure tenant restrictions v2 for specific partners
Suppose you use tenant restrictions to block access by default, but you want to allow users to access certain applications by using their own external accounts. For example, you want users to be able to access Microsoft Learn with their own Microsoft accounts. The instructions in this section describe how to add organization-specific settings that take precedence over the default settings.
Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Security Administrator or a Conditional Access Administrator.
Browse to Entra ID > External Identities > Cross-tenant access settings.
Select Organizational settings.
Note
If the organization that you want to add was already added to the list, you can skip adding it and go directly to modifying the settings.
Select Add organization.
On the Add organization pane, enter the full domain name (or tenant ID) for the organization.
For example, search for the following tenant ID for a Microsoft account:
9188040d-6c67-4c5b-b112-36a304b66dad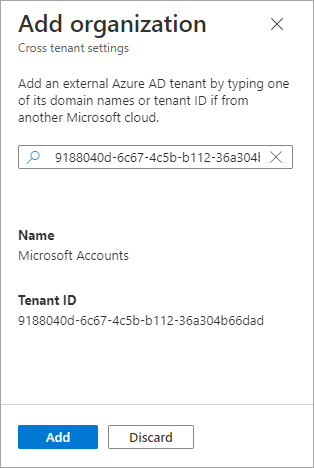
Select the organization in the search results, and then select Add.
Modify the settings. Find the organization in the Organizational settings list, and then scroll horizontally to see the Tenant restrictions column. At this point, all tenant restrictions settings for this organization are inherited from your default settings. To change the settings for this organization, select the Inherited from default link.
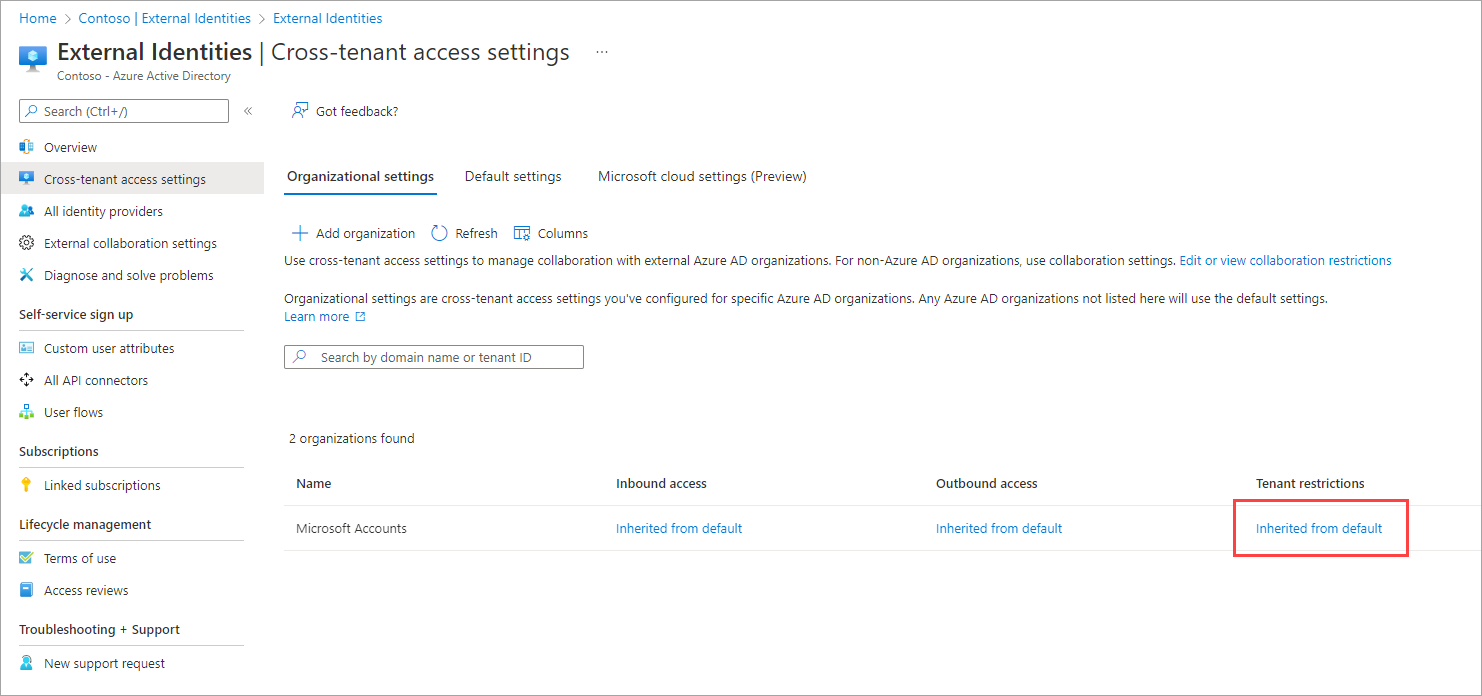
The Tenant restrictions pane for the organization appears. Copy the values for Tenant ID and Policy ID. You'll use them later when you configure Windows clients to enable tenant restrictions.
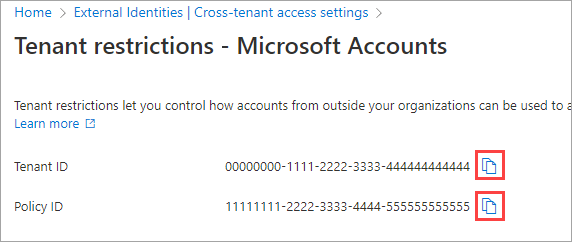
Select Customize settings, and then select the External users and groups tab. Under Access status, choose an option:
- Allow access: Allows users and groups specified under Applies to who are signed in with external accounts to access external apps (specified on the External applications tab).
- Block access: Blocks users and groups specified under Applies to who are signed in with external accounts from accessing external apps (specified on the External applications tab).
For the Microsoft accounts example in this article, we select Allow access.
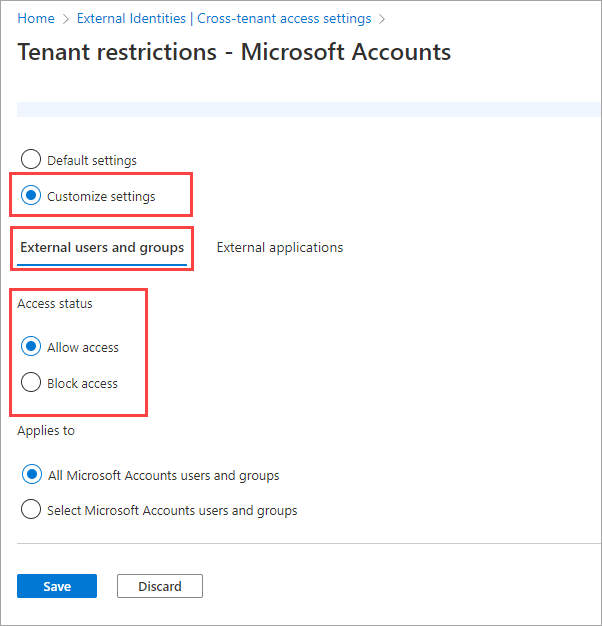
Under Applies to, select All <organization> users and groups.
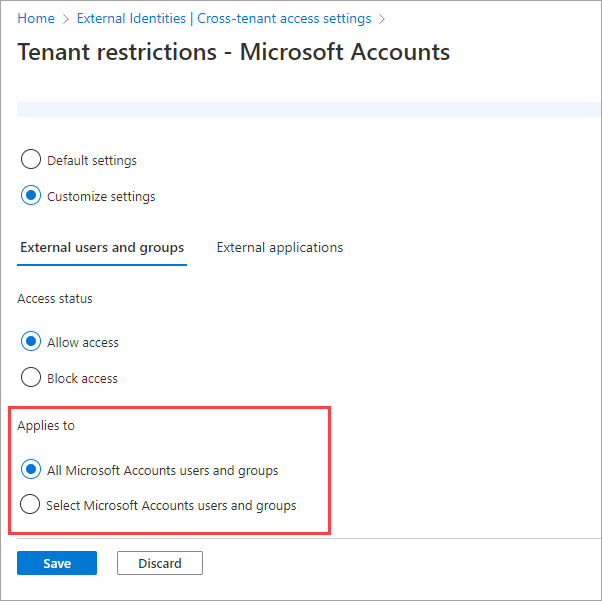
Note
User granularity isn't supported with Microsoft accounts, so the Select <organization> users and groups capability isn't available. For other organizations, you could choose Select <organization> users and groups, and then perform these steps:
- Select Add external users and groups.
- On the Select pane, enter the username or group name in the search box.
- Select the user or group in the search results.
- If you want to add more, select Add and repeat these steps.
- When you finish selecting the users and groups that you want to add, select Submit.
Select the External applications tab. Under Access status, choose whether to allow or block access to external applications:
- Allow access: Allows your users to access the external applications specified under Applies to when the users are using external accounts.
- Block access: Blocks your users from accessing the external applications specified under Applies to when the users are using external accounts.
For the Microsoft accounts example in this article, we select Allow access.
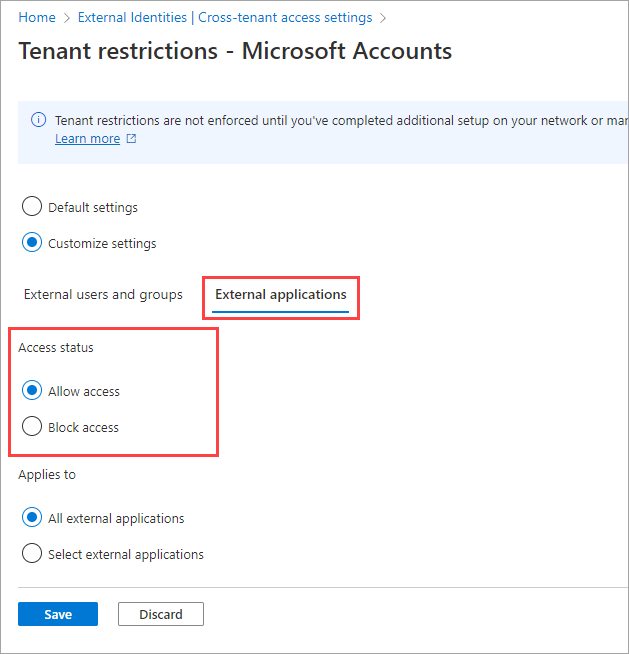
Under Applies to, select one of the following options:
- All external applications: Applies the action that you chose under Access status to all external applications.
- Select external applications: Applies the action that you chose under Access status to all external applications.
For the Microsoft accounts example in this article, we choose Select external applications.
Note
If you block access to all external applications, you also need to block access for all of your users and groups (on the External users and groups tab).
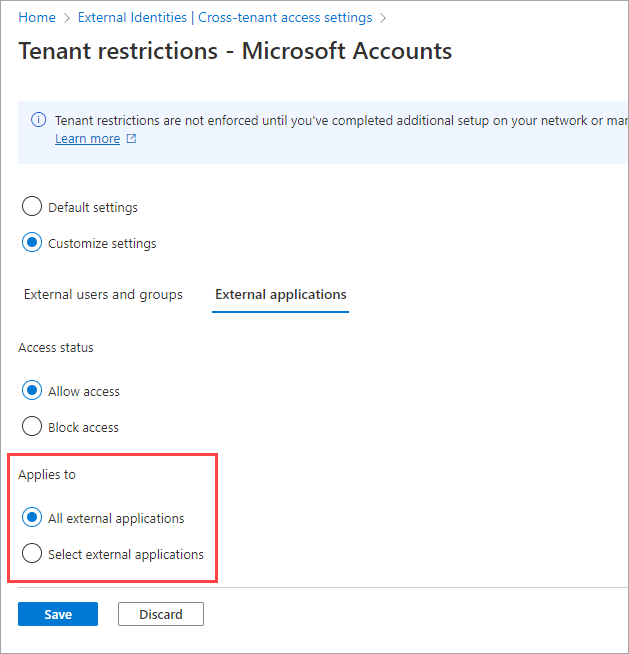
If you chose Select external applications, take the following steps:
- Select Add Microsoft applications or Add other applications. For the Microsoft Learn example in this article, we choose Add other applications.
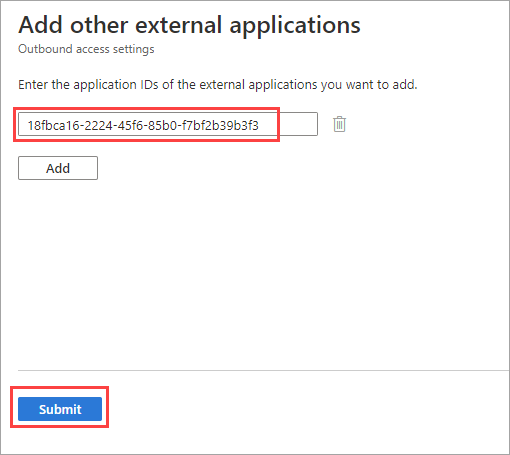
- In the search box, enter the application name or the application ID (either the client app ID or the resource app ID). (See a list of IDs for commonly used Microsoft applications.) For the Microsoft Learn example in this article, we enter the application ID
18fbca16-2224-45f6-85b0-f7bf2b39b3f3. - Select the application in the search results, and then select Add.
- Repeat the preceding steps for each application that you want to add.
- When you finish selecting applications, select Submit.
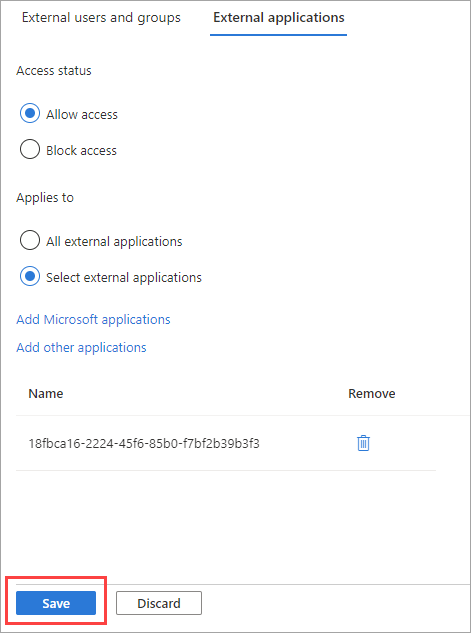
The applications that you selected are listed on the External applications tab. Select Save.
Note
Blocking the Microsoft account tenant doesn't block:
- Device traffic that doesn't come from users. Examples include traffic for Autopilot, Windows Update, and organizational data collection.
- B2B authentication of consumer accounts.
- Passthrough authentication, used by many Azure apps and Office.com, where apps use Microsoft Entra ID to sign in consumer users in a consumer context.
Configure tenant restrictions v2 on the client side
There are three options for enforcing tenant restrictions v2 for clients:
- Use universal tenant restrictions v2 as part of Microsoft Entra Global Secure Access
- Set up tenant restrictions v2 on your corporate proxy
- Enable tenant restrictions on Windows-managed devices (preview)
Option 1: Use universal tenant restrictions v2 as part of Microsoft Entra Global Secure Access
Universal tenant restrictions v2 as part of Microsoft Entra Global Secure Access provides authentication plane protection for all devices and platforms.
Option 2: Set up tenant restrictions v2 on your corporate proxy
To ensure that sign-ins are restricted on all devices and apps in your corporate network, configure your corporate proxy to enforce tenant restrictions v2. Although configuring tenant restrictions on your corporate proxy doesn't provide data plane protection, it does provide authentication plane protection.
Important
If you previously set up tenant restrictions, you need to stop sending restrict-msa to login.live.com. Otherwise, the new settings will conflict with your existing instructions to the Microsoft account's sign-in service.
Configure the tenant restrictions v2 header as follows:
Header name Header value Sample value sec-Restrict-Tenant-Access-Policy<TenantId>:<policyGuid>aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee:1aaaaaa1-2bb2-3cc3-4dd4-5eeeeeeeeee5TenantIDis your Microsoft Entra tenant ID. Find this value by signing in to the Microsoft Entra admin center and browsing to Entra ID > Overview > Properties.policyGUIDis the object ID for your cross-tenant access policy. Find this value by calling/crosstenantaccesspolicy/defaultand using the returnedidfield.
On your corporate proxy, send the tenant restrictions v2 header to the following Microsoft sign-in domains:
- login.live.com
- login.microsoft.com
- login.microsoftonline.com
- login.windows.net
This header enforces your tenant restrictions v2 policy on all sign-ins on your network. This header doesn't block anonymous access to Teams meetings, SharePoint files, or other resources that don't require authentication.
Important
Tenant restrictions v1 and v2 on the proxy require decryption of requests to sign-in URLs such as login.microsoftonline.com. Microsoft supports the decryption of traffic for those sign-in domains for the purpose of header insertion for tenant restrictions. This decryption is a valid exception to the policies at Use third-party network devices or solutions with Microsoft 365.
Tenant restrictions v2 with no support for break and inspect
For non-Windows platforms, you can break and inspect traffic to add the tenant restrictions v2 parameters into the header via proxy. However, some platforms don't support break and inspect, so tenant restrictions v2 doesn't work. For these platforms, the following features of Microsoft Entra ID can provide protection:
- Conditional Access: Allow use of only managed or compliant devices
- Conditional Access: Manage access for guest or external users
- B2B collaboration: Restrict outbound rules by cross-tenant access for the same tenants listed in the parameter Restrict-Access-To-Tenants
- B2B collaboration: Restrict invitations to B2B users to the same domains listed in the Restrict-Access-To-Tenants parameter
- Application management: Restrict how users consent to applications
- Intune: Apply an app policy through Intune to restrict usage of managed apps to only the UPN of the account that enrolled the device (under Allow only configured organization accounts in apps)
Although these alternatives provide protection, you can cover certain scenarios only through tenant restrictions. Examples include the use of a browser to access Microsoft 365 services through the web instead of the dedicated app.
Option 3: Enable tenant restrictions on Windows-managed devices (preview)
After you create a tenant restrictions v2 policy, you can enforce the policy on each Windows 10 or Windows 11 device by adding your tenant ID and the policy ID to the device's Tenant restrictions configuration.
When you enable tenant restrictions on a Windows device, corporate proxies aren't required for policy enforcement. Devices don't need to be Microsoft Entra ID managed to enforce tenant restrictions v2. Domain-joined devices that are managed with Group Policy are also supported.
Note
Tenant restrictions v2 on Windows is a partial solution that helps protect the authentication and data planes for some scenarios. It works on managed Windows devices. It doesn't protect the .NET stack, Chrome, or Firefox.
Use Group Policy to deploy tenant restrictions
You can use Group Policy to deploy the tenant restrictions configuration to Windows devices. Refer to these resources:
- Administrative Templates for Windows 10 November 2021 Update (21H2)
- Group Policy Settings Reference Spreadsheet for Windows 10 November 2021 Update (21H2)
Test the policy on a device
To test the tenant restrictions v2 policy on a device, follow these steps.
Note
The device must be running Windows 10 or Windows 11 with the latest updates.
On the Windows computer, select the Windows logo key, enter gpedit, and then select Edit group policy (Control panel).
Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Tenant Restrictions.
Right-click Cloud Policy Details on the right pane, and then select Edit.
Retrieve the Tenant ID and Policy ID values that you recorded earlier (in step 7 under Step 1: Configure default tenant restrictions) and enter them in the following fields. Leave all other fields blank.
Microsoft Entra Directory ID: Enter the Tenant ID value that you recorded earlier by signing in to the Microsoft Entra admin center and browsing to Entra ID > Overview > Properties.
Policy GUID: The ID for your cross-tenant access policy. It's the Policy ID value that you recorded earlier.
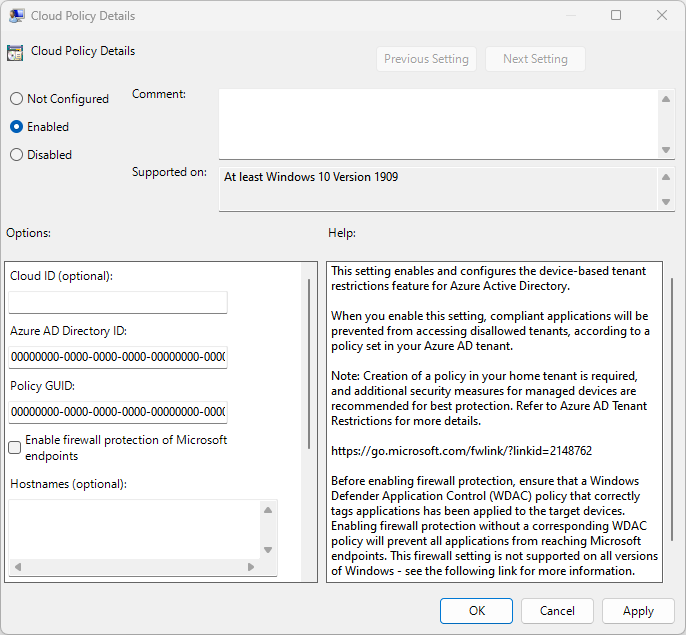
Select OK.
View tenant restrictions v2 events
View events related to tenant restrictions in Event Viewer:
- In Event Viewer, open Applications and Services Logs.
- Go to Microsoft > Windows > TenantRestrictions > Operational and look for events.
Block Chrome, Firefox, and .NET applications like PowerShell
To block applications, you need to set up App Control for Business in Windows (formerly Windows Defender Application Control [WDAC]) and enable a Windows Firewall setting.
Set up App Control for Business to control access to Microsoft resources
App Control for Business is a policy engine built into Windows that allows you to control which applications can run on your user's devices. For tenant restrictions v2, you need to use App Control for Business to block unenlightened apps (apps that don't provide tenant restrictions v2 protection) from accessing Microsoft resources. This requirement allows you to keep using the browsers and apps of your choice, while knowing that data protected by Microsoft Entra can be accessed only through secure means.
Unenlightened apps don't use the Windows networking stack, so they don't benefit from the tenant restrictions v2 features added to Windows. They can't send the signal to login.live.com for Microsoft Entra, or to Microsoft resources that indicate that tenant restrictions v2 protection is required. As such, you can't rely on unenlightened apps to provide data plane protection.
You can use App Control for Business in two ways to help protect against unenlightened apps:
- Prevent the use of unenlightened apps entirely (that is, block PowerShell or Chrome entirely from running). You can use a standard App Control for Business policy that controls which apps can run.
- Allow the use of unenlightened apps, but block them from accessing Microsoft resources. For this method, you use a special App Control for Business policy called an app ID tagging policy (
AppIdTaggingPolicy).
For both options, you must first create an App Control for Business policy. Then, optionally, convert it to an app ID tagging policy. Finally, apply it to your devices after testing it on a test machine.
For more information, see Creating your App Control AppId tagging policies.
Note
The following steps require an up-to-date Windows device for access to the latest PowerShell cmdlets needed to create the policy.
Step 1: Use the App Control Policy Wizard to create a policy
Install the App Control Policy Wizard.
Select Create a policy and choose your policy format. The default is Multiple policy, base policy.
Choose your base template (recommended: Default Windows or Allow Microsoft). For detailed steps, see Template base policies.
When you convert the policy into an app ID tagging policy, the wizard assumes that policy rules are set. You can set them here, but it's not required. These policy rules include Advanced Boot Options Menu, Disable Script Enforcement, Enforce Store Applications, Audit Mode, and User Mode Code Integrity.
Choose the save location of your policy XML and create your policy.
Step 2: Convert the policy into an app ID tagging policy
After you create your policy in the wizard, or create your own by using PowerShell, convert the .xml output to an app ID tagging policy. The tagging policy marks the apps for which you want to allow access to Microsoft resources. The GUID output is your new policy ID.
Set-CIPolicyIdInfo -ResetPolicyID .\policy.xml -AppIdTaggingPolicy -AppIdTaggingKey "M365ResourceAccessEnforced" -AppIdTaggingValue "True"
Step 3: Compile and deploy the policy for testing
After you edit the policy and convert it to an app ID tagging policy, compile it with the policy ID that matches the file name:
ConvertFrom-CIPolicy .\policy.xml ".\{PolicyID}.cip"
Then deploy the policy to your CiPolicies\Active directory:
copy ".\{Policy ID}.cip" c:\windows\system32\codeintegrity\CiPolicies\Active\
Refresh the policies on your system by calling RefreshPolicy.exe.
Enable the Windows Firewall setting
You can use the Windows Firewall feature to block unprotected apps from accessing Microsoft resources via Chrome, Firefox, and .NET applications like PowerShell. These applications would be blocked or allowed in accordance with the tenant restrictions v2 policy.
For example, if you add PowerShell to your Customer Identification Program (CIP) policy for tenant restrictions v2, and you have graph.microsoft.com in your tenant restrictions v2 policy's endpoint list, PowerShell should be able to access it with the firewall enabled.
On the Windows computer, select the Windows logo key, enter gpedit, and then select Edit group policy (Control panel).
Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Tenant Restrictions.
Right-click Cloud Policy Details on the right pane, and then select Edit.
Select the Enable firewall protection of Microsoft endpoints checkbox, and then select OK.
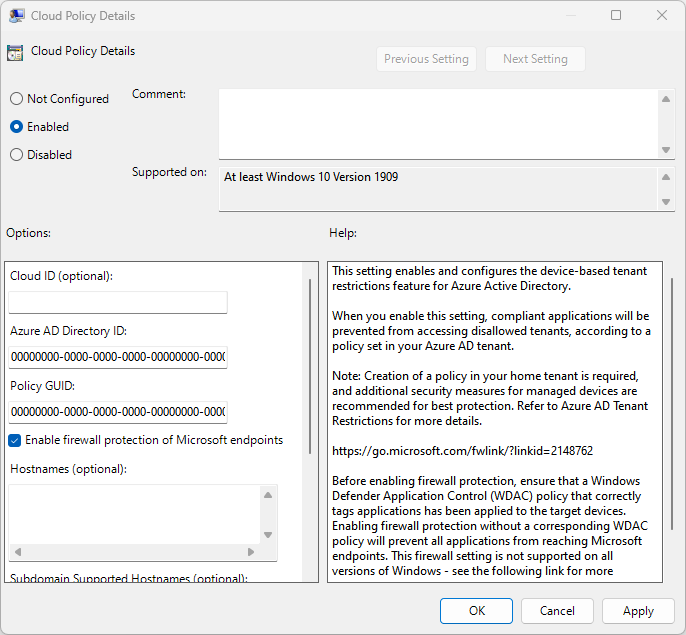
Refresh Group Policy on your device by running
gpudate:gupdate /forceRestart the device.
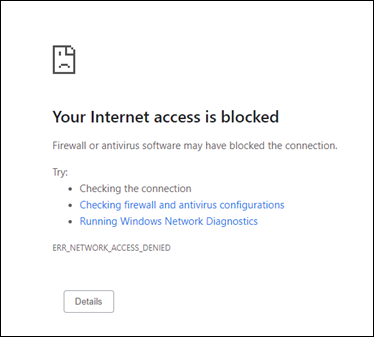
Test that tenant restrictions v2 blocks access
After you enable the firewall and the App Control for Business setting, try signing in by using a Chrome browser and access office.com. Sign-in should fail with the following message.
Tenant restrictions and data plane support (preview)
The following resources enforce tenant restrictions v2. These resources address token infiltration scenarios where a bad actor accesses the resource directly with an infiltrated token or anonymously.
- Teams
- SharePoint Online, like a OneDrive app
- Exchange Online, like an Outlook app
- Office.com and Office apps
Tenant restrictions and Microsoft Forms (preview)
When tenant restrictions v2 is enforced, it automatically blocks all anonymous or unauthenticated identity access to externally hosted forms from Microsoft Forms.
Tenant restrictions and Microsoft Teams (preview)
Teams, by default, has open federation. It doesn't block anyone from joining a meeting that an external tenant hosts. For greater control over access to Teams meetings, you can use federation controls in Teams to allow or block specific tenants. You can also use these federation controls along with tenant restrictions v2 to block anonymous access to Teams meetings.
To enforce tenant restrictions for Teams, you need to configure tenant restrictions v2 in your Microsoft Entra cross-tenant access settings. You also need to set up federation controls in the Teams admin portal and restart Teams. Tenant restrictions v2 implemented on the corporate proxy doesn't block anonymous access to Teams meetings, SharePoint files, and other resources that don't require authentication.
If you're considering using tenant restrictions for Teams, keep the following points about identity in mind:
- Teams currently allows users to join any externally hosted meeting by using their corporate-provided or home-provided identity. You can use outbound cross-tenant access settings to control which users with a corporate-provided or home-provided identity can join externally hosted Teams meetings.
- Tenant restrictions prevent users from using an externally issued identity to join Teams meetings.
Note
The Microsoft Teams app has a dependency on SharePoint Online and Exchange Online apps. We recommend setting the tenant restrictions v2 policy on the Office 365 app instead of setting the policy on Microsoft Teams services, SharePoint Online, or Exchange Online separately. If you allow or block one of the applications (SharePoint Online, Exchange Online, and so on) that are part of Office 365, it will also affect apps like Microsoft Teams. Similarly, if the Microsoft Teams app is allowed or blocked, SharePoint Online and Exchange Online within the Teams app will be affected.
Pure anonymous meeting join
Tenant restrictions v2 automatically blocks all unauthenticated and externally issued identity access to externally hosted Teams meetings.
For example, suppose Contoso uses Teams federation controls to block the Fabrikam tenant. If someone with a Contoso device uses a Fabrikam account to join a Contoso Teams meeting, they're allowed into the meeting as an anonymous user. If Contoso also enables tenant restrictions v2, Teams blocks anonymous access, and the user can't join the meeting.
Meeting join through an externally issued identity
You can configure the tenant restrictions v2 policy to allow specific users or groups with externally issued identities to join specific externally hosted Teams meetings. With this configuration, users can sign in to Teams with their externally issued identities and join the specified tenant's externally hosted Teams meetings.
| Authentication identity | Authenticated session | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Tenant member user Example: A user uses their home identity as a member user (such as user@<mytenant>.com). |
Authenticated | Tenant restrictions v2 allows access to the Teams meeting. Tenant restrictions v2 isn't applied to tenant member users. The inbound/outbound policy for cross-tenant access applies. |
| Anonymous Example: A user tries to use an unauthenticated session in an InPrivate browser window to access a Teams meeting. |
Not authenticated | Tenant restrictions v2 blocks access to the Teams meeting. |
| Externally issued identity Example: A user uses any identity other than their home identity (such as user@<externaltenant>.com). |
Authenticated as an externally issued identity | The tenant restrictions v2 policy allows or blocks access to the Teams meeting. The user can join the meeting if the policy allows it. Otherwise, access is blocked. |
Tenant restrictions v2 and SharePoint Online (preview)
SharePoint Online supports tenant restrictions v2 on both the authentication plane and the data plane.
Authenticated sessions
When tenant restrictions v2 is enabled on a tenant, unauthorized access is blocked during authentication. If a user directly accesses a SharePoint Online resource without an authenticated session, they're prompted to sign in. If the tenant restrictions v2 policy allows access, the user can access the resource. Otherwise, access is blocked.
Anonymous access (preview)
If a user tries to access an anonymous file by using their home tenant or corporate identity, the user can access the file. But if the user tries to access the anonymous file by using any externally issued identity, access is blocked.
For example, assume that a user is using a managed device configured with tenant restrictions v2 for Tenant A. If the user selects an anonymous access link generated for a Tenant A resource, they should be able to access the resource anonymously. But if the user selects an anonymous access link generated for SharePoint Online in Tenant B, they're prompted to sign in. Anonymous access to resources through an externally issued identity is always blocked.
Tenant restrictions v2 and OneDrive (preview)
Authenticated sessions
When tenant restrictions v2 is enabled on a tenant, unauthorized access is blocked during authentication. If a user directly accesses a OneDrive resource without an authenticated session, they're prompted to sign in. If the tenant restrictions v2 policy allows access, the user can access the resource. Otherwise, access is blocked.
Anonymous access (preview)
Like SharePoint, OneDrive supports tenant restrictions v2 on both the authentication plane and the data plane. Blocking anonymous access to OneDrive is also supported. For example, enforcement of the tenant restrictions v2 policy works at the OneDrive endpoint (microsoft-my.sharepoint.com).
Not in scope
OneDrive for consumer accounts (via onedrive.live.com) doesn't support tenant restrictions v2. Some URLs (such as onedrive.live.com) are unconverged and use the legacy stack. When a user accesses the OneDrive consumer tenant through these URLs, the policy isn't enforced. As a workaround, you can block https://onedrive.live.com/ at the proxy level.
Tenant restrictions v2 and service principals
Tenant restrictions v2 blocks access from a service principal. You can enable client signaling by using:
A firewall or corporate proxy. Sign in by using the service principal:
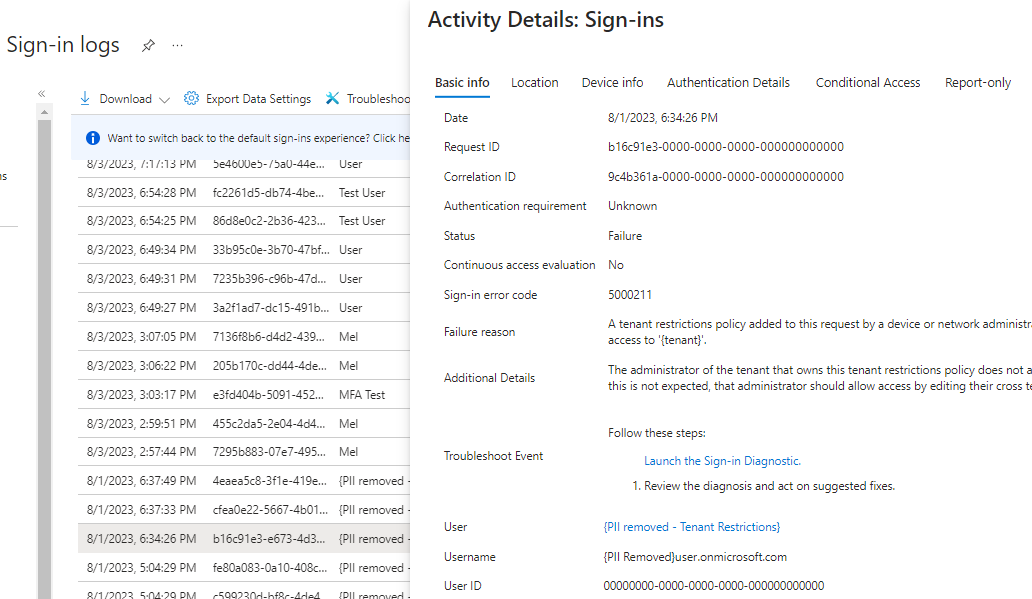
$client_id = "00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444" $clientSecret = Get-Credential -Username $client_id Connect-MgGraph -TenantId "aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee" -ClientSecretCredential $clientSecretThe sign-in fails with:
Connect-MgGraph : ClientSecretCredential authentication failed: AADSTS5000211: A tenant restrictions policy added to this request by a device or network administrator does not allow access to 'tenant'.A Windows GPO. You need to check Enable firewall protection of Microsoft endpoints and App Control for Business enablement. See Block Chrome, Firefox, and .NET applications like PowerShell earlier in this article.
Tenant restrictions with the Microsoft Enterprise SSO plug-in for Apple devices
The Microsoft Enterprise SSO plug-in for Apple devices provides single sign-on (SSO) for Microsoft Entra accounts on macOS, iOS, and iPadOS across all applications that support Apple's Enterprise SSO feature. To use the Microsoft Enterprise SSO plug-in for Apple devices, you need to exclude certain URLs from network proxies, interception, and other enterprise systems.
If your organization uses Apple OS versions released after 2022, there's no need to exclude Microsoft sign-in URLs from TLS inspection. If you're using the tenant restrictions feature, you can do TLS inspection on Microsoft sign-in URLs and add the necessary headers on the request. For more information, see Microsoft Enterprise SSO plug-in for Apple devices.
You can validate the networking configuration on a macOS device to make sure that SSO configuration isn't broken due to TLS inspection.
Sign-in logs
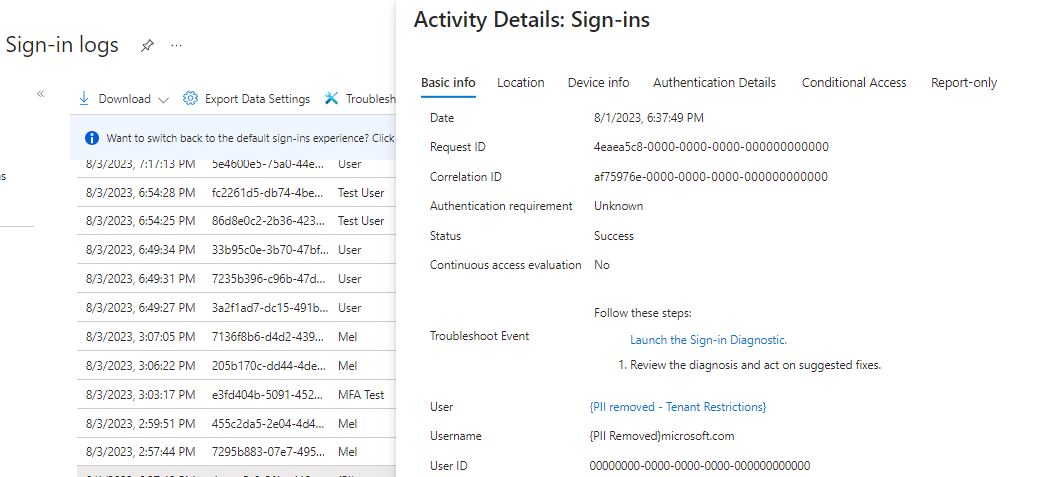
Microsoft Entra sign-in logs let you view details about sign-ins with a tenant restrictions v2 policy in place. When a B2B user signs in to a resource tenant to collaborate, a sign-in log is generated in both the home tenant and the resource tenant. These logs include information such as the application being used, email addresses, tenant name, and tenant ID for both the home tenant and the resource tenant. The following example shows a successful sign-in.
If sign-in fails, the activity details give information about the reason for the failure.
Audit logs
Audit logs provide records of system and user activities, including activities that guest users initiated. You can view audit logs for the tenant under Monitoring, or you can view audit logs for a specific user by going to the user's profile.
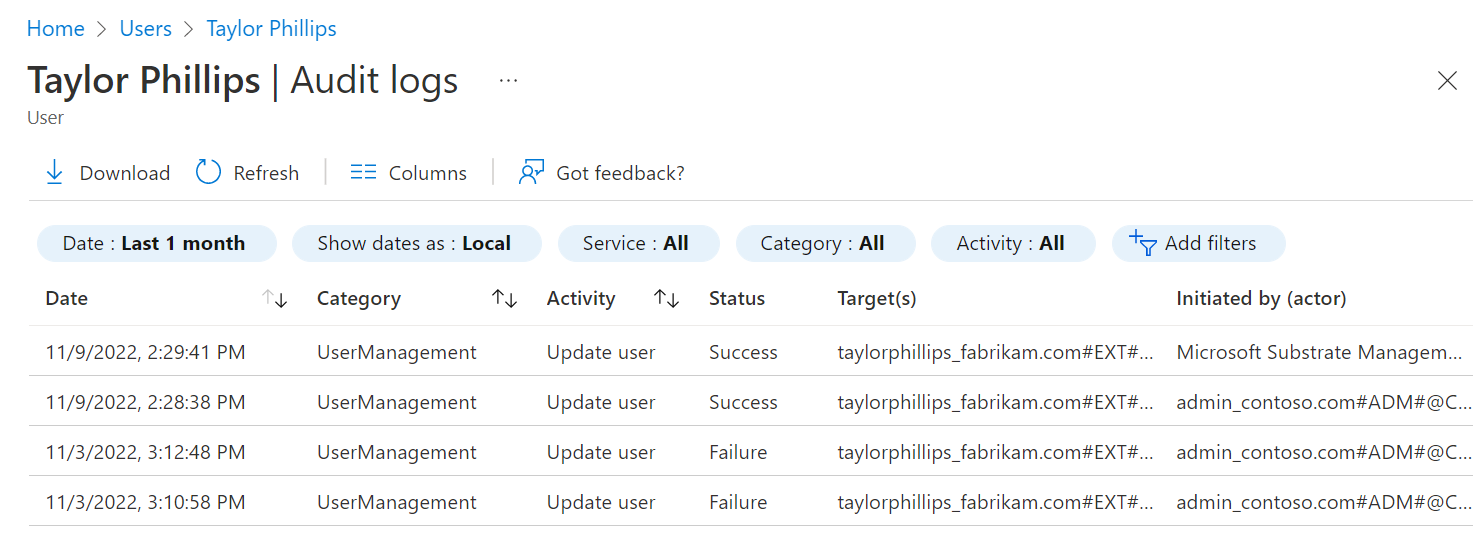
To get more details about the event, select the event in the log.
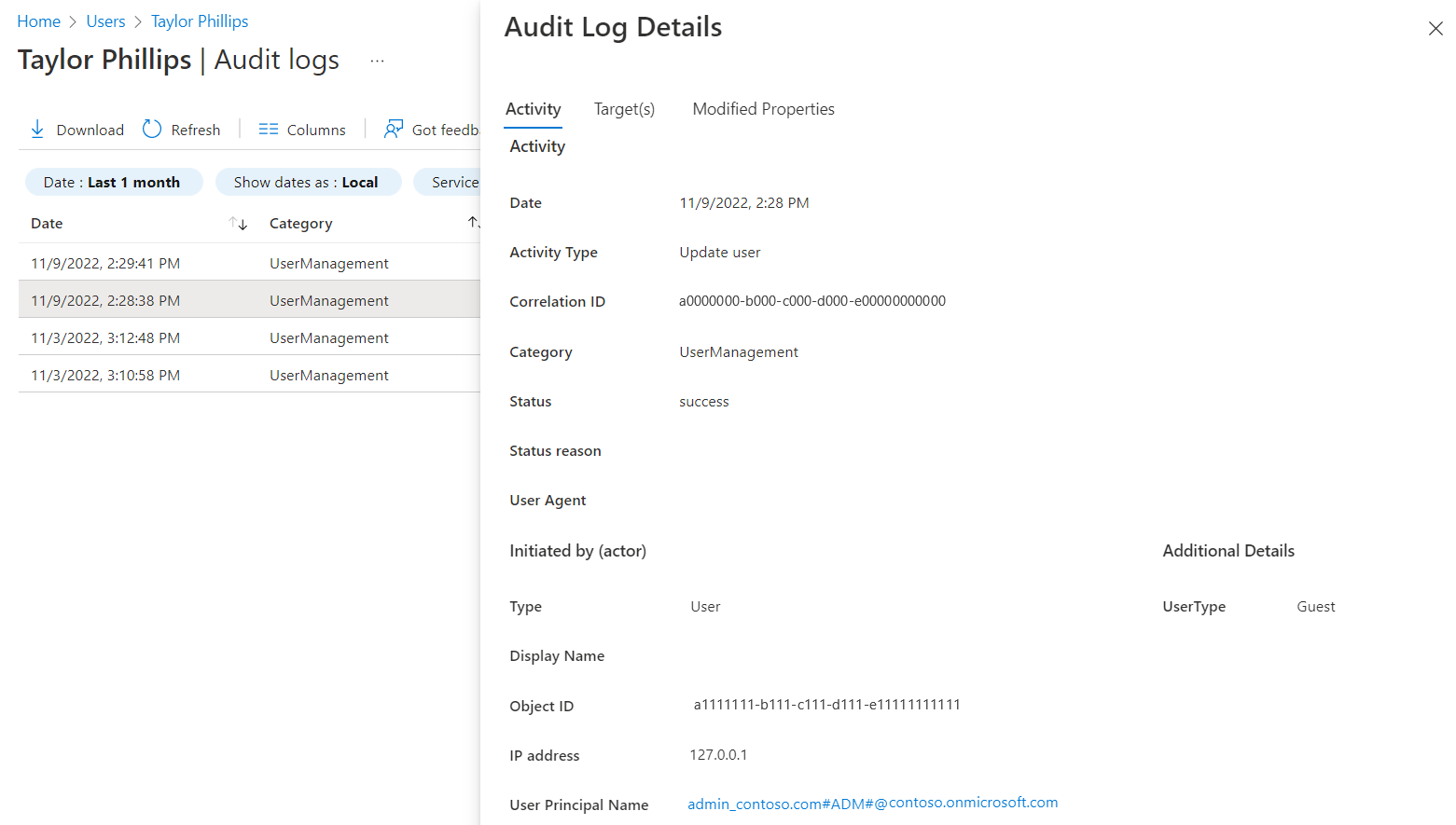
You can also export these logs from Microsoft Entra ID and use the reporting tool of your choice to get customized reports.
Microsoft Graph
Use Microsoft Graph to get policy information.
HTTP request
Get the default policy:
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/policies/crossTenantAccessPolicy/defaultReset to the system default:
POST https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/policies/crossTenantAccessPolicy/default/resetToSystemDefaultGet partner configurations:
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/policies/crossTenantAccessPolicy/partnersGet a specific partner configuration:
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/policies/crossTenantAccessPolicy/partners/9188040d-6c67-4c5b-b112-36a304b66dadUpdate a specific partner:
PATCH https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/policies/crossTenantAccessPolicy/partners/9188040d-6c67-4c5b-b112-36a304b66dad
Request body
"tenantRestrictions": {
"usersAndGroups": {
"accessType": "allowed",
"targets": [
{
"target": "AllUsers",
"targetType": "user"
}
]
},
"applications": {
"accessType": "allowed",
"targets": [
{
"target": "AllApplications",
"targetType": "application"
}
]
}
}
Known limitations
Tenant restrictions v2 is supported on all clouds. However, tenant restrictions v2 is not enforced with cross-cloud requests.
Tenant restrictions v2 doesn't work with the macOS Platform SSO feature with client signaling via corporate proxy. Customers who use tenant restrictions v2 and Platform SSO should use universal tenant restrictions v2 with Global Secure Access client signaling. This is an Apple limitation in which Platform SSO is not compatible with tenant restrictions when an intermediary network solution injects headers. An example of such a solution is a proxy that uses a certificate trust chain outside Apple system root certificates.