Use the cluster autoscaler in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
To keep up with application demands in AKS, you might need to adjust the number of nodes that run your workloads. The cluster autoscaler component watches for pods in your cluster that can't be scheduled because of resource constraints. When the cluster autoscaler detects issues, it scales up the number of nodes in the node pool to meet the application demands. It also regularly checks nodes for a lack of running pods and scales down the number of nodes as needed.
This article shows you how to enable and manage the cluster autoscaler in AKS, which is based on the open-source Kubernetes version.
Before you begin
This article requires Azure CLI version 2.0.76 or later. Run az --version to find the version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install Azure CLI.
Use the cluster autoscaler on an AKS cluster
Important
The cluster autoscaler is a Kubernetes component. Although the AKS cluster uses a virtual machine scale set for the nodes, don't manually enable or edit settings for scale set autoscaling. Let the Kubernetes cluster autoscaler manage the required scale settings. For more information, see Can I modify the AKS resources in the node resource group?
Enable the cluster autoscaler on a new cluster
Create a resource group using the
az group createcommand.az group create --name myResourceGroup --location eastusCreate an AKS cluster using the
az aks createcommand and enable and configure the cluster autoscaler on the node pool for the cluster using the--enable-cluster-autoscalerparameter and specifying a node--min-countand--max-count. The following example command creates a cluster with a single node backed by a virtual machine scale set, enables the cluster autoscaler, sets a minimum of one and maximum of three nodes:az aks create \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --node-count 1 \ --vm-set-type VirtualMachineScaleSets \ --load-balancer-sku standard \ --enable-cluster-autoscaler \ --min-count 1 \ --max-count 3It takes a few minutes to create the cluster and configure the cluster autoscaler settings.
Enable the cluster autoscaler on an existing cluster
Update an existing cluster using the
az aks updatecommand and enable and configure the cluster autoscaler on the node pool using the--enable-cluster-autoscalerparameter and specifying a node--min-countand--max-count. The following example command updates an existing AKS cluster to enable the cluster autoscaler on the node pool for the cluster and sets a minimum of one and maximum of three nodes:az aks update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --enable-cluster-autoscaler \ --min-count 1 \ --max-count 3It takes a few minutes to update the cluster and configure the cluster autoscaler settings.
Disable the cluster autoscaler on a cluster
Disable the cluster autoscaler using the
az aks updatecommand and the--disable-cluster-autoscalerparameter.az aks update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --disable-cluster-autoscalerNodes aren't removed when the cluster autoscaler is disabled.
Note
You can manually scale your cluster after disabling the cluster autoscaler using the az aks scale command. If you use the horizontal pod autoscaler, it continues to run with the cluster autoscaler disabled, but pods might end up unable to be scheduled if all node resources are in use.
Re-enable the cluster autoscaler on a cluster
You can re-enable the cluster autoscaler on an existing cluster using the az aks update command and specifying the --enable-cluster-autoscaler, --min-count, and --max-count parameters.
Use the cluster autoscaler on node pools
Use the cluster autoscaler on multiple node pools
You can use the cluster autoscaler with multiple node pools and can enable the cluster autoscaler on each individual node pool and pass unique autoscaling rules to them.
Update the settings on an existing node pool using the
az aks nodepool updatecommand.az aks nodepool update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --cluster-name myAKSCluster \ --name nodepool1 \ --update-cluster-autoscaler \ --min-count 1 \ --max-count 5
Disable the cluster autoscaler on a node pool
Disable the cluster autoscaler on a node pool using the
az aks nodepool updatecommand and the--disable-cluster-autoscalerparameter.az aks nodepool update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --cluster-name myAKSCluster \ --name nodepool1 \ --disable-cluster-autoscaler
Re-enable the cluster autoscaler on a node pool
You can re-enable the cluster autoscaler on a node pool using the az aks nodepool update command and specifying the --enable-cluster-autoscaler, --min-count, and --max-count parameters.
Note
If you plan on using the cluster autoscaler with node pools that span multiple zones and leverage scheduling features related to zones, such as volume topological scheduling, we recommend you have one node pool per zone and enable --balance-similar-node-groups through the autoscaler profile. This ensures the autoscaler can successfully scale up and keep the sizes of the node pools balanced.
Update the cluster autoscaler settings
As your application demands change, you might need to adjust the cluster autoscaler node count to scale efficiently.
Change the node count using the
az aks updatecommand and update the cluster autoscaler using the--update-cluster-autoscalerparameter and specifying your updated node--min-countand--max-count.az aks update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --update-cluster-autoscaler \ --min-count 1 \ --max-count 5
Note
The cluster autoscaler enforces the minimum count in cases where the actual count drops below the minimum due to external factors, such as during a spot eviction or when changing the minimum count value from the AKS API.
Use the cluster autoscaler profile
You can configure more granular details of the cluster autoscaler by changing the default values in the cluster-wide autoscaler profile. For example, a scale down event happens after nodes are under-utilized after 10 minutes. If you have workloads that run every 15 minutes, you might want to change the autoscaler profile to scale down under-utilized nodes after 15 or 20 minutes. When you enable the cluster autoscaler, a default profile is used unless you specify different settings.
Important
The cluster autoscaler profile affects all node pools that use the cluster autoscaler. You can't set an autoscaler profile per node pool. When you set the profile, any existing node pools with the cluster autoscaler enabled immediately start using the profile.
Cluster autoscaler profile settings
The following table lists the available settings for the cluster autoscaler profile:
| Setting | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
scan-interval |
How often the cluster is reevaluated for scale up or down. | 10 seconds |
scale-down-delay-after-add |
How long after scale up that scale down evaluation resumes. | 10 minutes |
scale-down-delay-after-delete |
How long after node deletion that scale down evaluation resumes. | scan-interval |
scale-down-delay-after-failure |
How long after scale down failure that scale down evaluation resumes. | Three minutes |
scale-down-unneeded-time |
How long a node should be unneeded before it's eligible for scale down. | 10 minutes |
scale-down-unready-time |
How long an unready node should be unneeded before it's eligible for scale down. | 20 minutes |
ignore-daemonsets-utilization (Preview) |
Whether DaemonSet pods will be ignored when calculating resource utilization for scale down. | false |
daemonset-eviction-for-empty-nodes (Preview) |
Whether DaemonSet pods will be gracefully terminated from empty nodes. | false |
daemonset-eviction-for-occupied-nodes (Preview) |
Whether DaemonSet pods will be gracefully terminated from non-empty nodes. | true |
scale-down-utilization-threshold |
Node utilization level, defined as sum of requested resources divided by capacity, in which a node can be considered for scale down. | 0.5 |
max-graceful-termination-sec |
Maximum number of seconds the cluster autoscaler waits for pod termination when trying to scale down a node. | 600 seconds |
balance-similar-node-groups |
Detects similar node pools and balances the number of nodes between them. | false |
expander |
Type of node pool expander uses in scale up. Possible values include most-pods, random, least-waste, and priority. |
random |
skip-nodes-with-local-storage |
If true, cluster autoscaler doesn't delete nodes with pods with local storage, for example, EmptyDir or HostPath. |
false |
skip-nodes-with-system-pods |
If true, cluster autoscaler doesn't delete nodes with pods from kube-system (except for DaemonSet or mirror pods). |
true |
max-empty-bulk-delete |
Maximum number of empty nodes that can be deleted at the same time. | 10 nodes |
new-pod-scale-up-delay |
For scenarios such as burst/batch scale where you don't want CA to act before the Kubernetes scheduler could schedule all the pods, you can tell CA to ignore unscheduled pods before they reach a certain age. | 0 seconds |
max-total-unready-percentage |
Maximum percentage of unready nodes in the cluster. After this percentage is exceeded, CA halts operations. | 45% |
max-node-provision-time |
Maximum time the autoscaler waits for a node to be provisioned. | 15 minutes |
ok-total-unready-count |
Number of allowed unready nodes, irrespective of max-total-unready-percentage. | Three nodes |
Set the cluster autoscaler profile on a new cluster
Create an AKS cluster using the
az aks createcommand and set the cluster autoscaler profile using thecluster-autoscaler-profileparameter.az aks create \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --node-count 1 \ --enable-cluster-autoscaler \ --min-count 1 \ --max-count 3 \ --cluster-autoscaler-profile scan-interval=30s
Set the cluster autoscaler profile on an existing cluster
Set the cluster autoscaler on an existing cluster using the
az aks updatecommand and thecluster-autoscaler-profileparameter. The following example configures the scan interval setting as 30s:az aks update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --cluster-autoscaler-profile scan-interval=30s
Configure cluster autoscaler profile for aggressive scale down
Note
Scaling down aggressively is not recommended for clusters experiencing frequent scale-outs and scale-ins within short intervals, as it could potentially result in extended node provisioning times under these circumstances. Increasing scale-down-delay-after-add can help in these circumstances by keeping the node around longer to handle incoming workloads.
az aks update \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--name myAKSCluster \
--cluster-autoscaler-profile scan-interval=30s, scale-down-delay-after-add=0s,scale-down-delay-after-failure=30s,scale-down-unneeded-time=3m,scale-down-unready-time=3m,max-graceful-termination-sec=30,skip-nodes-with-local-storage=false,max-empty-bulk-delete=1000,max-total-unready-percentage=100,ok-total-unready-count=1000,max-node-provision-time=15m
Configure cluster autoscaler profile for bursty workloads
az aks update \
--resource-group "myResourceGroup" \
--name myAKSCluster \
--cluster-autoscaler-profile scan-interval=20s,scale-down-delay-after-add=10m,scale-down-delay-after-failure=1m,scale-down-unneeded-time=5m,scale-down-unready-time=5m,max-graceful-termination-sec=30,skip-nodes-with-local-storage=false,max-empty-bulk-delete=100,max-total-unready-percentage=100,ok-total-unready-count=1000,max-node-provision-time=15m
Reset cluster autoscaler profile to default values
Reset the cluster autoscaler profile using the
az aks updatecommand.az aks update \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --name myAKSCluster \ --cluster-autoscaler-profile ""
Retrieve cluster autoscaler logs and status
You can retrieve logs and status updates from the cluster autoscaler to help diagnose and debug autoscaler events. AKS manages the cluster autoscaler on your behalf and runs it in the managed control plane. You can enable control plane node to see the logs and operations from the cluster autoscaler.
Set up a rule for resource logs to push cluster autoscaler logs to Log Analytics using the instructions here. Make sure you check the box for
cluster-autoscalerwhen selecting options for Logs.Select the Log section on your cluster.
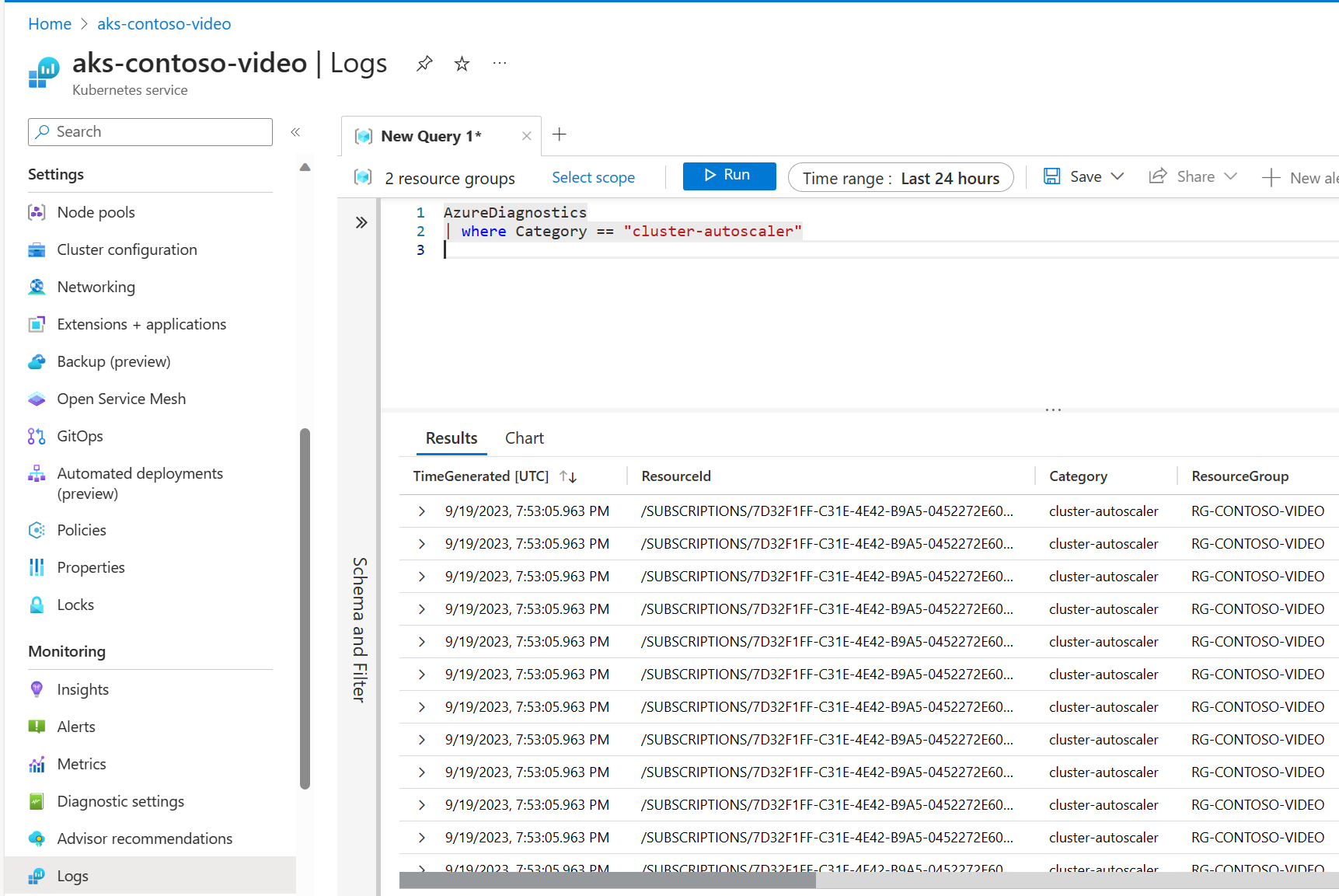
Enter the following example query into Log Analytics:
AzureDiagnostics | where Category == "cluster-autoscaler"As long as there are logs to retrieve, you should see logs similar to the following logs:
View cluster autoscaler scale-up not triggered events on CLI
kubectl get events --field-selector source=cluster-autoscaler,reason=NotTriggerScaleUpView cluster autoscaler warning events on CLI
kubectl get events --field-selector source=cluster-autoscaler,type=WarningThe cluster autoscaler also writes out the health status to a
configmapnamedcluster-autoscaler-status. You can retrieve these logs using the followingkubectlcommand:kubectl get configmap -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler-status -o yaml
For more information, see the Kubernetes/autoscaler GitHub project FAQ.
Cluster Autoscaler Metrics
You can enable control plane metrics (Preview) to see the logs and operations from the cluster autoscaler with the Azure Monitor managed service for Prometheus add-on
Next steps
This article showed you how to automatically scale the number of AKS nodes. You can also use the horizontal pod autoscaler to automatically adjust the number of pods that run your application. For steps on using the horizontal pod autoscaler, see Scale applications in AKS.
To further help improve cluster resource utilization and free up CPU and memory for other pods, see Vertical Pod Autoscaler.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for