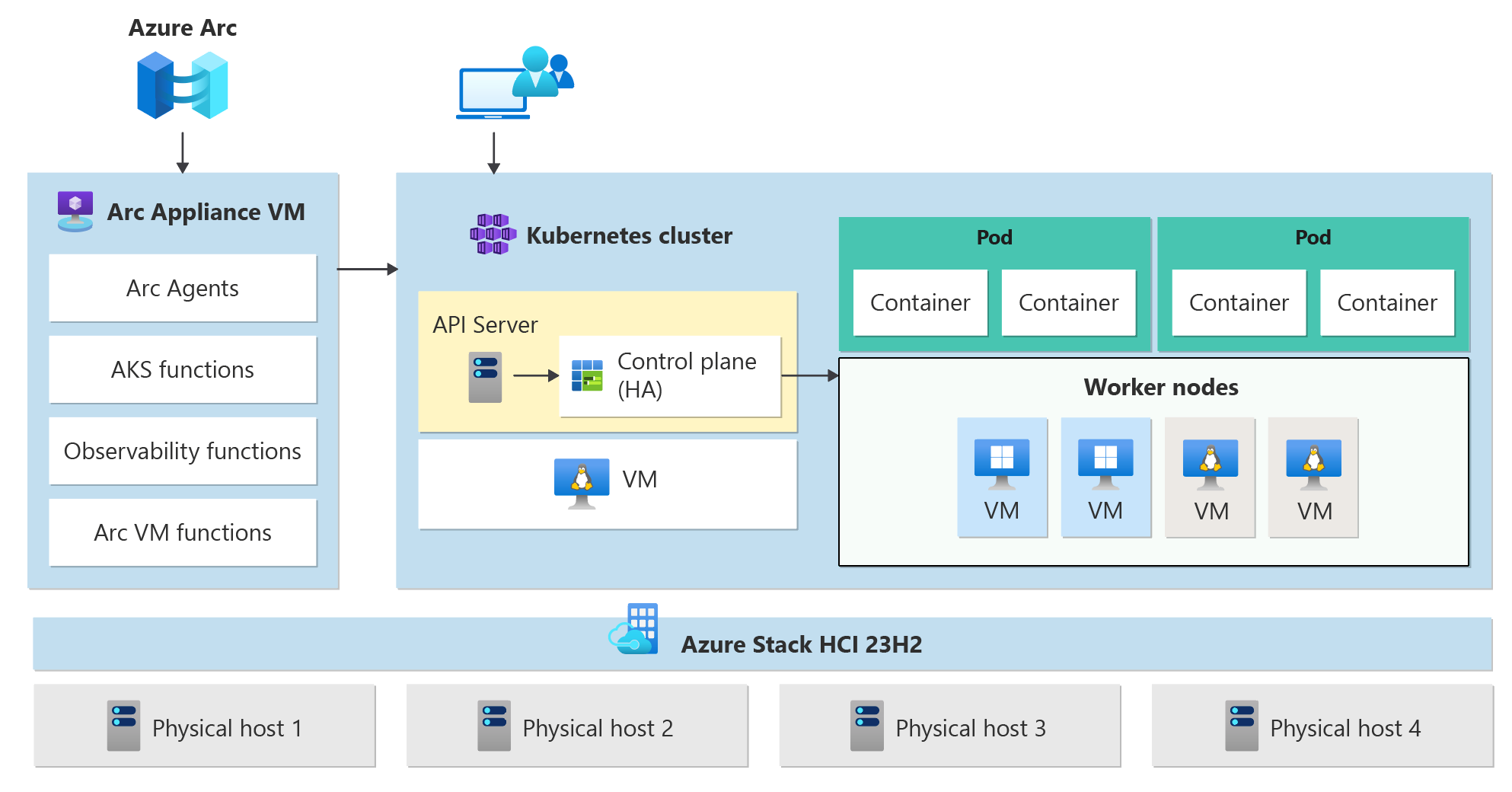
AKS on Azure Stack HCI 23H2 architecture
Applies to: Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) on Azure Stack HCI is an enterprise-grade Kubernetes container platform. It includes Microsoft-supported core Kubernetes, a purpose-built Windows container host, and a Microsoft-supported Linux container host, with a goal to have a simple deployment and lifecycle management experience.
This article introduces the core Kubernetes infrastructure components, such as the control plane, nodes, and node pools. Workload resources such as pods, deployments, and sets are also introduced, along with how to group resources into namespaces.
AKS architecture on Azure Stack HCI
AKS clusters on Azure Stack HCI use Arc Resource Bridge (also known as Arc appliance) to provide the core orchestration mechanism and interface for deploying and managing one or more AKS clusters. Containerized applications are deployed into AKS clusters.
AKS Arc uses a predefined configuration to deploy Kubernetes clusters effectively and with scalability in mind. A deployment operation creates multiple Linux or Windows virtual machines and joins them together to create one or more Kubernetes clusters.
Note
To help improve the reliability of the system, if you run multiple Cluster Shared Volumes (CSVs) in your cluster, by default virtual machine data is automatically spread out across all available CSVs in the cluster. This ensures that applications survive in the event of CSV outages.
Arc Resource Bridge
The Arc Resource Bridge connects a private cloud (for example, Azure Stack HCI, VMWare/vSphere, or SCVMM) to Azure and enables on-premises resource management from Azure. Azure Arc Resource Bridge provides the line of sight to private clouds required to manage resources such as Kubernetes clusters on-premises through Azure. Arc Resource Bridge includes the following core AKS Arc components:
- AKS Arc cluster extensions: A cluster extension is the on-premises equivalent of an Azure Resource Manager resource provider. Just as the Microsoft.ContainerService resource provider manages AKS clusters in Azure, the AKS Arc cluster extension, once added to your Arc Resource Bridge, helps manage Kubernetes clusters via Azure.
- Custom location: A custom location is the on-premises equivalent of an Azure region and is an extension of the Azure location construct. Custom locations provide a way for tenant administrators to use their data center with the right extensions installed, as target locations for deploying Azure service instances.
AKS clusters
AKS clusters are a high availability deployment of Kubernetes using Linux VMs for running Kubernetes control plane components and Linux node pools. You can deploy additional Windows Server Core-based node pools for running Windows containers. There can be one or more AKS clusters managed by Arc Resource Bridge.
An AKS cluster has 2 major components, as described in the following sections.
Control plane nodes
Kubernetes uses control plane nodes to ensure every component in the Kubernetes cluster is kept in the desired state. The control plane also manages and maintains the worker node pools that hold the containerized applications. AKS enabled by Arc deploys the KubeVIP load balancer to ensure that the API server IP address of the Kubernetes control plane is available at all times. Microsoft does not charge you for control plane nodes, since control plane nodes do not host customer applications.
Control plane nodes run the following major components (not an exhaustive list):
- API server: Enables interaction with the Kubernetes API. This component provides the interaction for management tools, such as Azure CLI, the Azure portal, or kubectl.
- Etcd: A distributed key-value store that stores data required for lifecycle management of the cluster. It stores the control plane state.
Linux/Windows node pools
In Kubernetes, a node pool is a group of nodes within a cluster that share the same configuration. Node pools allow you to create and manage sets of nodes that have specific roles, capabilities, or hardware configurations, enabling more granular control over the infrastructure of your AKS cluster. You can deploy Linux or Windows node pools in your AKS cluster. However, you need to have at least 1 Linux nodepool to host the Arc agents to maintain connectivity with Azure.
Mixed-OS deployments
If a given workload cluster consists of both Linux and Windows worker nodes, it must be scheduled onto an OS that can support provisioning the workload. Kubernetes offers two mechanisms to ensure that workloads land on nodes with a target operating system:
- Node Selector is a simple field in the pod spec that constrains pods to only be scheduled onto healthy nodes matching the operating system.
- Taints and tolerations work together to ensure that pods aren't scheduled onto nodes unintentionally. A node can be "tainted" so as to not accept pods that don't explicitly tolerate its taint through a "toleration" in the pod spec.
For more information, see node selectors and taints and tolerations.
Lifecycle management
Azure Arc is automatically enabled on all your Kubernetes clusters created using AKS Arc. You can use your Microsoft Entra ID for connecting to your clusters from anywhere. Azure Arc enables you to use familiar tools like the Azure portal, Azure CLI, and Azure Resource Manager templates to create and manage your Kubernetes clusters.
Cloud-based updates for infrastructure components
Azure Stack HCI 23H2 consolidates all the relevant updates for the OS, software agents, Azure Arc infrastructure, and OEM drivers and firmware into a unified monthly update package. This comprehensive update package is identified and applied from the cloud through the Azure Update Manager tool.
AKS is now part of Azure Stack HCI starting from version 23H2. The lifecycle management of AKS enabled by Azure Arc infrastructure follows the same approach as any other components on Azure Stack HCI 23H2. This approach provides a flexible foundation to integrate and manage various aspects of the Azure Stack HCI solution in one place, including the management of the OS, core agents and services, and the solution extension. AKS enabled by Arc infrastructure components, as part of solution extensions, are updated by the update package of Azure Stack HCI 23H2.
For more information, see the Update overview for Azure Stack HCI, version 23H2.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for