Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: AKS on Azure Local
The main purpose of a load balancer is to distribute traffic across multiple nodes in a Kubernetes cluster. This can help prevent downtime and improve overall performance of applications. AKS enabled by Azure Arc supports creating a MetalLB load balancer instance on your Kubernetes cluster using the MetalLB extension for Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes.
Prerequisites
- An Azure Arc enabled Kubernetes cluster with at least one Linux node. You can create a Kubernetes cluster on Azure Local using the Azure CLI or the Azure portal. AKS on Azure Local clusters are Arc enabled by default.
- Make sure you have enough IP addresses for the load balancer. For AKS on Azure Local, ensure that the IP addresses reserved for the load balancer don't conflict with the IP addresses in Arc VM logical networks and control plane IPs. For more information about IP address planning and networking in Kubernetes, see Networking requirements for Kubernetes and IP address planning for Kubernetes.
- This how-to guide assumes you understand how MetalLB works. For more information, see the overview for MetalLB for Kubernetes.
Deploy MetalLB load balancer using the Azure Arc extension
Warning
IP address conflict checking is not currently supported. It's recommended that you perform this check when you create load balancers.
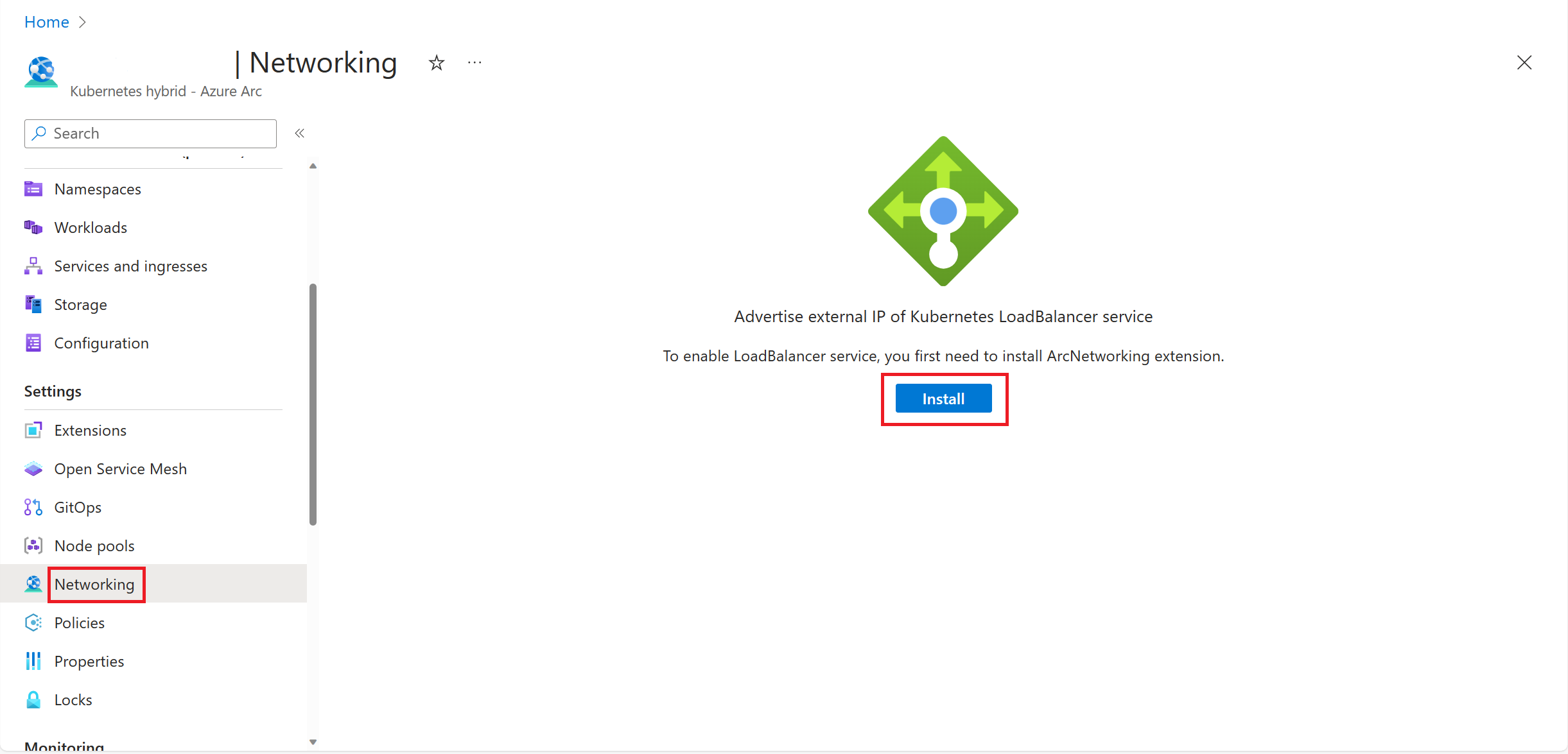
Once you successfully create your Kubernetes cluster, navigate to the Networking blade in the Azure portal and select Install:
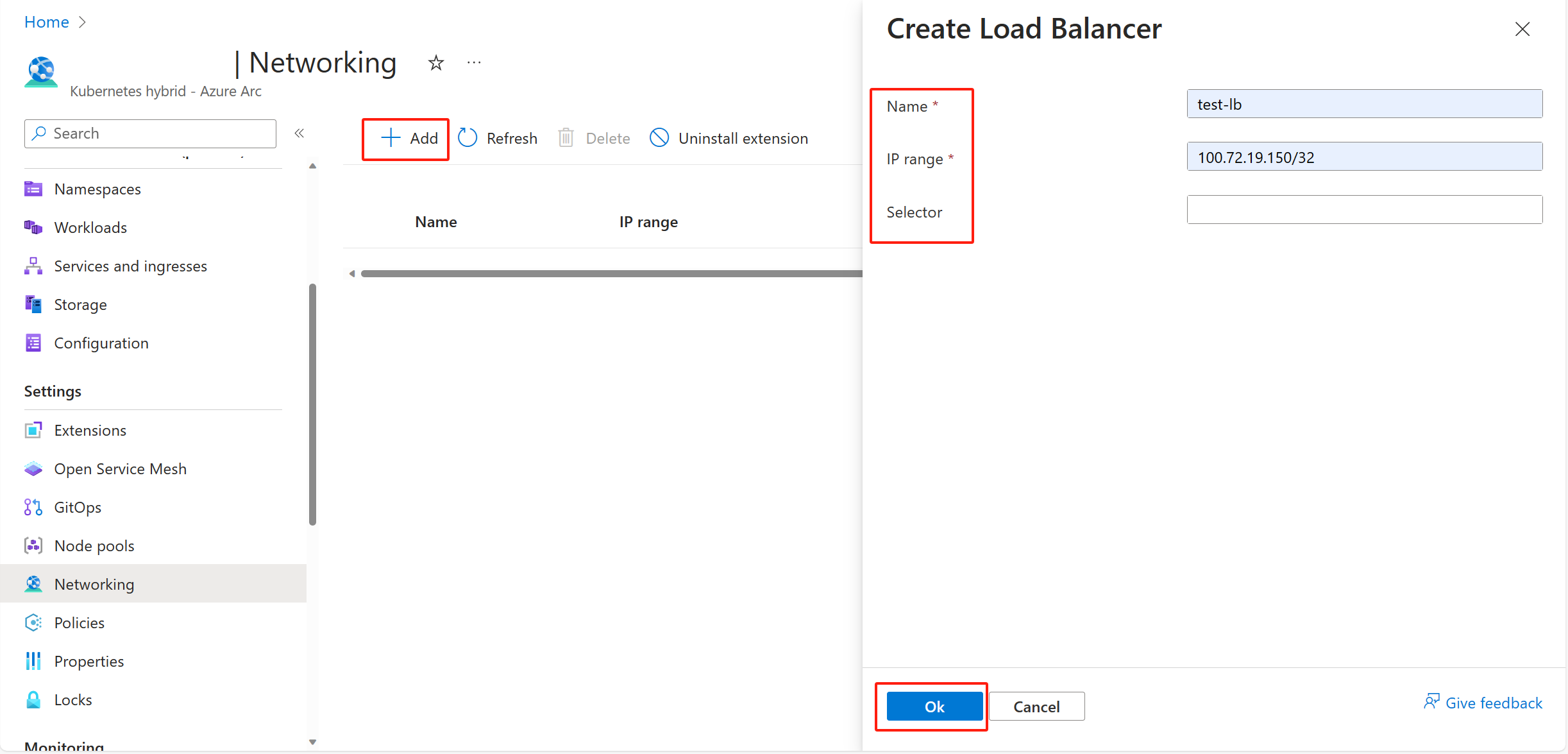
After the extension is successfully installed, you can create a load balancer service. Select Add and fill in the load balancer name and its IP range. The Service Selector field is optional. Then select OK.
- The IP range should be set to available IPs depending on your environment. The IP range should be in CIDR notation; for example, 192.168.50.51/28 or 192.168.50.1-192.168.50.100. Multiple IP ranges must be separated by commas.
- The advertise mode can be ARP, BGP, or Both. If you use BGP or Both, you must configure BGP peers.
- Service Selector limits the set of services that can get an IP from the load balancer. The default option (null or empty string) means that the load balancer applies for all services. Selector should be in a format of a list of key-value pairs such as a:b,c:d, where the key-value pairs are separated by a comma.
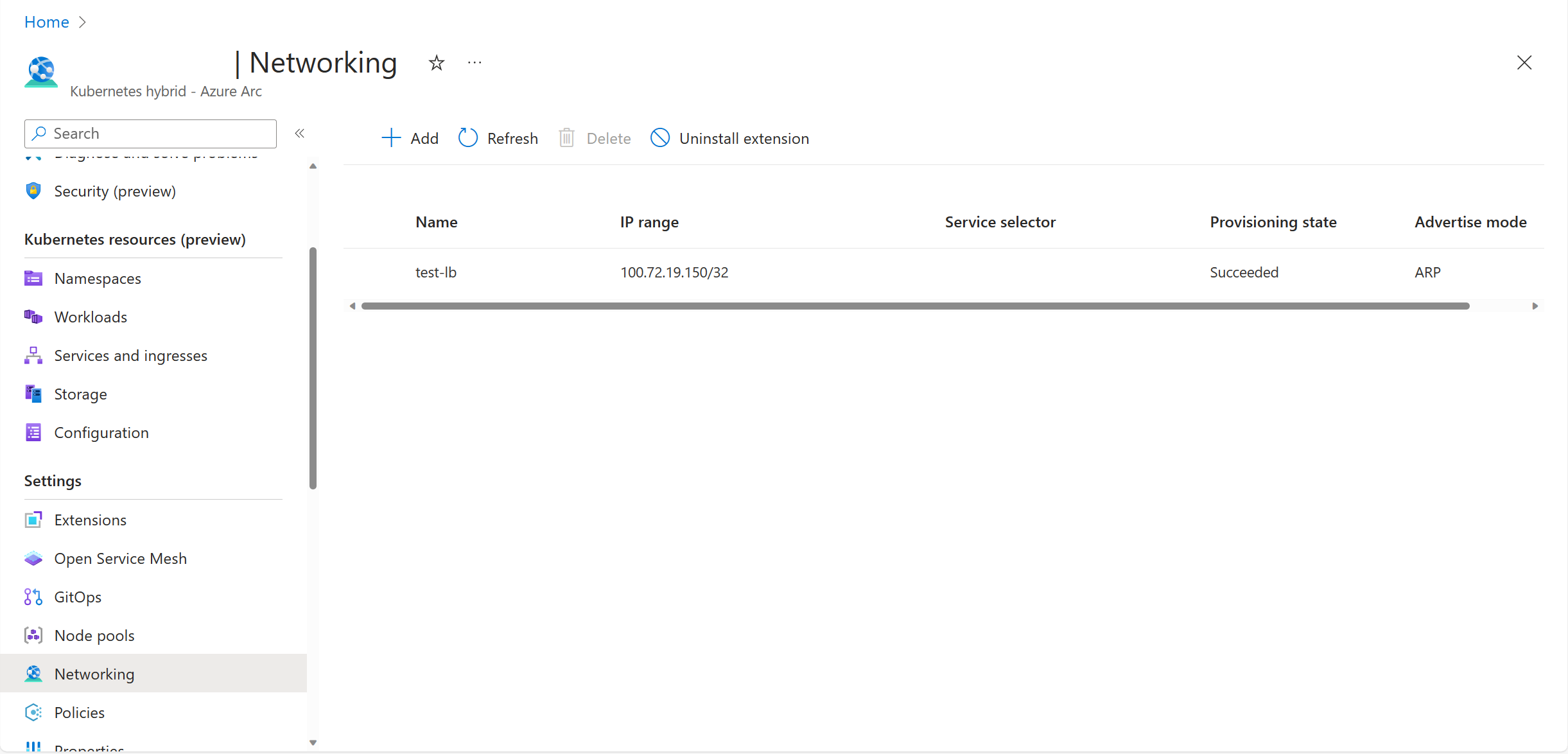
Once the load balancer is successfully created, it's shown in the list as follows. Provisioning state shows the operation result:
Clean up resources
To clean up resources, do the following:
- When one of the load balancers is no longer needed, select the start of the row for the load balancer and select Delete. Then select Yes.
- When the load balancer service is no longer needed, delete all existing load balancers and then select Uninstall. Select Yes to uninstall the MetalLB extension.
Next steps
Use GitOps Flux v2 Arc extension to deploy applications on your Kubernetes cluster