Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
By using any programming language that supports REST calls, you can perform asynchronous data-refresh operations on your Azure Analysis Services tabular models, including synchronization of read-only replicas for query scale-out.
Data-refresh operations can take some time depending on many factors including data volume, level of optimization using partitions, etc. Traditionally, these operations have been invoked with existing methods such as using TOM (Tabular Object Model), PowerShell cmdlets, or TMSL (Tabular Model Scripting Language). However, these methods can require often unreliable, long-running HTTP connections.
The REST API for Azure Analysis Services enables data-refresh operations to be carried out asynchronously. By using the REST API, long-running HTTP connections from client applications aren't necessary. There are also other built-in features for reliability, such as auto retries and batched commits.
Base URL
The base URL follows this format:
https://<rollout>.asazure.windows.net/servers/<serverName>/models/<resource>/
For example, consider a model named AdventureWorks on a server named myserver, located in the West US Azure region. The server name is:
asazure://westus.asazure.windows.net/myserver
The base URL for this server name is:
https://westus.asazure.windows.net/servers/myserver/models/AdventureWorks/
By using the base URL, resources and operations can be appended based on the following parameters:
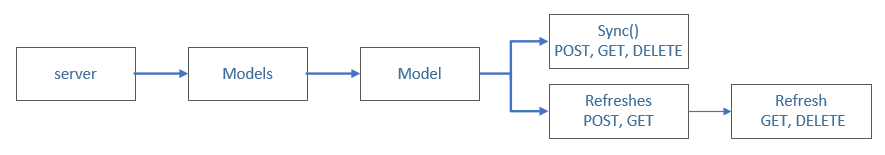
- Anything that ends in s is a collection.
- Anything that ends with () is a function.
- Anything else is a resource/object.
For example, you can use the POST verb on the Refreshes collection to perform a refresh operation:
https://westus.asazure.windows.net/servers/myserver/models/AdventureWorks/refreshes
Authentication
All calls must be authenticated with a valid Microsoft Entra ID (OAuth 2) token in the Authorization header and must meet the following requirements:
The token must be either a user token or an application service principal.
The token must have the audience set to exactly
https://*.asazure.windows.net. Note that*isn't a placeholder or a wildcard, and the audience must have the*character as the subdomain. Custom audiences, such ashttps://customersubdomain.asazure.windows.net, are not supported. Specifying an invalid audience results in authentication failure.The user or application must have sufficient permissions on the server or model to make the requested call. The permission level is determined by roles within the model or the admin group on the server.
Important
Currently, server admin role permissions are necessary.
POST /refreshes
To perform a refresh operation, use the POST verb on the /refreshes collection to add a new refresh item to the collection. The Location header in the response includes the refresh ID. The client application can disconnect and check the status later if necessary because it's asynchronous.
Only one refresh operation is accepted at a time for a model. If there's a current running refresh operation and another is submitted, the 409 Conflict HTTP status code is returned.
The body may resemble the following:
{
"Type": "Full",
"CommitMode": "transactional",
"MaxParallelism": 2,
"RetryCount": 2,
"Objects": [
{
"table": "DimCustomer",
"partition": "DimCustomer"
},
{
"table": "DimDate"
}
]
}
Parameters
The default value is applied if the parameter isn't specified.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
Type |
Enum | The type of processing to perform. The types are aligned with the TMSL refresh command types: full, clearValues, calculate, dataOnly, automatic, and defragment. add type isn't supported. |
automatic |
CommitMode |
Enum | Determines if objects are committed in batches or committed only when the entire operation completes. Modes include: transactional, partialBatch. |
transactional |
MaxParallelism |
Int | This value determines the maximum number of threads on which to run processing commands in parallel. This value aligned with the MaxParallelism property that can be set in the TMSL Sequence command or using other methods. | 10 |
RetryCount |
Int | Indicates the number of times the operation retries before failing. | 0 |
Objects |
Array | An array of objects to be processed. Each object includes: "table" when processing the entire table or "table" and "partition" when processing a partition. If no objects are specified, the whole model is refreshed. | Process the entire model |
Specifying partialBatch for CommitMode is useful when doing an initial load of large datasets that could take hours. If the refresh operation fails after successfully committing one or more batches, the successfully committed batches will remain committed (it will not roll back successfully committed batches).
Note
At time of writing, the batch size is the MaxParallelism value, but this value could change.
Status values
| Status value | Description |
|---|---|
notStarted |
Operation not yet started. |
inProgress |
Operation in progress. |
timedOut |
Operation timed out based on user specified timeout. |
cancelled |
Operation canceled by user or system. |
failed |
Operation failed. |
succeeded |
Operation succeeded. |
GET /refreshes/<refreshId>
To check the status of a refresh operation, use the GET verb on the refresh ID. Here's an example of the response body. If the operation is in progress, inProgress is returned in status.
{
"startTime": "2017-12-07T02:06:57.1838734Z",
"endTime": "2017-12-07T02:07:00.4929675Z",
"type": "full",
"status": "succeeded",
"currentRefreshType": "full",
"objects": [
{
"table": "DimCustomer",
"partition": "DimCustomer",
"status": "succeeded"
},
{
"table": "DimDate",
"partition": "DimDate",
"status": "succeeded"
}
]
}
GET /refreshes
To get a list of historical refresh operations for a model, use the GET verb on the /refreshes collection. Here's an example of the response body.
Note
At time of writing, the last 30 days of refresh operations are stored and returned, but this number could change.
[
{
"refreshId": "1344a272-7893-4afa-a4b3-3fb87222fdac",
"startTime": "2017-12-07T02:06:57.1838734Z",
"endTime": "2017-12-07T02:07:00.4929675Z",
"status": "succeeded"
},
{
"refreshId": "474fc5a0-3d69-4c5d-adb4-8a846fa5580b",
"startTime": "2017-12-07T01:05:54.157324Z",
"endTime": "2017-12-07T01:05:57.353371Z",
"status": "succeeded"
}
]
DELETE /refreshes/<refreshId>
To cancel an in-progress refresh operation, use the DELETE verb on the refresh ID.
POST /sync
Having performed refresh operations, it may be necessary to synchronize the new data with replicas for query scale-out. To perform a synchronize operation for a model, use the POST verb on the /sync function. The Location header in the response includes the sync operation ID.
GET /sync status
To check the status of a sync operation, use the GET verb passing the operation ID as a parameter. Here's an example of the response body:
{
"operationId": "cd5e16c6-6d4e-4347-86a0-762bdf5b4875",
"database": "AdventureWorks2",
"UpdatedAt": "2017-12-09T02:44:26.18",
"StartedAt": "2017-12-09T02:44:20.743",
"syncstate": 2,
"details": null
}
Values for syncstate:
- 0: Replicating. Database files are being replicated to a target folder.
- 1: Rehydrating. The database is being rehydrated on read-only server instance(s).
- 2: Completed. The sync operation completed successfully.
- 3: Failed. The sync operation failed.
- 4: Finalizing. The sync operation has completed but is performing cleanup steps.
Code sample
Here's a C# code sample to get you started, RestApiSample on GitHub.
To use the code sample
- Clone or download the repo. Open the RestApiSample solution.
- Find the line client.BaseAddress = … and provide your base URL.
The code sample uses service principal authentication.
Service principal
See Create service principal - Azure portal and Add a service principal to the server administrator role for more info and follow the steps on how to set up a service principal and assign the necessary permissions in Azure AS. Then complete the following extra steps:
- In the code sample, find string authority = …, replace common with your organization's tenant ID.
- Comment/uncomment so the ClientCredential class is used to instantiate the cred object. Ensure the <App ID> and <App Key> values are accessed in a secure way or use certificate-based authentication for service principals.
- Run the sample.