Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article shows how to secure an Azure service resource with an Azure network security perimeter and access it through Azure API Management.
As an example, you configure an Azure Storage account with a network security perimeter to allow traffic from your subscription (containing the API Management instance), use API Management's managed identity to authenticate to Azure Storage, and verify access with the API Management test console. Trusted service connectivity and public access to the storage account will be disabled.
Why use a network security perimeter with API Management?
A network security perimeter provides a supported, centralized perimeter to explicitly allow traffic while keeping public access disabled. It provides:
- Modern token trust model: Managed identity tokens now include trust mode claims that no longer permit implicit network bypass. A network security perimeter establishes the explicit network path your backend requires.
- Centralized governance: A network security perimeter consolidates per‑service network rules into a single perimeter, improving consistency and observability across protected resources.
- Works without a virtual network: For API Management instances not isolated with a virtual network, network security perimeter enables secure access by subscription or IP range. If virtual network isolation is available and preferred, you can continue to use that approach.
Note
Beginning March 2026, API Management is retiring trusted service connectivity from the gateway to select backend Azure services. If those backends such as Azure storage accounts rely on trusted Microsoft services or resource instances for network access, you must migrate. A network security perimeter provides the supported, centralized perimeter to explicitly allow traffic while keeping public access disabled.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription and Owner or Contributor permissions.
- An Azure API Management instance with a system-assigned or user-assigned managed identity enabled.
- An Azure Storage account
- Configure a container and at least one test blob (for example, a JSON file).
- To begin, enable public network access to the storage account. By default, this setting also enables trusted Microsoft services and resource instances to access the storage account. You modify access later when associating the network security perimeter.
Overview of steps
Configure API Management to call Azure Storage using a managed identity.
Block public network access to the storage account.
Create a network security perimeter profile and associate the storage account.
Add an inbound access rule to allow API Management traffic.
Move network security perimeter access mode from transition to enforced.
Step 1. Configure API Management to call Azure Storage by using managed identity
Configure API Management to call Azure Storage. Add a test API and operation, and configure a policy to authenticate by using API Management's managed identity.
- In the Azure portal, go to your API Management instance.
- Ensure that a system-assigned or user-assigned managed identity is enabled. For steps, see Use managed identities in API Management.
- Go to the storage account and grant the managed identity access:
- In the left menu, select Access control (IAM) > Add role assignment.
- Select Storage Blob Data Reader role (or Contributor, if write access is required) and assign to the API Management managed identity.
- Complete the role assignment steps.
Configure an API operation to call Azure Storage
Add an HTTP API that fronts the Azure Storage blob URI (for example,
https://<storage-account-name>.blob.core.windows.net/apimtest).Add a GET operation targeting the container.
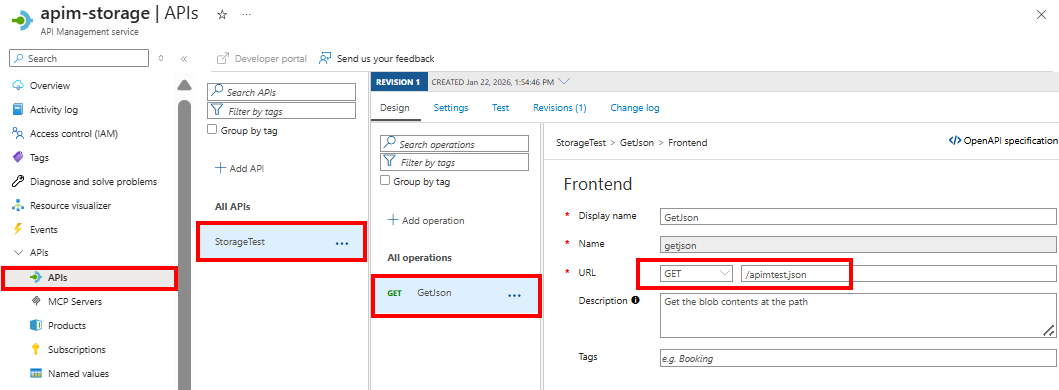
On the Design tab, select the operation and then select the policy editor (
</>). Edit the operation's policy definition to add the API version header and managed identity authentication.
In the following example:
The
authentication-managed-identitypolicy assumes that the API Management instance has a system-assigned managed identity enabled and can access Azure Storage. To use a user-assigned managed identity, set aclient-idattribute in the policy. For more information, see the policy reference.The
set-headerpolicy sets the required Storage REST API version header.<policies> <inbound> <base /> <!-- Authenticate to Storage using API Management managed identity --> <authentication-managed-identity resource="https://storage.azure.com/" /> <!-- Set Storage API version header --> <set-header name="x-ms-version" exists-action="override"> <value>2025-11-05</value> </set-header> </inbound> <backend> <forward-request /> </backend> <outbound> <base /> </outbound> <on-error> <base /> </on-error> </policies>
Note
- The
resourcevalue should behttps://storage.azure.com/for Azure Storage. - Ensure the managed identity is assigned the appropriate RBAC role.
Test the API operation
Before configuring the network security perimeter, test that the API operation can reach the storage account.
- In the left menu, under APIs, select your API and operation.
- Select the Test tab.
- Select Test and call the operation. Optionally select Trace to capture detailed telemetry.
Expected results:
- The call succeeds with a
200 OKresponse and returns the blob content. - If you enabled Trace, you can verify that API Management added the managed identity token to the Authorization header.
Step 2. Block public network access to the storage account
If you now block public network access to the storage account, the API call from API Management fails because trusted service connectivity is disabled.
- In the Azure portal, go to your storage account.
- In the left menu, under Security + networking, select Networking.
- On the Public access tab, select Manage. Disable public network access.
- Select Save.
Test the API operation
Test that the API operation can no longer reach the storage account.
- In the Azure portal, go to your API Management instance.
- In the left menu, under APIs, select your API and operation.
- Select the Test tab.
- Select Test and call the operation. Optionally select Trace to capture detailed telemetry.
Expected result:
- The call fails with a
403 Forbiddenresponse.
Step 3. Create a network security perimeter profile and associate the storage account
For typical steps to create a network security perimeter and associate an Azure resource with a profile, see Create a network security perimeter and profile. Brief steps follow:
- In the Azure portal, search for Network Security Perimeters and select it.
- Select + Create and provide a name and region. Accept the defaults for other settings and create the perimeter.
- After deployment, go to the Settings > Associated resources blade to associate the storage account with an existing or new profile.
Step 4: Add an inbound access rule to allow API Management traffic
To allow API Management to reach the storage account through the perimeter, add an inbound rule. The simplest approach is by Azure subscription.
- In the left menu of our network security perimeter, select Settings > Profiles, then select the profile you associated with the storage account.
- In the left menu, select Settings > Inbound access rules > + Add:
- Enter a name for the rule.
- Select Source type Subscriptions, then in Allowed sources select the subscription that contains your API Management instance.
- Select Add.
Note
If you select IP address-based control, specify API Management's outbound public IP address range in the inbound rule. Ensure you include all outbound IP addresses for your API Management instance.
Confirm the network configuration in the storage account
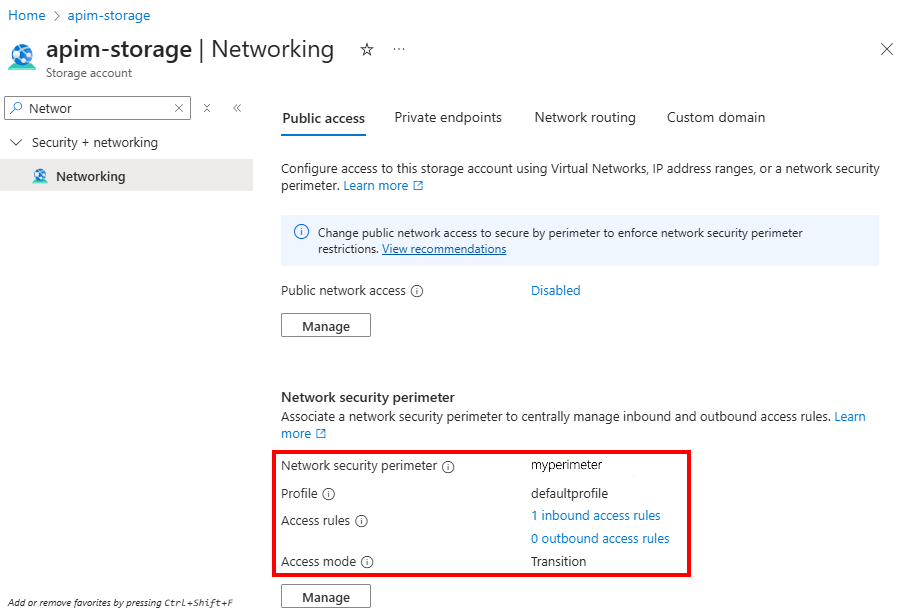
- In the Azure portal, go to your storage account.
- In the left menu, under Security + networking, select Networking.
- Under Network security perimeter, confirm that the storage account is associated with your network security perimeter profile and that the access rule is listed.
Test the API operation
Test that the API operation can reach the storage account in the network security perimeter.
- In the Azure portal, go to your API Management instance.
- In the left menu, under APIs, select your API and operation.
- Select the Test tab.
- Select Test and call the operation. Optionally select Trace to capture detailed telemetry.
Expected result:
- The call succeeds with a
200 OKresponse and returns the blob content.
Step 5. Move access mode to enforced
A network security perimeter supports the following access modes:
- Transition: Applies both existing per-resource network settings and network security perimeter rules. This mode is the default when you first associate a resource.
- Enforced: Applies only network security perimeter rules. Use this mode once you validate access.
After you validate access in transition mode, set the network security perimeter's access mode to enforced. For more information, see Steps to configure publicNetworkAccess and accessMode properties.