Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Application Gateway for Containers allows you to rewrite HTTP headers of client requests and responses from backend targets.
Usage details
Header rewrites take advantage of Application Gateway for Container's IngressExtension custom resource.
Background
Header rewrites enable you to modify the request and response headers to and from your backend targets.
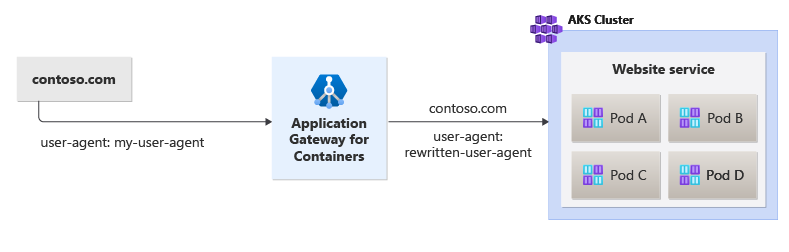
The following figure illustrates an example of a request with a specific user agent being rewritten to a simplified value called rewritten-user-agent when the request is initiated to the backend target by Application Gateway for Containers:
Prerequisites
If following the BYO deployment strategy, ensure you have set up your Application Gateway for Containers resources and ALB Controller
If following the ALB managed deployment strategy, ensure you have provisioned your ALB Controller and provisioned the Application Gateway for Containers resources via the ApplicationLoadBalancer custom resource.
Deploy sample HTTP application Apply the following deployment.yaml file on your cluster to create a sample web application to demonstrate the header rewrite.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/azure-docs/refs/heads/main/articles/application-gateway/for-containers/examples/traffic-split-scenario/deployment.yamlThis command creates the following on your cluster:
- a namespace called
test-infra - two services called
backend-v1andbackend-v2in thetest-infranamespace - two deployments called
backend-v1andbackend-v2in thetest-infranamespace
- a namespace called
Deploy the required Ingress API resources
Create an Ingress resource to listen for requests to contoso.com:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-01
namespace: test-infra
annotations:
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-name: alb-test
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-namespace: alb-test-infra
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-ingress-extension: header-rewrite
spec:
ingressClassName: azure-alb-external
rules:
- host: contoso.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: backend-v1
port:
number: 8080
EOF
Note
When the ALB Controller creates the Application Gateway for Containers resources in ARM, it'll use the following naming convention for a frontend resource: fe-<8 randomly generated characters>
If you would like to change the name of the frontend created in Azure, consider following the bring your own deployment strategy.
Once the ingress resource is created, ensure the status shows the hostname of your load balancer and that both ports are listening for requests.
kubectl get ingress ingress-01 -n test-infra -o yaml
Example output of successful Ingress creation.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend: FRONTEND_NAME
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-id: /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourcegroups/yyyyyyyy/providers/Microsoft.ServiceNetworking/trafficControllers/zzzzzz
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"networking.k8s.io/v1","kind":"Ingress","metadata":{"annotations":{"alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend":"FRONTEND_NAME","alb.networking.azure.io/alb-id":"/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourcegroups/yyyyyyyy/providers/Microsoft.ServiceNetworking/trafficControllers/zzzzzz", "alb.networking.azure.io/alb-ingress-extension":"header-rewrite"},"name"
:"ingress-01","namespace":"test-infra"},"spec":{"ingressClassName":"azure-alb-external","rules":[{"host":"contoso.com","http":{"paths":[{"backend":{"service":{"name":"backend-v1","port":{"number":8080}}},"path":"/","pathType":"Prefix"}]}}]}}
creationTimestamp: "2023-07-22T18:02:13Z"
generation: 2
name: ingress-01
namespace: test-infra
resourceVersion: "278238"
uid: 17c34774-1d92-413e-85ec-c5a8da45989d
spec:
ingressClassName: azure-alb-external
rules:
- host: contoso.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: backend-v1
port:
number: 8080
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- hostname: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.fzyy.alb.azure.com
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
Once the Ingress is created, next we need to define an IngressExtension with the header rewrite rules.
In this example, we set a static user-agent with a value of rewritten-user-agent.
This example also demonstrates addition of a new header called AGC-Header-Add with a value of AGC-value and removes a request header called client-custom-header.
Tip
For this example, while we can use the HTTPHeaderMatch of "Exact" for a string match, a demonstration is used in regular expression for illustration of further capabilities.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: alb.networking.azure.io/v1
kind: IngressExtension
metadata:
name: header-rewrite
namespace: test-infra
spec:
rules:
- host: contoso.com
rewrites:
- type: RequestHeaderModifier
requestHeaderModifier:
set:
- name: "user-agent"
value: "rewritten-user-agent"
add:
- name: "AGC-Header-Add"
value: "AGC-value"
remove:
- "client-custom-header"
EOF
Once the IngressExtension resource is created, ensure the resource returns No validation errors and is valid.
kubectl get IngressExtension header-rewrite -n test-infra -o yaml
Verify the status of the Application Gateway for Containers resource has been successfully updated.
Test access to the application
Now we're ready to send some traffic to our sample application, via the FQDN assigned to the frontend. Use the following command to get the FQDN.
fqdn=$(kubectl get ingress ingress-01 -n test-infra -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}')
If you specify the server name indicator using the curl command, contoso.com for the frontend FQDN, a response from the backend-v1 service is returned.
fqdnIp=$(dig +short $fqdn)
curl -k --resolve contoso.com:80:$fqdnIp http://contoso.com
Via the response we should see:
{
"path": "/",
"host": "contoso.com",
"method": "GET",
"proto": "HTTP/1.1",
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"User-Agent": [
"curl/7.81.0"
],
"X-Forwarded-For": [
"xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"
],
"X-Forwarded-Proto": [
"http"
],
"X-Request-Id": [
"dcd4bcad-ea43-4fb6-948e-a906380dcd6d"
]
},
"namespace": "test-infra",
"ingress": "",
"service": "",
"pod": "backend-v1-5b8fd96959-f59mm"
}
Specifying a user-agent header with the value my-user-agent should return a response from the backend service of rewritten-user-agent:
fqdnIp=$(dig +short $fqdn)
curl -k --resolve contoso.com:80:$fqdnIp http://contoso.com -H "user-agent: my-user-agent"
Via the response we should see:
{
"path": "/",
"host": "fabrikam.com",
"method": "GET",
"proto": "HTTP/1.1",
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"User-Agent": [
"curl/7.81.0"
],
"X-Forwarded-For": [
"xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"
],
"X-Forwarded-Proto": [
"http"
],
"X-Request-Id": [
"adae8cc1-8030-4d95-9e05-237dd4e3941b"
]
},
"namespace": "test-infra",
"ingress": "",
"service": "",
"pod": "backend-v1-5b8fd96959-f59mm"
}
Specifying a client-custom-header header with the value moo should be stripped from the request when Application Gateway for Containers initiates the connection to the backend service:
fqdnIp=$(dig +short $fqdn)
curl -k --resolve contoso.com:80:$fqdnIp http://contoso.com -H "client-custom-header: moo"
Via the response we should see:
{
"path": "/",
"host": "fabrikam.com",
"method": "GET",
"proto": "HTTP/1.1",
"headers": {
"Accept": [
"*/*"
],
"User-Agent": [
"curl/7.81.0"
],
"X-Forwarded-For": [
"xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"
],
"X-Forwarded-Proto": [
"http"
],
"X-Request-Id": [
"kd83nc84-4325-5d22-3d23-237dd4e3941b"
]
},
"namespace": "test-infra",
"ingress": "",
"service": "",
"pod": "backend-v1-5b8fd96959-f59mm"
}
Congratulations, you have installed ALB Controller, deployed a backend application and modified header values via Ingress API on Application Gateway for Containers.