Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Application Gateway for Containers allows you to return a redirect response to the client based three aspects of a URL: protocol, hostname, and path. For each redirect, a defined HTTP status code may be returned to the client to define the nature of the redirect.
Usage details
URL redirects take advantage of the RequestRedirect rule filter as defined by Kubernetes Gateway API.
Redirection
A redirect sets the response status code returned to clients to understand the purpose of the redirect. The following types of redirection are supported:
- 301 (Moved permanently): Indicates that the target resource is assigned a new permanent URI. Any future references to this resource use one of the enclosed URIs. Use 301 status code for HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
- 302 (Found): Indicates that the target resource is temporarily under a different URI. Since the redirection can change on occasion, the client should continue to use the effective request URI for future requests.
Redirection capabilities
Protocol redirection is commonly used to tell the client to move from an unencrypted traffic scheme to traffic, such as HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
Hostname redirection matches the fully qualified domain name (fqdn) of the request. This is commonly observed in redirecting an old domain name to a new domain name; such as
contoso.comtofabrikam.com.Path redirection has two different variants:
prefixandfull.Prefixredirection type will redirect all requests starting with a defined value. For example, a prefix of /shop would match /shop and any text after. For example, /shop, /shop/checkout, and /shop/item-a would all redirect to /shop as well.Fullredirection type matches an exact value. For example, /shop could redirect to /store, but /shop/checkout wouldn't redirect to /store.
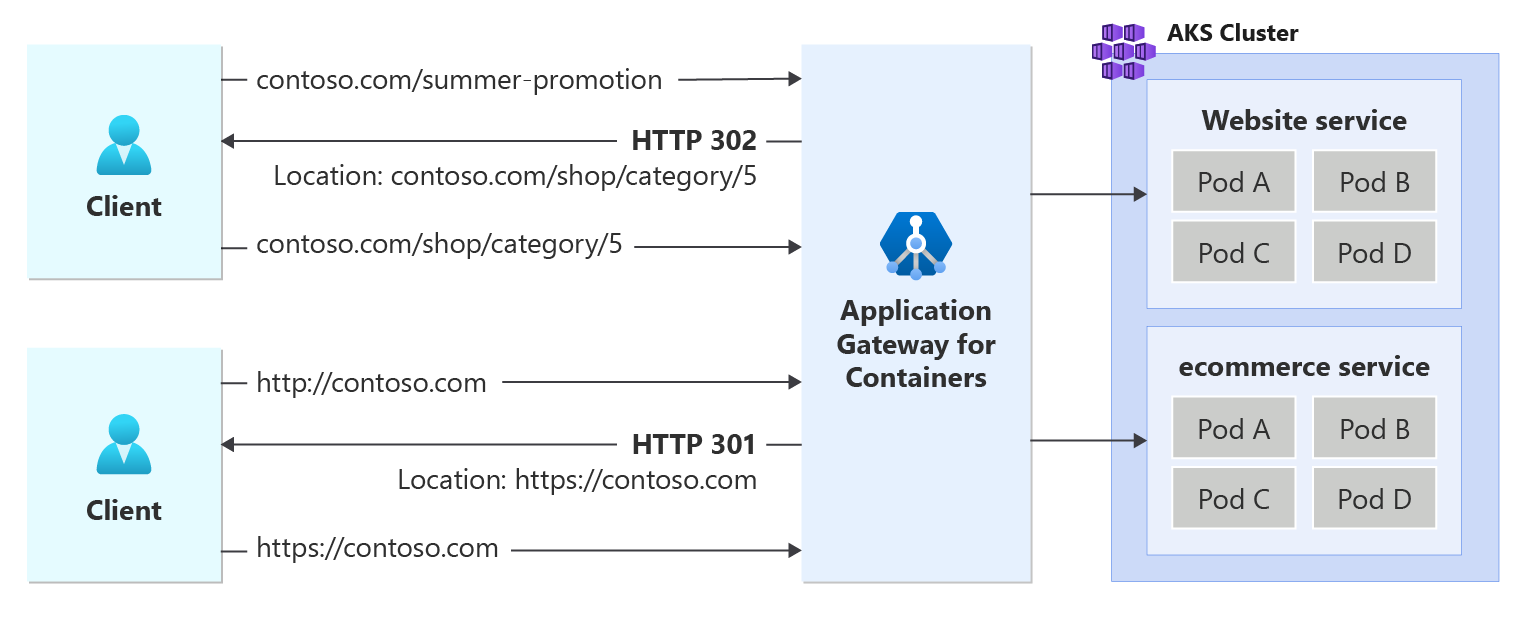
The following figure illustrates an example of a request destined for contoso.com/summer-promotion being redirected to contoso.com/shop/category/5. In addition, a second request initiated to contoso.com via http protocol is returned a redirect to initiate a new connection to its https variant.
Prerequisites
If following the BYO deployment strategy, ensure you set up your Application Gateway for Containers resources and ALB Controller.
If following the ALB managed deployment strategy, ensure you provision your ALB Controller and provision the Application Gateway for Containers resources via the ApplicationLoadBalancer custom resource.
Deploy sample HTTP application:
Apply the following deployment.yaml file on your cluster to deploy a sample TLS certificate to demonstrate redirect capabilities.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/azure-docs/refs/heads/main/articles/application-gateway/for-containers/examples/https-scenario/ssl-termination/deployment.yamlThis command creates the following on your cluster:
- a namespace called
test-infra - one service called
echoin thetest-infranamespace - one deployment called
echoin thetest-infranamespace - one secret called
listener-tls-secretin thetest-infranamespace
- a namespace called
Deploy the required IngressExtension resources
Create an IngressExtension resource to handle HTTP to HTTPS redirect for
contoso.comkubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: alb.networking.azure.io/v1 kind: IngressExtension metadata: name: http-to-https namespace: test-infra spec: rules: - host: contoso.com requestRedirect: statusCode: 301 scheme: https EOFCreate an IngressExtension resource to handle a path based redirect from
contoso.com/summer-promotiontocontoso.com/shop/category/5.kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: alb.networking.azure.io/v1 kind: IngressExtension metadata: name: summer-promotion-redirect namespace: test-infra spec: rules: - host: contoso.com requestRedirect: statusCode: 302 path: type: ReplaceFullPath replaceFullPath: /shop/category/5 EOF
Deploy the required Ingress resources
Create the first Ingress resource to listen for HTTPS requests.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-https namespace: test-infra annotations: alb.networking.azure.io/alb-namespace: alb-test-infra alb.networking.azure.io/alb-name: alb-test alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend: ingress-fe spec: ingressClassName: azure-alb-external tls: - hosts: - contoso.com secretName: listener-tls-secret rules: - host: contoso.com http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: echo port: number: 80 EOFCreate the second Ingress resource to listen on port 80 and redirect to HTTPS.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-http namespace: test-infra annotations: alb.networking.azure.io/alb-namespace: alb-test-infra alb.networking.azure.io/alb-name: alb-test alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend: ingress-fe alb.networking.azure.io/alb-ingress-extension: http-to-https spec: ingressClassName: azure-alb-external rules: - host: contoso.com http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: echo port: number: 80 EOFCreate a third Ingress resource to listen on port 80 and 443 for
contoso.com/summer-promotionand redirect tocontoso.com/shop/category/5.kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-summer-promotion-redirect namespace: test-infra annotations: alb.networking.azure.io/alb-namespace: alb-test-infra alb.networking.azure.io/alb-name: alb-test alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend: ingress-fe alb.networking.azure.io/alb-ingress-extension: summer-promotion-redirect spec: ingressClassName: azure-alb-external tls: - hosts: - contoso.com secretName: listener-tls-secret rules: - host: contoso.com http: paths: - path: /summer-promotion pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: ignored-for-redirect port: number: 80 EOF
Note
When the ALB Controller creates the Application Gateway for Containers resources in Azure Resource Manager, it uses the following naming convention for a frontend resource: fe-<eight randomly generated characters>.
If you want to change the name of the frontend resource created in Azure, consider following the bring-your-own deployment strategy.
For each Ingress resource, ensure the status is valid, the listener is Programmed, and an address is assigned to the ingress resource. For all three Ingress resources, you should see the same hostname in this example.
kubectl get ingress ingress-https -n test-infra -o yaml
Example output of successful Ingress creation.
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- hostname: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.fzyy.alb.azure.com
ports:
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
Test access to the application
Now we're ready to send some traffic to our sample application, via the FQDN assigned to the frontend. Use the following command to get the FQDN.
fqdn=$(kubectl get ingress ingress-http -n test-infra -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}')
When you specify the server name indicator using the curl command, http://contoso.com should return a response from the Application Gateway for Containers with a location header defining a 301 redirect to https://contoso.com.
fqdnIp=$(dig +short $fqdn)
curl -k --resolve contoso.com:80:$fqdnIp http://contoso.com/ -v
Via the response we should see:
* Added contoso.com:80:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx to DNS cache
* Hostname contoso.com was found in DNS cache
* Trying xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:80...
* Connected to contoso.com (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx) port 80 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: contoso.com
> User-Agent: curl/7.81.0
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
< location: https://contoso.com/
< date: Mon, 26 Feb 2024 22:56:23 GMT
< server: Microsoft-Azure-Application-LB/AGC
< content-length: 0
<
* Connection #0 to host contoso.com left intact
When you specify the server name indicator using the curl command, https://contoso.com/summer-promotion Application Gateway for Containers should return a 302 redirect to https://contoso.com/shop/category/5.
fqdnIp=$(dig +short $fqdn)
curl -k --resolve contoso.com:443:$fqdnIp https://contoso.com/summer-promotion -v
Via the response we should see:
> GET /summer-promotion HTTP/2
> Host: contoso.com
> user-agent: curl/7.81.0
> accept: */*
>
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS header, Supplemental data (23):
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Newsession Ticket (4):
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Newsession Ticket (4):
* old SSL session ID is stale, removing
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS header, Supplemental data (23):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS header, Supplemental data (23):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS header, Supplemental data (23):
< HTTP/2 302
< location: https://contoso.com/shop/category/5
< date: Mon, 26 Feb 2024 22:58:43 GMT
< server: Microsoft-Azure-Application-LB/AGC
<
* Connection #0 to host contoso.com left intact
Congratulations, you have installed ALB Controller, deployed a backend application, and used Ingress API to configure both an HTTP to HTTPS redirect and path based redirection to specific client requests.