Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to use the Header Rewrite in Application Gateway v2 SKU to add HTTP Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS) response header to better secure traffic through Application Gateway.
HSTS policy helps protect or minimize your sites against man-in-the-middle, cookie-hijacking, and protocol downgrade attacks. After a client has established the first successful HTTPS connection with your HSTS-enabled website, HSTS header ensures going forward the client can access only through HTTPS.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Before you begin
You need to have an Application Gateway v2 SKU deployment to complete the steps in this article. Rewriting headers isn't supported in the v1 SKU. If you don't have the v2 SKU, create an Application Gateway v2 SKU deployment before you begin.
Sign in to Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account.
Create required objects
To configure HSTS policy, you must first complete these steps:
Create the objects that are required for adding an HSTS header:
HTTP Listener: Create a basic or multisite HTTP listener. This listener must listen on port 80, and the protocol must be set to HTTP.
HTTPS Listener: Create a basic or multisite HTTPS listener. This listener must listen on port 443, have the protocol set to HTTPS, and contain a certificate.
Create a routing rule that redirects all the traffic from the HTTP listener to the HTTPS listener.
To learn more about how to set up http to https redirection, see HTTP to HTTPS Redirection.
Configure HSTS policy
In this example, we will add the Strict Transport Security (STS) response header, using the rewrite rules of application gateway.
Select All resources, and then select your application gateway.
Select Rewrites in the left pane.
Select Rewrite set:
Provide a name for the rewrite set and associate it with a routing rule:
Enter the name for the rewrite set in the Name box.
Select one or more of the rules listed in the Associated routing rules list. You can select only rules that haven't been associated with other rewrite sets. The rules that have already been associated with other rewrite sets are dimmed.
Select Next.

Create a rewrite rule:
Select Add rewrite rule.
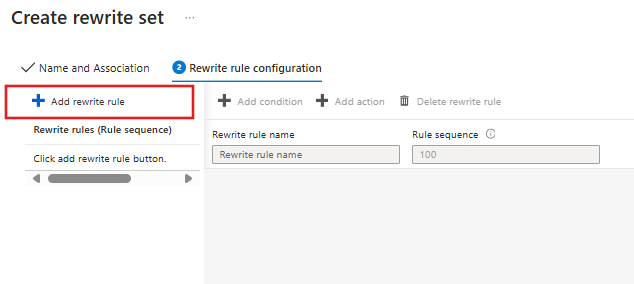
Enter a name for the rewrite rule in the Rewrite rule name box. Enter a number in the Rule sequence box.

Add an action to rewrite the response header:
In the Rewrite type list, select Response Header.
In the Action type list, select Set.
Under Header name, select Common header.
In the Common header list, select Strict-Transport-Security.
Enter the header value. In this example, we'll use
max-age=31536000; includeSubdomains; preloadas the header value.Select OK.

Select Create to create the rewrite set:
Limitations and Recommendations
In order to maximize security, you must show HSTS policy as soon as possible when users begin an HTTPS session. In order to enforce HTTPS for a given domain, the browser only needs to observe the STS header once. Hence, it should be added to home pages and critical pages of a site. However, that is not sufficient, it is best practice to cover as much of the URL space as possible and prioritize non-cacheable content.
In this example, the response header Strict-Transport-Security is set to
max-age=31536000; includeSubdomains; preload. However, users can also set the header to equalmax-age=31536000; includeSubdomains, removing the preload. Preloading helps strengthen HSTS by ensuring clients always access the site using HTTPS, even if it is their first time accessing it. You must submit your domain and subdomains to https://hstspreload.org/ in order to ensure that users will never access the site using HTTP. Although the preload list is hosted by Google, all major browsers use this list.HSTS Policy will not prevent attacks against TLS itself or attacks on the servers.
Next steps
To learn more about directives, please visit https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Strict-Transport-Security
To learn more about how to set up some common header rewrite use cases, see common header rewrite scenarios.

