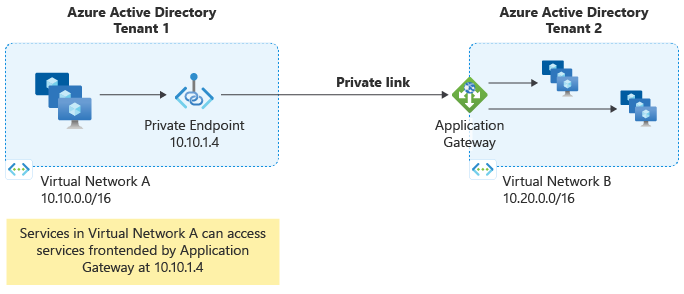
Azure Application Gateway Private Link enables you to establish secure, private connections to your Application Gateway from workloads spanning across virtual networks (VNets) and subscriptions. This feature provides private connectivity without exposing traffic to the public internet. For more information, see Application Gateway Private Link.
Configuration options
You can configure Application Gateway Private Link using multiple methods:
- Azure portal
- Azure PowerShell
- Azure CLI
Prerequisites
Before configuring Private Link, ensure you have:
- An existing Application Gateway
- A virtual network with a dedicated subnet for Private Link (separate from the Application Gateway subnet)
- Appropriate permissions to create and configure Private Link resources
Subnet considerations for Private Link configuration
To enable Private Link configuration, you must have a dedicated subnet that's separate from the Application Gateway subnet. This subnet is used exclusively for Private Link IP configurations and can't contain any Application Gateway instances.
- Each IP address allocated to this subnet supports up to 65,536 concurrent TCP connections through Private Link
- To calculate required IP addresses:
n × 65,536 connections, where n is the number of IP addresses provisioned
- Maximum of eight IP addresses per Private Link configuration
- Only dynamic IP address allocation is supported
- The subnet must have Private Link Service Network Policies disabled
Important
The combined length of the Application Gateway name and Private Link configuration name must not exceed 70 characters to avoid deployment failures.
To create a dedicated subnet for Private Link, see Add, change, or delete a virtual network subnet.
Disable network policies on the Private Link subnet
To allow Private Link connectivity, you must disable the Private Link Service Network Policies on the subnet designated for Private Link IP configurations.
To disable network policies, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Azure portal.
- Search for and select Virtual networks.
- Select the virtual network containing the Private Link subnet.
- In the left navigation pane, select Subnets.
- Select the subnet designated for Private Link.
- Under Private link service network policies, select Disabled.
- Select Save to apply the changes.
- Wait a few minutes for the changes to take effect.
- Verify the Private link service network policies setting is now Disabled.
The Private Link configuration defines the infrastructure that enables connections from Private Endpoints to your Application Gateway. Before creating the Private Link configuration, ensure that a listener is actively configured to use the target frontend IP configuration.
Follow these steps to create the Private Link configuration:
- Search for and select Application Gateways.
- Select your Application Gateway instance.
- In the left navigation pane, select Private link, then select + Add.
- Configure the following settings:
- Name: Enter a name for the Private Link configuration
- Private link subnet: Select the dedicated subnet for Private Link IP addresses
- Frontend IP Configuration: Select the frontend IP configuration that Private Link should forward traffic to
- Private IP address settings: Configure at least one IP address
- Select Add to create the configuration.
- From your Application Gateway settings, copy and save the Resource ID. This identifier is required when setting up Private Endpoints from different Microsoft Entra tenants.
A Private Endpoint is a network interface that uses a private IP address from your virtual network to connect securely to Azure Application Gateway. Clients use the Private Endpoint's private IP address to establish connections to the Application Gateway through a secure tunnel.
To create a Private Endpoint, follow these steps:
- In the Application Gateway portal, select the Private endpoint connections tab.
- Select + Private endpoint.
- On the Basics tab:
- Configure the resource group, name, and region for the Private Endpoint
- Select Next: Resource >
- On the Resource tab:
- Verify the target resource settings
- Select Next: Virtual Network >
- On the Virtual Network tab:
- Select the virtual network and subnet where the Private Endpoint network interface will be created
- Select Next: DNS >
- On the DNS tab:
- Configure DNS settings as needed
- Select Next: Tags >
- On the Tags tab:
- Optionally add resource tags
- Select Next: Review + create >
- Review the configuration and select Create.
Important
If the public or private IP configuration resource is missing when trying to select a Target sub-resource on the Resource tab of private endpoint creation, ensure a listener is actively utilizing the respected frontend IP configuration. Frontend IP configurations without an associated listener can't be shown as a Target sub-resource.
Note
When provisioning a Private Endpoint from a different Microsoft Entra tenant, you must use the Azure Application Gateway Resource ID and specify the frontend IP configuration name as the target sub-resource.
For example, if your private IP configuration is named PrivateFrontendIp in the portal, use PrivateFrontendIp as the target sub-resource value.
Use the following PowerShell commands to configure Private Link on an existing Application Gateway:
# Disable Private Link Service Network Policies
# https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/private-link/disable-private-endpoint-network-policy
$net =@{
Name = 'AppGW-PL-PSH'
ResourceGroupName = 'AppGW-PL-PSH-RG'
}
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork @net
($vnet | Select -ExpandProperty subnets | Where-Object {$_.Name -eq 'AppGW-PL-Subnet'}).PrivateLinkServiceNetworkPolicies = "Disabled"
# Apply the network policy changes
$vnet | Set-AzVirtualNetwork
# Get Application Gateway Frontend IP Name
$agw = Get-AzApplicationGateway -Name AppGW-PL-PSH -ResourceGroupName AppGW-PL-PSH-RG
# List the available Frontend IP configuration Names
$agw.FrontendIPConfigurations | Select Name
# Create Private Link IP configuration
$PrivateLinkIpConfiguration = New-AzApplicationGatewayPrivateLinkIpConfiguration `
-Name "ipConfig01" `
-Subnet ($vnet | Select -ExpandProperty subnets | Where-Object {$_.Name -eq 'AppGW-PL-Subnet'}) `
-Primary
# Add Private Link configuration to Application Gateway
Add-AzApplicationGatewayPrivateLinkConfiguration `
-ApplicationGateway $agw `
-Name "privateLinkConfig01" `
-IpConfiguration $PrivateLinkIpConfiguration
# Associate Private Link configuration with Frontend IP
$agwPip = ($agw | Select -ExpandProperty FrontendIpConfigurations| Where-Object {$_.Name -eq 'appGwPublicFrontendIp'}).PublicIPAddress.Id
$privateLinkConfiguration = ($agw | Select -ExpandProperty PrivateLinkConfigurations | Where-Object {$_.Name -eq 'privateLinkConfig01'}).Id
Set-AzApplicationGatewayFrontendIPConfig -ApplicationGateway $agw -Name "appGwPublicFrontendIp" -PublicIPAddressId $agwPip -PrivateLinkConfigurationId $privateLinkConfiguration
# Apply changes to Application Gateway
Set-AzApplicationGateway -ApplicationGateway $agw
# Configure Private Endpoint network (in the client/consumer virtual network)
# Disable Private Endpoint Network Policies
# https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/private-link/disable-private-endpoint-network-policy
$net =@{
Name = 'AppGW-PL-Endpoint-PSH-VNET'
ResourceGroupName = 'AppGW-PL-Endpoint-PSH-RG'
}
$vnet_plendpoint = Get-AzVirtualNetwork @net
($vnet_plendpoint | Select -ExpandProperty subnets | Where-Object {$_.Name -eq 'MySubnet'}).PrivateEndpointNetworkPolicies = "Disabled"
$vnet_plendpoint | Set-AzVirtualNetwork
# Create Private Link Endpoint - Group ID is the same as the frontend IP configuration
$privateEndpointConnection = New-AzPrivateLinkServiceConnection -Name "AppGW-PL-Connection" -PrivateLinkServiceId $agw.Id -GroupID "appGwPublicFrontendIp"
## Create the Private Endpoint
New-AzPrivateEndpoint -Name "AppGWPrivateEndpoint" -ResourceGroupName $vnet_plendpoint.ResourceGroupName -Location $vnet_plendpoint.Location -Subnet ($vnet_plendpoint | Select -ExpandProperty subnets | Where-Object {$_.Name -eq 'MySubnet'}) -PrivateLinkServiceConnection $privateEndpointConnection
PowerShell cmdlet reference
The following Azure PowerShell cmdlets are available for managing Application Gateway Private Link configurations:
Use the following Azure CLI commands to configure Private Link on an existing Application Gateway:
# Disable Private Link Service Network Policies on the Private Link subnet
# Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/private-link/disable-private-endpoint-network-policy
az network vnet subnet update \
--name AppGW-PL-Subnet \
--vnet-name AppGW-PL-CLI-VNET \
--resource-group AppGW-PL-CLI-RG \
--disable-private-link-service-network-policies true
# List available Frontend IP configurations
az network application-gateway frontend-ip list \
--gateway-name AppGW-PL-CLI \
--resource-group AppGW-PL-CLI-RG
# Create Private Link configuration and associate with Frontend IP
az network application-gateway private-link add \
--frontend-ip appGwPublicFrontendIp \
--name privateLinkConfig01 \
--subnet /subscriptions/XXXXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXX/resourceGroups/AppGW-PL-CLI-RG/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/AppGW-PL-CLI-VNET/subnets/AppGW-PL-Subnet \
--gateway-name AppGW-PL-CLI \
--resource-group AppGW-PL-CLI-RG
# Verify Private Link configuration
az network application-gateway private-link list \
--gateway-name AppGW-PL-CLI \
--resource-group AppGW-PL-CLI-RG
# Configure Private Endpoint network (in the client/consumer virtual network)
# Disable Private Endpoint Network Policies
az network vnet subnet update \
--name MySubnet \
--vnet-name AppGW-PL-Endpoint-CLI-VNET \
--resource-group AppGW-PL-Endpoint-CLI-RG \
--disable-private-endpoint-network-policies true
# Create Private Endpoint
# Note: Group ID must match the Frontend IP configuration name
az network private-endpoint create \
--name AppGWPrivateEndpoint \
--resource-group AppGW-PL-Endpoint-CLI-RG \
--vnet-name AppGW-PL-Endpoint-CLI-VNET \
--subnet MySubnet \
--group-id appGwPublicFrontendIp \
--private-connection-resource-id /subscriptions/XXXXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXX/resourceGroups/AppGW-PL-CLI-RG/providers/Microsoft.Network/applicationGateways/AppGW-PL-CLI \
--connection-name AppGW-PL-Connection
Note
To move a Private Endpoint to a different subscription, you must delete the existing connection between the Private Link and Private Endpoint. After deletion, create a new Private Endpoint connection in the target subscription to reestablish connectivity.
Caution
Private link configuration will momentarily cause traffic disruption (less than 1 minute) when enabled or disabled. Changes are recommended to be conducted during a maintenance window or period of low-traffic. During this time, you may see connection timeouts or 4XX http status codes returned on request. Add/Remove/Approval/Rejection of private endpoints will not cause traffic disruption.
Azure CLI reference
For comprehensive Azure CLI command reference for Application Gateway Private Link configuration, see Azure CLI - Application Gateway Private Link.
Next steps
To learn more about Azure Private Link and related services:
