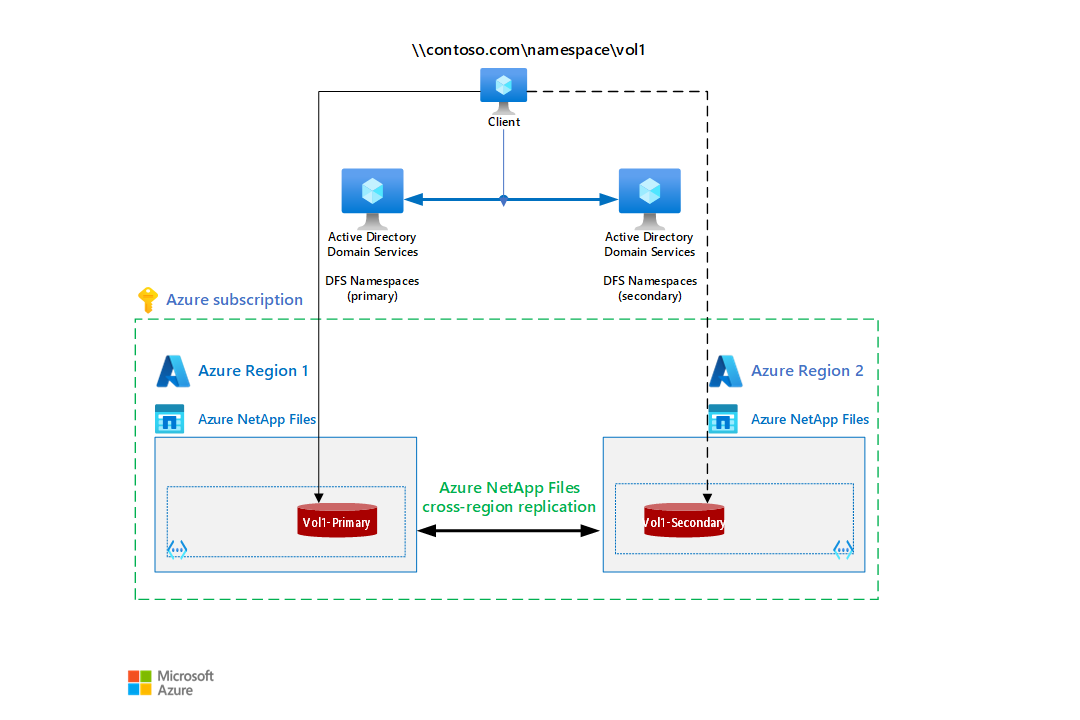
This architecture provides file shares that fail over automatically to a backup region in case of failure. The failover is transparent to the clients and applications that access the shares. The shares can be used for applications and virtual desktops that must be resilient to disruption, whether planned or unplanned.
Azure NetApp Files provides the file shares. Its cross-region replication capability replicates the shares from the primary region to the secondary. Distributed File System (DFS) Namespaces in Windows Server can group shared folders on different servers into one or more logically structured namespaces.
Potential use cases
This architecture applies to businesses that want to provide file shares for clients or applications that must be resilient to unplanned outages or service maintenance events. Some examples are:
- Service Message Block (SMB) protocol file shares for desktop environments.
- SMB file shares for applications.
Architecture
Download a Visio file of this architecture.
- There are two Azure regions, a primary and a secondary.
- The Azure subscription includes a virtual network and an Azure NetApp Files account for each region.
- The cross-region replication feature of Azure NetApp Files replicates the files and folders from the primary region to the secondary region. This technique doesn't need virtual machines.
- Access to the file shares is managed by DFS Namespaces, a feature of Windows Server. You can think of it as Domain Name Server (DNS) for file shares.
- The Windows servers and Active Directory Domain servers can be hosted on Azure or on-premises.
Components
- Azure NetApp Files provides enterprise-grade Azure file shares that are powered by NetApp. Azure NetApp Files makes it easy for enterprises to migrate and run complex file-based applications with no code changes. It also provides a way to replicate data asynchronously from an Azure NetApp Files volume in one region to an Azure NetApp Files volume in another region. This capability provides data protection during region-wide outages or disasters. For more information, see Cross-region replication of Azure NetApp Files volumes.
- DFS Namespaces is a role service in Windows Server that can group shared folders that are located on different servers into one or more logically structured namespaces. For more information, see DFS Namespaces overview.
Alternatives
- Instead of Azure NetApp Files, you can use a Windows Server Scale-Out File Server cluster with custom replication of the file shares across regions. For more information, see Scale-Out File Server for application data overview.
- Instead of Azure NetApp Files cross-region replication, you can use Azure File Sync to transform Windows Server into a quick cache of your Azure file shares. This might be appropriate for smaller file shares. For more information, see Deploy Azure File Sync.
Considerations
The Azure Well-Architected Framework provides reference guidance and best practices to apply to your architecture.
Availability
Replicating to a second region increases availability by protecting against regional service interruptions.
Performance efficiency
- Azure NetApp Files comes with three performance tiers: Standard, Premium, and Ultra. Cross-region replication can replicate between different tiers. When the primary region uses the Premium or Ultra tier, you can replicate to a lower tier, for example Standard. In case of a failover, you can then upgrade the tier of the secondary as required.
- The replication of the data is performed at the incremental block level—only changed data blocks are transferred—which minimizes data transfer.
Scalability
This solution can be used for file shares ranging from 4 tebibytes (TiB) to a total volume of 12.5 pebibytes (PiB) on a single Azure NetApp Files account.
Resiliency
- This solution has greater resiliency than a single-region deployment, and has failover capabilities.
- The secondary volume is read-only. It can be verified at any given time, increasing resiliency.
- You can run a disaster recovery test in isolation without interfering with the production deployment. The test uses the space-efficient volume clone feature to get a read/write copy of a volume in seconds.
Cost optimization
The cost of the solution depends on the size of the volume that's replicated, the rate of change, and the destination tier of the Azure NetApp Files capacity pool. For details, see Azure NetApp Files pricing or use the Azure Pricing calculator.
See Cost model for cross-region replication for more examples.
Deploy this scenario
To deploy on Azure, perform the following configuration tasks in the Windows Server DFS namespace:
- Deploy the primary Azure NetApp Files account.
- Create an SMB volume on the primary.
- Deploy the secondary Azure NetApp Files account.
- Replicate the volume to the secondary Azure NetApp Files account.
- Configure DFS Namespaces to point to the primary volume.
In case of a failover:
- Fail over the volumes of Azure NetApp Files.
- Change the targets in DFS Namespaces.
These tasks can be and should be automated.
See Disaster Recovery for Enterprise File Shares for a step-by-step deployment guide.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal authors:
- Max Melcher | Cloud Solution Architect
Next steps
- Register for NetApp Resource Provider
- Create a NetApp account
- Quickstart: Set up Azure NetApp Files and create an NFS volume
- Disaster Recovery for Enterprise File Shares