Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Apache Kafka is a highly scalable and fault tolerant distributed messaging system that implements a publish-subscribe architecture. It's used as an ingestion layer in real-time streaming scenarios, such as Internet of Things and real-time log monitoring systems. It's also used increasingly as the immutable append-only data store in Kappa architectures.
Apache®, Apache Spark®, Apache Hadoop®, Apache HBase, Apache Storm®, Apache Sqoop®, Apache Kafka®, and the flame logo are either registered trademarks or trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation in the United States and/or other countries. No endorsement by The Apache Software Foundation is implied by the use of these marks.
Migration approach
This article presents various strategies for migrating Kafka to Azure:
- Migrate Kafka to Azure infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Migrate Kafka to Azure Event Hubs for Kafka
- Migrate Kafka on Azure HDInsight
- Use Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) with Kafka on HDInsight
- Use Kafka on AKS with the Strimzi Operator
Here's a decision flowchart for deciding which strategy to use.
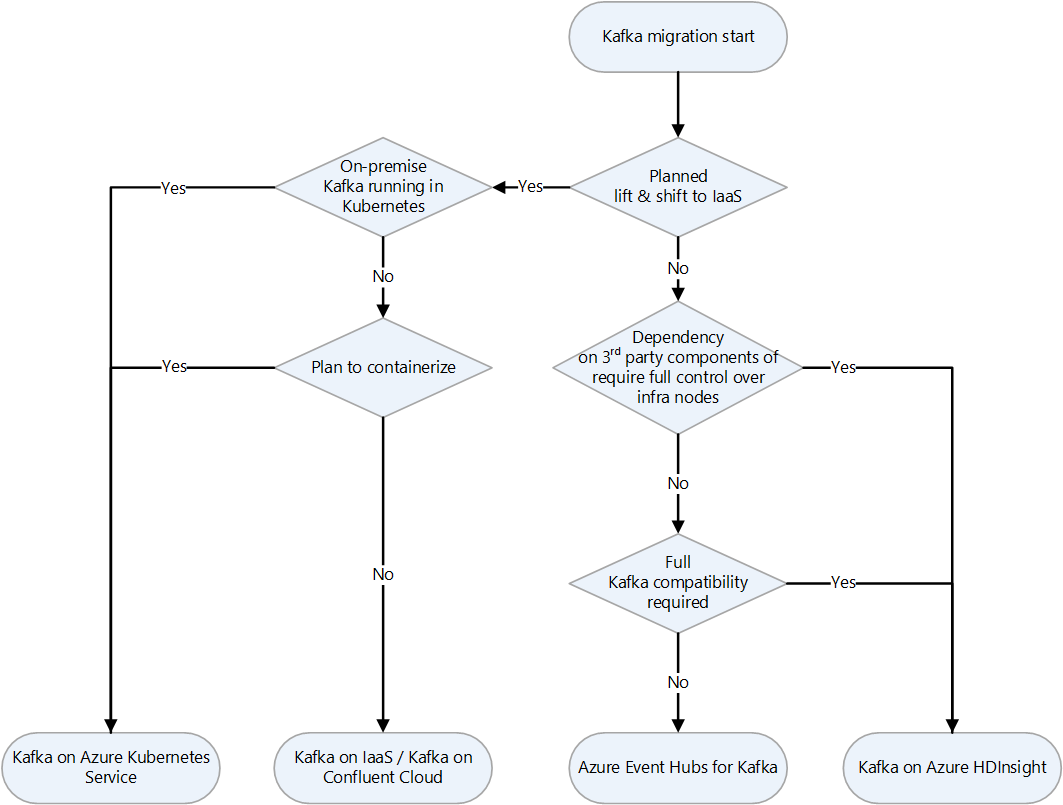
Migrate Kafka to Azure IaaS
For one way to migrate Kafka to Azure IaaS, see Kafka on Ubuntu virtual machines.
Migrate Kafka to Event Hubs for Kafka
Event Hubs provides an endpoint that's compatible with the Apache Kafka producer and consumer APIs. Most Apache Kafka client applications can use this endpoint, so you can use it as an alternative to running a Kafka cluster on Azure. The endpoint supports clients that use API versions 1.0 and later. For more information about this feature, see Event Hubs for Apache Kafka overview.
To learn how to migrate your Apache Kafka applications to use Event Hubs, see Migrate to Event Hubs for Apache Kafka ecosystems.
Features of Kafka and Event Hubs
| Similarities between Kafka and Event Hubs | Differences in Kafka and Event Hubs |
|---|---|
| Use partitions | Platform as a service versus software |
| Partitions are independent | Partitioning |
| Use a client-side cursor concept | APIs |
| Can scale to very high workloads | Runtime |
| Nearly identical conceptually | Protocols |
| Neither uses the HTTP protocol for receiving | Durability |
| Security | |
| Throttling |
Partitioning differences
| Kafka | Event Hubs |
|---|---|
| Partition count manages scale. | Throughput units manage scale. |
| You must load balance partitions across machines. | Load balancing is automatic. |
| You must manually reshard by using split and merge. | Repartitioning isn't required. |
Durability differences
| Kafka | Event Hubs |
|---|---|
| Volatile by default | Always durable |
| Replicated after an acknowledgment (ACK) is received | Replicated before an ACK is sent |
| Depends on disk and quorum | Provided by storage |
Security differences
| Kafka | Event Hubs |
|---|---|
| Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Simple Authentication and Security Layer (SASL) | Shared Access Signature (SAS) and SASL or PLAIN RFC 4618 |
| File-like access control lists | Policy |
| Optional transport encryption | Mandatory Transport Layer Security (TLS) |
| User based | Token based (unlimited) |
Other differences
| Kafka | Event Hubs |
|---|---|
| Doesn't throttle | Supports throttling |
| Uses a proprietary protocol | Uses AMQP 1.0 protocol |
| Doesn't use HTTP for send | Uses HTTP send and batch send |
Migrate Kafka on HDInsight
You can migrate Kafka to Kafka on HDInsight. For more information, see What is Apache Kafka in HDInsight?.
Use AKS with Kafka on HDInsight
For more information, see Use AKS with Apache Kafka on HDInsight.
Use Kafka on AKS with the Strimzi Operator
For more information, see Deploy a Kafka cluster on AKS by using Strimzi.
Kafka data migration
You can use Kafka's MirrorMaker tool to replicate topics from one cluster to another. This technique can help you migrate data after a Kafka cluster is provisioned. For more information, see Use MirrorMaker to replicate Apache Kafka topics with Kafka on HDInsight.
The following migration approach uses mirroring:
Move producers first. When you migrate the producers, you prevent production of new messages on the source Kafka.
After the source Kafka consumes all remaining messages, you can migrate the consumers.
The implementation includes the following steps:
Change the Kafka connection address of the producer client to point to the new Kafka instance.
Restart the producer business services and send new messages to the new Kafka instance.
Wait for the data in the source Kafka to be consumed.
Change the Kafka connection address of the consumer client to point to the new Kafka instance.
Restart the consumer business services to consume messages from the new Kafka instance.
Verify that consumers succeed in getting data from the new Kafka instance.
Monitor the Kafka cluster
You can use Azure Monitor logs to analyze logs that Apache Kafka on HDInsight generates. For more information, see Analyze logs for Apache Kafka on HDInsight.
Apache Kafka Streams API
The Kafka Streams API makes it possible to process data in near real-time and to join and aggregate data. For more information, see Introducing Kafka Streams: Stream Processing Made Simple - Confluent.
The Microsoft and Confluent partnership
Confluent provides a cloud-native service for Apache Kafka. Microsoft and Confluent have a strategic alliance. For more information, see the following resources:
- Confluent and Microsoft announce strategic alliance
- Introducing seamless integration between Microsoft Azure and Confluent Cloud
Contributors
Microsoft maintains this article. The following contributors wrote this article.
Principal authors:
- Namrata Maheshwary | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
- Raja N | Director, Customer Success
- Hideo Takagi | Cloud Solution Architect
- Ram Yerrabotu | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
Other contributors:
- Ram Baskaran | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
- Jason Bouska | Senior Software Engineer - Azure Patterns & Practices
- Eugene Chung | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
- Pawan Hosatti | Senior Cloud Solution Architect - Engineering
- Daman Kaur | Cloud Solution Architect
- Danny Liu | Senior Cloud Solution Architect - Engineering
- Jose Mendez Senior Cloud Solution Architect
- Ben Sadeghi | Senior Specialist
- Sunil Sattiraju | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
- Amanjeet Singh | Principal Program Manager
- Nagaraj Seeplapudur Venkatesan | Senior Cloud Solution Architect - Engineering
To see nonpublic LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
Azure product introductions
- Introduction to Azure Data Lake Storage
- What is Apache Spark in HDInsight?
- What is Apache Hadoop in HDInsight?
- What is Apache HBase in HDInsight?
- What is Apache Kafka in HDInsight?
- Overview of enterprise security in HDInsight
Azure product reference
- Microsoft Entra documentation
- Azure Cosmos DB documentation
- Azure Data Factory documentation
- Azure Databricks documentation
- Event Hubs documentation
- Azure Functions documentation
- HDInsight documentation
- Microsoft Purview data governance documentation
- Azure Stream Analytics documentation