This architectural pattern demonstrates how you can incorporate MDM into the Azure data services ecosystem to improve the quality of data used for analytics and operational decision making. MDM solves several common challenges, including:
- Identifying and managing duplicate data (match and merge).
- Flagging and resolving data quality issues.
- Standardizing and enriching data.
- Allowing data stewards to proactively manage and improve the data.
This pattern presents a modern approach to MDM. All technologies are deployable natively in Azure, including Profisee, which you can deploy via containers and manage with Azure Kubernetes Service.
Architecture
Download a Visio file of the diagrams used in this architecture.
Dataflow
The following dataflow corresponds to the preceding diagram:
Source data load: Source data from business applications copies to Azure Data Lake and stores it for further transformation and use in downstream analytics. Source data typically falls into one of three categories:
- Structured master data – The information that describes customers, products, locations, and so on. Master data is low-volume, high-complexity, and changes slowly over time. It's often the data that organizations struggle the most with in terms of data quality.
- Structured transactional data – Business events that occur at a specific point in time, such as an order, invoice, or interaction. Transactions include the metrics for that transaction (like sales price) and references to master data (like the product and customer involved in a purchase). Transactional data is typically high-volume, low-complexity, and doesn't change over time.
- Unstructured data – Data that can include documents, images, videos, social media content, and audio. Modern analytics platforms can increasingly use unstructured data to learn new insights. Unstructured data is often associated with master data, such as a customer associated with a social media account, or a product associated with an image.
Source master data load: Master data from source business applications loads into the MDM application "as is", with complete lineage information and minimal transformations.
Automated MDM processing: The MDM solution uses automated processes to standardize, verify, and enrich data, such as address data. The solution also identifies data quality issues, groups duplicate records (like duplicate customers), and generates master records, also called "golden records".
Data stewardship: As necessary, data stewards can:
- Review and manage groups of matched records
- Create and manage data relationships
- Fill in missing information
- Resolve data quality issues.
Data stewards can manage multiple alternate hierarchical roll-ups as required, such as product hierarchies.
Managed master data load: High-quality master data flows into downstream analytics solutions. This action simplifies the process since data integrations no longer require any data quality transformations.
Transactional and unstructured data load: Transactional and unstructured data loads into the downstream analytics solution where it combines with high-quality master data.
Visualization and analysis: Data is modeled and made available to business users for analysis. High-quality master data eliminates common data-quality issues, which result in improved insights.
Components
Azure Data Factory is a hybrid data integration service that lets you create, schedule, and orchestrate your ETL and ELT workflows.
Azure Data Lake provides limitless storage for analytics data.
Profisee is a scalable MDM platform that's designed to easily integrate with the Microsoft ecosystem.
Azure Synapse Analytics is the fast, flexible, and trusted cloud data warehouse that lets you scale, compute, and store data elastically and independently, with a massively parallel processing architecture.
Power BI is a suite of business analytics tools that delivers insights throughout your organization. Connect to hundreds of data sources, simplify data prep, and drive improvised analysis. Produce beautiful reports, then publish them for your organization to consume on the web and across mobile devices.
Alternatives
Absent a purpose-built MDM application, you can find some of the technical capabilities needed to build an MDM solution within the Azure ecosystem.
- Data quality - When loading to an analytics platform, you can build data quality into the integration processes. For example, apply data quality transformations in an Azure Data Factory pipeline with hardcoded scripts.
- Data standardization and enrichment - Azure Maps helps provide data verification and standardization for address data, which you can use in Azure Functions and Azure Data Factory. Standardization of other data might require development of hardcoded scripts.
- Duplicate data management - You can use Azure Data Factory to deduplicate rows where sufficient identifiers are available for an exact match. In this case, the logic to merge matched with appropriate survivorship would likely require custom hardcoded scripts.
- Data stewardship - Use Power Apps to quickly develop simple data stewardship solutions to manage data in Azure, along with appropriate user interfaces for review, workflow, alerts, and validations.
Scenario details
Many digital transformation programs use Azure as the core. But it depends on the quality and consistency of data from multiple sources, like business applications, databases, data feeds, and so on. It also delivers value through business intelligence, analytics, machine learning, and more. Profisee's Master Data Management (MDM) solution completes the Azure data estate with a practical method to "align and combine" data from multiple sources. It does so by enforcing consistent data standards on source data, like match, merge, standardize, verify, and correct. Native integration with Azure Data Factory and other Azure Data Services further streamlines this process to accelerate the delivery of Azure business benefits.
A core aspect of how MDM solutions function is that they combine data from multiple sources to create a "golden record master" that contains the best-known and trusted data for each record. This structure builds out domain-by-domain according to requirements, but it almost always requires multiple domains. Common domains are customer, product, and location. But domains can represent anything from reference data to contracts and drug names. In general, the better domain coverage that you can build out relative to the broad Azure data requirements the better.
MDM integration pipeline
Download a Visio file of this architecture.
The preceding image shows the details for integrating with the Profisee MDM solution. Notice that Azure Data Factory and Profisee include native REST integration support, providing a lightweight and modern integration.
Load source data to MDM: Azure Data Factory extracts data from the data lake, transforms it to match the master data model, and streams it into the MDM repository via a REST sink.
MDM processing: The MDM platform processes source master data through a sequence of activities to verify, standardize, and enrich the data, and to execute data-quality processes. Finally, MDM performs matching and survivorship to identify and group duplicate records and create master records. Optionally, data stewards can perform tasks that result in a set of master data for use in downstream analytics.
Load master data for analytics: Azure Data Factory uses its REST source to stream master data from Profisee to Azure Synapse Analytics.
Azure Data Factory templates for Profisee
In collaboration with Microsoft, Profisee has developed a set of Azure Data Factory templates that make it faster and easier to integrate Profisee into the Azure Data Services ecosystem. These templates use Azure Data Factories REST data source and data sink to read and write data from Profisee's REST Gateway API. They provide templates for both reading from and writing to Profisee.
Example Data Factory template: JSON to Profisee over REST
The following screenshots show an Azure Data Factory template that copies data from a JSON file in an Azure Data Lake to Profisee via REST.
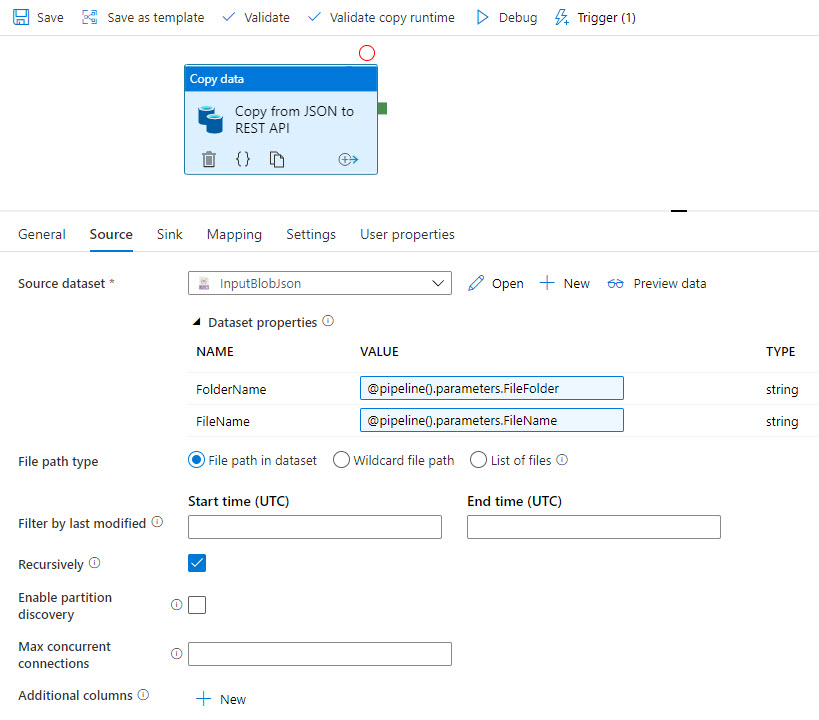
The template copies the source JSON data:
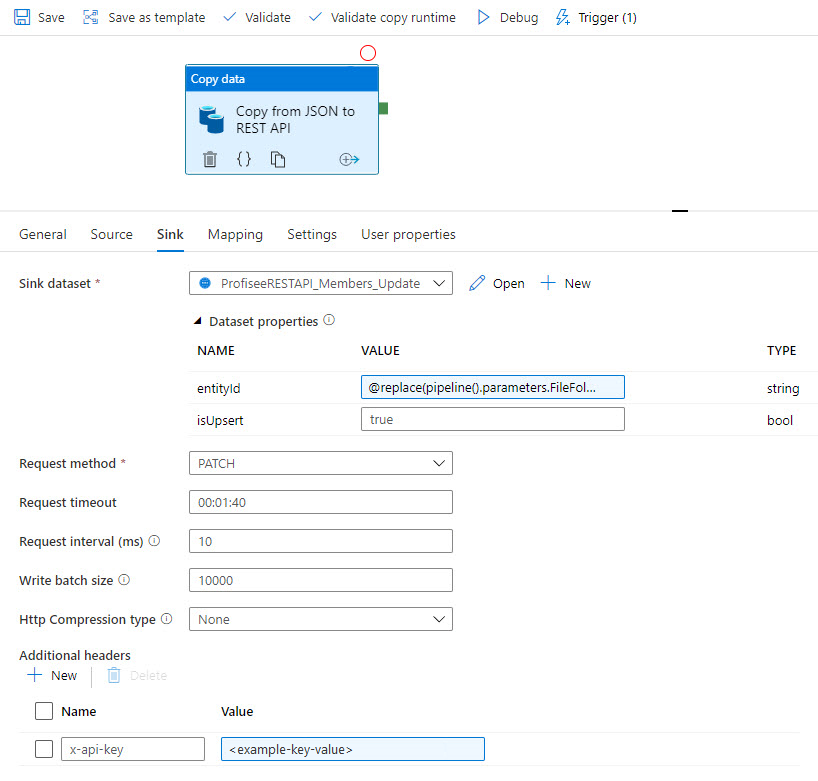
Then, the data syncs to Profisee via REST:
For more information, see Azure Data Factory templates for Profisee.
MDM processing
In an analytical MDM use case, data often processes through the MDM solution automatically to load data for analytics. The following sections show a typical process for customer data in this context.
1. Source data load
Source data loads into the MDM solution from source systems, including lineage information. In this case, we have two source records, one from CRM and one from the ERP application. Upon visual inspection, the two records appear to both represent the same person.
| Source Name | Source Address | Source State | Source Phone | Source ID | Standard Address | Standard State | Standard Name | Standard Phone | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alana Bosh | 123 Main Street | GA | 7708434125 | CRM-100 | |||||
| Bosch, Alana | 123 Main St. | Georgia | 404-854-7736 | CRM-121 | |||||
| Alana Bosch | (404) 854-7736 | ERP-988 |
2. Data verification and standardization
Verification and standardization rules and services help standardize and verify address, name, and phone number information.
| Source Name | Source Address | Source State | Source Phone | Source ID | Standard Address | Standard State | Standard Name | Standard Phone | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alana Bosh | 123 Main Street | GA | 7708434125 | CRM-100 | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosh | 770 843 4125 | |
| Bosch, Alana | 123 Main St. | Georgia | 404-854-7736 | CRM-121 | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 | |
| Alana Bosch | (404) 854-7736 | ERP-988 | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 |
3. Matching
With data standardized, matching occurs, identifying the similarity between records in the group. In this scenario, two records match each other exactly on Name and Phone, and the other fuzzy matches on Name and Address.
| Source Name | Source Address | Source State | Source Phone | Source ID | Standard Address | Standard State | Standard Name | Standard Phone | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alana Bosh | 123 Main Street | GA | 7708434125 | CRM-100 | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosh | 770 843 4125 | 0.9 |
| Bosch, Alana | 123 Main St. | Georgia | 404-854-7736 | CRM-121 | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 | 1.0 |
| Alana Bosch | (404) 854-7736 | ERP-988 | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 | 1.0 |
4. Survivorship
With a group formed, survivorship creates and populates a master record (also called a "golden record") to represent the group.
| Source Name | Source Address | Source State | Source Phone | Source ID | Standard Address | Standard State | Standard Name | Standard Phone | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alana Bosh | 123 Main Street | GA | 7708434125 | CRM-100 | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosh | 770 843 4125 | 0.9 |
| Bosch, Alana | 123 Main St. | Georgia | 404-854-7736 | CRM-121 | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 | 1.0 |
| Alana Bosch | (404) 854-7736 | ERP-988 | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 | 1.0 | ||||
| Master Record: | 123 Main St. | GA | Alana Bosch | 404 854 7736 |
This master record, along with improved source data and lineage information, loads into the downstream analytics solution, where it links to transactional data.
This example shows basic, automated MDM processing. You can also use data quality rules to automatically calculate and update values, and flag missing or invalid values for data stewards to resolve. Data stewards help manage the data, including managing hierarchical rollups of data.
The impact of MDM on integration complexity
As shown previously, MDM addresses several common challenges encountered when integrating data into an analytics solution. It includes correcting data quality issues, standardizing and enriching data, and rationalizing duplicate data. Incorporating MDM into your analytics architecture fundamentally changes the data flow by eliminating hardcoded logic in the integration process, and offloading it to the MDM solution, which significantly simplifies integrations. The following table outlines some common differences in the integration process with and without MDM.
| Capability | Without MDM | With MDM |
|---|---|---|
| Data quality | The integration processes include quality rules and transformations to help fix and correct data as it moves. It requires technical resources for both the initial implementation and ongoing maintenance of these rules, making data integration processes complicated and expensive to develop and maintain. | The MDM solution configures and enforces data quality logic and rules. Integration processes perform no data quality transformations, instead moving the data "as-is" into the MDM solution. Data integration processes are simple and affordable to develop and maintain. |
| Data standardization and enrichment | The integration processes include logic to standardize and align reference and master data. Develop integrations with third-party services to perform standardization of address, name, email, and phone data. | By using built-in rules and out-of-the-box integrations with third-party data services, you can standardize data within the MDM solution, which simplifies integration. |
| Duplicate data management | The integration process identifies and groups duplicate records that exist within and across applications based on existing unique identifiers. This process shares identifiers across systems (for example, SSN or email), and only matches and groups them when identical. More sophisticated approaches require significant investments in integration engineering. | Built-in machine learning matching capabilities identify duplicate records within and across systems, generating a golden record to represent the group. This process lets records be "fuzzy matched", grouping records that are similar, with explainable results. It manages groups in scenarios where the ML engine is unable to form a group with high confidence. |
| Data stewardship | Data stewardship activities only update data in the source applications, like ERP or CRM. Typically, they discover issues, like missing, incomplete, or incorrect data, when performing analytics. They correct the issues in the source application, and then update them in the analytics solution during the next update. Any new information to manage gets added to source applications, which takes time and is costly. | MDM solutions have built-in data stewardship capabilities that let users access and manage data. Ideally, the system flags issues and prompts data stewards to correct them. Quickly configure new information or hierarchies in the solution so that data stewards manage them. |
MDM use cases
While there are numerous use cases for MDM, a few use cases cover most real-world MDM implementations. Although these use cases focus on a single domain, they're unlikely built from only that domain. In other words, even these focused use cases most likely include multiple master data domains.
Customer 360
Consolidating customer data for analytics is the most common MDM use case. Organizations capture customer data across an increasing number of applications, creating duplicate customer data within and across applications with inconsistencies and discrepancies. This poor-quality customer data makes it difficult to realize the value of modern analytics solutions. Symptoms include:
- Hard to answer basic business questions like "Who are our top customers?" and "How many new customers did we have?", requiring significant manual effort.
- Missing and inaccurate customer information, making it difficult to roll up or drill down into data.
- Inability to analyze customer data across systems or business units due to an inability to uniquely identify a customer across organizational and system boundaries.
- Poor-quality insights from AI and machine learning due to poor-quality input data.
Product 360
Product data often spreads across multiple enterprise applications, such as ERP, PLM, or e-commerce. The result is a challenge understanding the total catalog of products that have inconsistent definitions for properties such as the product's name, description, and characteristics. And different definitions of reference data further complicate this situation. Symptoms include:
- Inability to support different alternative hierarchical rollup and drill-down paths for product analytics.
- Whether finished goods or material inventory, difficulty understanding exactly what products you have on hand, the vendors you purchase your products from, and duplicate products, leading to excess inventory.
- Difficulty rationalizing products due to conflicting definitions, which lead to missing or inaccurate information in analytics.
Reference data 360
In the context of analytics, reference data exists as numerous lists of data that help further describe other sets of master data. Reference data can include lists of countries and regions, currencies, colors, sizes, and units of measure. Inconsistent reference data leads to obvious errors in downstream analytics. Symptoms include:
- Multiple representations of the same thing. For example, the state Georgia shows as "GA" and "Georgia", which makes it difficult to aggregate and drill down into data consistently.
- Difficulty aggregating data from across applications due to an inability to crosswalk the reference data values between systems. For example, the color red shows as "R" in the ERP system and "Red" in PLM system.
- Difficulty matching numbers across organizations due to differences in agreed upon reference data values for categorizing data.
Finance 360
Financial organizations rely heavily on data for critical activities like monthly, quarterly, and annual reporting. Organizations with multiple finance and accounting systems often have financial data across multiple general ledgers, which they consolidate to produce financial reports. MDM can provide a centralized place to map and manage accounts, cost centers, business entities, and other financial data sets to a consolidated view. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty aggregating financial data across multiple systems into a consolidated view.
- Lack of process for adding and mapping new data elements in the financial systems.
- Delays in producing end of period financial reports.
Considerations
These considerations implement the pillars of the Azure Well-Architected Framework, which is a set of guiding tenets that can be used to improve the quality of a workload. For more information, see Microsoft Azure Well-Architected Framework.
Reliability
Reliability ensures your application can meet the commitments you make to your customers. For more information, see Overview of the reliability pillar.
Profisee runs natively on Azure Kubernetes Service and Azure SQL Database. Both services offer out-of-the-box capabilities to support high availability.
Performance efficiency
Performance efficiency is the ability of your workload to scale to meet the demands placed on it by users in an efficient manner. For more information, see Performance efficiency pillar overview.
Profisee runs natively on Azure Kubernetes Service and Azure SQL Database. You can configure Azure Kubernetes Service to scale Profisee up and out, depending on need. You can deploy Azure SQL Database in many different configurations to balance performance, scalability, and costs.
Security
Security provides assurances against deliberate attacks and the abuse of your valuable data and systems. For more information, see Overview of the security pillar.
Profisee authenticates users through OpenID Connect, which implements an OAuth 2.0 authentication flow. Most organizations configure Profisee to authenticate users against Microsoft Entra ID. This process ensures enterprise policies for authentication get applied and enforced.
Cost optimization
Cost optimization is about looking at ways to reduce unnecessary expenses and improve operational efficiencies. For more information, see Overview of the cost optimization pillar.
Running costs consist of a software license and Azure consumption. For more information, contact Profisee.
Deploy this scenario
To deploy this scenario:
- Deploy Profisee into Azure using an ARM template.
- Create an Azure Data Factory.
- Configure your Azure Data Factory to connect to a Git repository.
- Add Profisee's Azure Data Factory templates to your Azure Data Factory Git repository.
- Create a new Azure Data Factory Pipeline using a template.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal author:
- Sunil Sabat | Principal Program Manager
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- Understand the capabilities of the REST Copy Connector in Azure Data Factory.
- Learn more about Profisee running natively in Azure.
- Learn how to deploy Profisee to Azure using an ARM template.
- View the Profisee Azure Data Factory templates.
Related resources
Architecture guides
- Extract, transform, and load (ETL)
- Integration runtime in Azure Data Factory
- Choosing a data pipeline orchestration technology in Azure