Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you incorporate Azure Cache for Redis into an ASP.NET Core web application that connects to Azure Cache for Redis to store and retrieve data from the cache.
There are also caching providers in .NET core. To quickly start using Redis with minimal changes to your existing code, see:
- ASP.NET core Output Cache provider
- ASP.NET core Distributed Caching provider
- ASP.NET core Redis session provider
Skip to the code on GitHub
Clone the https://github.com/Azure-Samples/azure-cache-redis-samples GitHub repo and navigate to the quickstart/aspnet-core directory to view the completed source code for the steps ahead.
The quickstart/aspnet-core directory is also configured as an Azure Developer CLI (azd) template. Use the open-source azd tool to streamline the provisioning and deployment from a local environment to Azure. Optionally, run the azd up command to automatically provision an Azure Cache for Redis instance, and to configure the local sample app to connect to it:
azd up
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create one for free
- .NET Core SDK
Create an Azure Managed Redis instance
To create an Azure Managed Redis instance, sign in to the Azure portal and select Create a resource.
On the New page, in the search box type Azure Cache for Redis.
On the New Redis Cache tab, configure the settings for your new cache on the Basics .
Setting Choose a value Description Subscription Drop down and select your subscription. The subscription under which to create this new Azure Managed Redis instance. Resource group Drop down and select a resource group, or select Create new and enter a new resource group name. Name for the resource group in which to create your cache and other resources. By putting all your app resources in one resource group, you can easily manage or delete them together. Name Enter a name that is unique in the region. The cache name must be a string between 1 and 63 characters when combined with the cache's region name that contain only numbers, letters, or hyphens. (If the cache name is fewer than 45 characters long it should work in all currently available regions.) The name must start and end with a number or letter, and can't contain consecutive hyphens. Your cache instance's host name is \<DNS name\>.\<Azure region\>.redis.azure.net.Region Drop down and select a location. Azure Managed Redis is available in selected Azure regions. Data tier Select either In-memory for high-performance, or Flash for lower performance caches The in-memory tiers include Balanced, Memory Optimized, and Compute Optimized. Use the Flash tier to use in-memory (RAM) and on-disk (SSD) data storage. Cache Size Drop down and select a size. Cache size depends on tier. The smallest size is a Balanced tier. The size largest in-memory tier is a Memory Optimized tier. Performance Drop down and select a performance preference. Performance depends on the number of vCPUs. Number of vCPU varies with tier. Compute Optimized has the most vCPUs. For guidance on choosing the right performance tier, see Choosing the right tier.
Important
All in-memory tiers that use over 120 GB of storage are in Public Preview, including Memory Optimized M150 and higher; Balanced B150 and higher; and Compute Optimized X150 and higher. All these tiers and higher are in Public Preview.
All Flash Optimized tiers are in Public Preview.
Select Next: Networking , and select either a Public Endpoint or Private Endpoint.
Select Next: Active geo-replication. To use active geo-replication it must be enabled during provisioning. Caches without active geo-replication can't be added to or join active geo-replication groups later. For more information, see Configure active geo-replication for Azure Managed Redis instances.
Select the Next: Advanced tab.
Configure any Redis modules you want to add to the instance.
By default, for a new managed cache:
- Microsoft Entra ID is enabled.
- Access Keys Authentication is disabled for security reasons.
Important
For optimal security, we recommend that you use Microsoft Entra ID with managed identities to authorize requests against your cache if possible. Authorization by using Microsoft Entra ID and managed identities provides superior security and ease of use over shared access key authorization. For more information about using managed identities with your cache, see Use Microsoft Entra ID for cache authentication.
Set Clustering policy:
- Use Enterprise in order to use RedisSearch or other modules
- Use OSS for a clustered cache.
- Use Non-clustered (Preview) for a non-clustered cache.
For more information on choosing Clustering policy, see Cluster policy.
Important
You can't change the clustering policy of an Azure Managed Redis instance after you create it. If you're using RediSearch, the Enterprise cluster policy is required, and
NoEvictionis the only eviction policy supported.Important
If you're using this cache instance in a geo-replication group, eviction policies cannot be changed after the instance is created. Be sure to know the eviction policies of your primary nodes before you create the cache. For more information on active geo-replication, see Active geo-replication prerequisites.
Important
You can't change modules after you create a cache instance. Modules must be enabled at the time you create an Azure Cache for Redis instance. There is no option to enable the configuration of a module after you create a cache.
Select Next: Tags and skip.
Select Next: Review + create.
Review the settings and select Create.
It takes several minutes for the Redis instance to create. You can monitor progress on the Azure Managed Redis Overview page. When Status shows as Running, the cache is ready to use.
Create an Azure Cache for Redis instance
In the Azure portal, search for and select Azure Cache for Redis.
On the Azure Cache for Redis page, select Create > Azure Cache for Redis.
On the Basics tab of the New Redis Cache page, configure the following settings:
- Subscription: Select the subscription to use.
- Resource group: Select a resource group, or select Create new and enter a new resource group name. Putting all your app resources in the same resource group lets you easily manage or delete them together.
- Name: Enter a cache name that's unique in the region. The name must:
- Be a string of 1 to 63 characters.
- Contain only numbers, letters, and hyphens.
- Start and end with a number or letter.
- Not contain consecutive hyphens.
- Region: Select an Azure region near other services that use your cache.
- Cache SKU: Select a SKU to determine the available sizes, performance, and features for your cache.
- Cache size: Select a cache size. For more information, see Azure Cache for Redis overview.

Select the Networking tab, or select Next: Networking.
On the Networking tab, select a connectivity method to use for the cache. Private Endpoint is recommended for security. If you select Private Endpoint, select Add private endpoint and create the private endpoint.
Select the Advanced tab, or select Next: Advanced.
On the Advanced pane, configure the following options:
- Select Microsoft Entra Authentication or Access Keys Authentication. Microsoft Entra Authentication is enabled by default.
- Choose whether to Enable the non-TLS port.
- For a Premium cache, you can configure or disable Availability zones. You can't disable availability zones after the cache is created. For a Standard cache, availability zones are allocated automatically. Availability zones aren't available for Basic SKU.
- For a Premium cache, configure the settings for Replica count, Clustering and Shard count, System-assigned managed identity, and Data persistence.
The following image shows the Advanced tab for the Standard SKU.
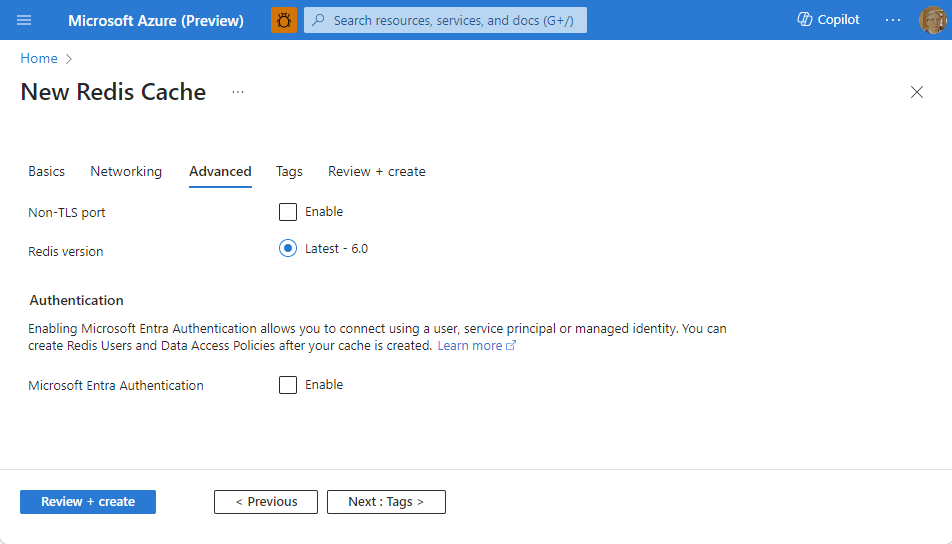
Important
Use Microsoft Entra ID with managed identities to authorize requests against your cache if possible. Authorization using Microsoft Entra ID and managed identity provides better security and is easier to use than shared access key authorization. For more information about using managed identities with your cache, see Use Microsoft Entra ID for cache authentication.
Optionally, select the Tags tab or select Next: Tags, and enter tag names and values to categorize your cache resources.
Select Review + create, and once validation passes, select Create.
The new cache deployment takes several minutes. You can monitor deployment progress on the portal Azure Cache for Redis page. When the cache Status displays Running, the cache is ready to use.
Microsoft Entra ID Authentication (recommended)
Use Microsoft Entra ID authentication on your cache
Azure Managed Redis caches have Microsoft Entra Authentication enabled by default.
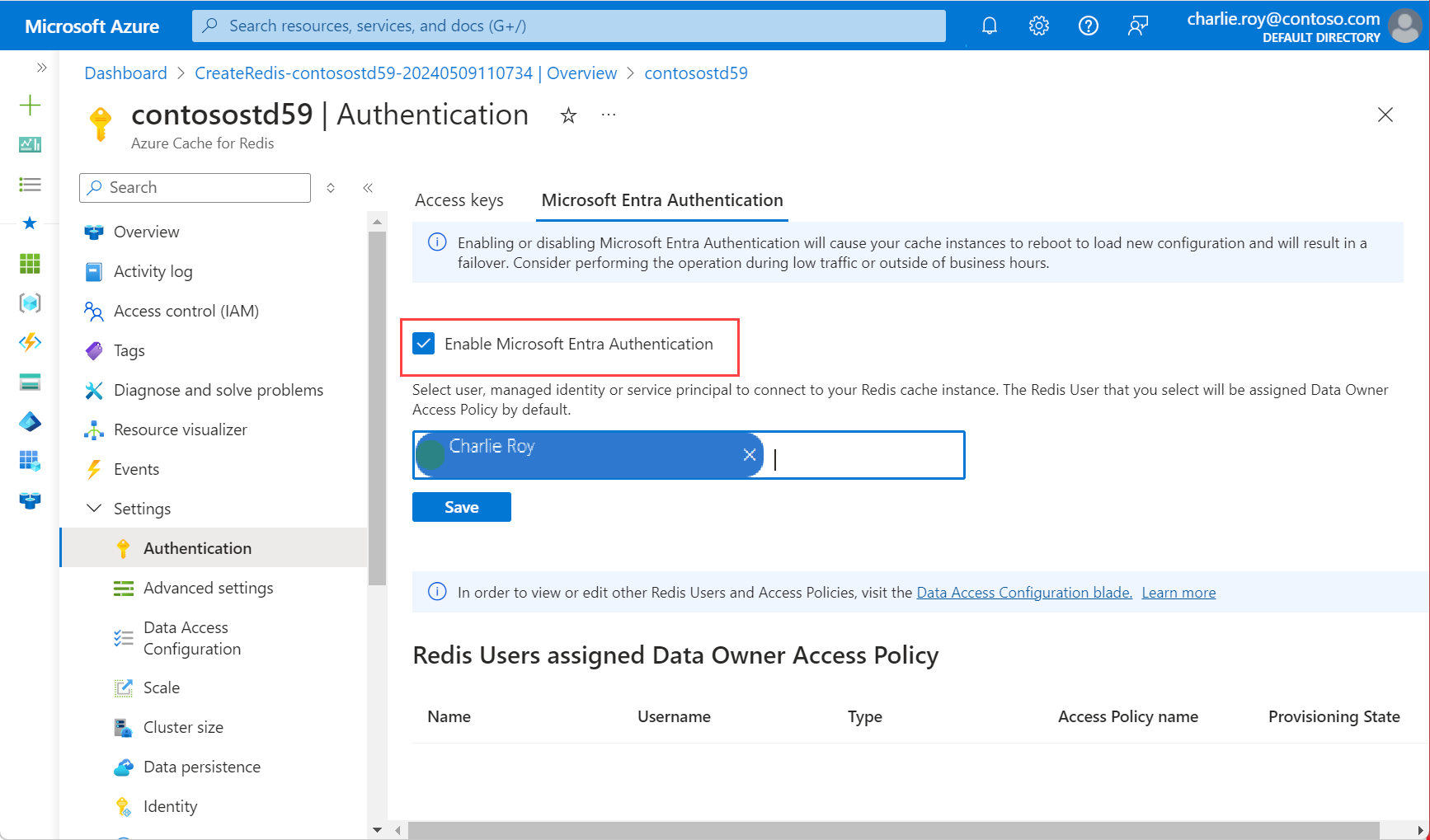
In the Azure portal, select the cache where you'd like to use Microsoft Entra token-based authentication.
Select Authentication from the Resource menu.
Select Select member and enter the name of a valid user. The user you enter is automatically assigned Data Owner Access Policy by default when you select Save. You can also enter a managed identity or service principal to connect to your cache instance.
For information on using Microsoft Entra ID with Azure CLI, see the reference pages for identity.
Install the Library for using Microsoft Entra ID Authentication
The Azure.StackExchange.Redis library contains the Microsoft Entra ID authentication method for connecting to Azure Redis services using Microsoft Entra ID. It is applicable to all Azure Cache for Redis, Azure Cache for Redis Enterprise, and Azure Managed Redis.
dotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.StackExchangeRedis
Connect to the cache using Microsoft Entra ID
Include the libraries in your code
using Azure.Identity; using StackExchange.RedisUsing the default Azure credentials to authenticate the client connection. This enables your code to use the signed-in user credential when running locally, and an Azure managed identity when running in Azure without code change.
var configurationOptions = await ConfigurationOptions.Parse($"{_redisHostName}").ConfigureForAzureWithTokenCredentialAsync(new DefaultAzureCredential()); ConnectionMultiplexer _newConnection = await ConnectionMultiplexer.ConnectAsync(configurationOptions); IDatabase Database = _newConnection.GetDatabase();
To edit the appsettings.json file
Edit the appsettings.json file. Then add the following content:
"_redisHostName":"<cache-hostname>"Replace
<cache-hostname>with your cache host name as it appears in the Overview blade of Azure Portal.For example, with Azure Managed Redis or the Enterprise tiers: my-redis.eastus.azure.net:10000
Save the file.
For more information, see StackExchange.Redis and the code in a GitHub repo.
To edit the appsettings.json file
Edit the appsettings.json file. Then add the following content:
"_redisHostName":"<cache-hostname>"Replace
<cache-hostname>with your cache host name as it appears in the Overview blade of Azure Portal.For example, with Azure Cache for Redis: my-redis.eastus.azure.net:6380
Save the file.
For more information, see StackExchange.Redis and the code in a GitHub repo.
Run the app locally
Execute the following command in your command window to build the app:
dotnet buildThen run the app with the following command:
dotnet runBrowse to
https://localhost:5001in your web browser.Select Azure Cache for Redis Test in the navigation bar of the web page to test cache access.

Clean up resources
If you want to continue to use the resources you created in this article, keep the resource group.
Otherwise, if you're finished with the resources, you can delete the Azure resource group that you created to avoid charges.
Important
Deleting a resource group is irreversible. When you delete a resource group, all the resources in it are permanently deleted. Make sure that you do not accidentally delete the wrong resource group or resources. If you created the resources inside an existing resource group that contains resources you want to keep, you can delete each resource individually instead of deleting the resource group.
To delete a resource group
Sign in to the Azure portal, and then select Resource groups.
Select the resource group you want to delete.
If there are many resource groups, use the Filter for any field... box, type the name of your resource group you created for this article. Select the resource group in the results list.
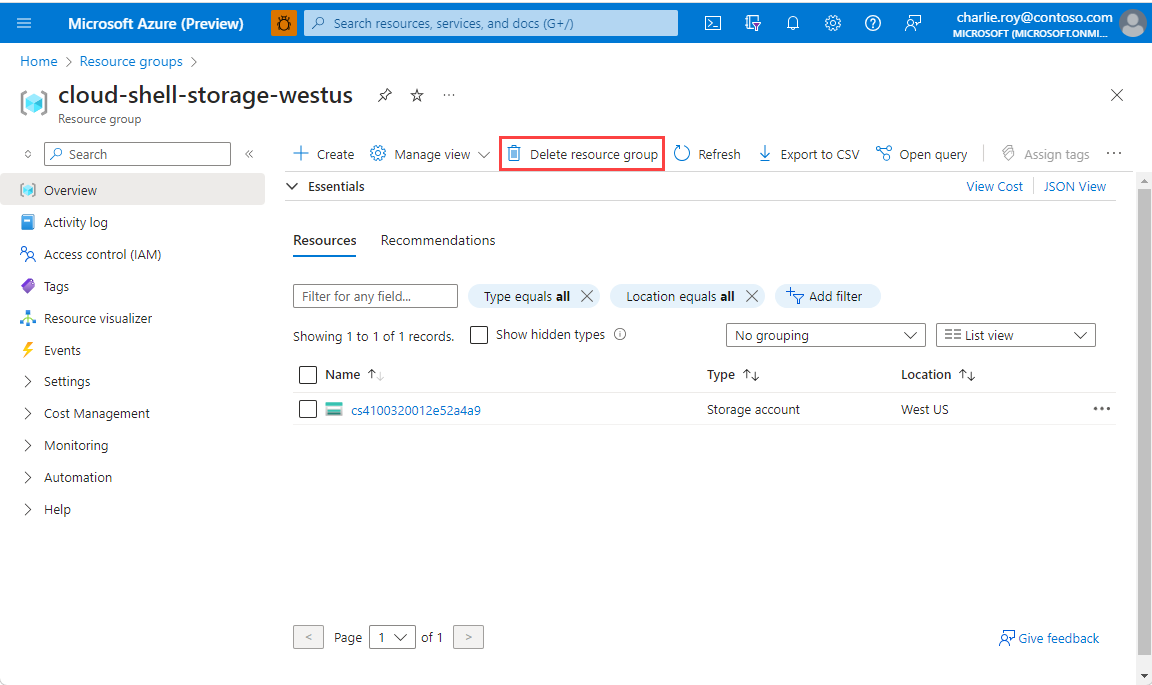
Select Delete resource group.
You're asked to confirm the deletion of the resource group. Type the name of your resource group to confirm, and then select Delete.

After a few moments, the resource group and all of its resources are deleted.