Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article shows how to set up Durable Functions to publish orchestration lifecycle events (such as created, completed, and failed) to a custom Azure Event Grid topic.
Following are some scenarios where this feature is useful:
DevOps scenarios like blue/green deployments: You might want to know if any tasks are running before implementing the side-by-side deployment strategy.
Advanced monitoring and diagnostics support: You can keep track of orchestration status information in an external store optimized for queries, such as Azure SQL Database or Azure Cosmos DB.
Long-running background activity: If you use Durable Functions for a long-running background activity, this feature helps you to know the current status.
Prerequisites
- Install Microsoft.Azure.WebJobs.Extensions.DurableTask in your Durable Functions project.
- Install the Azurite storage emulator or use an existing Azure Storage account.
- Install Azure CLI or use Azure Cloud Shell
Create a custom Event Grid topic
Create an Event Grid topic for sending events from Durable Functions. The following instructions show how to create a topic by using Azure CLI. You can also create the topic by using PowerShell or by using the Azure portal.
Create a resource group
Create a resource group with the az group create command. Currently, Azure Event Grid doesn't support all regions. For information about which regions are supported, see the Azure Event Grid overview.
az group create --name eventResourceGroup --location westus2
Create a custom topic
An Event Grid topic provides a user-defined endpoint that you post your event to. Replace <topic_name> with a unique name for your topic. The topic name must be unique because it becomes a DNS entry.
az eventgrid topic create --name <topic_name> -l westus2 -g eventResourceGroup
Get the endpoint and key
Get the endpoint of the topic. Replace <topic_name> with the name you chose.
az eventgrid topic show --name <topic_name> -g eventResourceGroup --query "endpoint" --output tsv
Get the topic key. Replace <topic_name> with the name you chose.
az eventgrid topic key list --name <topic_name> -g eventResourceGroup --query "key1" --output tsv
Now you can send events to the topic.
Configure Event Grid publishing
In your Durable Functions project, find the host.json file.
Durable Functions 1.x
Add eventGridTopicEndpoint and eventGridKeySettingName in a durableTask property.
{
"durableTask": {
"eventGridTopicEndpoint": "https://<topic_name>.westus2-1.eventgrid.azure.net/api/events",
"eventGridKeySettingName": "EventGridKey"
}
}
Durable Functions 2.x
Add a notifications section to the durableTask property of the file, replacing <topic_name> with the name you chose. If the durableTask or extensions properties don't exist, create them like this example:
{
"version": "2.0",
"extensions": {
"durableTask": {
"notifications": {
"eventGrid": {
"topicEndpoint": "https://<topic_name>.westus2-1.eventgrid.azure.net/api/events",
"keySettingName": "EventGridKey"
}
}
}
}
}
The possible Azure Event Grid configuration properties can be found in the host.json documentation. After you configure the host.json file, your function app sends lifecycle events to the Event Grid topic. This action starts when you run your function app both locally and in Azure.
Set the app setting for the topic key in the Function App and local.settings.json. The following JSON is a sample of the local.settings.json for local debugging using an Azure Storage emulator. Replace <topic_key> with the topic key.
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "UseDevelopmentStorage=true",
"EventGridKey": "<topic_key>"
}
}
If you're using the Storage Emulator instead of a real Azure Storage account, make sure it's running. It's a good idea to clear any existing storage data before executing.
If you're using a real Azure Storage account, replace UseDevelopmentStorage=true in local.settings.json with its connection string.
Create functions that listen for events
Using the Azure portal, create another function app to listen for events published by your Durable Functions app. It's best to locate it in the same region as the Event Grid topic.
Create an Event Grid trigger function
In your function app, select Functions, and then select + Add
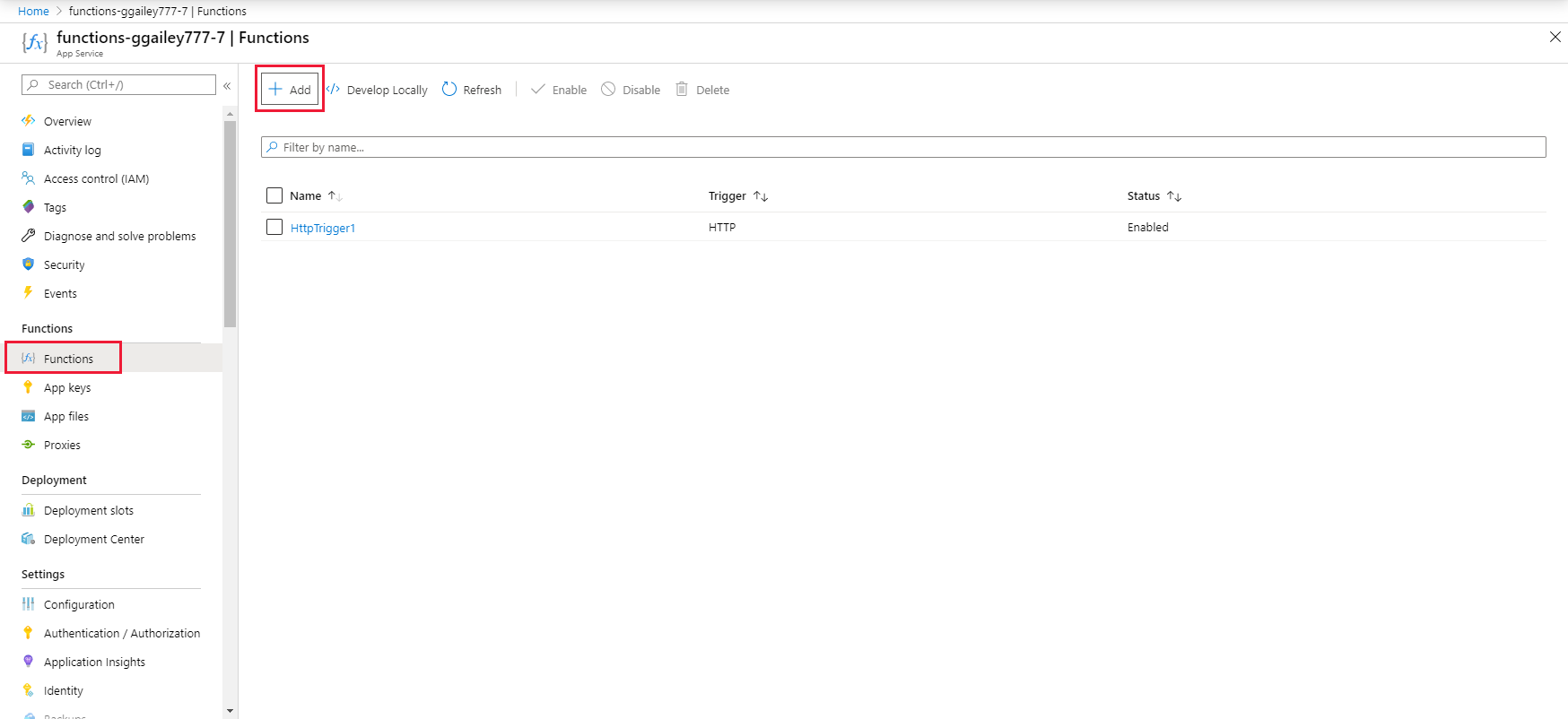
Search for Event Grid, and then select the Azure Event Grid trigger template.
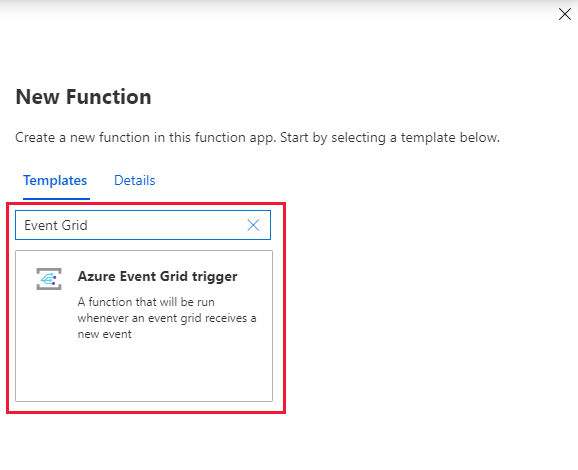
Name the new trigger, and then select Create Function.
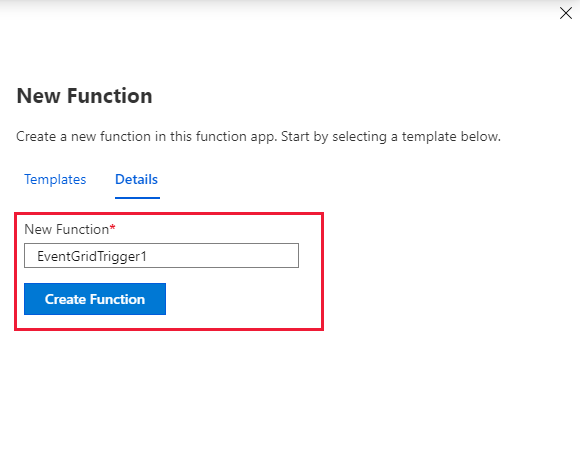
A function with the following code is created:
#r "Newtonsoft.Json" using Newtonsoft.Json; using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; public static void Run(JObject eventGridEvent, ILogger log) { log.LogInformation(eventGridEvent.ToString(Formatting.Indented)); }
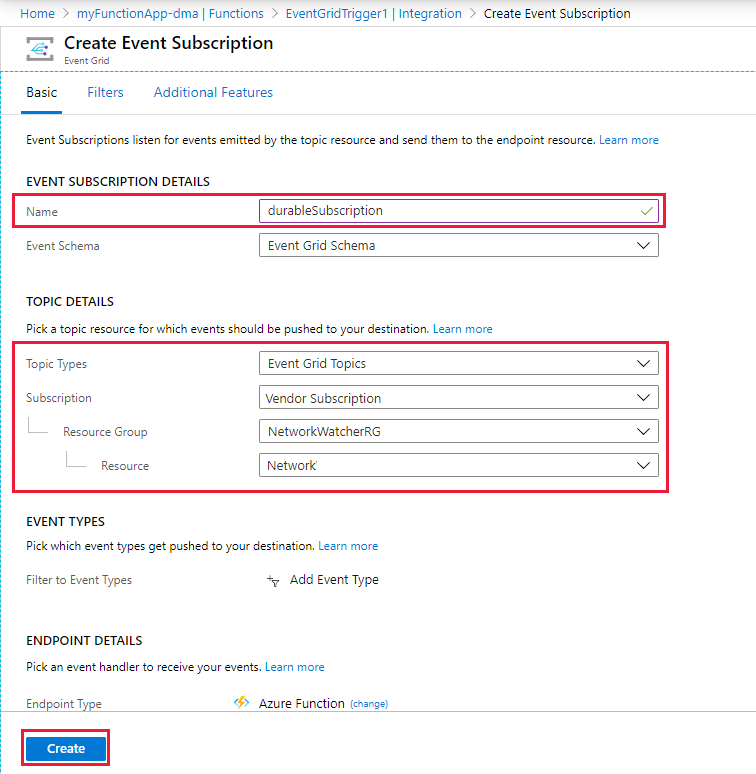
Add an Event Grid subscription
You can now add an Event Grid subscription for the Event Grid topic that you created. For more information, see Concepts in Azure Event Grid.
In your new function, select Integration and then select Event Grid Trigger (eventGridEvent).
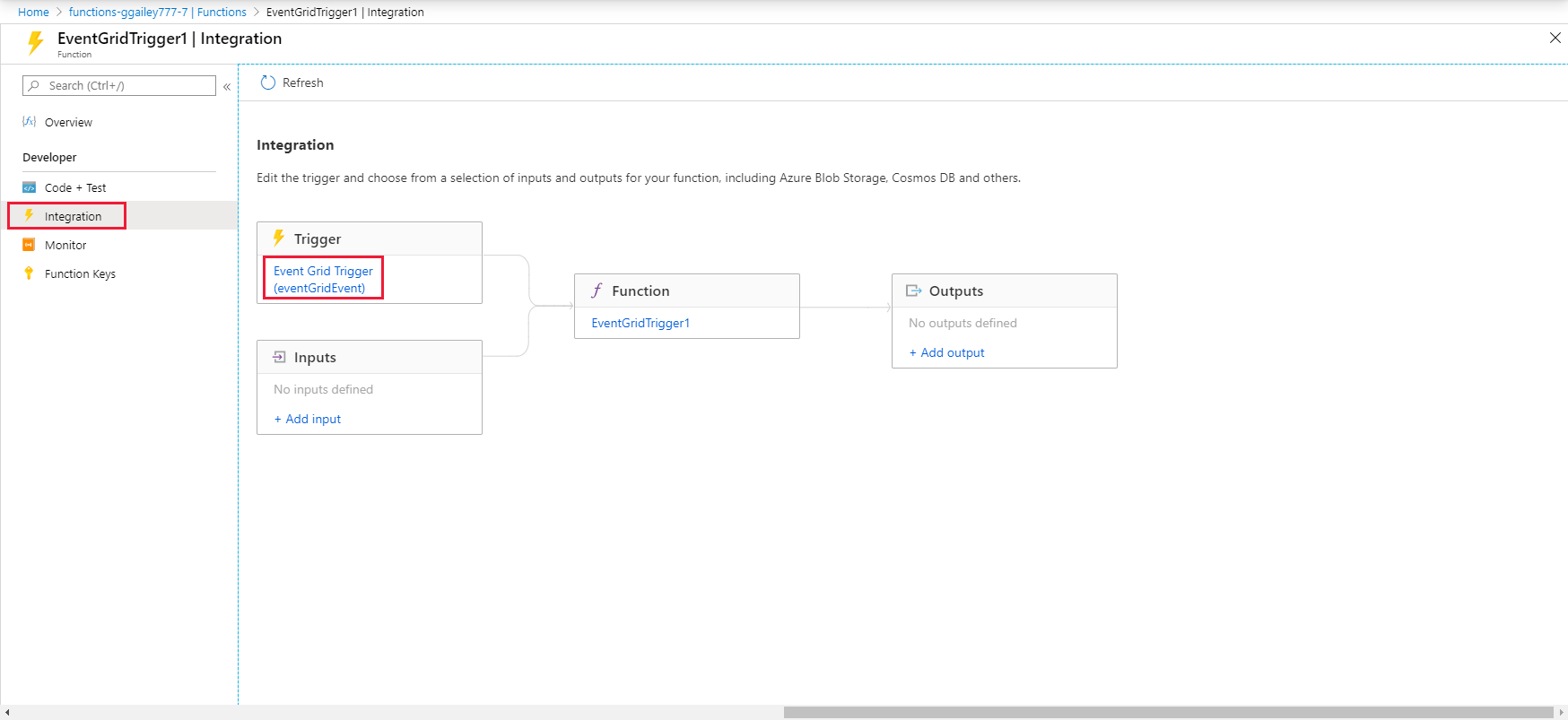
Select Create Event Grid Description.
Name your event subscription and select the Event Grid Topics topic type.
Select the subscription. Then, select the resource group and resource that you created for the Event Grid topic.
Select Create.
Now you're ready to receive lifecycle events.
Run Durable Functions app to send the events
In the Durable Functions project that you configured earlier, start debugging on your local machine and start an orchestration. The app publishes Durable Functions lifecycle events to Event Grid. Verify that Event Grid triggers the listener function you created by checking its logs in the Azure portal.
2019-04-20T09:28:21.041 [Info] Function started (Id=3301c3ef-625f-40ce-ad4c-9ba2916b162d)
2019-04-20T09:28:21.104 [Info] {
"id": "054fe385-c017-4ce3-b38a-052ac970c39d",
"subject": "durable/orchestrator/Running",
"data": {
"hubName": "DurableFunctionsHub",
"functionName": "Sample",
"instanceId": "055d045b1c8a415b94f7671d8df693a6",
"reason": "",
"runtimeStatus": "Running"
},
"eventType": "orchestratorEvent",
"eventTime": "2019-04-20T09:28:19.6492068Z",
"dataVersion": "1.0",
"metadataVersion": "1",
"topic": "/subscriptions/<your_subscription_id>/resourceGroups/eventResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.EventGrid/topics/durableTopic"
}
2019-04-20T09:28:21.104 [Info] Function completed (Success, Id=3301c3ef-625f-40ce-ad4c-9ba2916b162d, Duration=65ms)
2019-04-20T09:28:37.098 [Info] Function started (Id=36fadea5-198b-4345-bb8e-2837febb89a2)
2019-04-20T09:28:37.098 [Info] {
"id": "8cf17246-fa9c-4dad-b32a-5a868104f17b",
"subject": "durable/orchestrator/Completed",
"data": {
"hubName": "DurableFunctionsHub",
"functionName": "Sample",
"instanceId": "055d045b1c8a415b94f7671d8df693a6",
"reason": "",
"runtimeStatus": "Completed"
},
"eventType": "orchestratorEvent",
"eventTime": "2019-04-20T09:28:36.5061317Z",
"dataVersion": "1.0",
"metadataVersion": "1",
"topic": "/subscriptions/<your_subscription_id>/resourceGroups/eventResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.EventGrid/topics/durableTopic"
}
2019-04-20T09:28:37.098 [Info] Function completed (Success, Id=36fadea5-198b-4345-bb8e-2837febb89a2, Duration=0ms)
Event Schema
The following list explains the lifecycle events schema:
id: Unique identifier for the Event Grid event.subject: Path to the event subject.durable/orchestrator/{orchestrationRuntimeStatus}.{orchestrationRuntimeStatus}will beRunning,Completed,Failed, andTerminated.data: Durable Functions Specific Parameters.hubName: TaskHub name.functionName: Orchestrator function name.instanceId: Durable Functions instanceId.reason: Additional data associated with the tracking event. For more information, see Diagnostics in Durable Functions (Azure Functions)runtimeStatus: Orchestration Runtime Status. Running, Completed, Failed, Canceled.
eventType: "orchestratorEvent"eventTime: Event time (UTC).dataVersion: Version of the lifecycle event schema.metadataVersion: Version of the metadata.topic: Event Grid topic resource.
How to test locally
To test locally, read Local testing with viewer web app.