Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Learn how to use Azure virtual machine extensions to perform post-deployment configuration and automation tasks on Azure VMs. Many different VM extensions are available for use with Azure VMs. In this tutorial, you deploy a Custom Script extension from an Azure Resource Manager template (ARM template) to run a PowerShell script on a Windows VM. The script installs Web Server on the VM.
This tutorial covers the following tasks:
- Prepare a PowerShell script
- Open a quickstart template
- Edit the template
- Deploy the template
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
To complete this article, you need:
To increase security, use a generated password for the virtual machine administrator account. You can use Azure Cloud Shell to run the following command in PowerShell or Bash:
openssl rand -base64 32To learn more, run
man openssl randto open the manual page.Azure Key Vault is designed to safeguard cryptographic keys and other secrets. For more information, see Tutorial: Integrate Azure Key Vault in your ARM template deployment. We also recommend that you update your password every three months.
Prepare a PowerShell script
You can use an inline PowerShell script or a script file. This tutorial shows how to use a script file. A PowerShell script with the following content is shared from GitHub:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Web-Server -IncludeManagementTools
If you choose to publish the file to your own location, update the fileUri element in the template later in the tutorial.
Open a quickstart template
Azure Quickstart Templates is a repository for ARM templates. Instead of creating a template from scratch, you can find a sample template and customize it. The template used in this tutorial is called Deploy a simple Windows VM.
In Visual Studio Code, select File > Open File.
In the File name box, paste the following URL:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-quickstart-templates/master/quickstarts/microsoft.compute/vm-simple-windows/azuredeploy.jsonTo open the file, select Open. The template defines five resources:
Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines.
It's helpful to get some basic understanding of the template before you customize it.
Save a copy of the file to your local computer with the name azuredeploy.json by selecting File > Save As.
Edit the template
Add a virtual machine extension resource to the existing template with the following content:
{
"type": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions",
"apiVersion": "2025-04-01",
"name": "[format('{0}/{1}', variables('vmName'), 'InstallWebServer')]",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"dependsOn": [
"[format('Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/{0}',variables('vmName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.Compute",
"type": "CustomScriptExtension",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.7",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
"fileUris": [
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure/azure-docs-json-samples/master/tutorial-vm-extension/installWebServer.ps1"
],
"commandToExecute": "powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -File installWebServer.ps1"
}
}
}
For more information about this resource definition, see the extension reference. The following are some important elements:
name: Because the extension resource is a child resource of the virtual machine object, the name must have the virtual machine name prefix. See Set name and type for child resources.dependsOn: Create the extension resource after you've created the virtual machine.fileUris: The locations where the script files are stored. If you choose not to use the provided location, you need to update the values.commandToExecute: This command invokes the script.
To use an inline script, remove fileUris, and update commandToExecute to:
powershell.exe Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementTools && powershell.exe remove-item 'C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\iisstart.htm' && powershell.exe Add-Content -Path 'C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\iisstart.htm' -Value $('Hello World from ' + $env:computername)
This inline script also updates the iisstart.html content.
You must also open the HTTP port so that you can access the web server.
Find
securityRulesin the template.Add the following rule next to default-allow-3389.
{ "name": "AllowHTTPInBound", "properties": { "priority": 1010, "access": "Allow", "direction": "Inbound", "destinationPortRange": "80", "protocol": "Tcp", "sourcePortRange": "*", "sourceAddressPrefix": "*", "destinationAddressPrefix": "*" } }
Deploy the template
For the deployment procedure, see the Deploy the template section of Tutorial: Create ARM templates with dependent resources. We recommended that you use a generated password for the virtual machine administrator account. See this article's Prerequisites section.
From the Cloud Shell, run the following command to retrieve the public IP address of the VM:
(Get-AzPublicIpAddress -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName).IpAddress
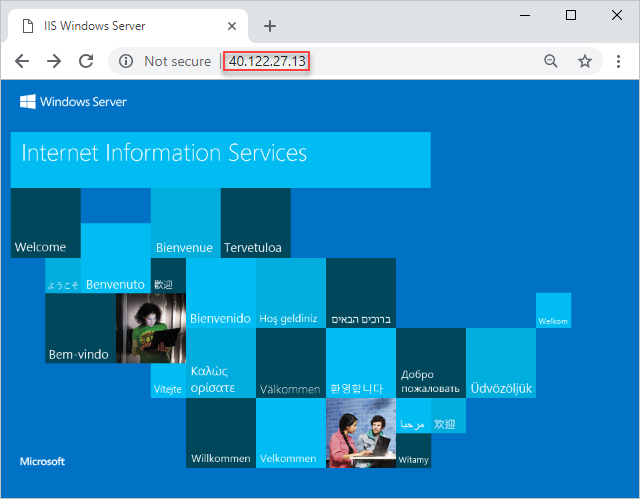
Paste the IP address into a Web browser. The default Internet Information Services (IIS) welcome page opens:
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the Azure resources you deployed, clean them up by deleting the resource group.
- In the Azure portal, in the left pane, select Resource group.
- In the Filter by name box, enter the resource group name.
- Select the resource group name. Six resources are displayed in the resource group.
- In the top menu, select Delete resource group.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you deployed a virtual machine and a virtual machine extension. The extension installed the IIS web server on the virtual machine. To learn how to use the Azure SQL Database extension to import a BACPAC file, see: