Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
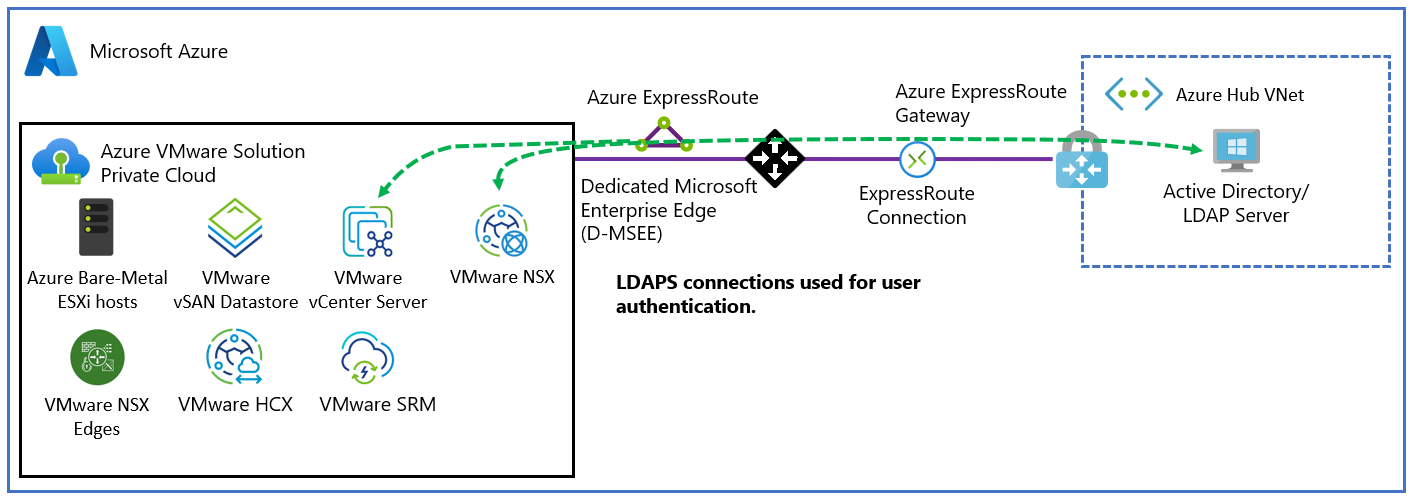
In Azure VMware Solution, VMware vCenter Server has a built-in local user account called CloudAdmin that's assigned the CloudAdmin role. You can configure users and groups in Windows Server Active Directory with the CloudAdmin role for your private cloud. In general, the CloudAdmin role creates and manages workloads in your private cloud. But in Azure VMware Solution, the CloudAdmin role has vCenter Server privileges that are different from other VMware cloud solutions and on-premises deployments.
Important
The local CloudAdmin user account should be used as an emergency access account for "break glass" scenarios in your private cloud. It's not intended to be used for daily administrative activities or for integration with other services.
In a vCenter Server and ESXi on-premises deployment, the administrator has access to the vCenter Server administrator@vsphere.local account and the ESXi root account. The administrator might also be assigned to more Windows Server Active Directory users and groups.
In an Azure VMware Solution deployment, the administrator doesn't have access to the Administrator user account or the ESXi root account. But the administrator can assign Windows Server Active Directory users and groups the CloudAdmin role in vCenter Server. The CloudAdmin role doesn't have permissions to add an identity source like an on-premises Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or Secure LDAP (LDAPS) server to vCenter Server. However, you can use Run commands to add an identity source and assign the CloudAdmin role to users and groups.
A user account in a private cloud can't access or manage specific management components that Microsoft supports and manages. Examples include clusters, hosts, datastores, and distributed virtual switches.
Note
In Azure VMware Solution, the vsphere.local single sign-on (SSO) domain is provided as a managed resource to support platform operations. You can't use it to create or manage local groups and users except for the ones that are provided by default with your private cloud.
You can set up vCenter Server to use an external Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory service to authenticate users. A user can sign in by using their Windows Server Active Directory account credentials or credentials from a third-party LDAP server. Then, the account can be assigned a vCenter Server role, like in an on-premises environment, to provide role-based access for vCenter Server users.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Export a certificate for LDAPS authentication. (Optional)
- Upload the LDAPS certificate to blob storage and generate a shared access signature (SAS) URL. (Optional)
- Configure NSX DNS for resolution to your Windows Server Active Directory domain.
- Add Windows Server Active Directory by using LDAPS (secure) or LDAP (unsecured).
- Add an existing Windows Server Active Directory group to the CloudAdmin group.
- List all existing external identity sources that are integrated with vCenter Server SSO.
- Assign additional vCenter Server roles to Windows Server Active Directory identities.
- Remove a Windows Server Active Directory group from the CloudAdmin role.
- Remove all existing external identity sources.
Note
The steps to export the certificate for LDAPS authentication and upload the LDAPS certificate to blob storage and generate an SAS URL are optional. If the
SSLCertificatesSasUrlparameter is not provided, the certificate is downloaded from the domain controller automatically through thePrimaryUrlorSecondaryUrlparameters. To manually export and upload the certificate, you can provide theSSLCertificatesSasUrlparameter and complete the optional steps.Run commands one at a time in the order that's described in the article.
Prerequisites
Ensure that your Windows Server Active Directory network is connected to your Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
Windows Server Active Directory authentication with LDAPS, see Configure LDAPS within Azure VMware Solution.
Configure DNS resolution for Azure VMware Solution to your on-premises Windows Server Active Directory. Set up a DNS forwarder in the Azure portal. For more information, see Configure a DNS forwarder for Azure VMware Solution.
Note
For more information about LDAPS and certificate issuance, contact your security team or your identity management team.
Export the certificate for LDAPS authentication (Optional)
First, verify that the certificate that's used for LDAPS is valid. If you don't have a certificate, complete the steps to create a certificate for LDAPS before you continue.
To verify that the certificate is valid:
Sign in to a domain controller on which LDAPS is active by using Administrator permissions.
Open the Run tool, enter mmc, and then select OK.
Select File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
In the list of snap-ins, select Certificates, and then select Add.
In the Certificates snap-in pane, select Computer account, and then select Next.
Keep Local computer selected, select Finish, and then select OK.
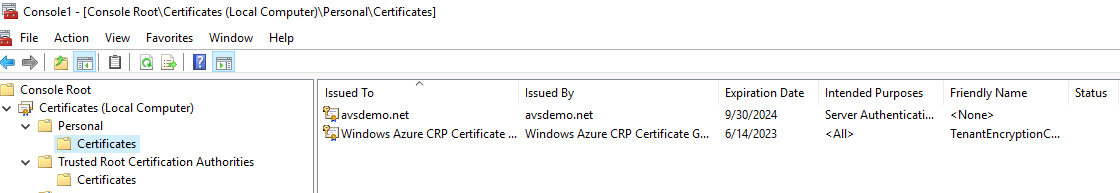
In the Certificates (Local Computer) management console, expand the Personal folder and select the Certificates folder to view the installed certificates.
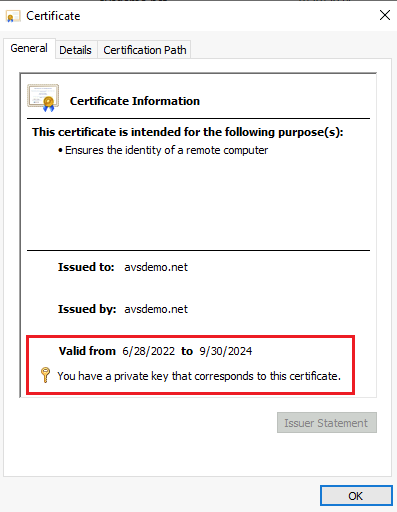
Double-click the certificate for LDAPS. Ensure that the certificate date Valid from and Valid to is current and that the certificate has a private key that corresponds to the certificate.
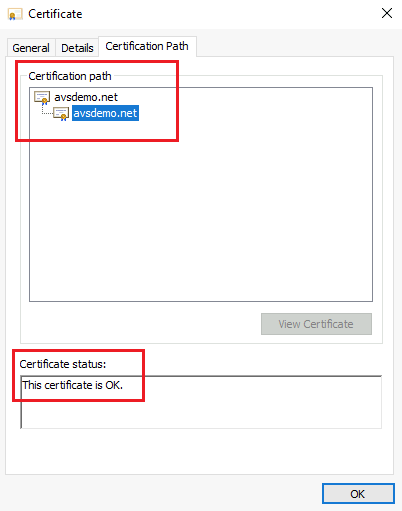
In the same dialog, select the Certification Path tab and verify that the value for Certification path is valid. It should include the certificate chain of root CA and optional intermediate certificates. Check that the Certificate status is OK.
Select OK.
To export the certificate:
- In the Certificates console, right-click the LDAPS certificate and select All Tasks > Export. The Certificate Export Wizard opens. Select Next.
- In the Export Private Key section, select No, do not export the private key, and then select Next.
- In the Export File Format section, select Base-64 encoded X.509(.CER), and then select Next.
- In the File to Export section, select Browse. Select a folder location to export the certificate, and enter a name. Then select Save.
Note
If more than one domain controller is set to use LDAPS, repeat the export procedure for each additional domain controller to export their corresponding certificates. Note that you can reference only two LDAPS servers in the New-LDAPSIdentitySource Run tool. If the certificate is a wildcard certificate, such as .avsdemo.net, export the certificate from only one of the domain controllers.
Upload the LDAPS certificate to blob storage and generate an SAS URL (Optional)
Next, upload the certificate file (in .cer format) you exported to an Azure Storage account as blob storage. Then, grant access to Azure Storage resources by using an SAS.
If you need multiple certificates, upload each one individually and generate an SAS URL for each certificate.
Important
Remember to copy all SAS URL strings. The strings aren't accessible after you leave the page.
Tip
An alternative method to consolidate certificates involves storing all the certificate chains in one file, as detailed in a VMware knowledge base article. Then, generate a single SAS URL for the file that contains all the certificates.
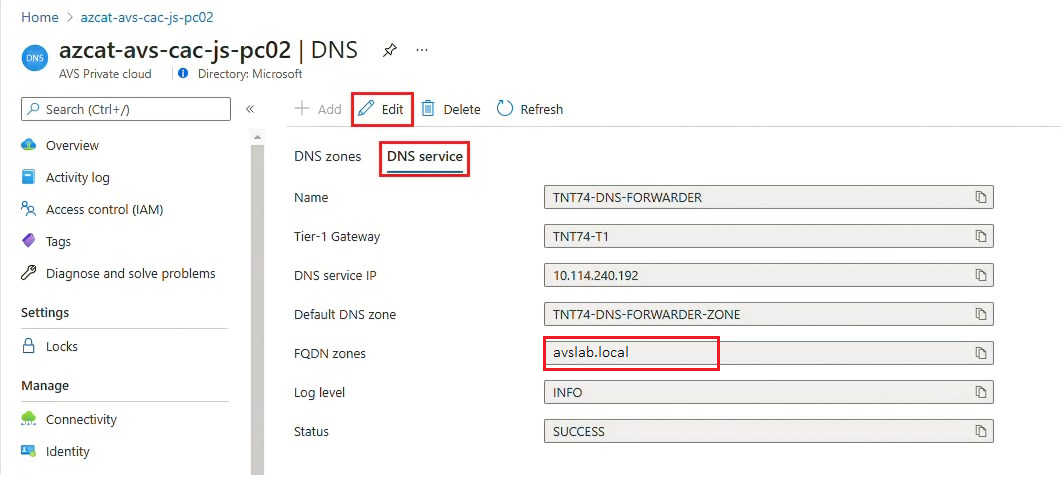
Set up NSX-T DNS for Windows Server Active Directory domain resolution
Create a DNS zone and add it to the DNS service. Complete the steps in Configure a DNS forwarder in the Azure portal.
After you complete these steps, verify that your DNS service includes your DNS zone.
Your Azure VMware Solution private cloud should now properly resolve your on-premises Windows Server Active Directory domain name.
Add Windows Server Active Directory by using LDAP via SSL
To add Windows Server Active Directory over LDAP with SSL as an external identity source to use with SSO to vCenter Server, run the New-LDAPSIdentitySource cmdlet.
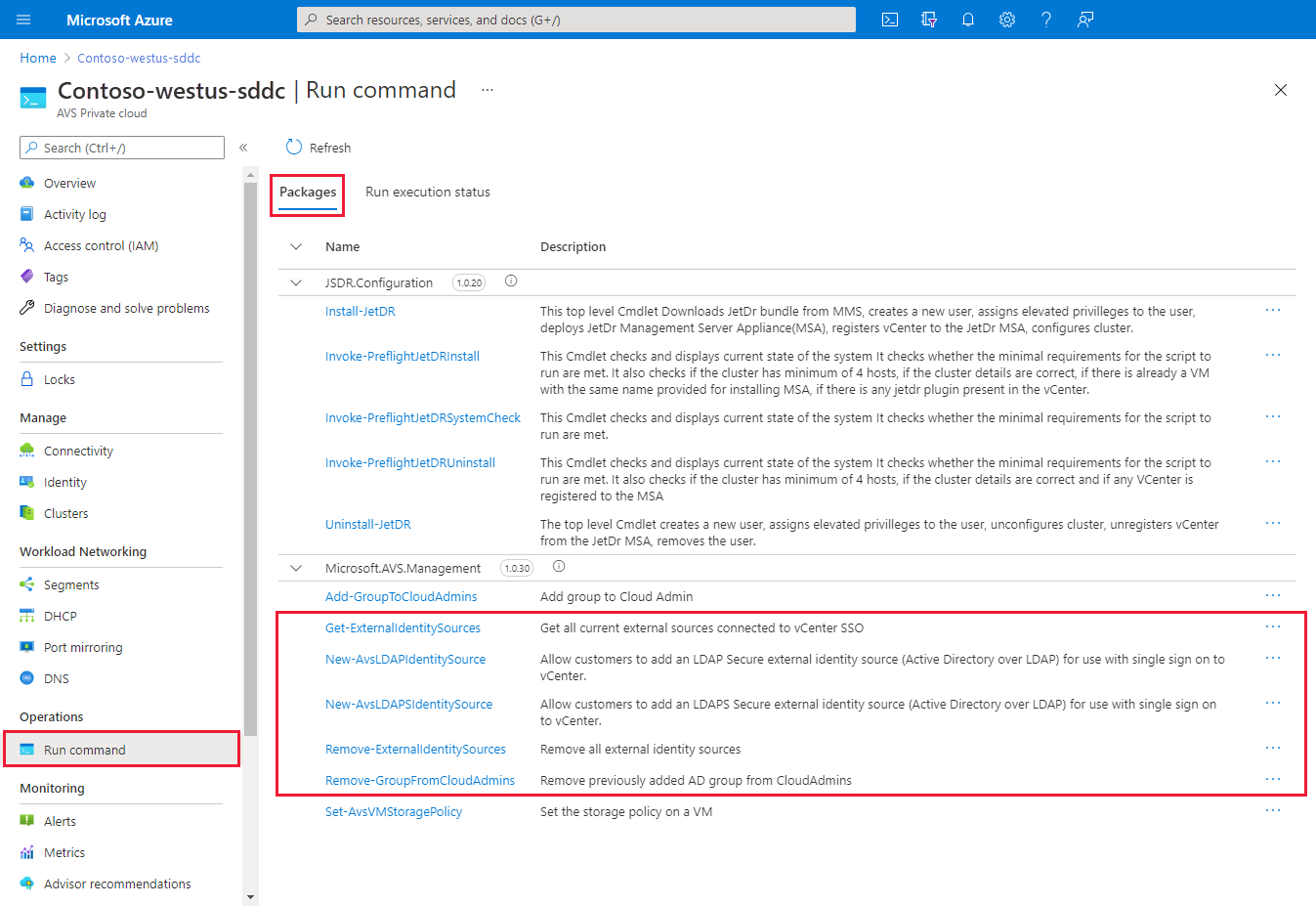
Go to your Azure VMware Solution private cloud and select Run command > Packages > New-LDAPSIdentitySource.
Provide the required values or modify the default values, and then select Run.
Name Description GroupName The group in the external identity source that grants CloudAdmin access. For example, avs-admins. SSLCertificatesSasUrl The path to SAS strings that contain the certificates for authentication to the Windows Server Active Directory source. Separate multiple certificates with a comma. For example, pathtocert1,pathtocert2. Credential The domain username and password for authentication with the Windows Server Active Directory source (not CloudAdmin). Use the <username@avslab.local>format.BaseDNGroups The location to search for groups. For example, CN=group1, DC=avsldap,DC=local. Base DN is required for LDAP authentication. BaseDNUsers The location to search for valid users. For example, CN=users,DC=avsldap,DC=local. Base DN is required for LDAP authentication. PrimaryUrl The primary URL of the external identity source. For example, ldaps://yourserver.avslab.local:636.SecondaryURL The secondary fallback URL if the primary fails. For example, ldaps://yourbackupldapserver.avslab.local:636.DomainAlias For Windows Server Active Directory identity sources, the domain's NetBIOS name. Add the NetBIOS name of the Windows Server Active Directory domain as an alias of the identity source, typically in the avsldap\ format. DomainName The domain's fully qualified domain name (FQDN). For example, avslab.local. Name A name for the external identity source. For example, avslab.local. Retain up to The retention period of the cmdlet output. The default value is 60 days. Specify name for execution An alphanumeric name. For example, addExternalIdentity. Timeout The period after which a cmdlet exits if it isn't finished running. To monitor progress and confirm successful completion, check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane.
Important
If the Run command New-LDAPSIdentitySource fails, utilize the Run command Debug-LDAPSIdentitySources to troubleshoot the issue.
Add Windows Server Active Directory by using LDAP
Note
We recommend that you use the method to add Windows Server Active Directory over LDAP by using SSL.
To add Windows Server Active Directory over LDAP as an external identity source to use with SSO to vCenter Server, run the New-LDAPIdentitySource cmdlet.
Select Run command > Packages > New-LDAPIdentitySource.
Provide the required values or modify the default values, and then select Run.
Name Description Name A name for the external identity source. For example, avslab.local. This name appears in vCenter Server. DomainName The domain's FQDN. For example, avslab.local. DomainAlias For Windows Server Active Directory identity sources, the domain's NetBIOS name. Add the Windows Server Active Directory domain's NetBIOS name as an alias of the identity source, typically in the *avsldap* format. PrimaryUrl The primary URL of the external identity source. For example, ldap://yourserver.avslab.local:389.SecondaryURL The secondary fallback URL if there's a primary failure. BaseDNUsers The location to search for valid users. For example, CN=users,DC=avslab,DC=local. Base DN is required for LDAP authentication. BaseDNGroups The location to search for groups. For example, CN=group1, DC=avslab,DC=local. Base DN is required for LDAP authentication. Credential The domain username and password for authentication with the Windows Server Active Directory source (not CloudAdmin). The user must be in the <username@avslab.local>format.GroupName The group in your external identity source that grants CloudAdmin access. For example, avs-admins. Retain up to The retention period for the cmdlet output. The default value is 60 days. Specify name for execution An alphanumeric name. For example, addExternalIdentity. Timeout The period after which a cmdlet exits if it isn't finished running. To monitor the progress, check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane.
Add an existing Windows Server Active Directory group to a CloudAdmin group
Important
Nested groups aren't supported. Using a nested group might cause loss of access.
Users in a CloudAdmin group have user rights that are equal to the CloudAdmin (<cloudadmin@vsphere.local>) role that's defined in vCenter Server SSO. To add an existing Windows Server Active Directory group to a CloudAdmin group, run the Add-GroupToCloudAdmins cmdlet.
Select Run command > Packages > Add-GroupToCloudAdmins.
Enter or select the required values, and then select Run.
Name Description GroupName The name of the group to add. For example, VcAdminGroup. Retain up to The retention period of the cmdlet output. The default value is 60 days. Specify name for execution An alphanumeric name. For example, addADgroup. Timeout The period after which a cmdlet exits if it isn't finished running. Check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane to see the progress.
List external identity sources
To list all external identity sources that are already integrated with vCenter Server SSO, run the Get-ExternalIdentitySources cmdlet.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Note
If you need access to the Azure for US Government portal, go to
<https://portal.azure.us/>.Select Run command > Packages > Get-ExternalIdentitySources.
Enter or select the required values, and then select Run.
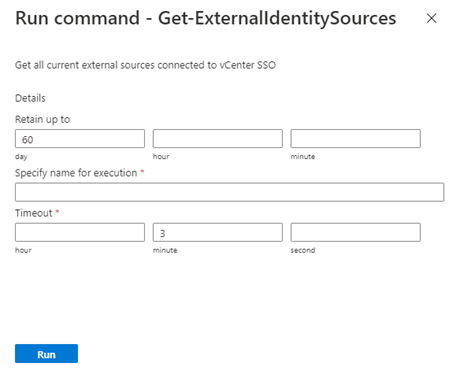
Name Description Retain up to The retention period of the cmdlet output. The default value is 60 days. Specify name for execution An alphanumeric name. For example, getExternalIdentity. Timeout The period after which a cmdlet exits if it isn't finished running. To see the progress, check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane.
Assign more vCenter Server roles to Windows Server Active Directory identities
After you add an external identity over LDAP or LDAPS, you can assign vCenter Server roles to Windows Server Active Directory security groups based on your organization's security controls.
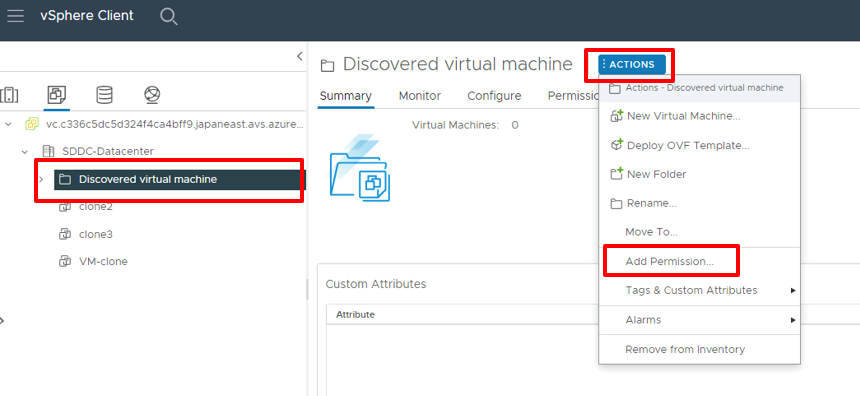
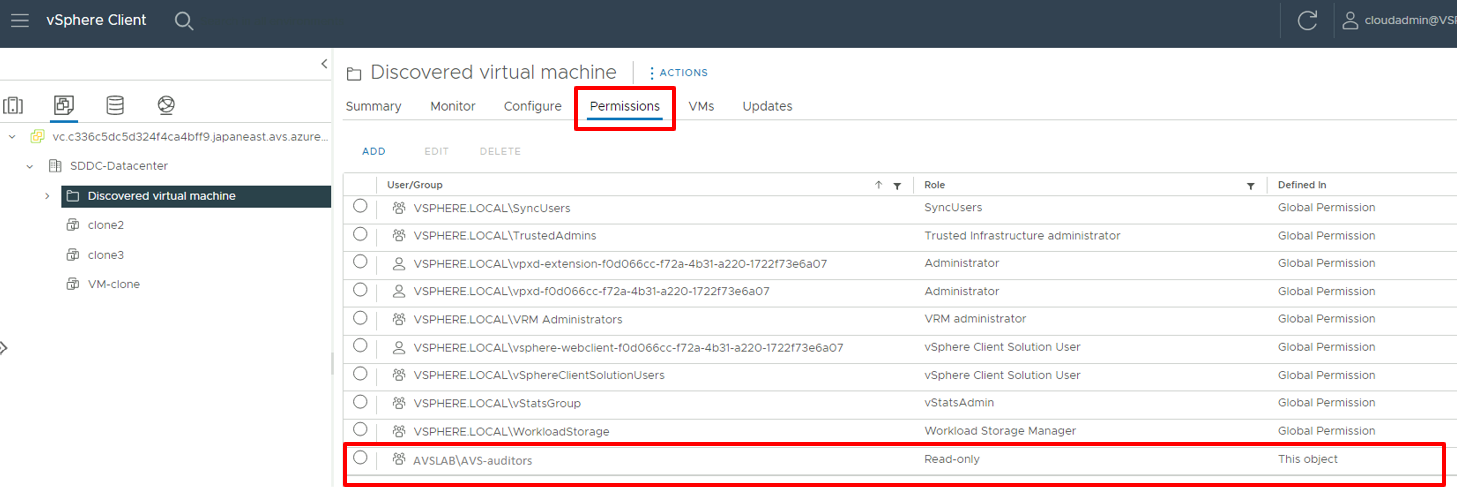
Sign in to vCenter Server as CloudAdmin, select an item from the inventory, select the Actions menu, and then select Add Permission.
In the Add Permission dialog:
- Domain: Select the previously added instance of Windows Server Active Directory.
- User/Group: Enter the user or group name, search for it, and then select it.
- Role: Select the role to assign.
- Propagate to children: Optionally, select the checkbox to propagate permissions to child resources.
Select the Permissions tab and verify that the permission assignment was added.
Users can now sign in to vCenter Server by using their Windows Server Active Directory credentials.
Remove a Windows Server Active Directory group from the CloudAdmin role
To remove a specific Windows Server Active Directory group from the CloudAdmin role, run the Remove-GroupFromCloudAdmins cmdlet.
Select Run command > Packages > Remove-GroupFromCloudAdmins.
Enter or select the required values, and then select Run.
Name Description GroupName The name of the group to remove. For example, VcAdminGroup. Retain up to The retention period of the cmdlet output. The default value is 60 days. Specify name for execution An alphanumeric name. For example, removeADgroup. Timeout The period after which a cmdlet exits if it isn't finished running. To see the progress, check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane.
Remove all existing external identity sources
To remove all existing external identity sources at once, run the Remove-ExternalIdentitySources cmdlet.
Select Run command > Packages > Remove-ExternalIdentitySources.
Enter or select the required values, and then select Run:
Name Description Retain up to The retention period of the cmdlet output. The default value is 60 days. Specify name for execution An alphanumeric name. For example, remove_ExternalIdentity. Timeout The period after which a cmdlet exits if it isn't finished running. To see the progress, check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane.
Rotate an existing external identity source account's username or password
Rotate the password of the account that's used for authentication with the Windows Server Active Directory source in the domain controller.
Select Run command > Packages > Update-IdentitySourceCredential.
Enter or select the required values, and then select Run.
Name Description Credential The domain username and password that are used for authentication with the Windows Server Active Directory source (not CloudAdmin). The user must be in the <username@avslab.local>format.DomainName The FQDN of the domain. For example, avslab.local. To see the progress, check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane.
Warning
If you don't provide a value for DomainName, all external identity sources are removed. Run the cmdlet Update-IdentitySourceCredential only after the password is rotated in the domain controller.
Renew existing certificates for LDAPS identity source
Renew the existing certificates in your domain controllers.
Optional: If the certificates are stored in default domain controllers, this step is optional. Leave the SSLCertificatesSasUrl parameter blank and the new certificates will be downloaded from the default domain controllers and updated in vCenter automatically. If you choose to not use the default way, export the certificate for LDAPS authentication and upload the LDAPS certificate to blob storage and generate an SAS URL. Save the SAS URL for the next step.
Select Run command > Packages > Update-IdentitySourceCertificates.
Provide the required values and the new SAS URL (optional), and then select Run.
Field Value DomainName* The FQDN of the domain, for example avslab.local. SSLCertificatesSasUrl (optional) A comma-delimited list of SAS path URI to Certificates for authentication. Ensure permissions to read are included. To generate, place the certificates in any storage account blob and then right-click the cert and generate SAS. If the value of this field isn't provided by a user, the certificates will be downloaded from the default domain controllers. Check Notifications or the Run Execution Status pane to see the progress.