Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to restore data from a backup vault. To restore data, you use the Recover Data wizard in the Microsoft Azure Recovery Services (MARS) Agent.
Key features
The MARS Agent enables seamless restoration of files to Windows Server. By using this feature, you can:
- Restore data to the same machine from which the backups were taken.
- Restore data to an alternate machine.
- Restore the backup data from the secondary region, if you have Cross Region Restore enabled on your vault.
Use the Instant Restore feature to mount a writeable recovery point snapshot as a recovery volume. You can then explore the recovery volume and copy files to a local computer, thus selectively restoring files.
Note
The January 2017 Azure Backup update is required if you want to use Instant Restore to restore data. Also, the backup data must be protected in vaults in locales listed in the support article. Consult the January 2017 Azure Backup update for the latest list of locales that support Instant Restore.
Use Instant Restore with Recovery Services vaults in the Azure portal. If you stored data in Backup vaults, they've been converted to Recovery Services vaults. If you want to use Instant Restore, download the MARS update, and follow the procedures that mention Instant Restore.
Note
Azure has two different deployment models you can use to create and work with resources: Azure Resource Manager and classic. This article covers the use of the Resource Manager deployment model. We recommend the Resource Manager deployment model for new deployments instead of the classic deployment model.
Recover data to the same machine using Instant Restore
If you accidentally deleted a file, MARS allows you to restore it to the same machine (from which the backup is taken).
To recover the data to the same machine, follow these steps:
Open the Microsoft Azure Backup snap-in. If you don't know where the snap-in was installed, search the computer or server for Microsoft Azure Backup.
The desktop app should appear in the search results.
Select Recover Data to start the wizard.
On the Getting Started page, to restore the data to the same server or computer, select This server (
<server name>) > Next.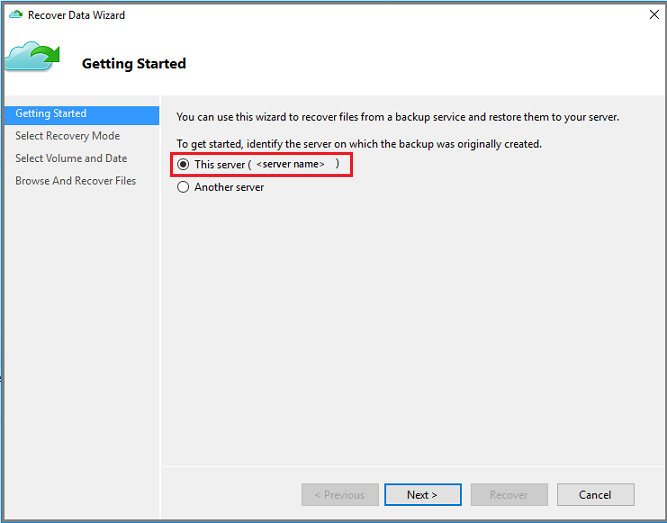
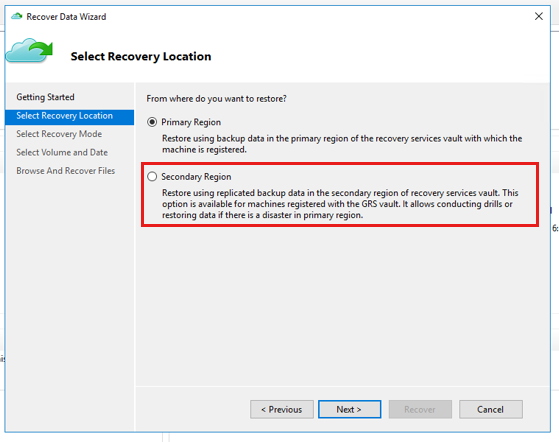
If you have enabled Cross Region Restore (preview) and want to restore from the secondary region, select Secondary Region. Else, select Primary Region.
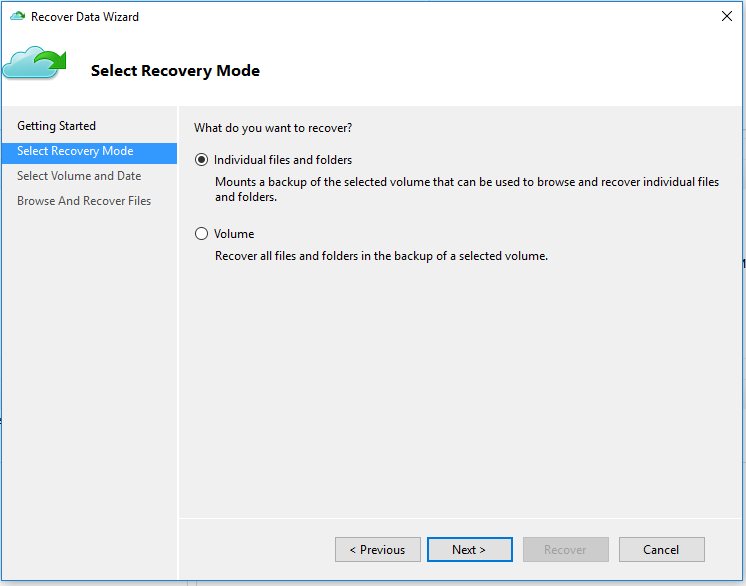
On the Select Recovery Mode page, choose Individual files and folders > Next.
Important
The option to restore individual files and folders requires .NET Framework 4.5.2 or later. If you don't see the Individual files and folders option, you must upgrade .NET Framework to version 4.5.2 or later, and try again.
Tip
The Individual files and folders option allows for quick access to the recovery point data. It's suitable for recovering individual files, and is recommended for a total size of less than 80 GB. It offers transfer or copy speeds up to 6 MBps during recovery. The Volume option recovers all backed up data in a specified volume. This option provides faster transfer speeds (up to 40 MBps), and is recommended for recovering large-sized data or entire volumes.
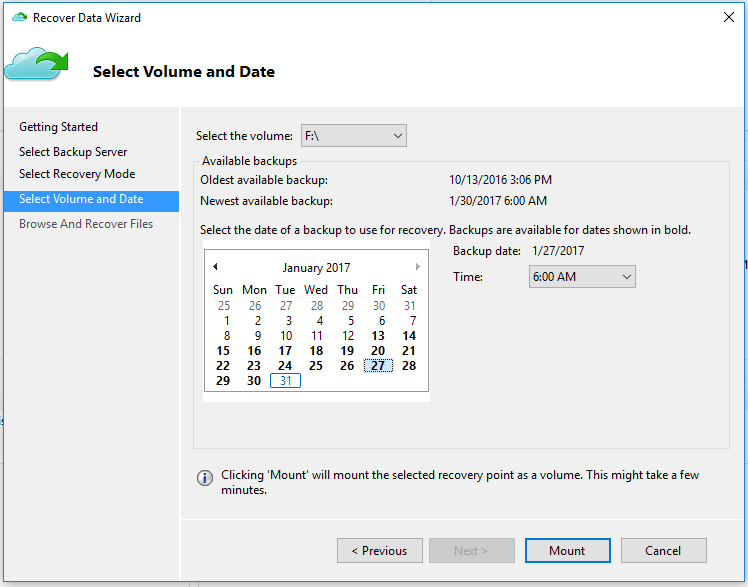
On the Select Volume and Date page, select the volume that contains the files and folders you want to restore.
On the calendar, select a recovery point. Dates in bold indicate the availability of at least one recovery point. If multiple recovery points are available within a single date, choose the specific recovery point from the Time drop-down menu.
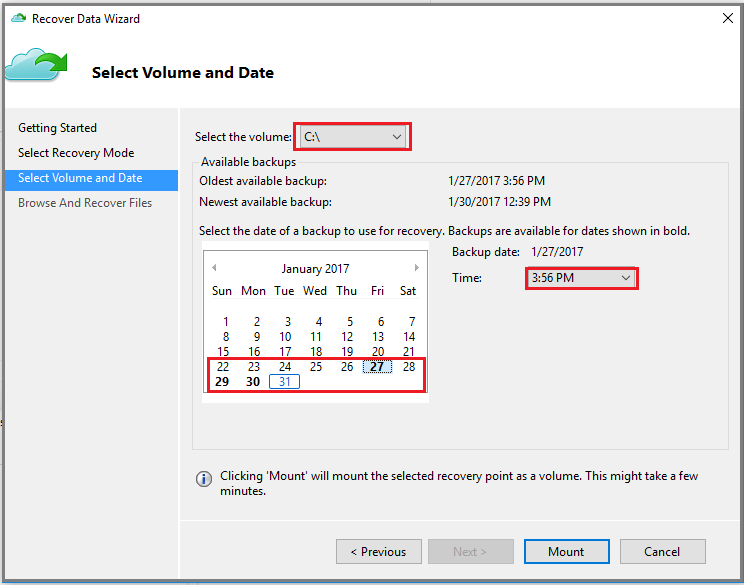
After choosing the recovery point to restore, select Mount.
Azure Backup mounts the local recovery point, and uses it as a recovery volume.
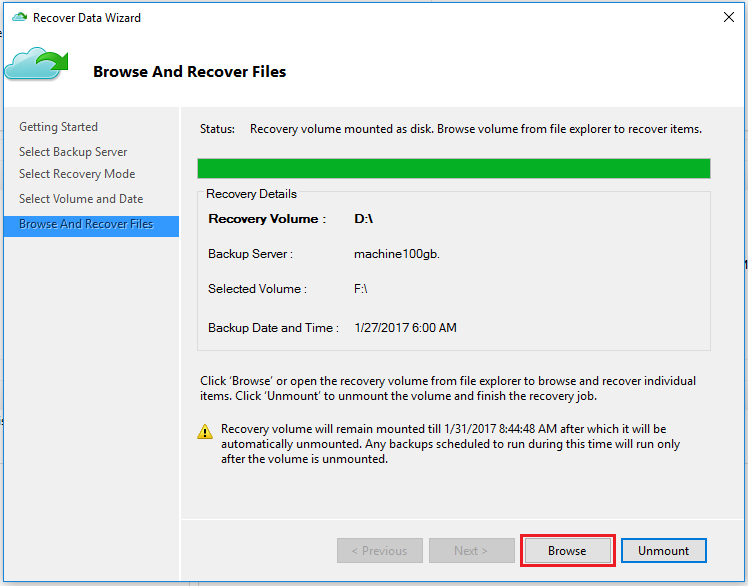
On the Browse and Recover Files page, select Browse to open Windows Explorer, and find the files and folders you want.
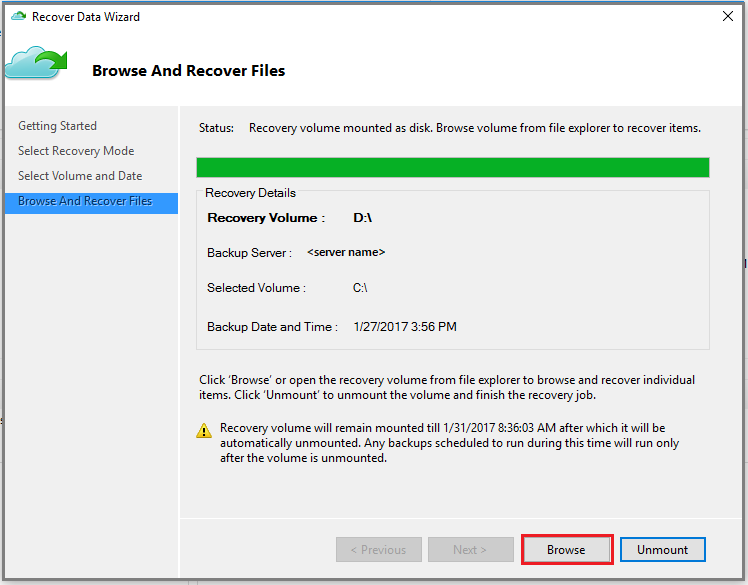
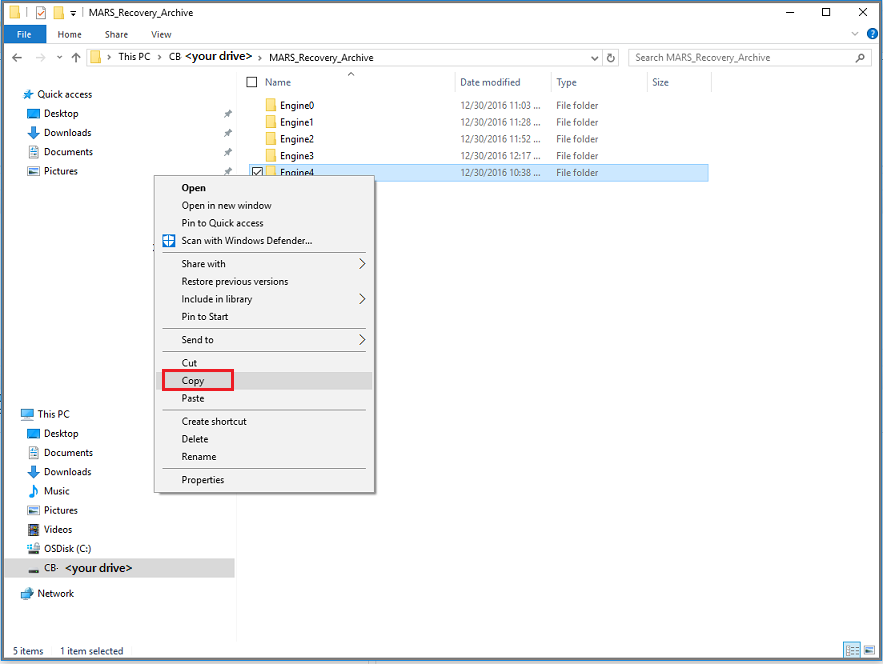
In Windows Explorer, copy the files and folders you want to restore, and paste them to any location local to the server or computer. You can open or stream the files directly from the recovery volume, and verify that you're recovering the correct versions.
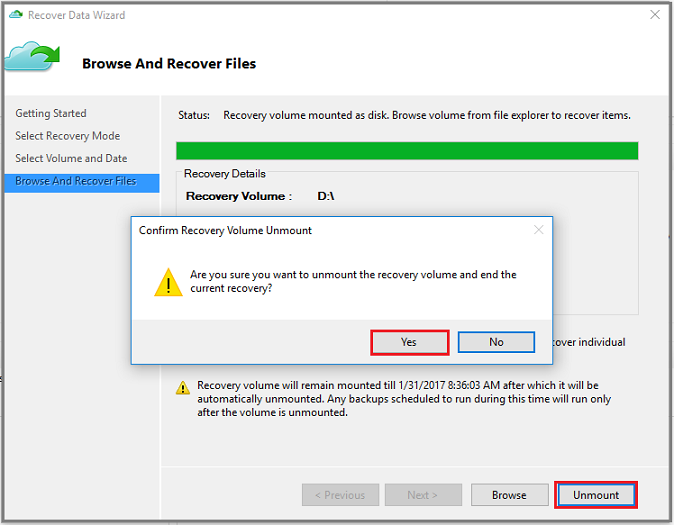
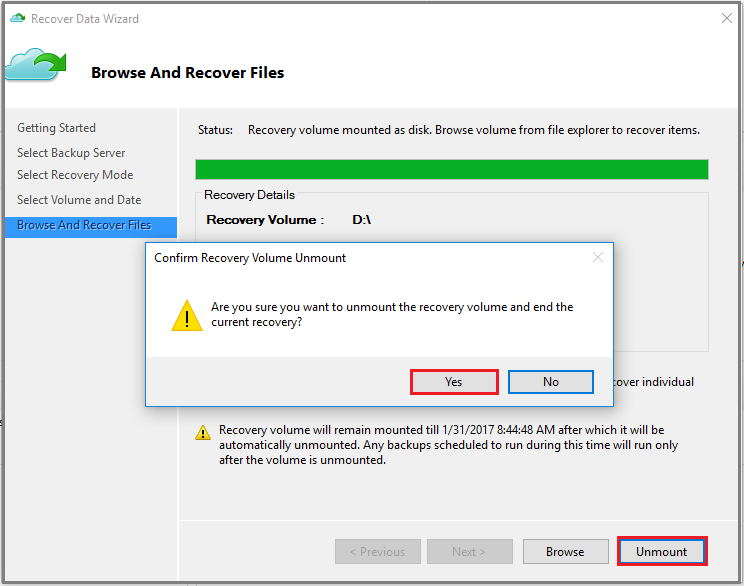
When you're finished, on the Browse and Recover Files page, select Unmount. Then select Yes to confirm that you want to unmount the volume.
Important
If you don't select Unmount, the recovery volume will remain mounted for 6 hours from the time when it was mounted. However, the mount time is extended to a maximum of 7 days in case of an ongoing file-copy. No backup operations will run while the volume is mounted. Any backup operation scheduled to run during the time when the volume is mounted will run after the recovery volume is unmounted.
Restore data to an alternate machine using Instant Restore
If your entire server is lost, you can still recover data from Azure Backup to a different machine. Before you proceed, review the following terminology:
- Source machine – The original machine from which the backup was taken, and which is currently unavailable.
- Target machine – The machine to which the data is being recovered.
- Sample vault – The Recovery Services vault to which the source machine and target machine are registered.
Note
Backups can't be restored to a target machine that's running an earlier version of the operating system. For example, a backup taken from a Windows 7 computer can be restored on a Windows 7 (or later) computer. A backup taken from a Windows 10 computer can't be restored to a Windows 7 computer.
To recover the data to an alternate machine, follow these steps:
Open the Microsoft Azure Backup snap-in on the target machine.
Ensure that the target machine and the source machine are registered to the same Recovery Services vault.
Select Recover Data to open the Recover Data Wizard.

On the Getting Started page, select Another server.
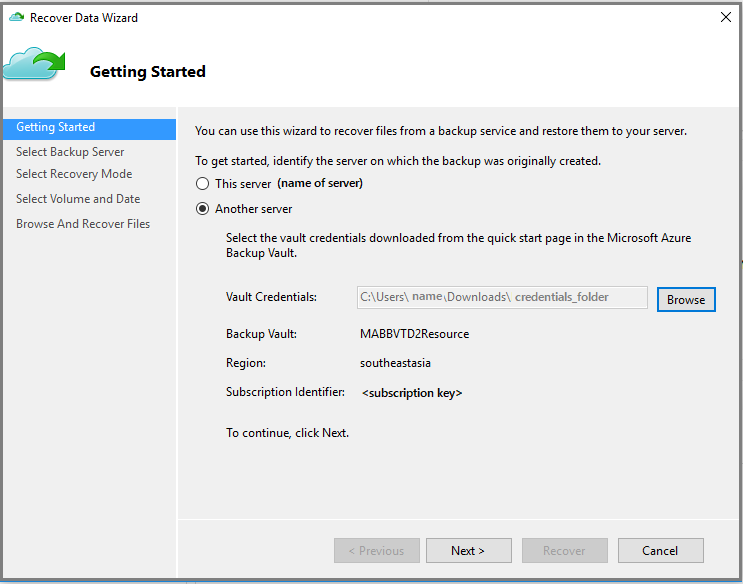
Provide the vault credential file that corresponds to the sample vault.
If the vault credential file is invalid (or expired), download a new vault credential file from the sample vault in the Azure portal. After you provide a valid vault credential, the name of the corresponding backup vault appears.
If you want to use Cross Region Restore to restore backup data from the secondary region, you need to download the Secondary Region vault credential file* from the Azure portal, and then pass the file in the MARS agent.
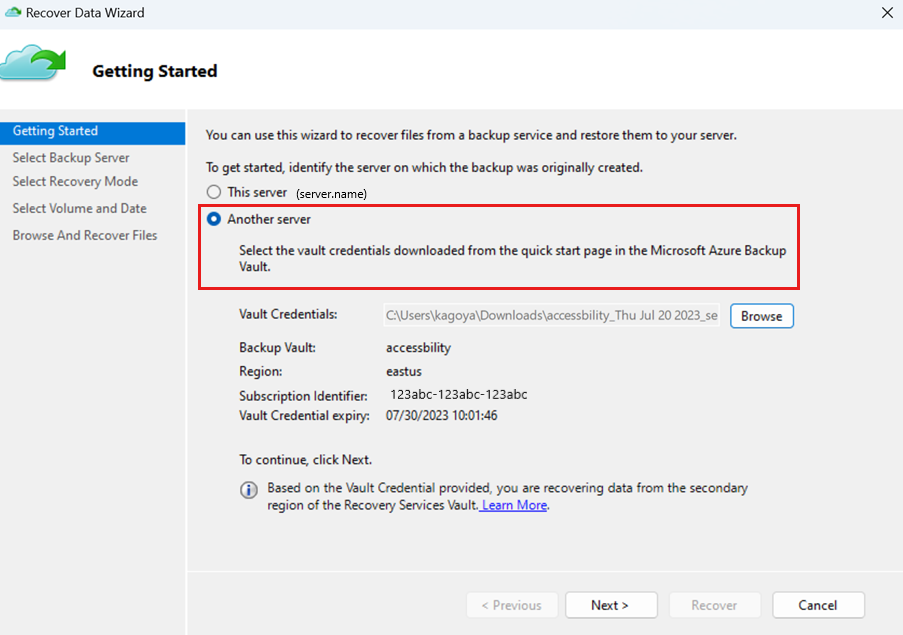
Select Next to continue.
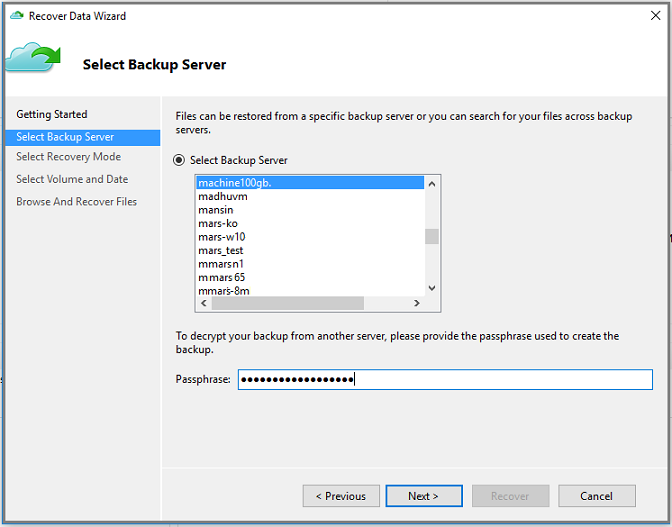
On the Select Backup Server page, select the source machine from the list of displayed machines, and provide the passphrase. Then select Next.
On the Select Recovery Mode page, select Individual files and folders > Next.
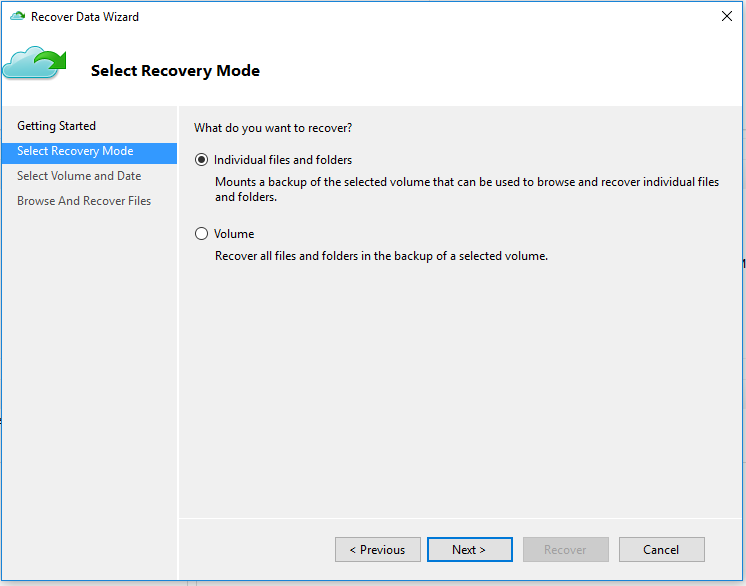
On the Select Volume and Date page, select the volume that contains the files and folders you want to restore.
On the calendar, select a recovery point. Dates in bold indicate the availability of at least one recovery point. If multiple recovery points are available within a single date, choose the specific recovery point from the Time drop-down menu.
Select Mount to locally mount the recovery point as a recovery volume on your target machine.
On the Browse And Recover Files page, select Browse to open Windows Explorer, and find the files and folders you want.
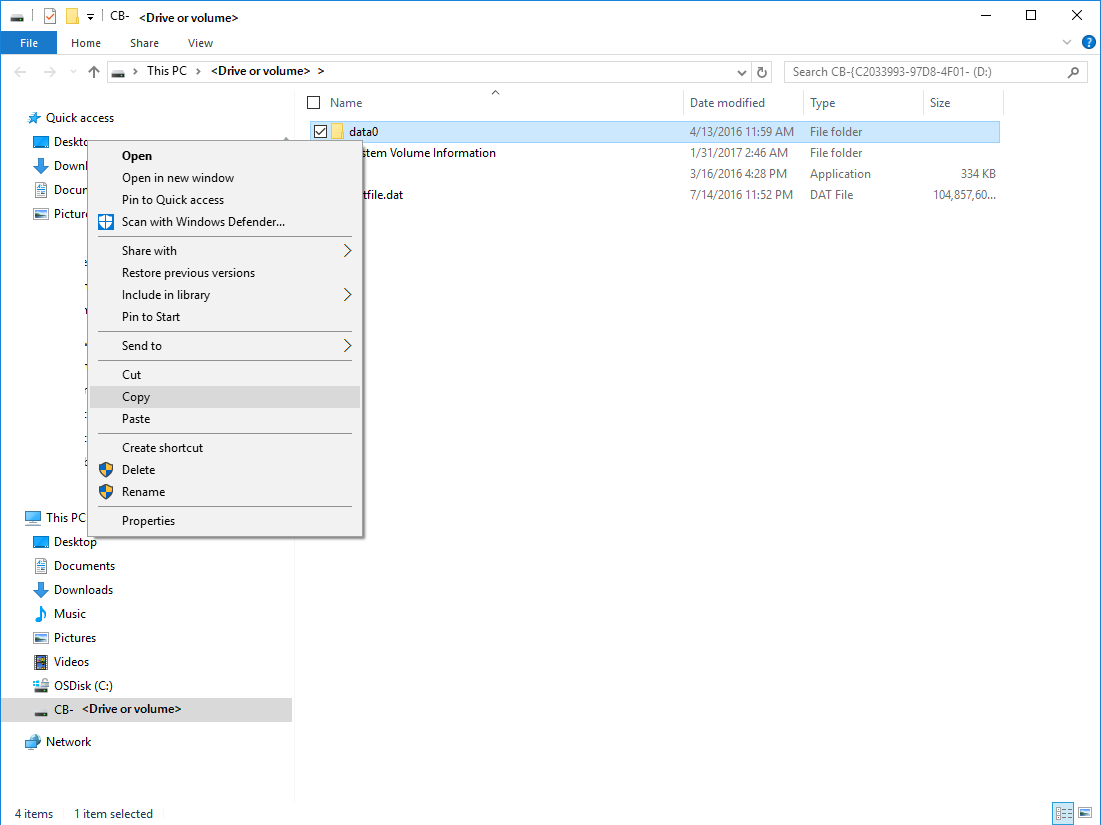
In Windows Explorer, copy the files and folders from the recovery volume, and paste them to your target machine location. You can open or stream the files directly from the recovery volume, and verify that the correct versions are recovered.
When you're finished, on the Browse and Recover Files page, select Unmount. Then select Yes to confirm that you want to unmount the volume.
Important
If you don't select Unmount, the recovery volume will remain mounted for 6 hours from the time when it was mounted. However, the mount time is extended up to a maximum of 24 hours in the case of an ongoing file-copy. No backup operations will run while the volume is mounted. Any backup operation scheduled to run during the time when the volume is mounted will run after the recovery volume is unmounted.
Next steps
Now that you've recovered your files and folders, you can manage your backups.