Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to configure and view Azure Backup reports.
A common requirement for backup admins is to obtain insights on backups based on data that spans a long period of time. Use cases for such a solution include:
- Allocating and forecasting of cloud storage consumed.
- Auditing of backups and restores.
- Identifying key trends at different levels of granularity.
Azure Backup provides a reporting solution that uses Azure Monitor logs and Azure workbooks. These resources help you get rich insights on your backups across your entire backup estate.
Supported scenarios
The following table lists the supported scenarios to configure Azure Backup reports:
| Report | Solution | Description | Scope | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backup Reports | Backup | Gain visibility into backup jobs, instances, usage, policies, policy adherence, and optimization. | - Azure VM - SQL database in Azure VMs - SAP HANA database in Azure VMs - Backup Agent - Backup Server - Data Protection Manager (DPM) - Azure Files - Azure Disk - Azure Blob (operational tier) - PostgreSQL database (Single Server) |
Consolidated |
| Backup Configuration Status | Backup | Information on whether all of your VMs are configured for backup. | Azure VM | Out-of-Box |
| Backup Job History | Backup | Information on the successful and failed backup jobs over a specified duration of time. | - Azure VM - Backup Agent (MARS) - Backup Server (MABS) - Data Protection Manager (DPM) - Azure Database for PostgreSQL Server - Azure Blobs - Azure Disks |
Out-of-Box |
| ** Backup Schedule and Retention** | Backup | Information on schedule and retention of all the backup items so that you can verify if they meet the business requirements. | - Azure VM - Azure Files |
Out-of-Box |
| User Triggered Operations | Backup | Information on user triggered operations on Recovery Services vaults over a specified period of time. | Recovery Services vault | Out-of-Box |
| Azure Site Recovery Job History | Azure Site Recovery | Information on the successful and failed Azure Site Recovery jobs over a specified duration of time. Note that only jobs triggered on replicated items and recovery plans currently appear in this report. |
- Azure VM - V2A - H2A |
Out-of-Box |
| Azure Site Recovery Replication History | Azure Site Recovery | Information on the replicated items over a specified duration of time. | - Azure VM - V2A - H2A |
Out-of-Box |
Get started
To start using the reports, follow these steps:
1. Create a Log Analytics workspace or use an existing one
Set up one or more Log Analytics workspaces to store your Backup reporting data. The location and subscription where this Log Analytics workspace can be created is independent of the location and subscription where your vaults exist.
To set up a Log Analytics workspace, see Create a Log Analytics workspace in the Azure portal.
By default, the data in a Log Analytics workspace is retained for 30 days. To see data for a longer time horizon, change the retention period of the Log Analytics workspace. To change the retention period, see Configure data retention and archive policies in Azure Monitor Logs.
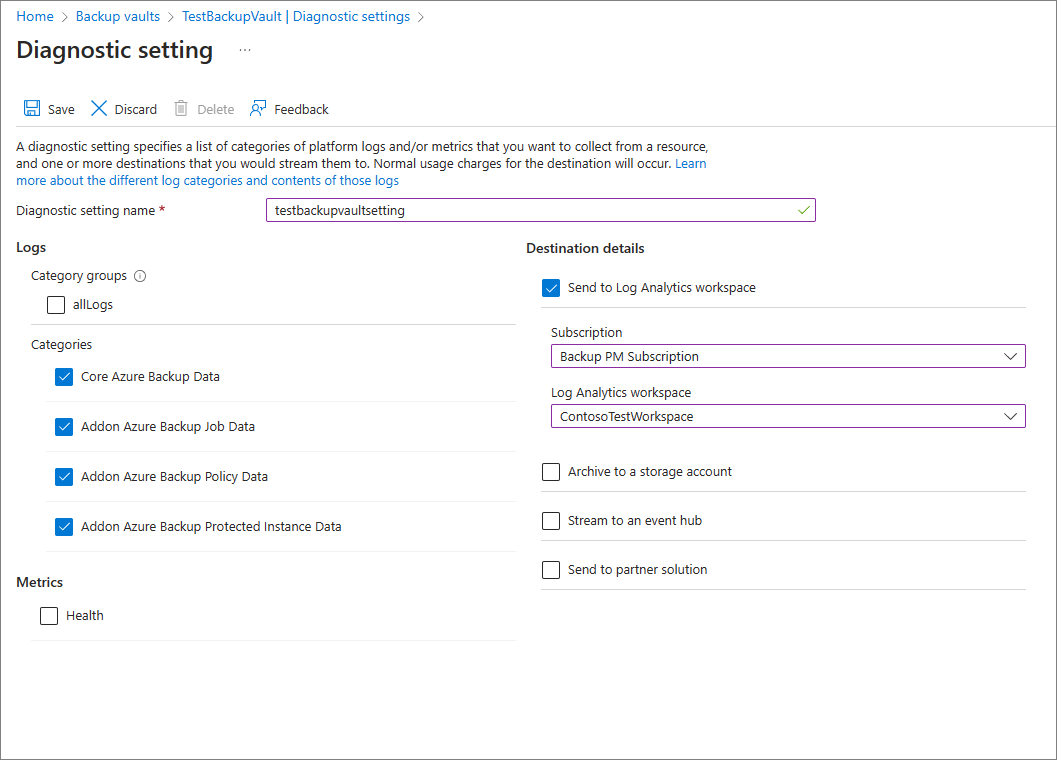
2. Configure diagnostics settings to send data to Log Analytics
Azure Resource Manager resources, such as Recovery Services vaults, record information about scheduled operations and user-triggered operations as diagnostics data. To configure diagnostics settings for your vaults, follow these steps:
Choose a vault type:
In the monitoring section of your Recovery Services vault, select Diagnostics settings and specify the target for the Recovery Services vault's diagnostic data. To learn more about using diagnostic events, see Use diagnostics settings for Recovery Services vaults.
Azure Backup also provides a built-in Azure Policy definition, which automates the configuration of diagnostics settings for all Recovery Services vaults in a given scope. To learn how to use this policy, see Configure vault diagnostics settings at scale.
Note
After you configure diagnostics, it might take up to 24 hours for the initial data push to complete. After data starts flowing into the Log Analytics workspace, you might not see data in the reports immediately because data for the current partial day isn't shown in the reports. For more information, see Conventions used in Backup reports. We recommend that you start viewing the reports two days after you configure your vaults to send data to Log Analytics.
Configure appropriate data retention to store historical data
Learn how to configure data retention to store historical data for the required duration.
Conventions used in Backup reports
- Filters work from left to right and top to bottom on each tab. That is, any filter only applies to all those widgets that are positioned either to the right of that filter or below that filter.
- Selecting a colored tile filters the widgets below the tile for records that pertain to the value of that tile. For example, selecting the Protection Stopped tile on the Backup Items tab filters the grids and charts below to show data for backup items in the Protection Stopped state.
- Tiles that aren't colored aren't selectable.
- Data for the current partial day isn't shown in the reports. So, when the selected value of Time Range is Last 7 days, the report shows records for the last seven completed days. The current day isn't included.
- The report shows details of jobs (apart from log jobs) that were triggered in the selected time range.
- The values shown for Cloud Storage and Protected Instances are at the end of the selected time range.
- The Backup items displayed in the reports are those items that exist at the end of the selected time range. Backup items that were deleted in the middle of the selected time range aren't displayed. The same convention applies for Backup policies as well.
- If the selected time range spans a period of 30 days of less, charts are rendered in daily view, where there is one data point for every day. If the time range spans a period greater than 30 days and less than (or equal to) 90 days, charts are rendered in weekly view. For larger time ranges, charts are rendered in monthly view. Aggregating data weekly or monthly helps in better performance of queries and easier readability of data in charts.
- The Policy Adherence grids also follow a similar aggregation logic as described above. However, there are a couple of minor differences. The first difference is that for items with weekly backup policy, there is no daily view (only weekly and monthly views are available). Further, in the grids for items with weekly backup policy, a 'month' is considered as a 4-week period (28 days), and not 30 days, to eliminate partial weeks from consideration.
Performance of reports
If you observe data discrepancy issues in Backup Reports, perform these preliminary checks:
Ensure that all vaults are sending the required diagnostics logs to the Log Analytics workspace.
Ensure that you've selected right filters in Backup Reports.
Review the following limits in Backup Reports:
After you configure diagnostics, it might take up to 24 hours for the initial data push to complete. After data starts flowing into the Log Analytics workspace, you might not see data in the reports immediately because data for the current partial day isn't shown in the reports. We recommend you start viewing the reports two days after you configure your vaults to send data to Log Analytics.
SQL log backup jobs are currently not displayed in Backup Reports.
As mentioned above, the reports don't show data for the current partial day, and take only full days (UTC) into consideration.
For example, in the report, even if you select a time range of 23/3 4:30 PM – 24/3 10:00 AM, internally the query runs for the period 23/3 12:00 AM UTC – 24/3 11:59 PM UTC. This meaning that the time component of the datetime is overridden by the query.
Similarly, if today's date is March 29, data is only shown upto the end (11:59 pm UTC) of March 28. For jobs that were created on March 29, you can see them when you check the reports on the next day, that is, March 30.
If none of the above explains the data seen in the report, please contact Microsoft Support.
Query load times
The widgets in the Backup report are powered by Kusto queries, which run on the user's Log Analytics workspaces. These queries typically involve the processing of large amounts of data, with multiple joins to enable richer insights. As a result, the widgets might not load instantaneously when the user views reports across a large backup estate. This table provides a rough estimate of the time that different widgets can take to load, based on the number of Backup items and the time range for which the report is being viewed.
| # Data sources | Time horizon | Approximate load times |
|---|---|---|
| ~5 K | 1 month | Tiles: 5-10 secs Grids: 5-10 secs Charts: 5-10 secs Report-level filters: 5-10 secs |
| ~5 K | 3 months | Tiles: 5-10 secs Grids: 5-10 secs Charts: 5-10 secs Report-level filters: 5-10 secs |
| ~10 K | 3 months | Tiles: 15-20 secs Grids: 15-20 secs Charts: 1-2 mins Report-level filters: 25-30 secs |
| ~15 K | 1 month | Tiles: 15-20 secs Grids: 15-20 secs Charts: 50-60 secs Report-level filters: 20-25 secs |
| ~15 K | 3 months | Tiles: 20-30 secs Grids: 20-30 secs Charts: 2-3 mins Report-level filters: 50-60 secs |
What happened to the Power BI reports?
The earlier Power BI template app for reporting, which sourced data from an Azure storage account, is on a deprecation path. We recommend that you start sending vault diagnostic data to Log Analytics to view reports.
In addition, the V1 schema of sending diagnostics data to a storage account or an LA Workspace is also on a deprecation path. This means that if you've written any custom queries or automations based on the V1 schema, you're advised to update these queries to use the currently supported V2 schema.